Veterinary Immunology: Parasite Immunity and Host Defense Mechanisms
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
_ block or significantly delay the innate and acquired defenses of their host to persist long enough to reproduce.
Parasites
Fungal infections can be later destroyed by _
T-cell mediated mechanism (Acquired immunity)
__ functions primarily in fungal infections by activating macrophages & promoting epithelial growth
T-cells
the youngs are more resistant to Babesiosis (tick-borne ds) than old animals
True
_ is important in controlling protozoa in the blood & ICF
Humoral response
__ is mostly directed against intracellular parasites
Cell-mediated immune response
__ production by macrophage is useful when combined with reactive oxygen radicals
Nitric oxide
This is the product from NO and Reactive O2 radicals, which are are lethal for many intracellular protozoa
Nitrogen radicals
It is the resistance acquired after a primary infection has become chronic and that is only effective if the parasite persists in the host; significant for Toxoplasmosis & Babesiosis
Premunition
Which immune responses are triggered upon exposure to Toxoplasma gondii?
Th1 and Th2 immune responses occur.
_ involves antibodies together with complement destroys extracellular organisms & reduces spread of organism between cells which has little influence to intracellular forms
Th2 response
Intracellular organisms are destroyed by __
IL-12 dependent Th1 Cell-mediated response
Th1 cells secrete _ that activates macrophages
IFN-γ
Cytotoxic T cells can destroy Toxoplasma tachyzoites & Toxoplasma-infected cells. However, T. gondii tachyzoites can transform themselves into a cyst form containing __, which is a cyst that is non-immunogenic
Bradyzoites
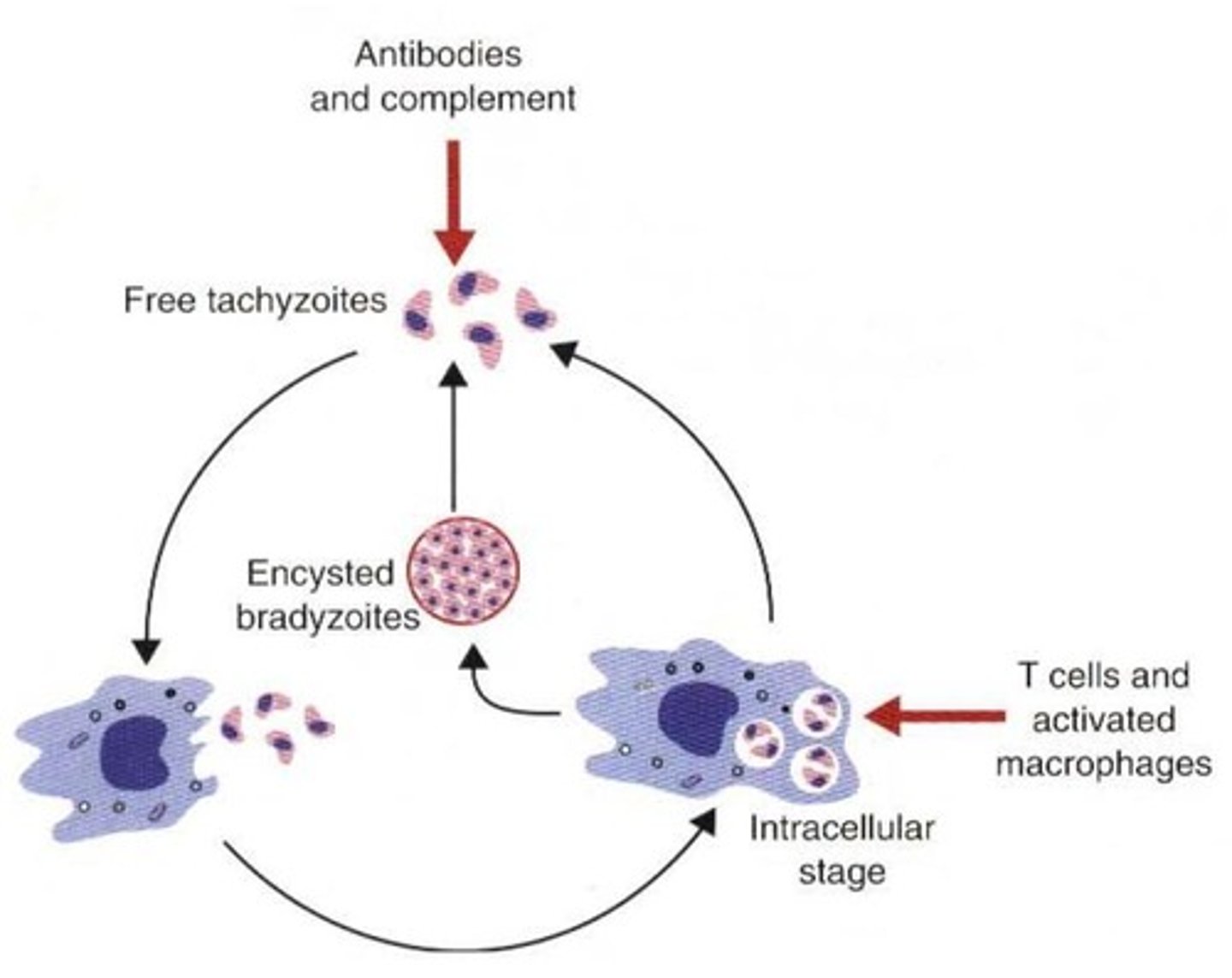
This is limited to coccidiosis, babesiosis, leishmaniasis, giardiasis, theileriosis
Vaccination against Protozoan Infections
Live coccidial vaccines are usually administered to poultry, which consists of virulent, drug-sensitive organisms administered repeatedly in very low doses, called _
Trickle infection
_ are more susceptible in helminth infection due to hormones
Females
Bos indicus cattle develop greater resistance to __ than Bos Taurus
Cooperia oncophora
In age, _ are more resistant
Mature adults
Helminth immunity humoral factors include _ , which is the most significant mechanism of helminth resistant
Ig-E dependent eosinophil mediated response.
