biol454 lymphocyte development 2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
what are 2 main problems with VDJ gene rearrangement?
huge potential to generate nonfunctional gene arrangements/non functional Ag receptors
huge potential to generate self-Ag reactivity
how does VDJ gene rearrangement generate nonfunctional Ag receptors?
out of frame VDJ rearrangements
premature stop codons
how does generation of self-Ag reactivity occur from VDJ rearrangement?
junctional diversity is not germline encoded
potential to recognize self and cause autoimmune disease
what provides a maturation and differentiation microenvironment for B cell development?
bone marrow
B cell development
what location…
regulates construction of an antigen receptor
ensures each cell has only one specificity
checks and disposes of self-reactive B cells
exports useful cells to periphery
provides site for antibody production
bone marrow
what are the two checkpoints for T/B cell development?
Pre-B/T antigen receptor expression (3)
Antigen receptor expression (5)
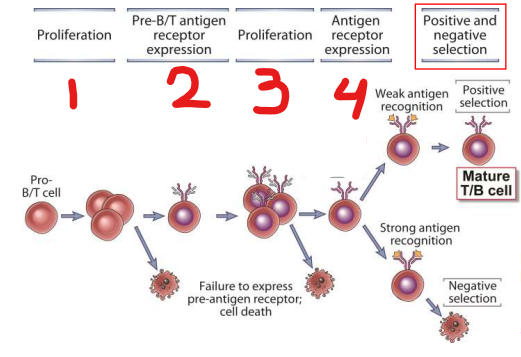
which steps of development are checkpoints?
2.4
B cell maturation
RAG and TDT expression occur when ? develops into ?
Pro-B into Pre-B
which stage of maturation has a recombined H chain gene and a pre-B receptor?
Pre-B cell
which stages of maturation have no response to antigens?
stem cell, pro-b, pre-b
name the stages of maturation for B cells (start to finish)
stem cell
pro-B cell
pre-B cell
immature B cell
mature B cell
what is an unproductive gene rearrangement?
rearrangements that do not give rise to functional proteins
what is a productive gene rearrangement?
gives rise to functional protein (full length chain)
for gene rearrangements, in what scenario does the B cell precursor die (due to apoptosis)
both rearrangements on homologous chromosomes are unproductive
(t/f) only successfully rearranged heavy chains can associate with V pre-B receptor
true
Pre-BCR is made up of what two components?
V pre-B and heavy chain
Pre-BCR is expressed on the surface of what lymphocyte?
Pre-B cell
which cell receptor is responsible for…
inhibition of H chain recombination
proliferation of pre-B cells
stimulation of light chain recombination
shutting off surrogate light chain transcription
pre-B cell
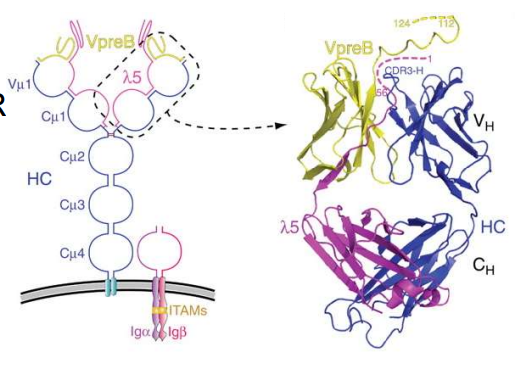
what lymphocyte is this?
pre-BCR
(t/f) no part of pre-BCR is similar to BCR
false, the V region is “similar” to BCR
what happens when VpreB makes surface pre-BCR dimerize?
it sends a signal
what causes…
survival, proliferation
decreased VDJ gene rearrangement
HC allelic exclusion
decreased pre-BCR and IL-7 signaling
increased light chain VJ gene rearrangement
self-aggregation/cross-linking induced signaling of pre-BCR
B cell development in bone marrow requires what?
stromal cells
what growth factors (cytokines) are produced by stromal cells? what are they recognized by?
stem cell factor (SCF) - Kit on B cell precursor
IL-7 - stimulates pro and pre-B cells via IL-7 receptor
in a common lymphoid progenitor cell, what are the adhesion dependent contacts? (for the CLP and stromal cell)
CLP: VLA-4
stroma: VCAM-1
what lymphocyte recognizes SCF on the stroma with a Kit receptor?
early pro-B cell
expression of what receptor turns of rearrangement of H chain genes?
pre-B cell receptor (pre-BCR)
when expressed on cell surface, what turns of RAG genes?
