L64: disorders of oral cavity
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
what causes dysfunction to injury of the oral cavity?
caustic substances (chemical erosions or ulcers)
antibiotic use
high blood glucose
how does high blood glucose cause dysfunction of oral cavity?
allows for colonization by sugar-loving pathogens
while rare, what can cause oral infections
protective mechanisms of oral cavity and the epithelial barrier has been compromised
what can mechanical penetration of oral mucosa lead allow for?
allows pathogens opportunity to enter vascular channels or drain lymphatic vessels
what is needed for organisms to multiply in the oral cavity?
epithelial surfaces
lymphoid tissues
what does small lacerations in the oral mucosa allow for?
introduction of bacteria that can cause specific systemic diseases
what are the defense mechanisms of the oral cavity?
stratified epithelial surface
taste buds
microbiota
saliva
how is the stratified epithelial surface a defense mechanism?
resistant to trauma and some irritants
how are taste buds a defense mechanism?
reject potentially toxic materials based on taste and tongue feel
how does microbiota act as a defense mechanism?
occupy attachment sites that would otherwise be available to pathogens
how does saliva act as a defense mechanism?
provide flushing action
forms a protective coating of mucosa
contain antimicrobial lysozyme
eliminates neutrophils at end of their lifespan
what happens if saliva does not eliminate neutrophils at the end of their lifespan?
stomatitis
what are the general categories of lesions?
developmental anomalies
degeneration
necrosis
disturbance of growth
disturbance of circulation
inflammation
neoplasia
immune-mediated disease
trauma
pathological pigmentation
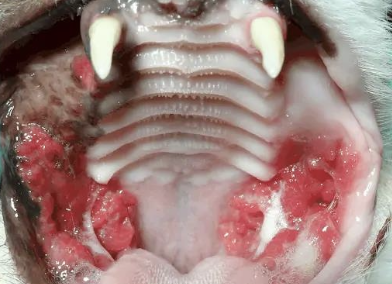
what is this image showing?
inflammation
what is this image showing?
hyperplasia
what is another name for palatoschisis?
cleft palate
what is palatoschisis?
Failure of fusion of the lateral palatine processes of the maxilla
what are the causes of cleft palate?
genetic/hereditary
toxic
teratogenic defect
what are the consequences of cleft palate?
failure to suckle and starvation
aspiration pneumonia
what drug can lead to cleft palate in kittens when given to the mom during pregnancy?
griseofulvine
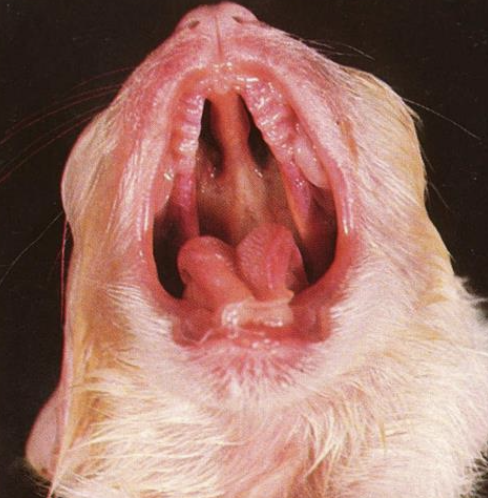
what does this image show?
palatoschisis
what is another name for cheiloschisis?
cleft lip
cleft lip
incomplete fusion of the frontonasal process with the maxillary processes
where do rabbits typically get cleft lip and what do we call it?
split upper lip; “hare lip”
what are the consequences of congenital anomalies of the oral cavity?
difficulty sucking, prehension, and mastication of food = starvation
aspiration pneumonia
malposition of teeth
what are the morphological types of stomatitides?
stomatitis
gingivitis
vesicular
erosive and ulcerative
necrotizing
eosinophilic
lymphoplasmacytic
chronic ulcerative paradental
what mucous membranes can get inflammed in the mouth?
oral cavity
gingiva
what is the effect of having inflammation of mucous membranes?
loss of mucosa leading to erosions, ulcerations, and necrosis
macules
lesion that appears as flat patch of discoloration
papule
solid raised lesion
vesicles
pus or fluid filled raised lesion
what are the causes of inflammation of the oral cavity?
infectious agents
chemical injury
trauma
intoxicants
autoimmune disease
systemic disease
how can inflammation appear clinically?
anorexia due to pain when chewing
hypersalivation
what is gingivitis the first and most consistent sign of?
FIV infection
what are the types of stoamtititis?
catarrhal
vesicular
erosive and ulcerative
proliferative
pseudomembranous
necrotizing
what are the causes of vesicular stomatitis?
thermic and chemical agents
autoimmune disease
developmental defects
infectious agents
what are the specific infectious causes of vesicular stomatitis?
