2.1 Molecules to metabolism
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Urea
A nitrogen-containing compound that can be naturally produced in urine or artificially synthesized
Purpose of urea
Produced when there is an excess of amino acids in the body as to excrete the nitrogen from the amino acids
Natural synthesis of urea
Produced in the liver and then transported by the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is filtered and passed out of the body in urine
Vitalism
Theory that the origin and phenomena of life are due to a vital principle, different from purely chemical or physical forces, that is only present in living organisms
Falsification of vitalsim
In 1828, German chemist Wohler synthesized urea using silver isocyanate and ammonium chloride, the first artificial synthesis of a compound
Carbohydrates
Molecules composed of C, H, and O. H and O in a 2:! ratio
Lipids
Broad class of molecules that are insoluble in water. Includes fatty acids, triglycerides, steroids and waxes
Proteins
Molecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids (contains C, H, O, and N)
Nucleic acids
Chains of subunits called nucleotides (containing C, H, O, N and P)
Types of nucleic acids
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
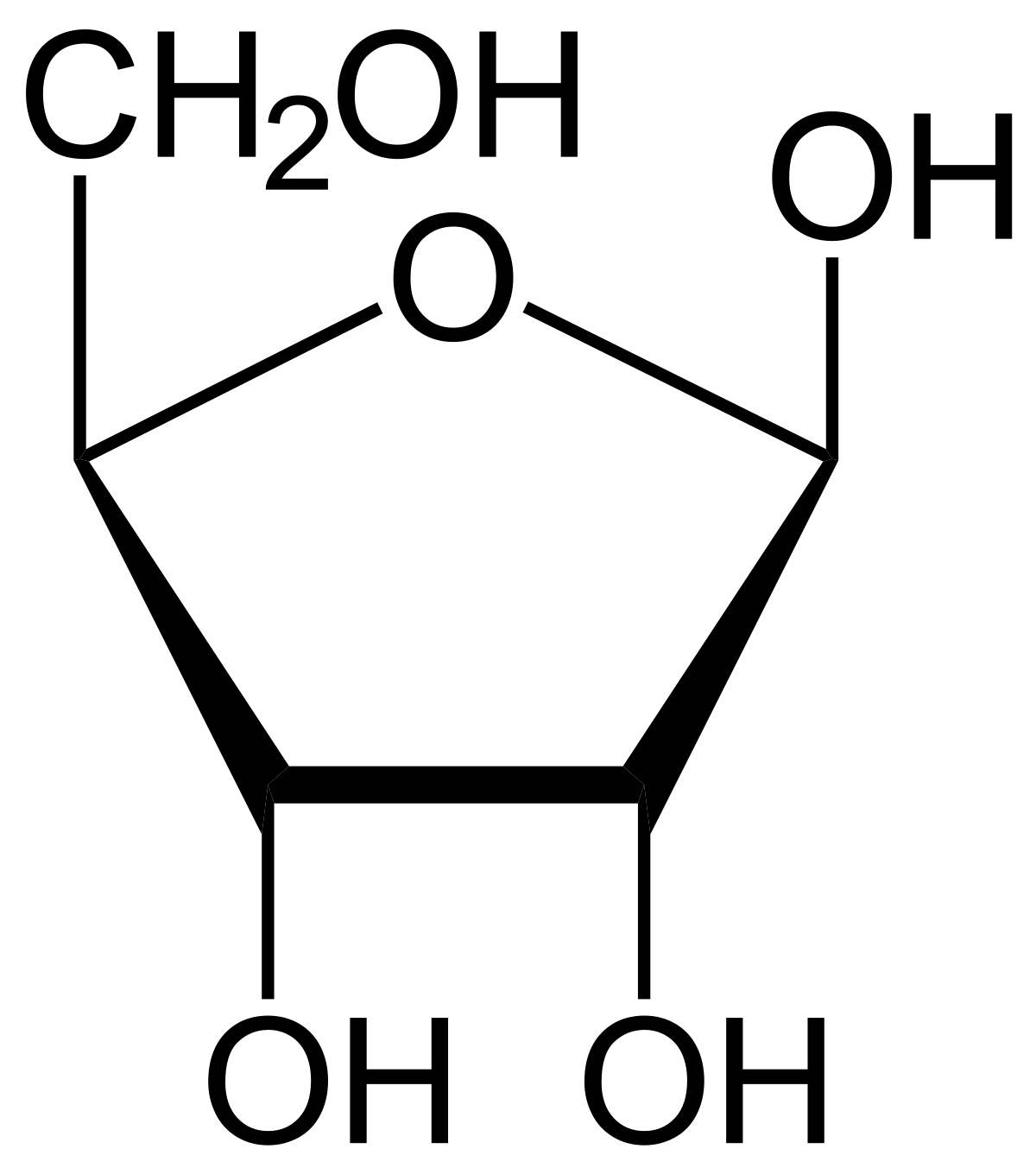
Drawing ribose
formula: C5H10O5
