Glycolysis, TCA, Oxidative Phosphorylation
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
Stages of cellular respiration are
1. acetyl coA production (glycolysis)
2. acetyl coA oxidation (TCA)
3. electron transfer and oxidative phosphorylation (ETC)
Most of the major energy-generating pathways of cells eventually result in production of
acetyl coA (2C unit)
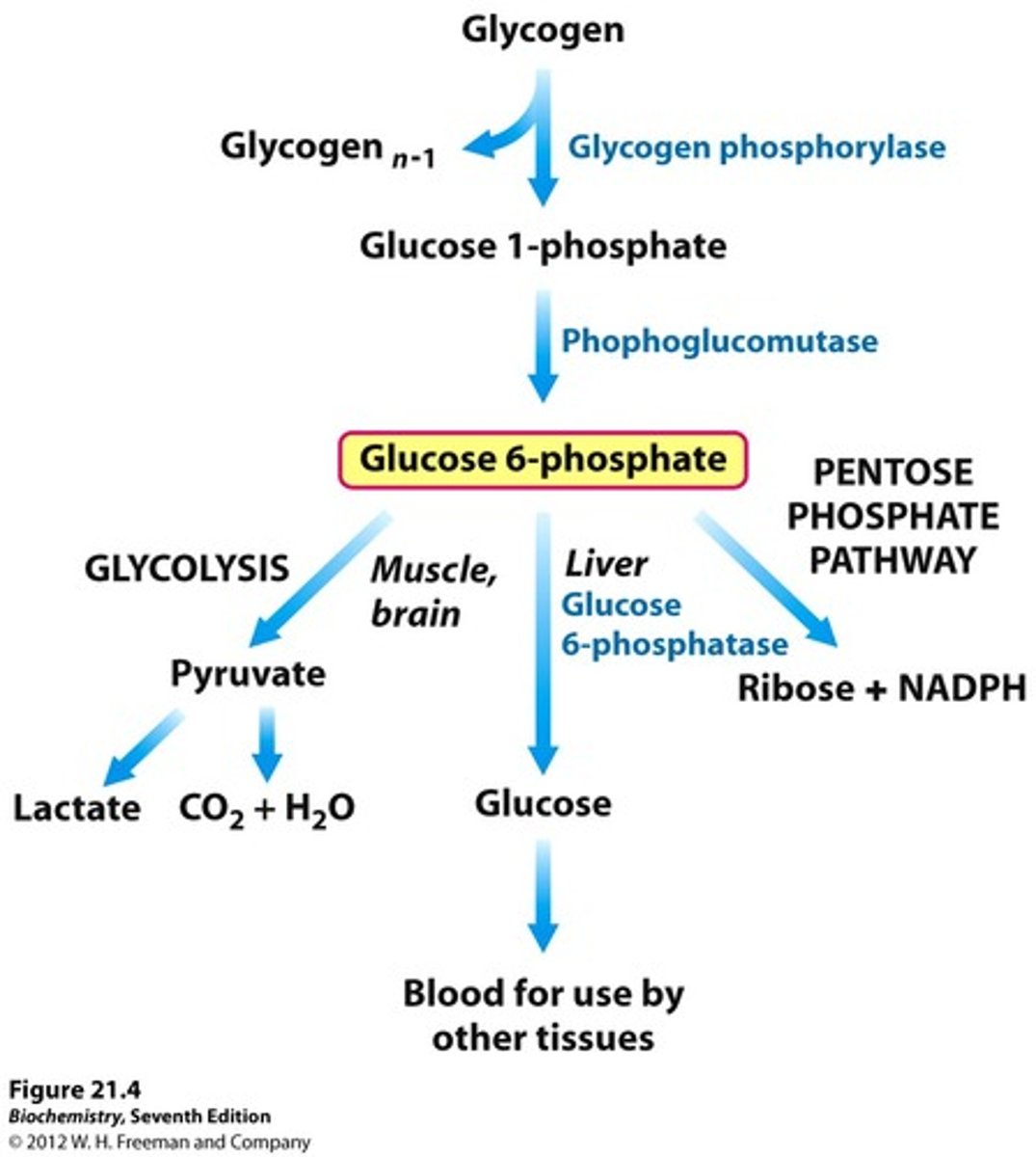
What is glucose converted to for storage?
