botany chapters 1-5
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
189 Terms
Robert Hooke, 1665
Who discovered cells and when were they discovered?
Cell theory
All living organisms are composed of cells and cells form a unifying structural basis of organization
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, 1838
Who developed the cell theory and when?
Robert Brown, 1831
Who discovered the nucleus and when?
Rudolf Virchow, 1858
Who argued there is no spontaneous generation of cells and when was it argued?
Louis Pasteur, 1862
Who experimentally disproved spontaneous generation and when was it disproved?
Light microscopes
Increase magnification as light passes through a series of transparent lenses made of glass or calcium fluoride crystals
Compound microscope
• Light passes through thinly sliced material
• In general can distinguish organelles 2 micrometers or larger in diameter
• Can magnify up to 1500x
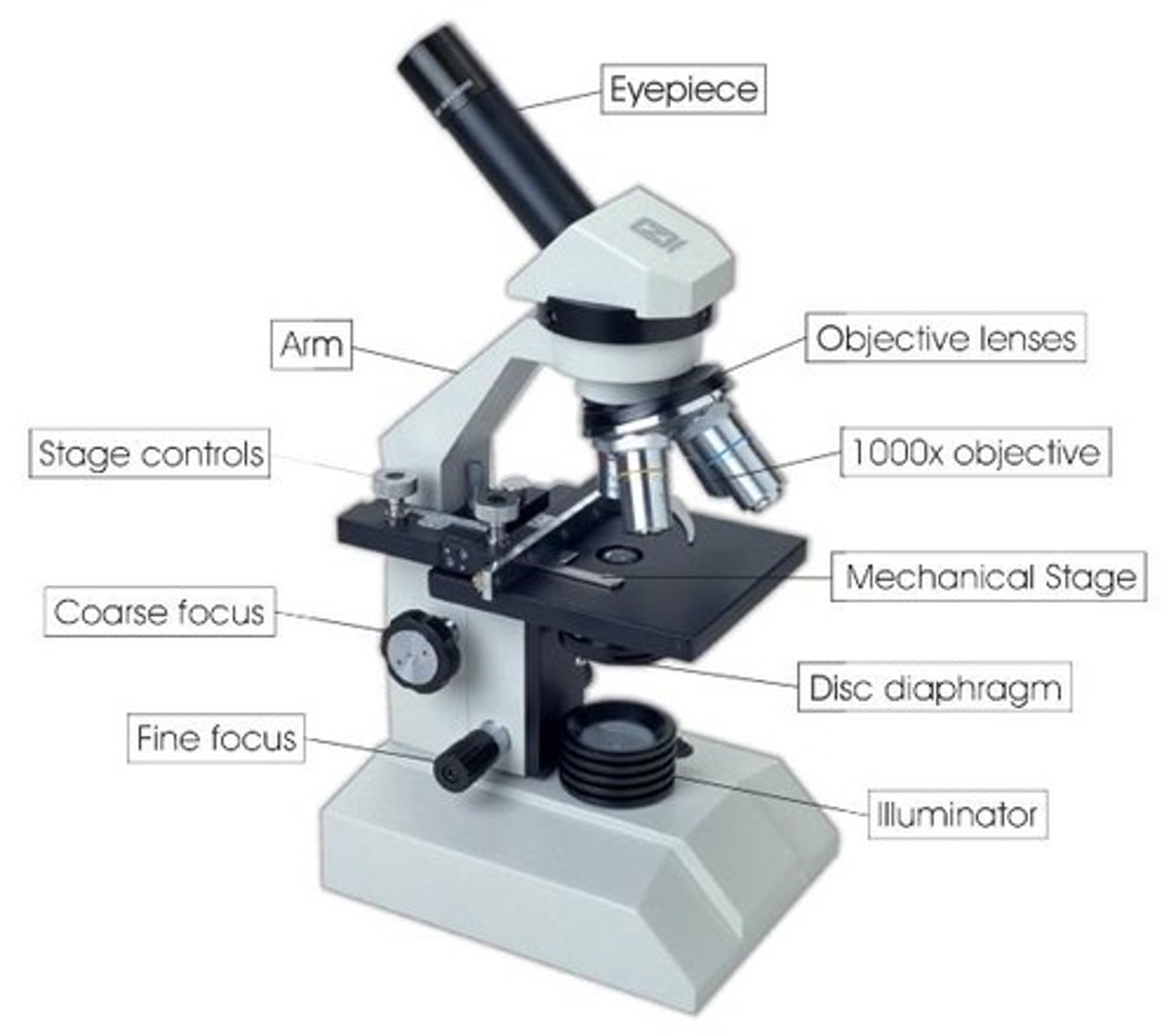
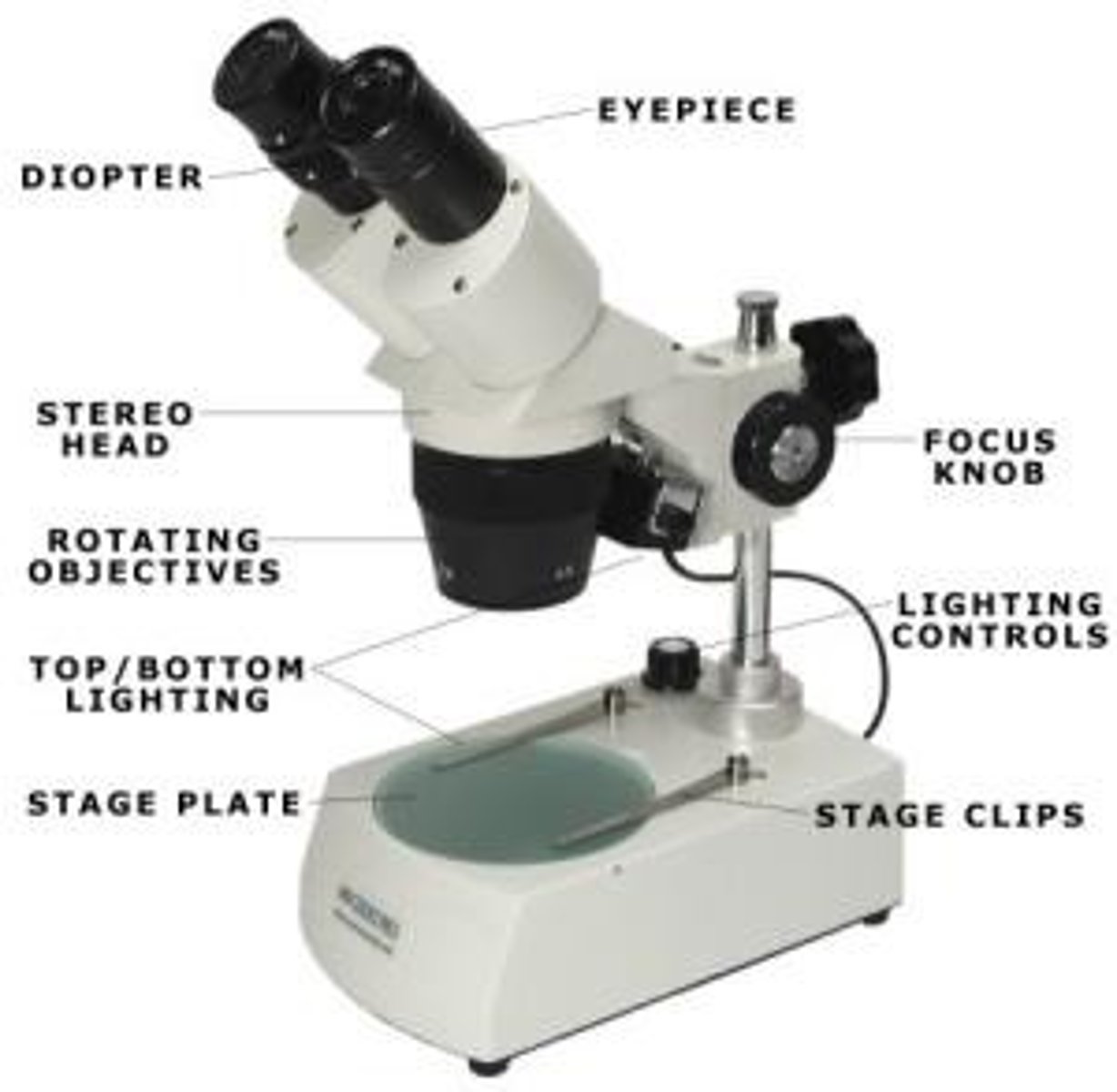
Dissecting microscope
• Allow three-dimensional viewing of opaque objects
• Can magnify up to 30x
Electron microscopes
Use a beam of electrons produced when high-voltage electricity is passed through a wire
Transmission electron microscope
Up to 200,000x magnification, but material must be sliced extremely thin

Scanning electron microscope
• Up to 10,000x magnification
• Surface detail can be observed on thick objects.

