Ch 7: Membrane Structure and Function
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Selective permeability
the plasma membrane allows some substances to cross more easily than others
Amphipathic molecules
molecules that contain hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions (such as the phospholipids and proteins of the cell membrane)
Fluid mosaic model
the theory that a membrane is a fluid structure with a myriad of proteins embedded in it
Peripheral proteins
proteins not embedded in the cell membrane, but loosely bonded to the surface or exposed integral proteins
Integral proteins
proteins that penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
many are transmembrane proteins
the regions in the hydrophobic interior of the membrane are nonpolar amino acids typically in alpha helices
the exposed regions are polar
some have a hydrophilic channel down the center allowing passage of substances
Transmembrane proteins
proteins that span the membrane (though some stop in the interior)
Glycolipids
carbs bonded to lipids
when present in membranes, carbs are short and branched
Glycoproteins
carbs bonded to proteins, which often are present in membranes
Six Major Membrane Protein Functions
cell-cell recognition
transport
enzymatic activity
signal transduction
intercellular joining
attachment to cytoskeleton and ECM
Transport proteins
hydrophilic molecules avoid contact with the interior of the plasma membrane by passing through these proteins that span the membrane
some are channel proteins - have hydrophilic channel
some are carrier proteins - hold on to molecules and pass them through membranes
specific to certain molecules
Aquaporin
channel proteins that regulate the passage of water through the plasma membrane in some cells
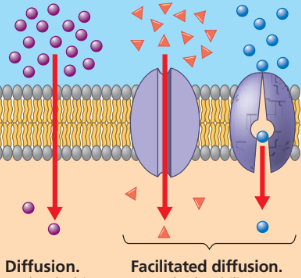
Diffusion
the movement of molecules so that they spread out evenly in the available space
caused by the constant motion/thermal energy of molecules
a spontaneous process
Concentration gradient
the region along which the density of a substance decreases
the path diffusion will follow
Passive transport
the type of diffusion that does not require energy
Osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane, causing solute concentrations to become equal
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water
Isotonic
solute concentration is the same inside and outside of the plasma membrane
no net water movement
Hypertonic (solution)
the solute concentration is higher outside of the plasma membrane
water leaves the cell, causing shriveling and possible death
Hypotonic (solution)
the solute concentration is higher inside of the plasma membrane
water enters the cell, possibly causing it to lyse (burst)
Osmoregulation
the ability of a cell to control solute concentrations and water balance
Turgid
when a plant cell is very firm, which is healthy
occurs in a hypotonic environment
Flaccid
when a plant cell is limp
occurs in an isotonic environment
Plasmolysis
the plant cell shrivels and the plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall
occurs in a hypertonic environment
can cause wilting or death
Facilitated diffusion
polar ions and molecules impeded by the plasma membrane diffuse passively with the help of transport proteins - channel or carrier
Ion channels
channel proteins that transport ions
Gated channels
channel proteins that open in response to stimulus - electrical or receptor based
Active transport
pumping a solute against its concentration gradient, which requires energy (usually ATP)
these transport proteins are all carrier proteins
enables cells to maintain an internal concentration of solutes that differs from their environment
Sodium-potassium pump
an active transport carrier protein
it exchanges Na for K across the plasma membrane
accepting the terminal phosphate group from ATP allows this protein to change shape
exchanges 3 Na for 2 K, creating opposite charges
electrogenetic pump
Membrane potential
separation of opposite charges across the plasma membrane causes this
acts like a battery
cytoplasmic side is negative (anions)
EC side is positive (cations)
Electrochemical gradient
drives diffusion of ions across a cell membrane
driven by two forces
chemical force - ion concentration gradient
electrical force - effect of membrane potential on ion movement
Electrogenic pump
a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
sodium-potassium pump in humans
proton pump in plants, fungi, bacteria
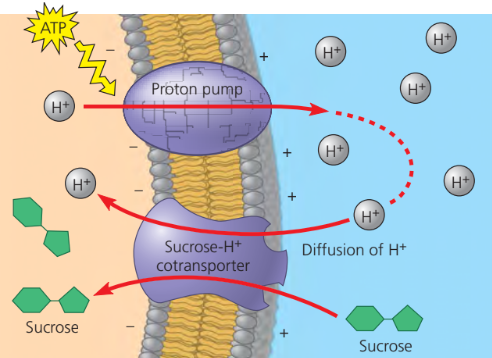
Proton pump
actively transports protons out of the cell
electrogenetic pump for plants, bacteria, fungi
contributes to membrane potential
Cotransport
when one ATP powered pump indirectly drives the active transport of several other solutes
Exocytosis
the process of the cell secreting biological molecules by fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
transport vesicles from the golgi meet the plasma membrane
proteins rearrange the lipids so the membranes fuse
the contents of the vesicle leave the cell, and the vesicle becomes part of the plasma membrane
Endocytosis
the cell takes in biological molecules and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
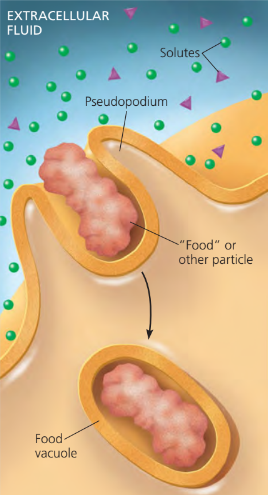
Phagocytosis
a cell engulfs a particle by wrapping it in pseudopodia, forming a food vacuole
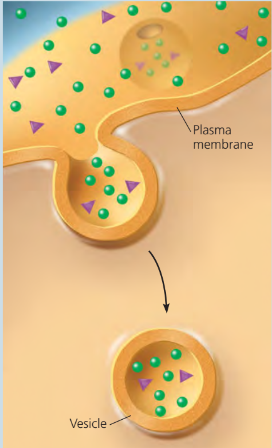
Pinocytosis
when a cell “gulps” droplets of extracellular fluid containing necessary molecules into tiny vesicles
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
receptor proteins bind to ligands, triggering the coated pit area to collapse into a vesicle
the ligands are released, then the vesicle recycles the receptor proteins back to the plasma membrane
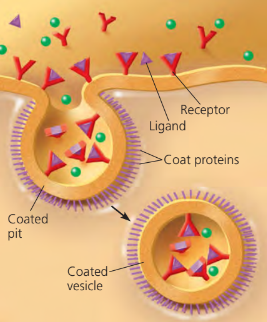
Ligand
any molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site on another molecule
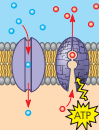
Transport
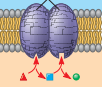
Enzymatic activity
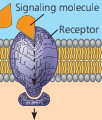
Signal transduction
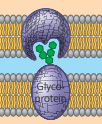
Cell-cell recognition
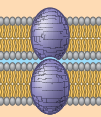
Intercellular joining
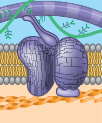
Attachment to cytoskeleton and ECM