Benzyl Alcohol to Benzoic Acid and the Recrystallisation of Benzoic Acid
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Appearance of phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) at room temperature
Colourless liquid
Why is potassium permanganate added?
Ensure the complete oxidation of phenylmethanol
Phenylmethanol + sodium carbonate + heat + potassium permanganate changes
Purple to brown
Forms sodium benzoate
Why is sodium carbonate added?
Speed up the reaction
Why was the reaction acidified with hydrochloric acid?
Neutralise sodium carbonate
Convert sodium benzoate to benzoic acid
Test the solution to make sure it's acidic enough
Blue litmus paper - turns red
What happens when hydrochloric acid and sodium sulphite is added and the solution is cooled?
Brown colour disappears and white crystals form
MnO2 is being reduced (Mn4+ --> Mn2+), crystallisation of benzoic acid occurs
Why was the flask placed in ice before filtration?
Ensure all benzoic acid crystallises out because it's less soluble in cold water, maximises yield
What causes the smell of almonds?
Benzaldehyde
Method to dry crystals
Place on radiator
Technique to purify benzoic acid crystals
Recrystallisation
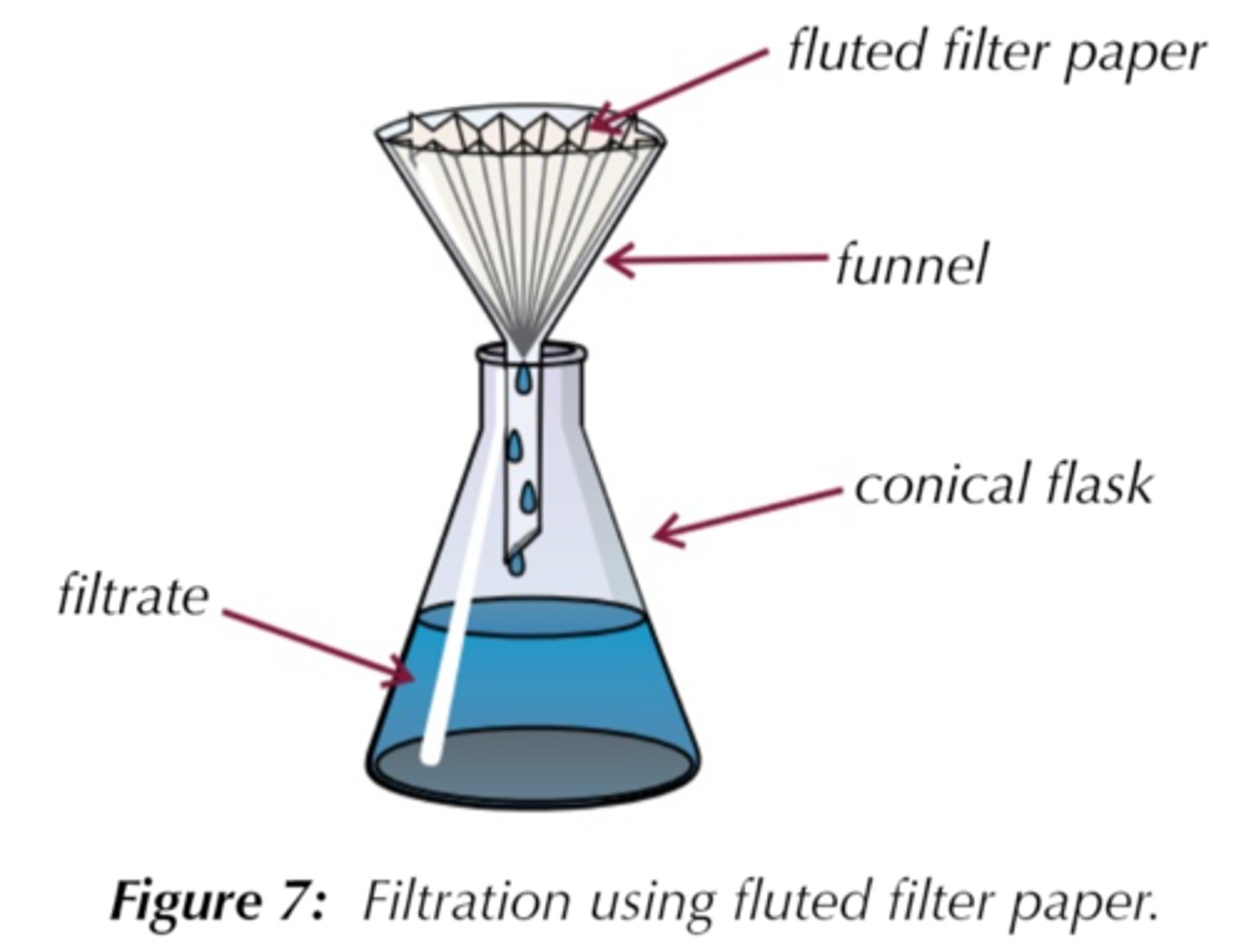
Recrystallisation apparatus
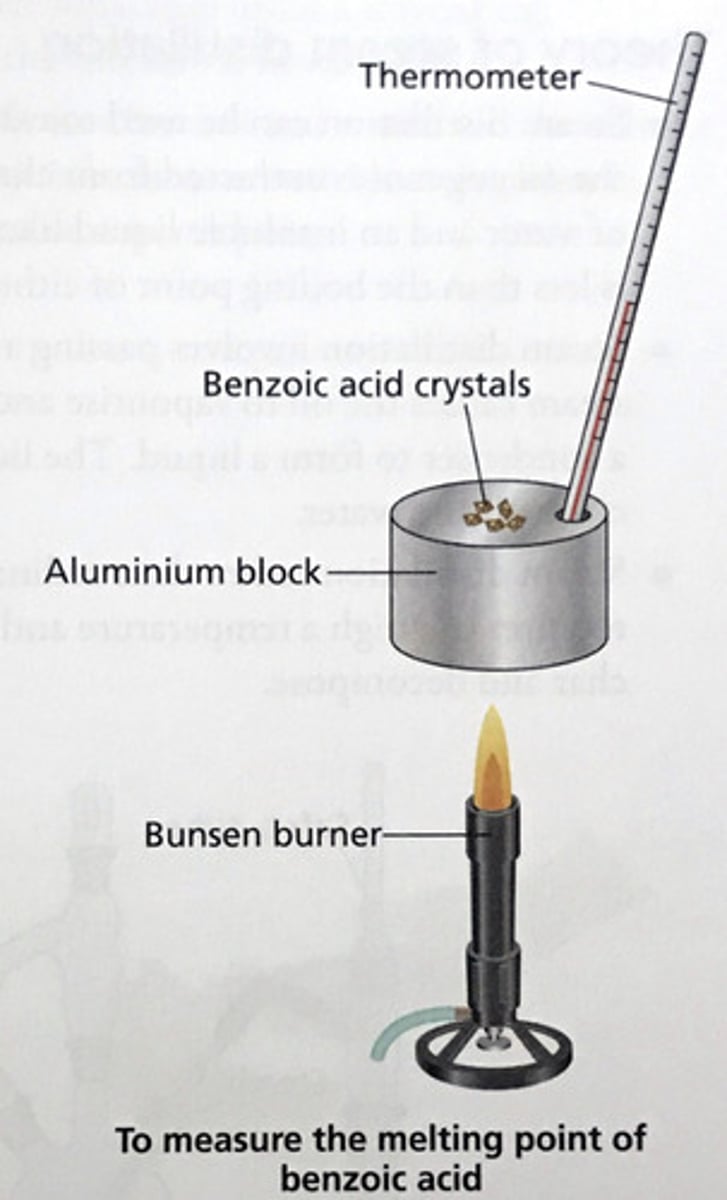
Measuring the melting point of crystals
1. Place crystal sample on aluminium melting block
2. Heat slowly while observing crystals
3. Record temperature range at which melting occurs
Examples of impurities
MnO2, sodium sulphite, HCl
Melting point difference between pure and impure crystals
Melting point of pure crystals higher, closer to 122 degrees Celcius
Measure the melting point of benzoic acid