Muscle Anatomy and Physiology- Oxygen Supply / Cellular Respiration, Muscular Responses/Interaction
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Sarcomere
a repeating pattern of myofibril units along each muscle fiber; creates the light and dark striations that we see
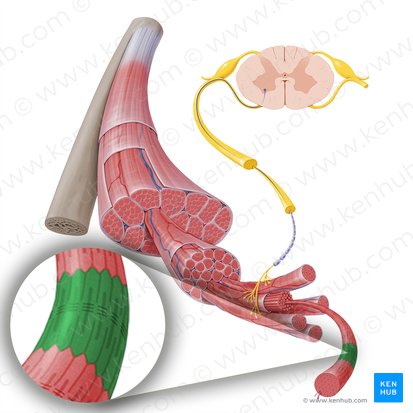
Thick filaments
aka myosin filaments they are responsible for force generation during muscle contraction
Thin filaments
aka actin filaments a key component of muscle contraction in striated muscle include tropomyosin and troponin
Motor unit
specialized nerve cells that control voluntary movements, such as walking, talking, and breathing.
ADP/ATP cycle
the cellular mechanism for storing and releasing energy
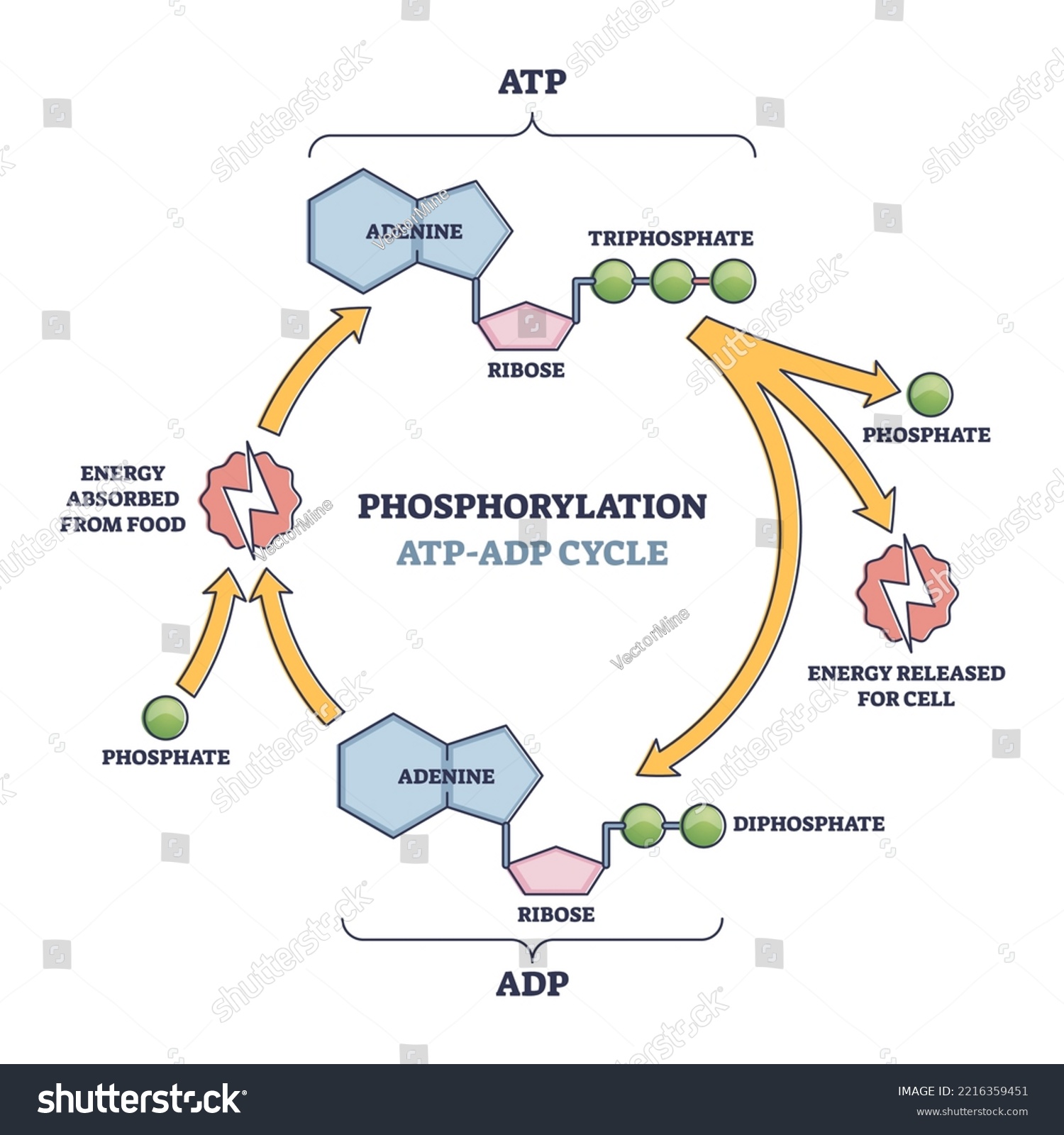
Creatine phosphate
involved in the ATP/CP System stores energy that quickly converts ADP to ATP; made by Mitochondria for storage in the muscle
ATP/CP cycle
aka phosphagen system a rapid, anaerobic energy system that provides energy for short bursts of high-intensity exercise, primarily lasting up to about 10 seconds. It relies on the breakdown of creatine phosphate (CP) to rapidly replenish ATP.
Aerobic respiration
the process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP (energy), carbon dioxide, and water produces more ATP
Myoglobin
O2 binding site in muscle
Oxygen debt
