OTM 507: Neuro part 2
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Lower motor neuron
Cell body in grey matter of ventral horn, axons travel to skeletal muscle, axons bundle together to form ventral root which joins with dorsal root to form spinal nerve
Cranial nerves have LMN
Upper motor neurons
Cell body in cortical areas or brainstem, project to LMN and interneurons in brainstem or spinal cord
Motor tracts
bundle of UMN in the CNS that transmit output information
Apraxia
impaired ability to carry out motor activities despite intact motor function due to difficulties planning motor activities
Cortical Spinal tract
A major descending motor tract
- Carries motor information from the motor cortex to the spinal cord
- Decussation of the cortical-spinal tract occurs in medulla
Corticobulbar tract
Goes from motor cortex to brainstem,
Decussate at brainstem where CN's III-XII transition from UMN to LMN
Synapse with LMN the control muscles of the face, tongue, pharynx, larynx, sternocleidomastoid, and trapezius
Ipsilateral and contralateral synapses
LMN lesions
weakness, atrophy, fasciculations (muscle twitches), decreased reflexes, decreased tone (flacidity)
UMN lesions
weakness, increased reflexes, increased tone (spasticity, rigidity, posturing), Babinksi, hoffmans test, clonus
Spinal Cord Injury
Sensory, LMN, UMN
All or part of spinal cord is damaged
Cerebral vascular accident (CVA)
Ischemic/hemorrhagic in any of the blood vessels of the brain
Sensory, UMN
Spasticity, weakness, Babinski, hyperreflexia
Cerebral palsy
Stroke in utero
Sensory, UMN
Cortical areas of movement impaired
Weakness, spasticity, increased tone, balance/postural deficits, contractures, possible cognitive changes, non-progressive, permanent disabilities and variable
Multiple Sclerosis
Sensory, UMN, cognitive
affects brain and spinal cord
CNS disorder, comes and goes
Weakness, hypertonia, spasticity, hyperreflexia, vision deficits, pain, coordination difficulties
Guillain Barre syndrome
Peripheral nervous system disorder that attacks Schwann cells
Sensory, LMN, autoimmune
Can follow a viral infection/vaccinations
weakness, pain, tingling, sensory deficits, autonomic dysfunction (constipation, tachycardic, diaphoretic)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Motor neuron disease
UMN and LMN degeneration
Weakness progresses, poor prognosis
Transverse myelitis
inflammatory disease of the spinal cord
motor, sensory, autonomic functions
Sensory, UMN, LMN
LMN if anterior horn cells involved
Can recover 100% but may have residual symptoms
Spinal muscle atrophy
Genetic, LMN affected
Weakness, atrophy, hypotonia, fasciculations
Can be fatal
Gene replacement therapy promising
Peripheral nerve injury
LMN affected, compressing, stretching, trauma, nerve transmission disruption
Often sensory involvement
Carpal tunnel, Cubital tunnel, Sciatica, Herniated disc
Hypotonia
low muscle tone, low resistance to stretch
Hypertonia
higher muscle tone, high resistance to stretch
Spasticity and rigidity
Spasticity
velocity (speed) dependent resistance to stretch
Rigidity
Decerebrate, decorticate, cogwheel, lead pipe
Stretch resistance
Flaccidity
no resistance to stretch
Functional tests
pronator drift
Alternating movements: toe tap, supination-pronation, hand tapping, finger tapping
Mechanoreceptors
mechanical deformation of the receptor by touch, pressure, stretch, or vibration
Chemoreceptors
substances released by cells, includes damaged cells after injury or infection
Thermoreceptors
transmit information regarding heat or cold
Nociceptors
sensation of pain
Proprioceptors
muscle and joint
Fine touch
A variety or specific receptors
Meisner's corpuscles: light touch, vibration
Merkel's discs: pressure
Course touch
Mediated by free endings throughout the skin
Non discriminative, tickle, itch, pressure, pain
!st order Somatosensory Neurons
Peripheral sensory neurons have two axons
Distal: messages from receptor to cell body
Proximal: from cell body into spinal cord or spinal brainstem
2nd order Somatosensory Neurons
spinal cord or brainstem into thalamus
3rd order Somatosensory Neurons
Thalamus to sensory cortex
Conscious relay
Make distinctions and decisions regarding stimuli
Touch, proprioception, pain, temperature
Divergent
Transmitted to many areas of brainstem and cerebrum
Conscious and unconscious
Unconscious relay
Automatic adjustments, posture
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus system (DCML)
Discriminative touch, vibration, proprioception, Stereognosis
1. Synapse in Nucleus gracilis or cuneatus
2. Decussates in medulla
3. Thalamus
4. Cortex/ Homunculus
Fasiculus gracilis
lower limb DCML
Fasiculus cuneatus
upper limb DCML
Spinothalamic
Anterior: mechanical receptors, crude touch, pressure
Lateral: temperature, pain/nociception
Decussates in spinal cord
Reflexes grades
0: no response
1+: low response
2+: normal
3+: higher than normal
4+: hyperactive
0-1+: LMN lesion
3+-4+: UMN lesion
Ataxia
incoordination that is not a result of weakness
Positive Romberg - sensory ataxia
Use vision to compensate
Cerebellar ataxia
no change in coordination with eyes opened/closed, unable to stand with feet together with or w/o vision, normal vibratory sense, proprioception
Neuropathy
Dysfunction or pathologic condition of one or more peripheral nerves
Injury to peripheral nerve results in lack of sensation in the distribution of the nerve
