Lecture 2 - Bacterial Pathogens P1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
How are specimens directly examined?
via fixing on a slide, staining and examined under microscope
Why is direct examination of specimens useful? (3)
allows presumptive identification of organism
gram negative vs gram positive bacteria
yeast vs molds
provides evidence of infection even if culture is negative
sensitivity is usually lower than culture so it does not rule out infection
After cultures, bacteria are identified based on… (5)
growth patterns
colonial morphology
gram stain
biochemicals
automated identification systems, MALDI-TOF MS, molecular testing e.g. PCR
What growth patterns are observed after culturing? (3)
hemolysis pattern on blood agar plates
growth on selective media
growth in the presence/absence of oxygen
Which organs do not stain with gram stain techniques? (4)
organisms w/o a cell wall → mycoplasma/ureaplasma, chlamydia
acid fast bacteria → mycobacterium
viruses → too small
fungi stain unpredictably → may stain but also may not
What are examples of gram + cocci (3)
staphylococcus
streptococcus
enterococcus
What are examples of gram + bacilli
listeria monocytogenes
corynebacterium diphtheriae
bacillus anthracis Wh
What are gram + cocci organisms?
aerobic bacteria
spheres under microorganisms
What are gram + bacilli?
aerobic bacteria
rod shaped
What types Staph aureus are there? (6)
MSSA = methicillin susceptible
MRSA = methicillin resistant
CA-MRSA = community associated
HA-MRSA = healthcare associated
VISA = vanco intermediate (not fully susceptible)
VRSA = vanco resistant (but very RARE in Canada)
Where does Staph aureus reside on the body? (4)
skin → armpits, groin
mucous membranes
respiratory tract
air/environment
What are the associated infections of s. aureus? (8)
skin/soft tissue → boils, abscesses, impetigo, wound
osteomyelitis
joint
spesis
endocarditis
prostethic material infection → catheters, artificial joints
toxin mediated diseases → food poisoning, TSS
necrotizing pneumonia
Characteristics of S. Aureus (4)
Blood agar plate → forms gold colonies
Catalase → +
Gram positive → cocci in clusiters
Coagulase → +
Folliculitis
infection of hair follicles by s. aureus
presents as itchy bumps but not severe
Impetigo
A superficial infection of the epidermis (gold crusting) caused by s. aureus
Erysipelas
Infection of the upper dermis → raised, clear demaracaion
caused by s. aureus
deeper infection than impetigo
Cellulitis
Infection of deeper dermis and subq fat caused by s.aureus
severe, pt can be quite ill developing fever/chills
can enter bloodstream
Scalded skin syndrome
occurs mostly in infants/newborns
blistering, loss of superficial layer of skin → severe
fever, skin pain, irritability
due to exfoliative toxin
What are the virulence factors of s. aureus? (8)
catalase: breaks down H2O2, protective for bacteria
coagulase: causes fibrin clot formation on the cell surface → may protect against phagocytosis of the host
hyluronidase → breaks down tissue
hemolysins → causes the breakdown of RBC
panton valentine leukocidin → causes destruction of WBCs by pore formation on membranes
Exfliative toxins → destroy connections between keratinocytes; responsible for SSSS
TSST-1 → toxic shock syndrome toxin
entereotoxins → can cause TSS and food poisoning
What are some types of coagulase negative staph?
s. epidermidis
s. saprophyticus
but this is a big family → lots of species
Where do S. epidermidis like to reside?
skin
mucous membranes
respiratory tract
air, environment
Where do S. saprophyticus reside?
genitourinary mucous membranes in women of child bearing age → teens to about 40 y.o
What are associated infections with S. epidermidis?
usually causes prosthetic material infections
stich abscesses
IV catheter associated urinary tract
prosthetic joint infection
sepsis
endocarditis
How do we idenfity S. epidermidis?
grey/silver/white colonies on blood agar plate aka no hemolysis
catalase = +
coagulase = -
Which streptococci organisms are beta-hemolytic aka full hemolysis?
Group A -→ s. pyogenes
Group B → S. agalactiae
Which streptococci organisms are alpha hemolytic aka partial hemolysis?
s. pneumoniae
viridans group
What is gamma hemolytic streptococci?
no hemolysis observed
What are the types of streptococcci pygonees?
s. pygoenes aka Group A strep (GAS)
M- type
Where do S. pyogenes reside?
ubiquitous
skin
throats of asymptomatic carriers
What are associated infections of s. pyogenes? (4)
skin/soft tissue
pharyngitis, tonsillitis
immune mediated diseases
toxic mediated diseases
Pharyngitis (6)
aka strep throat
white patches at the lining of the throat
small, beta-hemolytic colonies
gram + cocci in chains
PYR positive
reacts with anti A antibodies
Scarlet fever
associated with pharyngeal infection
caused by strep. pyogenes
due to pyrogenic exotoxins
presents as red rash with sandpaper texture
small red spots on soft and hard palates
“strawberry tongue”
Necrotizing fasciitis (3)
caused by strep. pyogenes
infection of deep tissues that results in destruction of muscle fascia and subcut. fat
will need antibiotics immediately and surgery -→ very severe
What are the types of s. agalactiae?
s. agalactiae aka Group B strep (GBS) based on carb surface antigen
10 capsular subtypes
Where do S. agalactiae like to reside? (3)
vagina
cervix
GI tract
What are the associated infections with s.agalactiae?