Scanning tunneling microscope
• Uses a probe that tunnels electrons upon a sample
• Produces a map of sample surface
• Even atoms can become discernible
• First picture of DNA segment showing helical structure

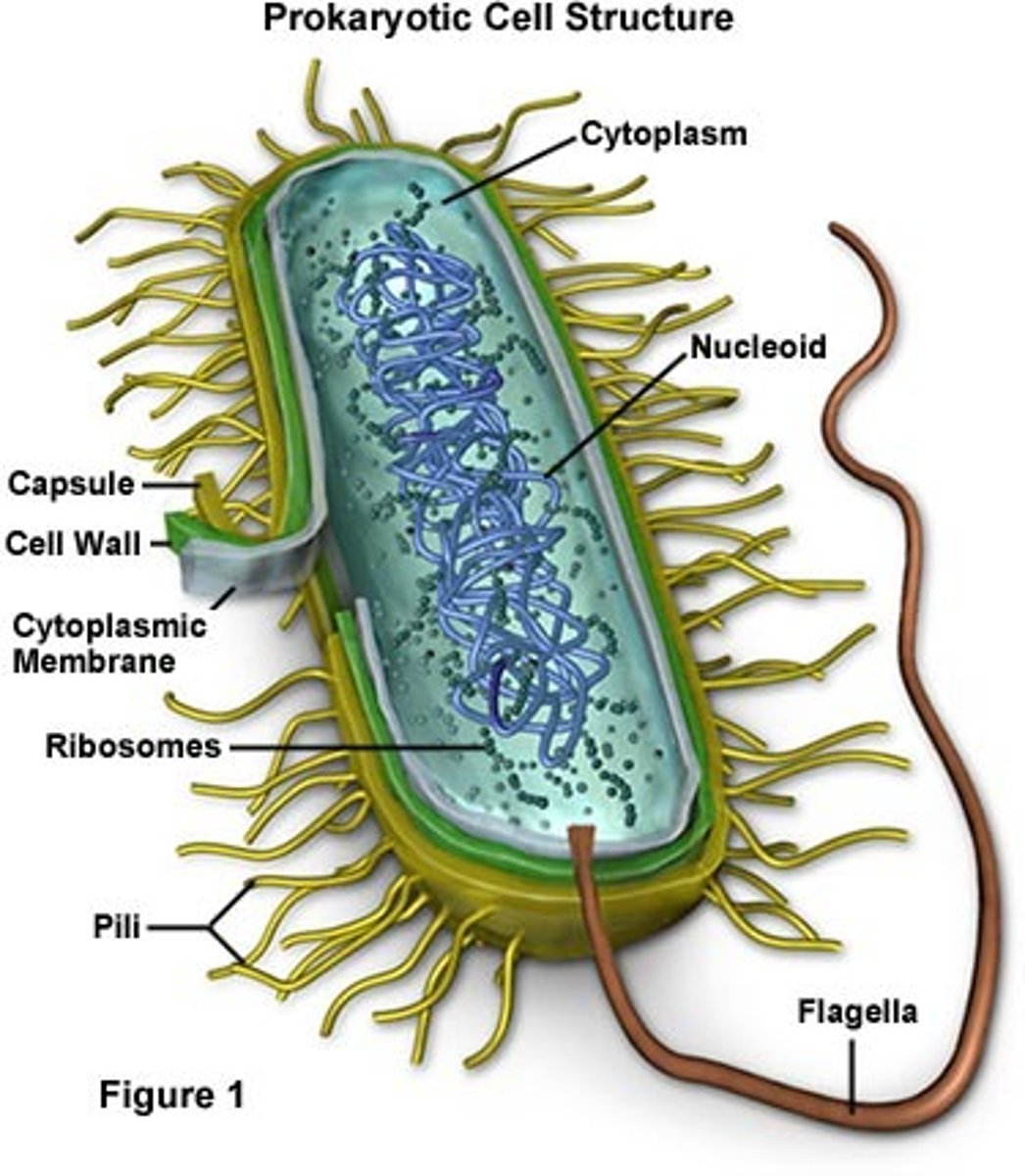
Prokaryotic cells
Lack a nucleus - bacteria
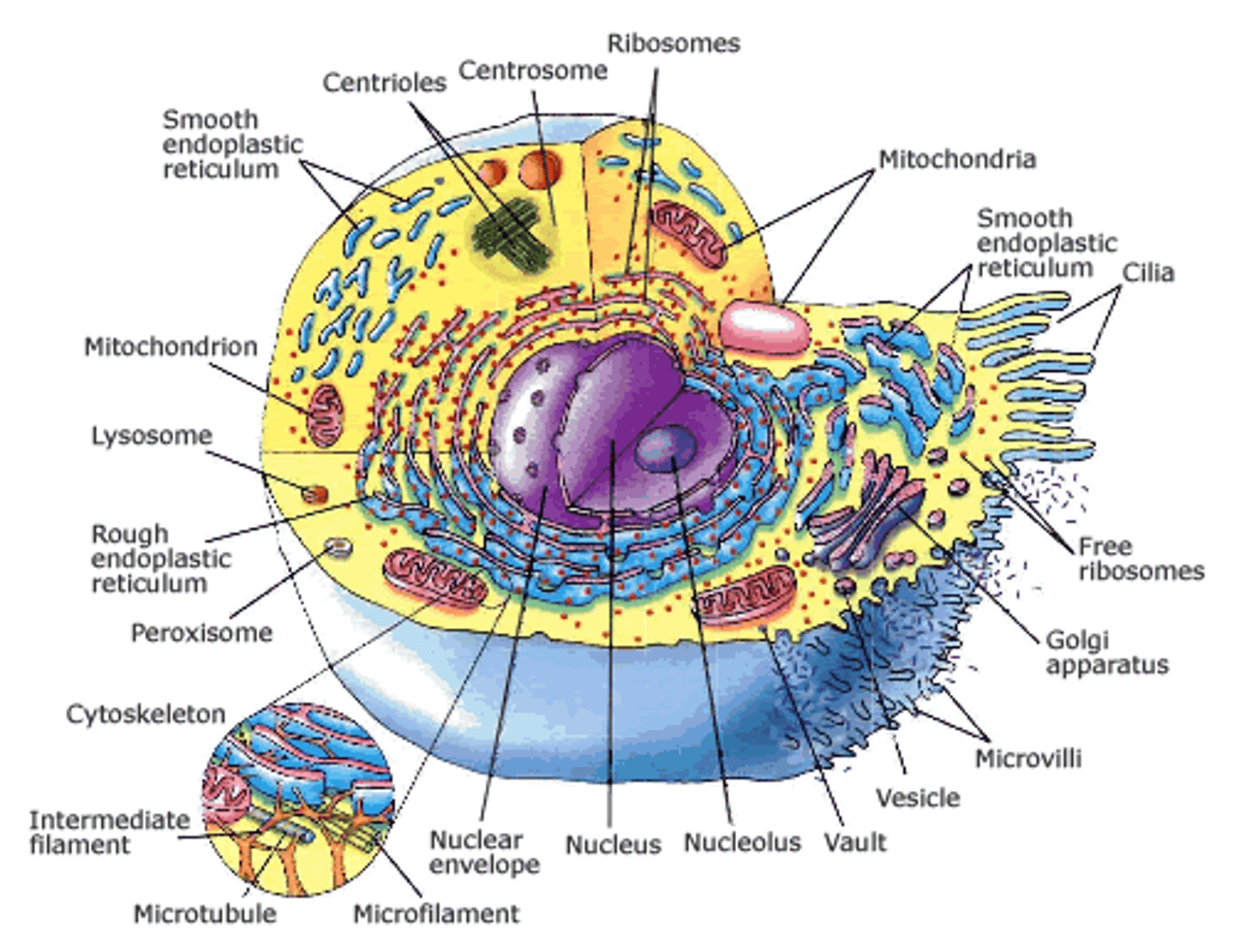
Eukaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus - plants and animals
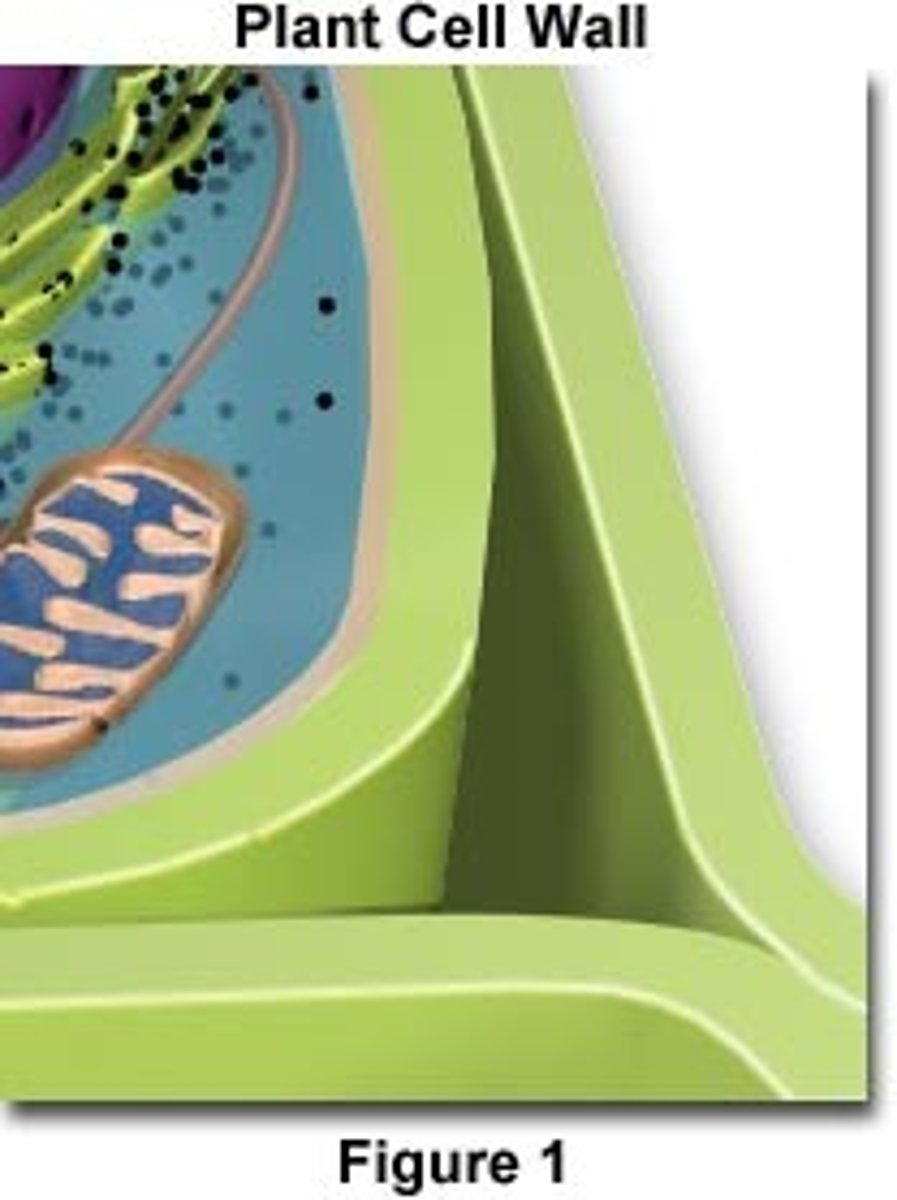
Cell walls
Rigid boundary of cells