glycogen
What is glucose oxidized to via the pentose phosphate pathway?
ribose 5-phosphate
What is glucose oxidized to via glycolysis?
pyruvate
3 fates of glucose
1. can be stored as a polysaccharide or as sucrose
2. oxidized to 3C compound pyruvate via glycolysis
3. oxidized to pentoses via pentose phosphate pathway
2 phases of glycolysis
preparatory phase
payoff phase
Step 1 of glycolysis
glucose uses a phosphate from ATP (turns ATP to ADP) and glucose is turned to glucose 6-phosphate
What converts glucose to glucose 6 phosphate?
hexokinase
Step 2 of glycolysis
Glucose 6-phosphate is converted to fructose 6-phosphate
What converts G6P to F6P?
phosphohexose isomerase
Step 3 of glycolysis
fructose 6-phosphate is converted to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate using another phsophate from ATP
What converts F6P to F1,6BP?
phosphofructokinase-1
Step 4 of glycolysis
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
What cleaves F1,6BP into its two products?
aldolase
Step 5 glycolysis
dihydroxyacetone is converted into another molecule of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
What converts dihydroxyacetone into G3P?
triose phosphate isomerase
What are the two priming reactions of glycolysis?
glucose to glucose 6-phosphate
fructose 6-phosphate to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
Step 6 of glycolysis
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidizied by NAD producing 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
What is generated by step 6?
2 NADH + H+
What converts G3P into 1,3BPG?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Step 6 involves...
phosphorylation and oxidation
Step 7 of glycolysis
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is dephosphorylated to form 3-phosphoglycerate
What is formed in step 7?
2 ATP
What catalyzes the formation of 3-PG from 1,3-BPG?
phosphoglycerate kinase
What type of phosphorylation occurs in step 7?
substrate level
Step 8 of glycolysis
3-phosphogylcerate is converted to 2-phosphoglycerate
What converts 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate?
phosphoglycerate mutase
Step 9 of glycolysis
2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate
What converts 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate?
enolase
Step 10 of glycolysis
phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate
What occurs in step 10?
substrate level phosphorylation
What converts phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate?
pyruvate kinase
In the prep phase of glycolysis, the energy of ATP is
invested
In what phase does energy gain come in glycolysis?
payoff phase
Preparatory phase
phosphorylation of glucose and its conversion to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The priming stage of the prep phase involves...
the input of 2 molecules of ATP with the conversion of glucose into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
The splitting stage of the prep phase does what?
splits the 6 C molecule of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate into 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Payoff phase
oxidative conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to pyruvate and the coupled formation of ATP and NADH
In the payoff oxidoreduction-phosphorylation stage ___________ molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are converted into ___________ molecules of pyruvate with the production of __________ molecules of ATP
2, 2, 4
How many NADH are produced at the end of glycolysis?
2
The sum reaction for the 10 consecutive steps of glycolysis comes to the generation of...
2 pyruvate
2 NADH
2 ATP
at the expense of 1 glucose molecule
In the reaction of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, what happens?
an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid with the reduction of NAD+ to NADH
1,3-bisphosphoglycerate has a large _____________ free energy of hydrolysis, which enables it to do what?
negative, participate in a subsequent reaction that yields ATP
How many molecules of ATP are invested in the priming stage?
2
The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase- phosphoglycerate kinase system is an example of
substrate level phosphorylation
Substrate level phosphorylation
The formation of ATP by directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism
Enolase catalyzes the elimination of
water from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphoenolpyruvate
Pyruvate kinase accomplishes...
substrate level phosphorylation by the synthesis of ATP with the conversion of the high-energy compound PEP into pyruvate
The reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase requires ________ and produces...