VS
FMD
SVD
feline calicivirus
what are the secondary lesions that occur from vesicular stomatitis?
erosions
ulcers
abscesses formation on the buccal mucosa
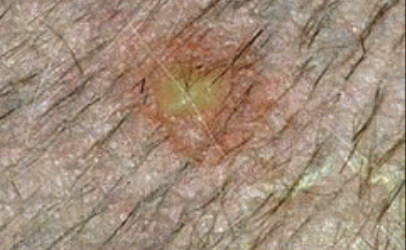
what is the image showing?
vesicle
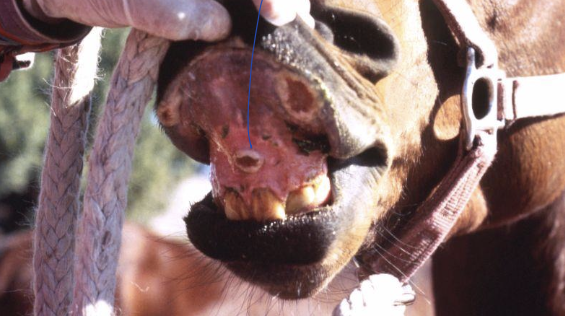
what is the image showing?
ulcer
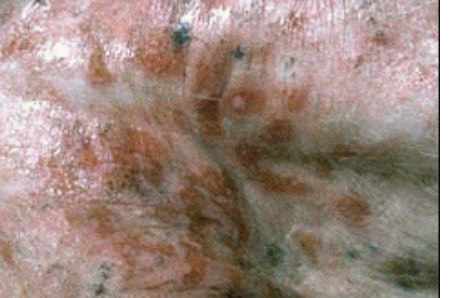
what is the image showing?
erosion
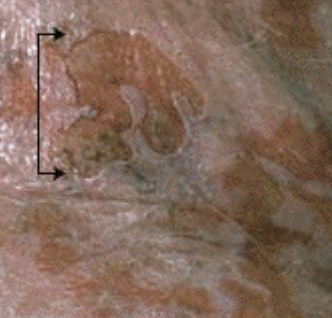
what are the arrows pointing to?
ulcer
what are the causes for erosive and ulcerative stomatitis?
viral
uremia
indolent ulcer in cats
vesicular disease
trauma from sharp teeth
chemicals
what are the sites of indolent ulcers in cats?
commissure of the upper lip, gingiva, tongue, palate, or regional lymph nodes
what viral infections lead to ulcerative stomatitis in cats?
calicivirus
FLV
FIV
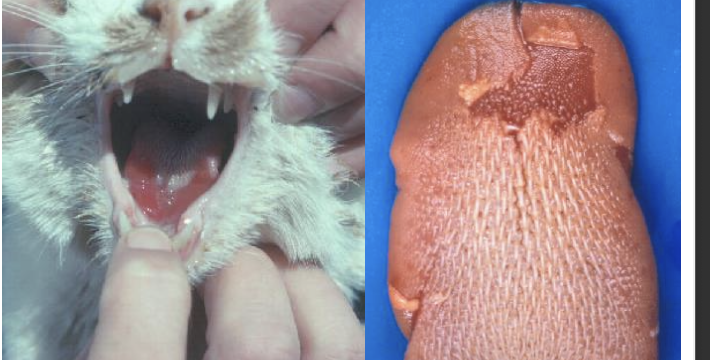
what is the image showing?
ulcerative stomatitis
CUPS
chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis
which breeds are susceptible to CUPS?
maltese dogs
cavalier king charles spaniels
what are the causes of CUPS?
“kissing ulcers” to dental plaque
immune system overreacting to chronic exposure to bacteria in plaque
what are the clinical signs of CUPS?
inappetence and anorexia due to pain
drooling
halitosis
smelly odor coming from mouth
what may occur if CUPS is left untreated?
bone resorption
what are lymphocytic-plasmacytic lesions in CUPS suggestive of?
suggestive of inflammation rather than infection
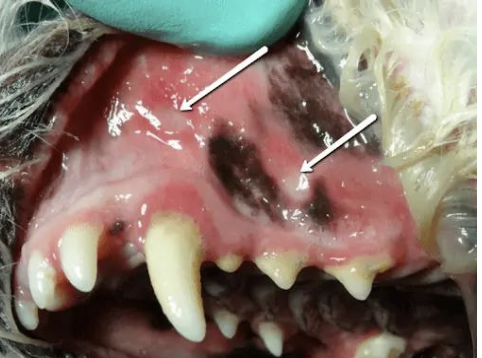
what is this image showing?