the amount of extra oxygen the body needs after strenuous exercise to restore itself to a resting state. This occurs because during intense activity, the body's oxygen supply can't keep up with its demand, leading to a buildup of lactic acid.
Fatigue
an inability to contract commonly caused from:
accumulation of lactic acid
psychological loss of desire
decreased blood flow
ion imbalances across the sarcolemma from heavy use
fast twitch
white (b/c they have less blood& o2) muscle fibers that contract rapidly and generate powerful movements, but fatigue faster
slow twitch
red (b/c they have more blood& o2) muscle fibers highly efficient at using oxygen to produce energy for sustained, low-intensity activities good for endurance as they fatigue slower
red fibers
slow twitch b/c they have more blood& o2 (aerobic) most hemoglobin
white fibers
fast twitch b/c they have less blood& o2 (anaerobic) less hemoglobin
Isometric contraction
muscle contracts but does not change length; generally against immovable objects
isotonic contraction
muscle contracts and changes length; against movable objects
Tone
continuous state of partial contraction; often gives muscles a sculpted look
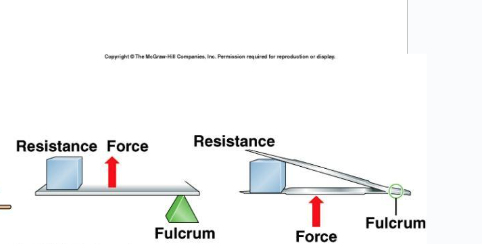
1 degree lever
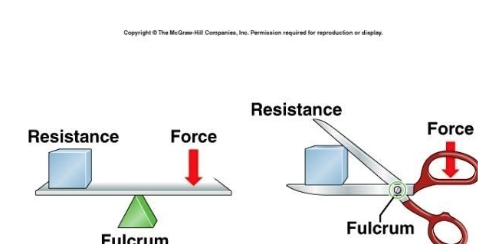
2 degree lever
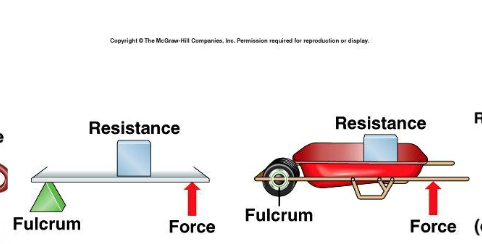
3 degree lever
Calculate Work
force x distance
Calculate Power
work / time
hemoglobin
O2 binding site in blood