Pain, sensory changes, reflex loss, Conscious proprioception and discriminative touch go first
Trauma
complete or partial severing of the spinal cord
Transection of the cord
sensation is prevented below the lesion
Hemisection of the cord
loss of pain and temp sensation contralateral below lesion
discriminative touch and proprioception are lost ipsilateral below lesion
Disease
compromises the function of specific areas in the spinal cord
Virus
infects the dorsal root ganglion
Shingles/Chicken pox/Varicella
Somatosensory cortex lesions
contralateral loss of sensation, conscious proprioception, two point discrimination, stereognosis, localization of touch and pinprick/pain stimuli, extinction test for neglect
Stroke, tumor
Cortical spinal tract (CST)
Most important descending pathway, motor control of limbs
1. arises from primary motor cortex
2. through internal capsule
3. cerebral peduncles (midbrain)
4. pons
5. Medullary pyramids
6. Decussate
7. spinal cord to anterior horn
8. Synapse with LMN
Lateral CST
85% pyramidal tract fibers descend contralaterally
Lateral white matter columns
Axons enter the sc central grey matter to synapse
Connects with LMN in ventral horn of the spinal cord
movement of more distal muscles
Anterior CST
15% CST continue into the sc ipsilaterally
decussates at appropriate level of spinal cord
Controls movements that involve multiple spinal segments
Synapse with LMN on muscles that control neck, shoulder, and trunk
Babinski reflex
Instant reflex where you stroke the bottom of the foot from the heel along the lateral side and base of the toes to the big toe
Positive sign: toes up or fanning
Negative sign: toes down
Hoffmans test
-Examiner grasps pt's 3rd digit DIP & briskly flicks the fingernail in a downward motion
-(+): thumb & forefinger come closer to one another
-Indicative of an UMN lesion
Disorders of the motor system
spinal cord injury
spinal muscle atrophy
CVA cerebral vascular accident
Cerebral palsy
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
CTS, cubital tunnel syndrome, Sciatica, Disc prolapse
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Hemi-section of the cord
- ipsilateral (same side) loss of vibration and loss of position sense
- contralateral (opposite side) loss of pain and thermal sense
Central cord syndrome
paint and temperature sense loss of upper extremities cause by injury to the middle portion of the spinal cord
Anterior cord syndrome
pain and temperature sense loss caused by injury to the anterior 2/3 of spinal cord
Posterior cord syndrome
vibration and proprioception sense loss caused by injury to posterior 1/3 of spinal cord
Cauda Equina Syndrome
-Injury at the L1 level and below resulting in a LMN lesion
-Flaccid paralysis w/no spinal reflex activity
Complete spinal cord injury
no motor or sensory at lowest level
Incomplete spinal cord injury
some sensory or motor spared
Transverse cord lesion
Both sides
vibration and position sense loss
pain and temperature sense loss
motor loss
Middle Cerebral artery CVA
stroke of MCA will interfere with motor cortex
Rubrospinal tract
Originates in red nucleus of the midbrain
Decussates in midbrain
Controls flexor tone in UE
Close proximity with LCST so injuries happen together
Spasticity after a stroke
Reticulospinal tract
Medial motor tract
Originates in the reticular formation of the brainstem (pons and medulla)
Controls postural muscles and proximal limb muscles
After stroke, responsible for muscle synergy
Vestibulospinal tract
Medial motor tract
Originates in vestibular nucleus of the pons and medulla
Maintains balance and posture through increased muscle tone and movement of the head and limbs
Nerve cells in vestibular nuclei receive afferents from inner ear and cerebellum
Axons descend undecussated through medulla and length of spinal cord
Synapse with neurons in anterior gray column of spinal cord
Vestibular nuclei
Brainstem nuclei that receive information from the vestibular organs through cranial nerve VIII (the vestibulocochlear nerve)
In pons and medulla
Internal capsule
contains both corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts (motor tracts); carries UMN (no LMN), a couple of its functions include carrying motor commands to lower motor neurons and sensory-related information from the thalamus to the cortex
Somatosensation
sensory information from the skin and musculoskeletal systems, superficial or cutaneous information from the skin
Touch, pain, temperature, proprioception
Learn from the world around us to react to body's needs
Necessary for accurate control of movements and protects against injury
Speed of information processing
determined by: diameter of axons, degree of axonal myelination, number of synapses in the pathway
Sensory receptors
Specialized, different receptors respond to specific stimuli
Mechanoreceptors, Chemoreceptors, Thermoreceptors, Nociceptors, Proprioceptors
Musculoskeletal innervation
muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, joint receptors, joint, muscle, and skin receptors required for accurate proprioception
Muscle spindle
respond to stretch, more numerous in muscles that control fine motor
Golgi tendon organs
located at musculoskeletal junction, slight changes in tension associated with contraction
Joint receptors
Receptors surrounding a joint that respond to pressure, acceleration, and deceleration of the joint.
