Nucleic acids and the cell cycle
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
3 characteristics of dna
helical, double stranded, anti parallel
how are two dna strands joined together
through base pairings of nucleotides and hydrogen bonds
antiparallel
paralell, except they run in opposite directions
3 components of a nucleotide
phosphate group, pentose sugar (5 carbon), and nitrogen containing base
sugar molecule in dna
deoxyribose (always contains 1 less oxygen)
sugar molecule in rna
ribose
nitrogen containing bases in dna
thymine, adenine, guanine, cytosine
nitrogen containing bases in rna
uracil, adeninem guanine, cytosine
complimentary base pairing
pairing of the nitrogenous base and one strand of dna with the base of another
complimentary base pairings in dna
adenine with thymine, guanine with cytosine
complimentary base pairing in rna
adenine with uracil, guanine with cytosine
purines
double ring nitrogen bases: adenine and guanine
pyramidines
signle ring nitrogen bases: cytosine, uracil, thymine
what makes up the backbone of a dna/rna strand
pentose sugar and phosphate groups - phosphate group always links to the 3rd carbon of one sugar and the 5th of another
what makes up the inside of a dna/rna strand
nitrogenous bases bonded together via hydrogen bonds
similarities of dna and rna
both made up of nucleotides, both twisted
differences in # of strands between dna and rna
dna is double stranded, rna is single stranded
dna’s function
to be coded to rna
rna’s function
