sound waves powerpoint
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
prerequisites for production of sound
a medium of transmission
a source of energy
a vibrating object that generates audible pressure
physical, psychological
sound can defined from ______ and _______ perspective
air medium
approx. 400 billion molecules per cubic inch
these molecules are random in motion with average speed of 1500 km per hour
atmosphere pressure: 100,000 N/m² or 1,000,000 dynes/cm²
mass, density, elasticity
important properties of any medium
mass
amount of matter that is present
density
amount of mass unit per volume
the car example
why does smoke from planes remain but not from cars? it is because of the density of air: when there is less, it takes longer for particles to disperse smoke
elasticity
the property of materials to return to their original shape after a force is applied
application of force on solid, liquid, or has → distortion of either shape, volume, or both
tendency to recover
elastic limit
limit until a medium will change form (a rubber band snapping after being pulled/stretched too far)
hooke’s law
the magnitude of restoring force of elasticity is directly proportional to the magnitude of spring displacement
Fr = -kx
Fr = restoring force of elasticity
X = magnitude of displacement of the spring
K = spring constant
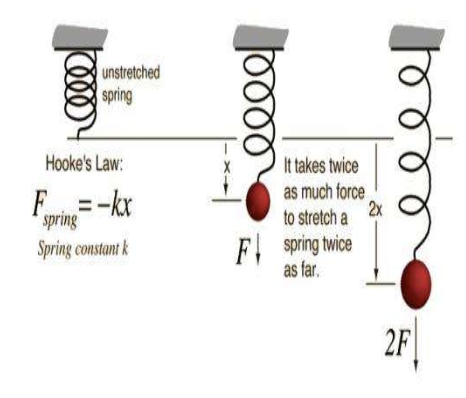
stiffness
why some springs require greater force than others to be compressed or extended
more, less
stiffness less = ____ compliant
stiffness more = ____ compliant
(inverse relationship)
mass, elasticity
important properties of source of sound
newton’s 1st law
all bodies remain at rest of in a state of uniform motion unless another force acts in opposition
newton’s 3rd law
for every action, there is equal and opposite reaction
directly
amount of inertia of an object is _____ related to mass of object
length, mass, time
all other quantities can be derived from these 3 quantities
MKS system
(M = meter, K = kilogram, S = second)
cgs system
(c = centimeter, g = gram, s = second)
displacement
change in position
involves direction and distance
vector quantity
vector
displacement, velocity, and force are ______ quantities
scalar
distance is a ______ quality
scalar quantities
Mass, time, and energy are described only by reference to magnitude, they have no direction…
any quantity that can be completely described by its magnitude only
vector quantities
a quantity that has both magnitude (size) and direction
average, instantaneous
_____ velocity refers to the total displacement of an object divided by the total time taken to travel that displacement, while _____ velocity is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time
newton’s 2nd law
the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force applied to the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object
F = ma (F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration)
trucks need more gas than cars because they are heavier
acceleration
time-rate change in velocity
delta c/time
(deltac = change in velocity)
force
unit Newton (N)
meaning of 1
1 N = 100,000 dynes
application → distortion or change in shape acceleration
pressure
Amount of force per unit area
inversely related to area, directly related to force
p=F/A [F=Force; A=Area]
Units
- MKS → N/m2
- cgs → dynes/cm2Alternative unit is Pascal (Pa)
- 1 Pa= 1 N/m2 = 10 dynes/cm2
momentum
mass x velocity
kinetic energy
a form of energy that results from an object in motion (types of motion = translation, rotation, vibration, etc.)
run = highest of this
potential energy
form of energy that results from object position or arrangement of parts, it is a stored energy
sit = highest of this
work
done when force succeeds in moving a body that the force acts upon, and the quantity of work is given by the product of magnitude
more of this = more displacement, more force
displacement = 0, 0 this (even with applied force)
W=Fd
work equation
MKS unit → joule
→ 1 joule= 1 N*1 M
cgs unit → erg
→ 1 erg=1 dyne*1cm
speed of sound
dependent on the characteristics of the medium
= square root of elasticity (E) / density (p)