Postpartum sepsis
neonatal pneumonia
neonatal sepsi
neonatal meningitis
What are the types of S.pneumoniae
~100 different capsular types
Where do S. pneumoniae reside?
upper resp. tract
Is asymptomatic carriage common for S. pneumoniae?
Yes
What are the associated infections of S. penumoniae
pneumonia
OM
sinusitis
sepsis
meningitis
What characteristics do S. penumoniae have when stained?
Gram +
diplococci
What are the viridans group streptococci (VGS)? (5)
s. mitis
s. anginousus
s. mutans
s. salivarius
s. bovis
5 groups total
Where to VGS organisms reside?
mouth
GI tract
respiratory tract
urogenital tract
environment
What are associated infections with VGS? (4)
dental caries
brain, oropharynx, GI tract abscesses
sepsis
endocarditis but usually in those with already abnormal heart valves
What are the 2 main species of enterococci?
e. faecalis
e faecium
What is VRE
Vancomycin resistant enterococci → part of the enterococci family
Where do enterococci organisms reside?
skin
mouth
GI tract
urogenital tract
environment
What are the associated infections of Enterococci?
post surgical wound infections → esp. GI or GU surgeries
intra-abdominal infections and abscesses
sepsis
endocarditis
Identification of enterococcus organisms
reacts with group D antiserum
grow in high salt (6.5%) at 10C and 40C and at high pH
survives exposure to 60C for 30 mins
hydrolyze esculin in the presence of bile
sometimes vancomycin resistant
silver colonies on blood agar plate
What are the Listeria?
has multiple species in this genus
BUT the only human pathogen is L. monocytogenes
Where do L.monocytogenes reside?
GI tract
environment
What are the associated infections of L. monocytogenes
usually causes disease in pregnant women, infants, the elderly, and those with certain underlying diseases (immunocomp., cancer, alcoholism)
How does L.monocytogenes infection humans?
by entering food production
What temperature can L. monocytogenes grow in?
4C
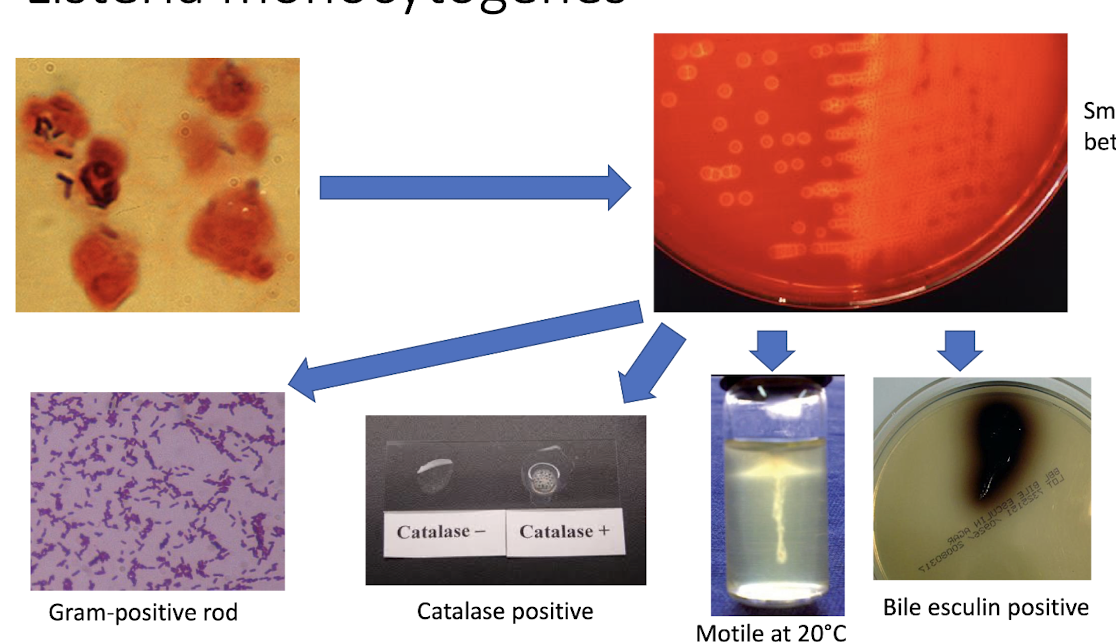
Identifying L.monocytognees?
bacilli structure when stained
small zone of beta hemolysis on blood agar
gram + rod
catalase +
motile at 20C
bile esculin +