to be coded into protiens
function of nucleic acids
contains codes (Nitrogen bases varying in sequence) determining characteristics of organisms
rna
an in between molecule of dna that passes the code along so protiens can be synthesized in ribosomes
chromatin
uncondensed genetic material that is a long, thin tangled mass of fibers
chromosomes
condesned chromatin packaged into linear bundles
centriole
a cell organelle composed of protien microtubules that produces spindle fibers
spindle fibres
a fibre composed of microtubules that attatch to chromosomes at the centromere region and move chromosomes around the cell
nuclear membrane
membrane surrounding genetic material to form the nucleus, seperating it from the rest of the cell
centromere
region of the chromosome where sister chromatids are joined
chromatid
an identical copy of a chromosome when joinedthe
the cell cycle
process of cell replicating through of asexual reproduction
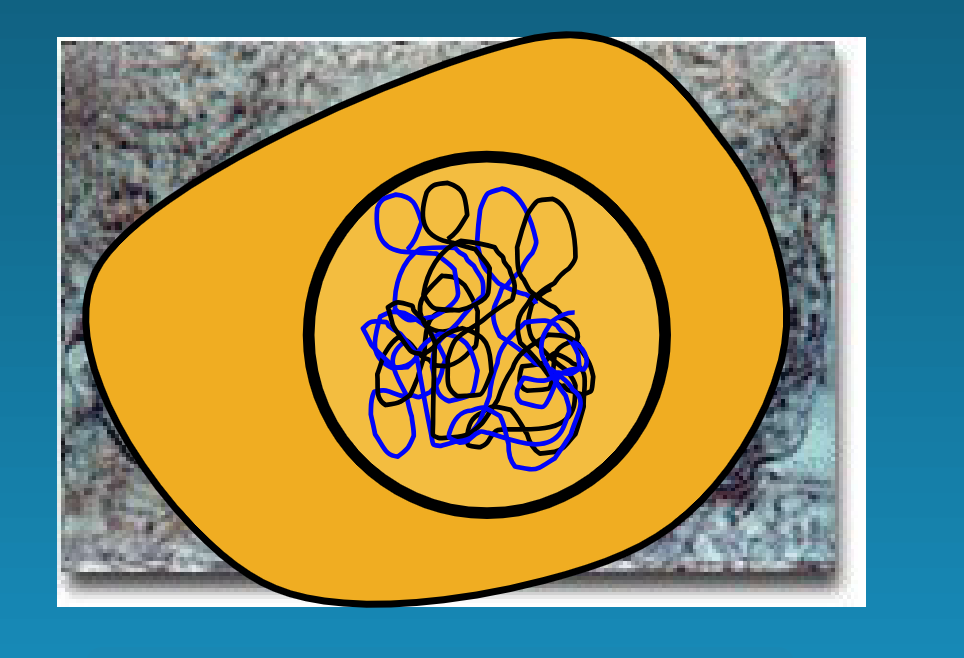
interphase
where the cell undergoes most of its growth and metoblism processes
G1
growth 1, all organelles and cell contents except for dna is duplicated, most growth occurs
S phase
synthesis, dna is duplicated by cell, most other processes haulted
g2 phase
growth 2, some growth and cell processes occur, cell double checks duplicated dna for any errors
aypoptosis
cell kills any problematic dna (mutations)
mitosis
the process resulting in 2 identical nuclei, asexual reproduction
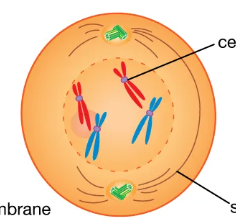