NAD+, NADH
Because the cytosol of cells only has a limited amount of NAD+, it is imperative for continuous glycolytic activity that the ____________ be converted back to ______________
NADH, NAD+
The last step of the glycolytic pathway is
oxidoreduction reaction catalyzed by lactate dehydrogenase
What does lactate dehydrogenase do?
converts pyruvate to lactate, yielding NAD+
oxidizes NADH to NAD+
NADH generated by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is converted back into NAD+ by
lactate dehydrogenase
Cells under what condition require lactate dehydrogenase for regeneration of cytosolic NAD+?
anaerobic conditions
What are the regulatory enzymes of the glycolytic pathway commonly considered to be?
hexokinase
phosphofructokinase-1
pyruvate kinase
What is the rate limiting enzyme of glycolysis?
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1)
What is the most important regulatory site of glycolysis in most tissues?
PFK-1
Most important negative allosteric effectors of glycolysis
citrate, ATP, hydride ions (low pH)
Most important positive allosteric effectors of glycolysis
AMP, fructose 2,6-bisphosphate, and Pi
Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is ___________ into two molecules of pyruvate, with energy conserved as ______________
oxidized, NADH and ATP
In the preparatory phase, ATP is invested to convert ________________ to _________________. _______________ is then broken down into two molecules of _________________
glucose, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
In the payoff phase, each of the two molecules of _________________ undergoes _______________. The energy of this _______________ is conserved in the formation of _______________
G3P, oxidation, oxidation, NADH and ATP
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA is what type of reaction?
oxidative decarboxylation
Pyruvate must enter the ___________ to enter the TCA cycle
mitochondria
Oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate is catalyzed by the
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
How many enzymes make up the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
3
How many coenzymes are required in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
5
In the TCA cycle, pyruvate from glycolysis is ____________ to _____________
oxidatively decarboxylated, acetate
What is acetate degraded to in the TCA cycle?
CO2
The NADH from the TCA cycle goes on to make more _____________ where?
ATP, ETC and oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate yields
a-ketoglutarate
Isocitrate dehydrogenase is a link to the ETC pathway because it makes
NADH
Acetyl coA is converted to what in TCA cycle in step 1?
citrate
What converts acetyl-CoA to citrate?
citrate synthase
What is put in and generated in the step that turns acetyl coA to citrate?
water put in, CoA-SH generated
Citrate is next converted to
isocitrate
What converts citrate to isocitrate?
aconitase
Isocitrate next yields
CO2, NADH, and a-ketoglutarate
What converts isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate?
isocitrate dehydrogenase
a-ketoglutarate is converted into
Succinyl CoA and CO2 and NADH
What converts a-ketoglutarate into succinyl-CoA?
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
Succinyl CoA is converted to
succinate + GTP
What converts succinyl CoA to succinate?
succinyl-CoA synthetase
Succinate is _________________ to form ______________
dehydrogenated, fumarate
What converts succinate to fumarate?
succinate dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase is seen where?
TCA cycle and ETC
What is yielded when succinate is dehydrogenated to fumarate?
FADH2
Fumarate is hydrated to
malate
What converts fumarate to malate?
fumarase
Malate is _______ to form ______________
dehydrogenated, oxaloacetate
Converts malate to oxaloacetate
malate dehydrogenase
What does oxaloacetate make?
acetyl CoA
Pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, is converted to ____________, the starting material for the TCA cycle, by what multienzyme complex?
acetyl-CoA, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
The TCA cycle is a central ____________ pathway in which compounds derived from the breakdown of _______________ are oxidized to _________________
catabolic, carbs, fats, and proteins, CO2
Acetyl-CoA enters the TCA cycle through its condensation with _____________ to form ________________
oxaloacetate, citrate
The TCA cycle converts ____________ to ______________ and releases __________ CO2
citrate, oxaloacetate, 2 CO2
For each acetyl-CoA oxidized, the energy gain consists of _______ NADH, __________ FADH2, and ____________ GTP
3, 1, 1
Steps that generate NADH
isocitrate dehydrogenase
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
malate dehydrogenase