5-membered ring with a side chain
C1 on the right of oxygen
-OH up in C1, down in C2 and C3
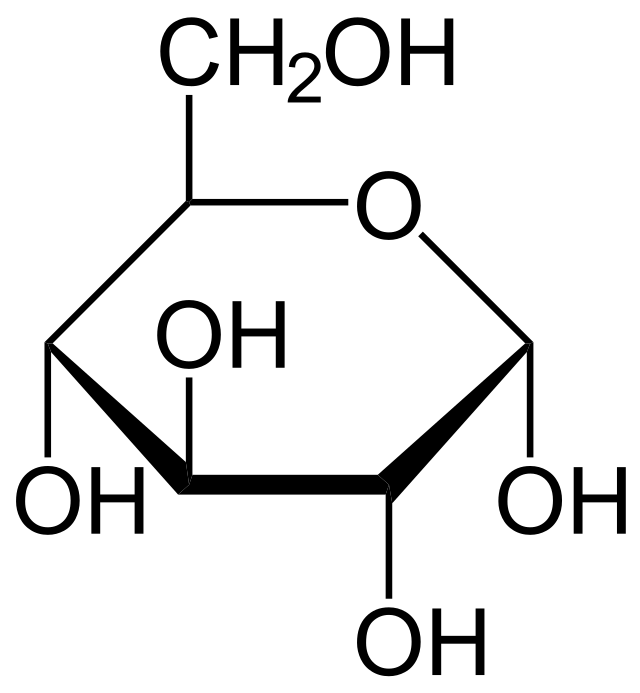
Drawing glucose
formula: C6H12O6
6-membered ring with a side chain
C1 on the right of oxygen
-OH down in C1, C2 and C4, up in C3
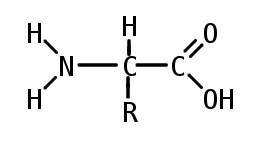
Drawing amino acids
carbon in the centre is bonded to
amine group -NH2
carboxyl group -COOH
H
R group
Drawing fatty acids
C-atoms form an unbranched chain
Bonded to each other by single bonds
At one end is part of a carboxyl group
At the other end the C-atom is bonded to three H atoms
All other C atoms are bonded to 2 H atoms
Metabolism
the sum of all the enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell or organism
Metabolic pathways
Process in which one type of molecule is transformed into another in a series of small steps
Anabolism
Synthesis of simpler molecules into complex molecules. Requires energy, usually as ATP
Anabolic processes
Condensation reactions
Protein synthesis using ribosomes
DNA synthesis during replication
Photosynthesis
Synthesis of complex carbohydrates
Catabolism
Breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules. Releases energy (due to breaking of bonds)
Catabolic processes
Hydrolysis
Digestion of food
Cell respiration
Digestion of complex carbon compounds in dead organic matter by decomposers