BCR
signaling takes place via ? and ?
Iga,, IgB
B cell development
at what stage of maturation does heavy chain rearrangement stop and light-chain rearrangement begins?
large pre-B cell
B cell development
at what stage of maturation does light-chain rearrangement stop?
immature B cell
B cell development
at what stage of maturation does heavy chain rearrangement begin?
early pro-B cell
monospecificity
1 functional IgH allele
1 functional IgL allele (kappa or lambda)
1 antigen specificity
polyspecificity
2 function IgH alleles
6 functional IgL alleles
12 different antigen specificities
allelic exclusion
property of expressing only one of two Ig alleles
what mechanism is this?
once a functional heavy chain is made, the pre-BCR can assemble and send signals
Rag1 and Rag2 proteins are redirected away from IgH locus
Rag1/2 is turned off when a functional light chain is made
mechanism for allelic exclusion
how does allelic exclusion enhance antibody efficiency?
it ensures one B cell and its clonal progeny will make homogenous antibodies with two identical binding sites
what stage of maturation is this?
RAG expression
Ig DNA/RNA: recombined H chain gene, kappa or lambda genes (VJ), mu, kappa, or lambda mRNA
Ig expression: membrane IgM (mu or kappa or lambda light chain)
response to antigen: negative selection (deletion), receptor editing
immature B
for rearrangement of (heavy/light chain), several rounds of rearrangement until productive
light
(t/f) about 85 pct of pre-B cells have productive L chain rearrangement
true
checkpoint (1/2) negative selection of B cells and receptor editing
checkpoint 2
what situation causes this to occur:
BCR signals through Ig-alpha and Ig-beta to turn on RAG and start rearrangement of lambda light chain to try and generate an antibody with lower affinity for self antigen
BCR with functional H and L chain sees self-protein
receptor editing occurs when…
BCR with functional H and L chain sees self-protein
signals through Iga and Igb to turn on RAG to rearrange lambda-light chain to generate antibody with lower affinity for self antigen
order of rearrangement for human Ig (ab) locus
heavy chain locus
kappa light chain locus
lambda light chain locus
H-chain gene rearrangement occurs in which stages of maturation for B cells?
early and late pro-B cell
in B cell development, at which stage of development does L chain gene rearrangement occur?
pre-B cell
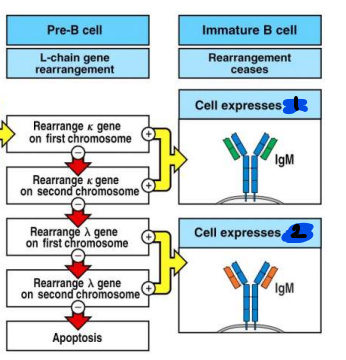
productive kappa gene on either the first or second chromosome results in the cell expressing…
mu/kappa IgM
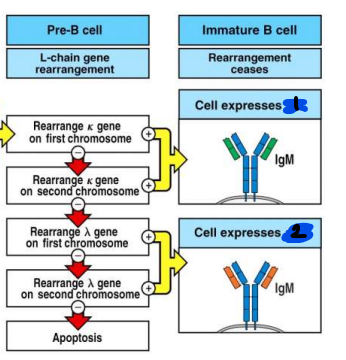
productive lambda gene on the first or second chromosome results in the cell expressing…
mu/lambda IgM
what happens if unproductive rearrangement occurs after rearrangement on BOTH chromsomes for kappa AND lambda?
