5 - Selecting MV Type and Mode
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
framework for MV selection
indication
pathology
treatment goals
patient interface (mask/tube)
location
duration
staff training
two methods of noninvasive ventilation
CPAP
NIV
pressure triggered, patient limited, flow cycle
critical care ventilators
full ventilatory support (FVS)
ventilator provides all energy for alveolar ventilation
RR > 8 breaths/min
adequate VT
preset volume/pressure
partial ventilatory support (PVS)
patient participates in WOB
RR < 6 breaths/min
breath delivery and modes
type of breath
mandatory, spontaneous, assisted
controlled variable
volume/pressure
timing
continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)
intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
continuous spontaneous ventilation (CSV)
mandatory breath delivery
breath delivery that is ventilator controlled
variables: time, VT, and inspiratory pressure
spontaneous breath delivery
breath delivery that is patient-controlled
variables: time, VT
based on patient’s demand and lung characteristics
assisted breath delivery
breath delivery that is ventilator- and patient-controlled
all/part of breath made by ventilator
categories of MV
volume
pressure
combined
volume control ventilation (VCV)
fixed volume, pressure variable
advantages of VCV
guaranteed volume and VE
can maintain PaCO2
disadvantages of VCV
risk of high pressure
risk of patient-ventilator asynchrony
VCV waveforms
pressure
changes with changes in Cstat and Raw
can show Pplat with breath hold
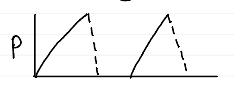
VCV waveforms
flow
constant
low mean airway pressure (MAP)

VCV waveforms
volume
consistent waveform
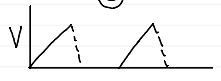
pressure control ventilation (PCV)
fixed pressure, volume variable
advantages of PCV
set max pressure
reduces risk of alveolar overdistention
decelerating flow pattern
disadvantages of PCV
volume varies
clinicians may be unfamiliar with mode
VT and VE decrease when lung characteristics worsen
PCV waveforms
pressure
square shape
holds for duration of i-time
does not change with Cstat and Raw
PCV waveforms
flow
variable
will change with Cstat and Raw

PCV waveforms
volume
decelerating ramp
variable
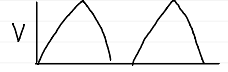
benefits of combined volume-pressure ventilation
fluctuates between modes to maintain minimal VT
allows patient to do more WOB
aids in weaning from MV
helps deliver minimal pressure
decreases risk of baro-/volutrauma
continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV)
every breath is mandatory
time/patient triggered
intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV)
set number of mandatory breaths
patient can breathe between set breaths
continuous spontaneous ventilation (CSV)
all breaths are spontaneous
patient triggered
control ventilation (historial mode)
MV mode
preset intervals (time-cycled)
patient “locked out” from any spontaneous efforts
only effective for patients that can’t participate in WOB (transected C2 or C3 nerve)
assisted ventilation (historical mode)
MV mode
ventilation cycles in response to patient inspiratory effort (patient triggered)
breath raised to set VT
unable to wean
volume controlled CMV (VC-CMV or VC-AC)
MV mode
all breaths mandatory
pressure controlled CMV (PC-AC)
MV mode
time/patient triggered
time cycled
IMV
MV mode
volume/pressure targeted breaths at set intervals (time triggered)
patient can breathe between set breaths
can have pressure support for spontaneous breaths
can’t synch with patient breaths
synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV)
MV mode
mandatory breaths synch with spontaneous breaths
may be volume/pressure controlled with or without pressure support (PS)
advantages of SIMV
maintain muscle strength
used for weaning
full/partial support can be adjusted
may reduce alkalosis
disadvantages of SIMV
may increase WOB
may increase wean time
patient difficulty with lowering set rate
no proper VT
CPAP
MV mode
improve oxygenation in patients with refractory hypoxemia and low FRC
pressure support ventilation (PSV)
MV mode
constant pressure during inspiration
patient triggered, pressure limited, flow cycled
other settings
flow acceleration %
inspiratory rise time
inspiratory rise time %
slope adjustment
inspiratory cycle %
inspiratory flow termination
expiratory flow sensitivity
volume support ventilation (VSV)
MV mode
target volume
not commonly used
airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) / BiVent
MV mode
patient breathes elevated baseline pressure
possible pressure released then re-established
BiPAP
MV mode
like CPAP but without constant pressure
settings: IPAP, EPAP, RR, FiO2
volume assured PS (VAPS)
combined MV mode
PS breath
as flow decelerates, flow continues until volume delivered
pressure regulated volume control (PRVC) / AutoFlow
combined MV mode
pressure changes to obtain set VT
high frequency ventilation (HFV)
ventilation with RR > 60
mandatory minimum ventilation (MMV)
MV mode
used for weaning
ventilator provides part of VE that patient can’t accomplish by increasing RR or pressure
adaptive support ventilation (ASV)
MV mode
variation of MMV
RT sets VE based on patient’s IBW and estimated VD
can adjust targeted ventilation based on patient needs
used for weaning
proportional assist ventilation (PAV)
MV mode
pressure, flow, and volume proportional to patient’s spontaneous effort
pressure depends on:
inspiratory flow and volume demand
degree of amplification chosen by RT
positive feedback system