Myotatic stretch reflex
muscle perceives quick stretch, information is relayed to spinal cord to alpha motor neurons, efferent produce a contraction of stretched muscle and inhibit antagonist
All at spinal cord level
1st order sensory neurons
peripheral sensory neurons have two axons
Distal and proximal
Distal 1st order
conduct messages from the receptor to the cell body
Proximal 1st order
project from the cell body into the spinal cord or spinal brainstem
2nd order sensory neurons
spinal cord or brainstem to thalamus
3rd order sensory neurons
thalamus to sensory cortex
Homunculus
a maplike representation of regions of the body in the brain part of the post central gyrus
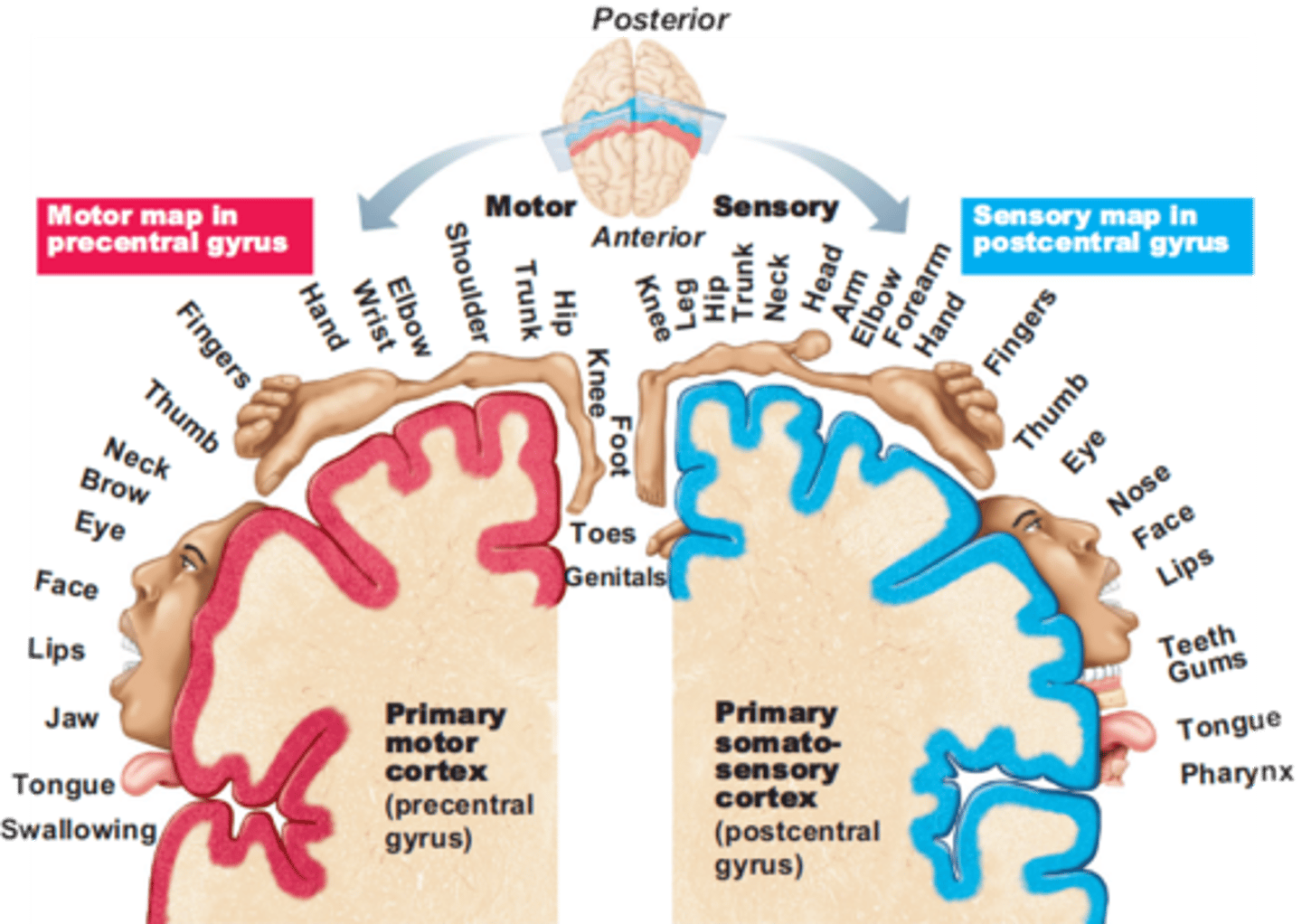
Discriminative touch
localization of touch and vibration and the ability to discriminate between two closely spaced points touching the skin
Stereognosis
identify object in hand without sight
Proprioception
The ability to tell where one's body is in space.
Vibration
able to sense and feel vibration in various parts of the body
Sensory ataxia
No sway with eyes open but loses balance with eyes closed