CUPS
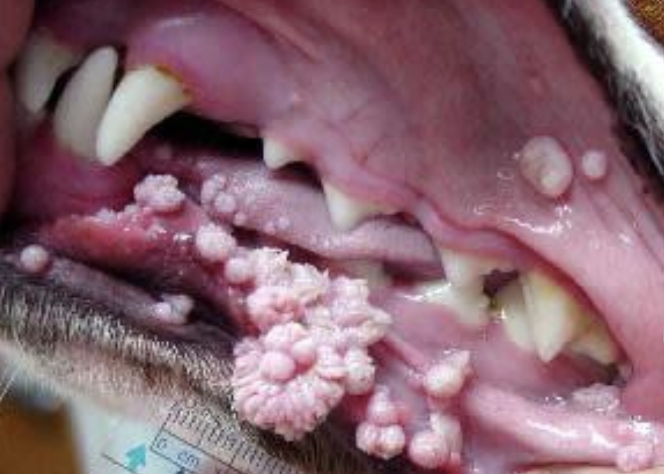
what is this image showing?
canine oral papillomatosis
what occurs after erosive and ulcerative stomatitis?
bacterial infection leading to oral necrobacillosis
how will proliferative stomatitis appear?
pustules and papules
where will papules from bovine papular stomatitis appear?
nares
muzzle
oral cavity
esophagus
rumen
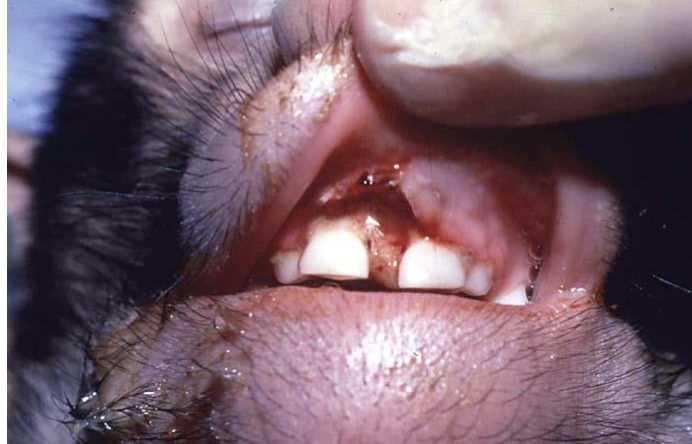
what is the image showing?
coagulative necrosis
what is another name for noma?
trench mouth
how will coagulative necrosis appear?
Dry yellow friable masses, foul
odor
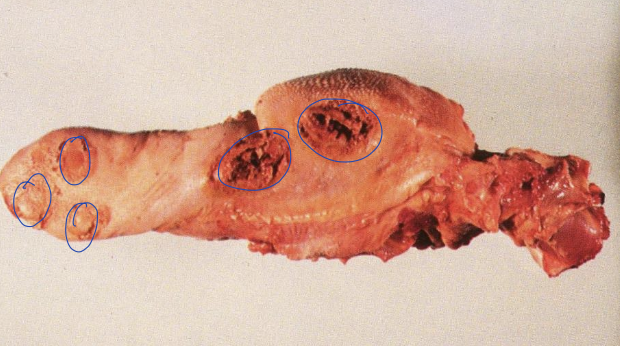
what is the image showing?
calf diphtheria
Lymphoplasmacytic stomatitis in
cats
infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells
in the lamina propria leading to hyperplasia and ulceration
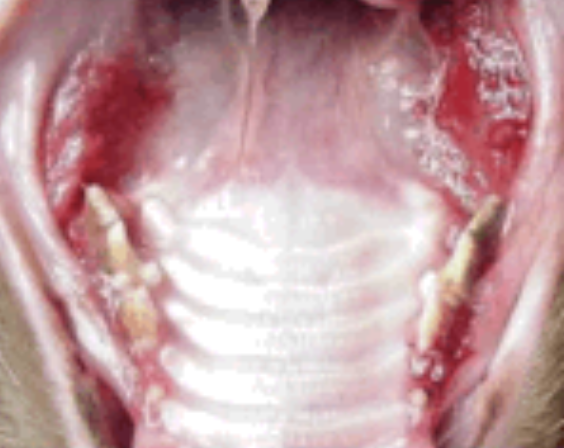
what is the image showing?