early prophase
nuclear membrane and nucleus disasemble, chromatin condenses into chromosomes. centrioles move to opposite poles and send out spindle fibers
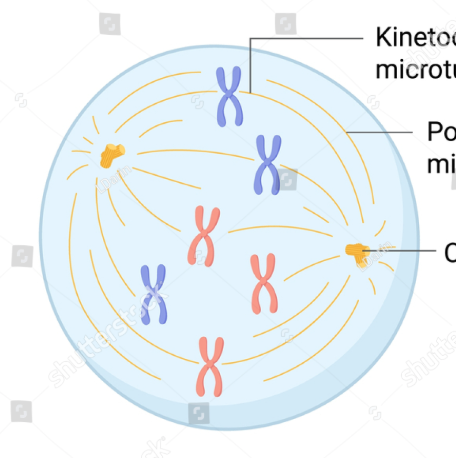
prometaphase
late prophase. centrioles and spindle fibers form mitotic spindle. spindle fibers from both centrosome complexes attatch to sister chromatids via kinetochore
kinetochore
structures of protiens associated with sections of dna at the centromere
centrosome
complex centriole and spindle fibres
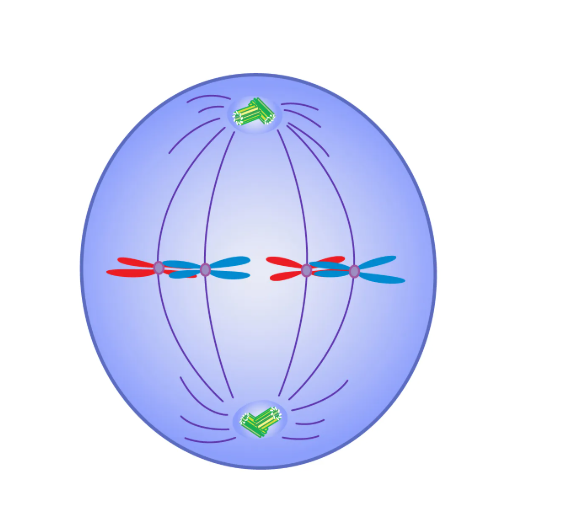
metaphase
sister chromatids get moved by spindle fibres to be lined up at the cell’s equator
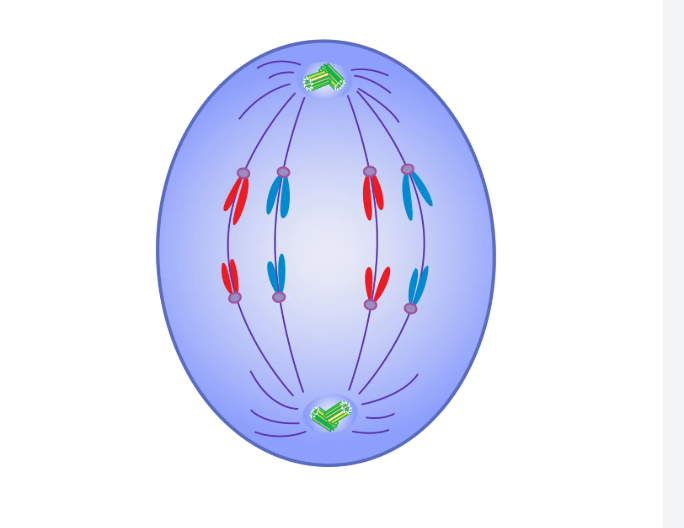
anaphase
sister chromatids seperate and move to opposite ends of the cell as the spindle fibres contract
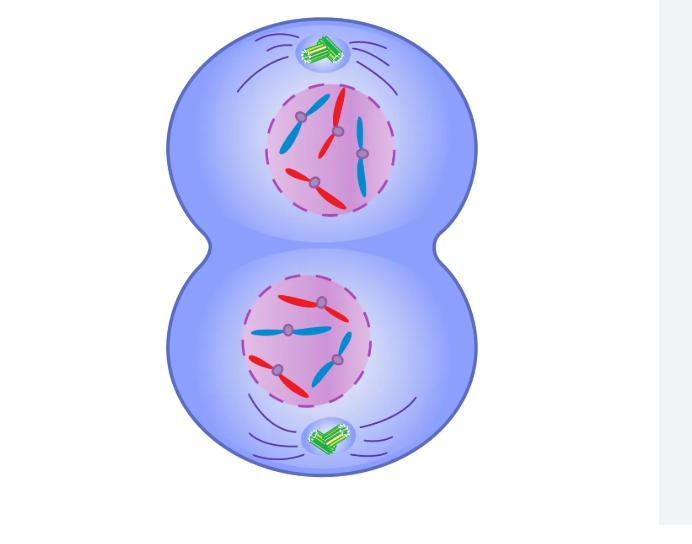
telophase
centrosome and spindle fibres dissasemble, nuclear membrane and nucleus form around both piles of chromosomes, chromosomes uncondense into chromatin
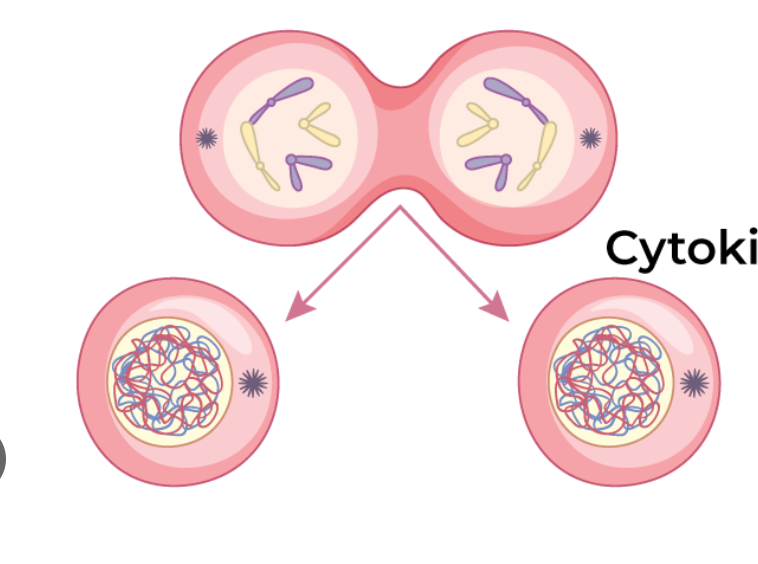
cytokenesis
cell membrane pinches into 2 identical cells. cytoplasm splits dividing the cell
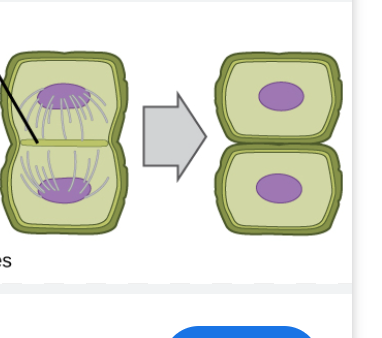
cytokenesis in plant cells
cell plate forms between nuclei, no centriole but has similar structure
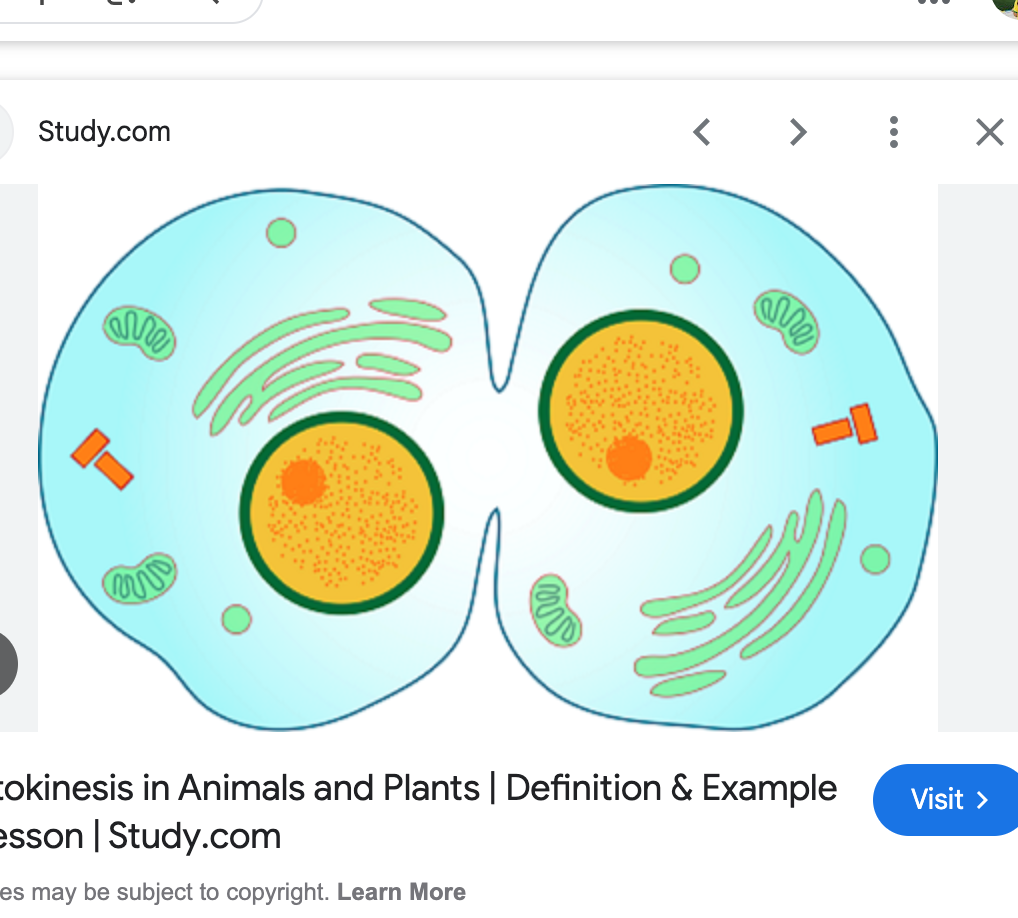
cytokenesis in animal cells
cleavage furrow develops between 2 cells, pinching them apart
3 reasons why cells undergo the cell cycle
growth, repair, replacement of cells
cancer
when cells begin to divide uncontrolobly