Module 7: Aggregate Expenditure
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the definition Consumption
Spending on New Goods and Services
What is the definition of Saving
Income not used on consumption
broader than money in banks
savings at the household level also excludes new housing
not consumption nor investment (Physical Capital)
What is the primary determinant of spending (or saving)?
Disposable Income
Disposable Income (Equation)
Yd = Y - T OR Yd = C + S
Yd is disposable income
Y is GDP (national income)
T is taxes
C is Consumption
S is Savings
What does the consumption function show?
The relationship between consumption and disposable income
Consumption Function (Equation)
Spending = Slope*(Disposable Income) + Constant
What is Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The ratio of the change in consumption to the change in disposable income
Marginal Propensity to Consume (Equation)
MPC = Δ Consumption / Δ Disposable Income (Yd)
Change in Consumption (Equation)
Δ C = MPC * Change in Yd
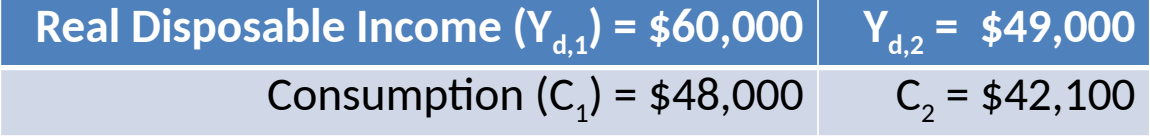
What is the MPC?
MPC = change in consumption / change in disposable income
(48000-42100) / (60000-49000)
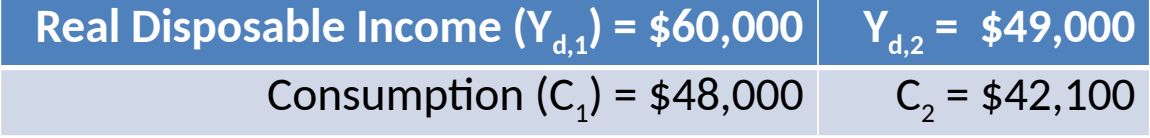
How much is saved in year 1?
Savings = disposable income - consumptions
60000-48000=12000
What is the Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)?
the ratio of the change in saving to the change in disposable income
Marginal Propensity to Save (Equation)
MPS = change in saving / change in real disposable income
MPS = 1 - MPS
What is dissaving?
Negative saving - when spending exceeds income
When savings (s) < equilibrium (o)
What is Autonomous Consumption
Consumption that is independent of disposable income
can be positive or negative
What is the consumption equation that INCLUDES Autonomous Consumption
Consumption = (MPC) * )Yd) + Auto. Cons.
What is the equilibrium equation for GDP?
GDP = Y = C + I + G + NX
Solve for Equilibrium (Y)
C= 0.8(Yd) + 0.7), I = 1.6, G = 1.5, T = 1.5, NX=-0.2
GDP is Y, and Y is in Yd, and Yd is composed of Y-T (taxes)
Build equation
Y = 0.8(Yd) + 0.7 + 1.6 + 1.5 - 0.2
Add values
Y = 0.8(Yd) + 3.6
Separate Yd into Y-T
Y = 0.8(Y-T) + 3.6
Distribute
Y = 0.8Y - 0.8T + 3.6
Add Tax Value and Multiply and Add
Y = 0.8Y - 0.8(1.5) + 3.6
Y = 0.8Y - 1.2 + 3.6
Y = 0.8Y + 2.4
Move Y to left side of equation and subtract
Y - 0.8Y = 2.4
0.2Y = 2.4
Solve for Y
Y = 2.4/0.2 = 12
Y = 12
What causes the consumption function to shift but NOT the AD
non-income determinants of consumption
Cost
this DOES NOT SHIFT AD
What causes the consumption function to shift AND the AD
Population
Wealth
Expected Future Income
Interest Rates
Confidence
Taxes
Consumption Tax Expectations
How does an increase in population shift the consumption function?
More people = more people consuming
More people consuming → shifts AD right
How does an increase in wealth shift the consumption function?
If liquidity increases → Consumption increases
If Availability of credit increases → Consumption increases
How does an decrease in interest rates shift the consumption function?
people are able to consume more with money that would otherwise be spent on interest rates
Do taxes increase or decrease if you want to shift the consumption function to the right?
Decrease - this leaves more money for people to consume
How do consumption tax expectations cause the consumption function to shift?
If they expect taxes to go up, they will consume more BEFORE it gets raised
What is planned investment?
New Physical Capital
Actual Investment = Planned Investment + Unplanned Investment
What are investment shifters?
Consumption shifters
Expectations of Future Profitability
Technology
What are other determinants of Investment?
Autonomous
GDP not driving
Autonomous Consumption
Interest Rates
changes investment more than GDP rates
Production and Employment Stable in Equilibrium
What does Government stand for in the Aggregate Expenditure Approach
Federal, state, and local government
does not include transfer payments
autonomous
not driven by GDP
What is Lump-Sum Tax (T)?
a tax that does not depend on income or the circumstances of the taxpayer
Autonomous
What is the Foreign Sector?
Next Exports (NX) = exports - imports
Autonomous
Depends on the economic conditions in each country
Autonomous variables are given and do not change with equilibrium
In planned Investment, what is short-run equilibrium
When aggregate expenditure equals aggregate production
Assume the economy is not growing
only consumption is a function of GDP since it is a function of disposable income
What does the Aggregate Expenditure equations look like in EQUILIBRIUM?
C + I + G + NX = GDP = Y
What does the aggregate expenditure equations look like when businesses have to change their inventories
C + I + G + NX > GDP
C + I + G + NX < GDP
How do businesses adjust back to equilibrium with inventory when the equation looks like the following: C + I + G + NX > GDP
unplanned drop in inventories
businesses increase output
GDP increases & returns to equilibrium
How do businesses adjust back to equilibrium with inventory when the equation looks like the following: C + I + G + NX < GDP
Unplanned rise in inventories
businesses cut output
GDP decreases and returns to equilibrium
How can $1.6 trillion of I generate $8 trillion of Y?
Autonomous spending multiplier
The Muliplier Effect - What is a multiplier?
ratio fo the change in the equilibrium level of real national income to the change in autonomous expenditures
(Spending) Multiplier (Equation)