Lymphoplasmacytic stomatitis in
cats
what is gingival hyperplasia secondary to?
chronic inflammation/periodontitis
gingival hyperplasia
hard, non-neoplastic focal or diffuse
thickened gingival composed of reactionary
proliferated fibrous connective tissue
what is gingival hyperplasia most common in?
brachycephalic breeds
boxers more than 5
sometimes horses
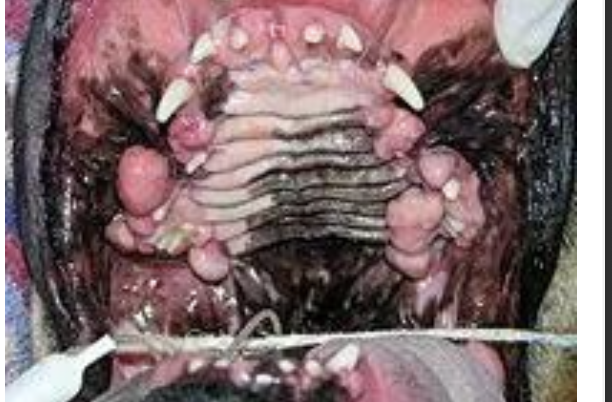
what is the image showing?
gingival hyperplasia
epulis
tumor-like mass(es) on the gingiva
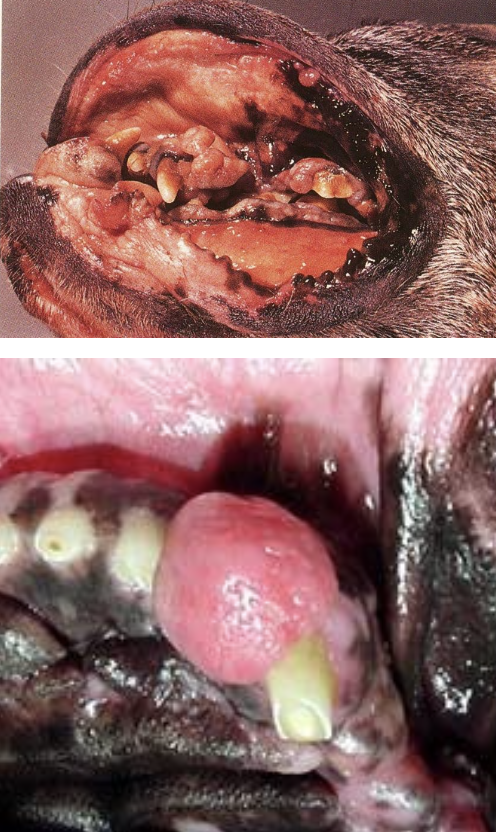
what is the image showing
epulis
what is the name for epulis?
peripheral odontogenic fibroma
what is the most common oral neoplasm seen in aged cats?
squamous cell carcinoma
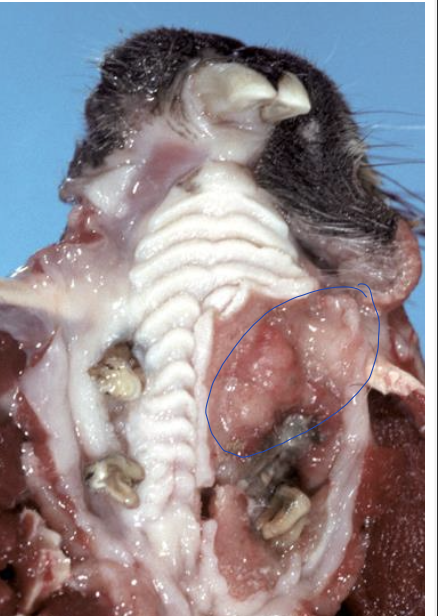
what is the image showing?
squamous cell carcinoma
how will squamous cell carcinoma lesions appear?
small, granular to large, ulcerated cauliflower-like masses
where will cats get squamous cell carcinomas?
tongue and gingiva
where will dogs get squamous cell carcinomas?
tonsil and gingiva
what is the most common oral tumor in dogs?
melanoma
what are the sites for melanoma of the oral cavity?
palate
tonsillar area
teeth alveoli
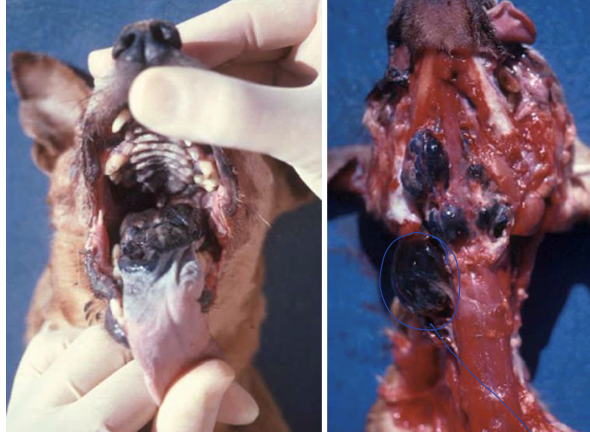
what is the image showing?