apoptosis
(t/f) the L chain is rearranged before H chain
false, heavy then light
B cells can continue to rearrange IgL genes, try to change L chain, lose self reactivity
receptor editing
B cells can die
clonal deletion or negative selection
B cells can become refractory to activation
clonal anergy
what event is:
essential for B cell development
only happens when there is a successful heavy chain associating with VpreB
pre-B cell receptor dimerization
B cells have several opportunities to rearrange their light antigen receptors. What is the order they are rearranged in?
first chromosome - kappa
second chromosome - kappa
first chromosome - lambda
second chromosome - lambda
signaling of immature BCR results in…
deletion or receptor editing
? is essential to the clonal nature of immunity
allelic exclusion
When mature B cells leave the bone marrow, what is expressed on their membrane?
IgM and IgD
What happens when a BCR binds specific Ag and is activated?
It makes mAbs
In Pre-B cells, pre-BCR signaling induces
developmental progression → light chain rearrangement
When an immature B cell receives BCR signal (self antigen), what occurs?
deletion and/or light chain receptor editing
When a mature B cell receives BCR signal (foreign antigen), what occurs?
cell activation
a thymus is larger in a fetus or an adult?
fetus
T cell precursors move from what two locations to develop?
bone marrow to thymus
mature T cells leave the thymus in ?, move to secondary lymphoid organs, circulate between ?, secondary lymphoid tissues and lymph
blood
the thymus contains… (2)
immature T cells (thymocytes)
dense network of epithelial cells (thymic stroma)
(t/f) In the absence of thymus, T cells do not develop
true
what is a nude mouse?
phenotype due to mutation in a gene required for terminal epithelial cell differentiation
immature thymocytes do not express… (3)
CD4, CD8, or TCR
What is a double negative lymphocyte?
CD4- CD8- cells
stage of maturation: ?
proliferation: late half
RAG expression: early half
TdT expression: no
TCR DNA, RNA: recombined beta chain gene, beta chain mRNA
TCR expression: Pre-T receptor (beta-chain/pre-T alpha)
surface markers: c-kit+, CD44- CD25+
anatomic site: thymus
response to antigen: none
Pre-T
Which stages of maturation for the T-cell have no response to antigen?
stem cell, pro-t, pre-t
which stage of maturation…
proliferation: no
RAG: yes
TdT: no
TCR DNA, RNA: recombined beta, alpha chain genes; beta and alpha chain mRNA
TCR expression: membrane alpha-beta TCR
surface markers: CD4+/CD8+/TCR
anatomic site: thymus
response to antigen: positive and negative selection
double positive
which stage of maturation is…
proliferation: no
RAG/TdT expression: no
TCR DNA, RNA: recombined beta, alpha chain genes; beta alpha chain mRNA
TCR expression: membrane alpha-beta TCR
surface markers: CD4+CD8-, CD4-CD8+
anatomic site: thymus
response of antigen: no
single positive immature T cell
what stabilizes the peptide/MHC TCR complex?
co-receptors
what binds to the a3 domain (Ig-like) of Class I
CD8
what binds to b2 domain (Ig-like) of class II
CD4
without … there is no T cell activation
co-receptor MHC engagement
if there is … there will be no positive selection of CD8 single positive T cells
no MHC1
if there is … then there will be no positive selection of CD4 single positive T cells
no MHC2
negative selection purges cells of high binders for…
self-MHC
CD(4/8) helper T cell co-receptor
CD4
CD(4/8) cytotoxic T cell co-receptor
8
T cells in the periphery have strong reaction against … with peptides from transplant
allogenic MHC (non-self-MHC alleles)
TCR specific for self-MHC/foreign-peptide may cross-react strongly with… (2)
peptide portion of nonself-MHC/peptide complex
MHC portion of the nonself-MHC/peptide complex