How do sensitized T cells interfere with helminths by developing _ reactions and destroying larval helminths.
hypersensitivity
Live cysts stimulate a what response?
Th2
Dead cysts stimulate what response?
Th1
_ production is essential in controlling worm burdens (seen in self-cure reaction in sheep infected with GI nematodes like H. contortus
Th-2 mediated IgE
What triggers mast cell degranulation in response to helminth antigens, following vasoactive molecules and proteases release
The combination of helminth antigens with mast cell-bound IgE.
Because eosinophils have FC receptors, they can bind to Ab-coated parasites, degranulation releases their granule contents directly on the __.
Worm cuticle
What are some molecules released from eosinophils that damage parasitic helminths?
Oxidants, nitric oxide, lytic enzymes, eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), and eosinophil neurotoxin.
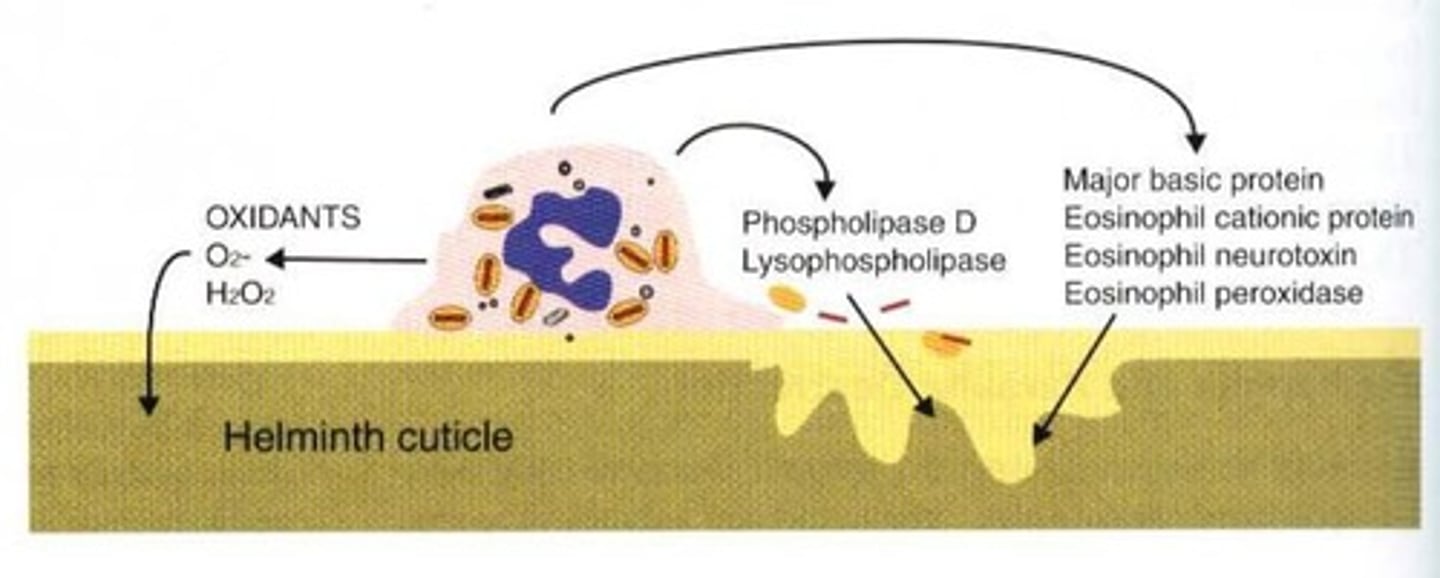
How do eosinophils interact with antibody-coated parasites?
Eosinophils bind to antibody-coated parasites via Fc receptors and release granule contents directly onto the worm cuticle.
_ can interfere with the complement system by secreting sulfated proteoglycans, → activate complement in the tissue fluid
Tapeworms
Many helminths express surface antioxidants such as _, that can neutralize the host’s respiratory burst & protect surface structures against oxidation
superoxide dismutase, glutathione-S-transferase
Arthropod saliva contains digestive enzymes and components designed to minimize host responses. One of them is _ that destroy bradykinin which mediates pain & itch
Kininases
in different ticks, in Ixodes scapularis; displaces properdin & enhances the _→ resulting to minimized host-scratching & grooming response
C3bBb convertase degradation
In__- the saliva impairs the maturation and antigen-presenting abilities of dendritic cells and inhibits host B cell proliferation
Ixodes ricinus
When arthropods bite or attach to a host, they inject saliva and provoke the ff:
Low Molecular weight salivary component may bind to skin proteins and acting as hapten → may stimulate a __ on subsequent exposure
Th1 response-delayed hypersensitivity reaction
Antigen of injected arthropod saliva antigen may bind to epidermal Langerhans cells and → stimulate _
Th1 response-cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity (Type IV)
Antigen of injected arthropod saliva antigen may stimulate a Th2 response → Increased IgE → _ (intense local inflammation with pruritus)
T1 hypersensitivity
although immune responses can reduce arthropod feeding & reproduction, _ rarely kill the arthropods because they only reduce arthropod feeding & reproduction
Th2