melanoma
how will melanomas appear?
black or brown firm dome shaped mass
what species will get papillomas?
young dogs and cattle
what are the sites for papillomas?
lips
cheeks
tongue
palate
larynx
esophagus
are papillomas benign or malignant?
benign
papilloma virus infection
intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies in
keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
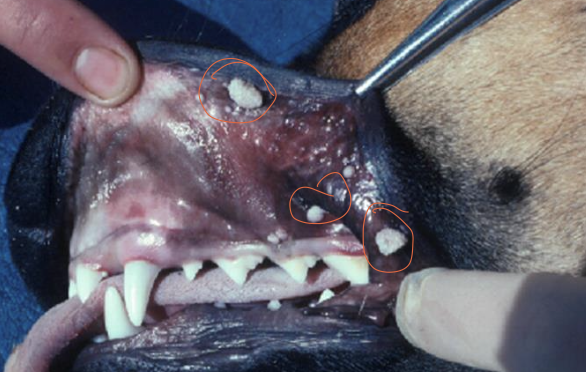
what is the image showing?
papilloma
papillomas will have spontaneous regression within what time?
1-3 months with long lasting immunity
in which species are fibrosarcomas most common?
cats
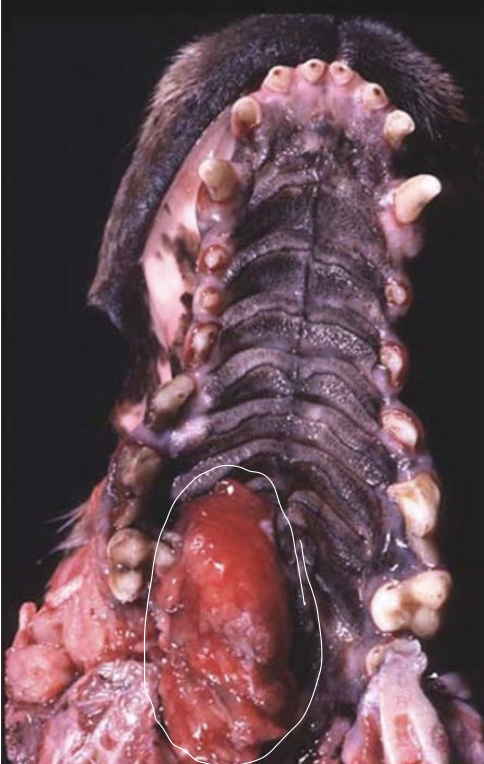
what is the image showing?
fibrosacroma
what are the sites for fibrosarcoma?
maxilla
gums
lips (dogs)
how do fibrosarcomas appear?
solitary, firm, red, fleshy mass
where do osteogenic sarcomas originate from?
the alveolar processes of the
mandible and maxilla
MCQ: A 3-year-old domestic shorthair cat presents with red, inflamed gums, fetid breath, and decreased appetite. Histological examination reveals hyperplasia and ulceration of the oral mucosa with infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the lamina propria. What is the most likely diagnosis?
lymphoplasmacytic stomatitis
MCQ: A young dog presents with multiple white, friable, cauliflower-like masses on the lips, cheeks, and tongue. Histopathological examination reveals intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies in keratinocytes of the stratum spinosoum. What is the most likely diagnosis?
papilloma
what do nerve endings of the tongue provide data about?
digestibility of ingesta
Epitheliotropic viruses
Replicate in the epithelium of the oral cavity & tongue
what bacteria causes wooden tongue in cattle?
actinobacillus lignieresii
wooden tongue in cattle
a stiff, fibrotic swelling that prevents function of the tongue
what is the defense mechanism of the tongue?
Thick, nonabsorptive, nonkeratinizing, stratified squamous epithelium
what bacteria causes thrush in the tongue?
Candida albicans
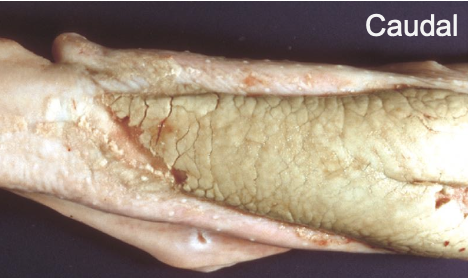
what is the image showing?
thrush
what can cause glossitis?
antibiotic therapy
incrased serum glucose concentrations
immunodeficiency