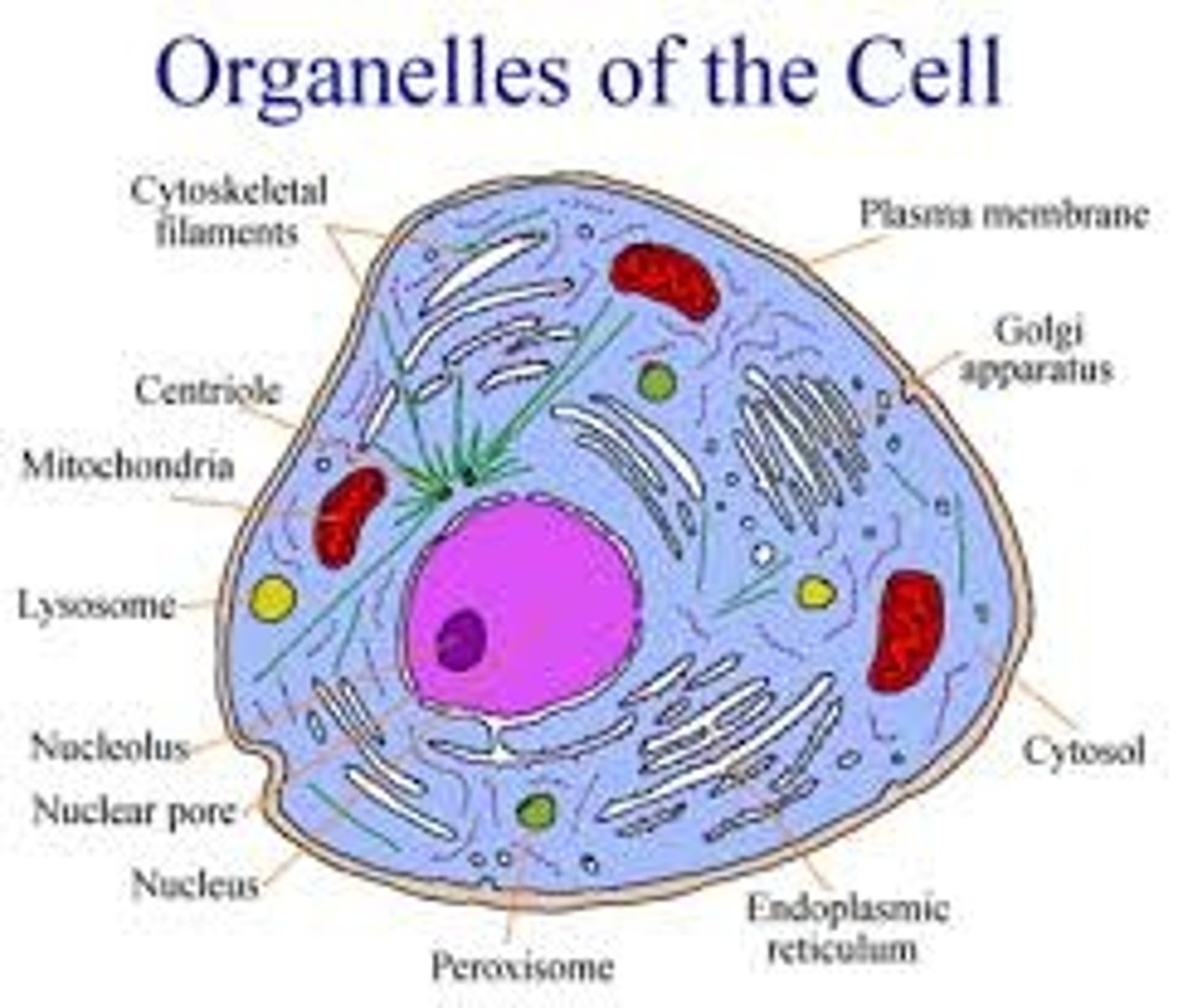
Organelles
Membrane-bound bodies found within eukaryotic cells that have various shapes and sizes with specialized functions
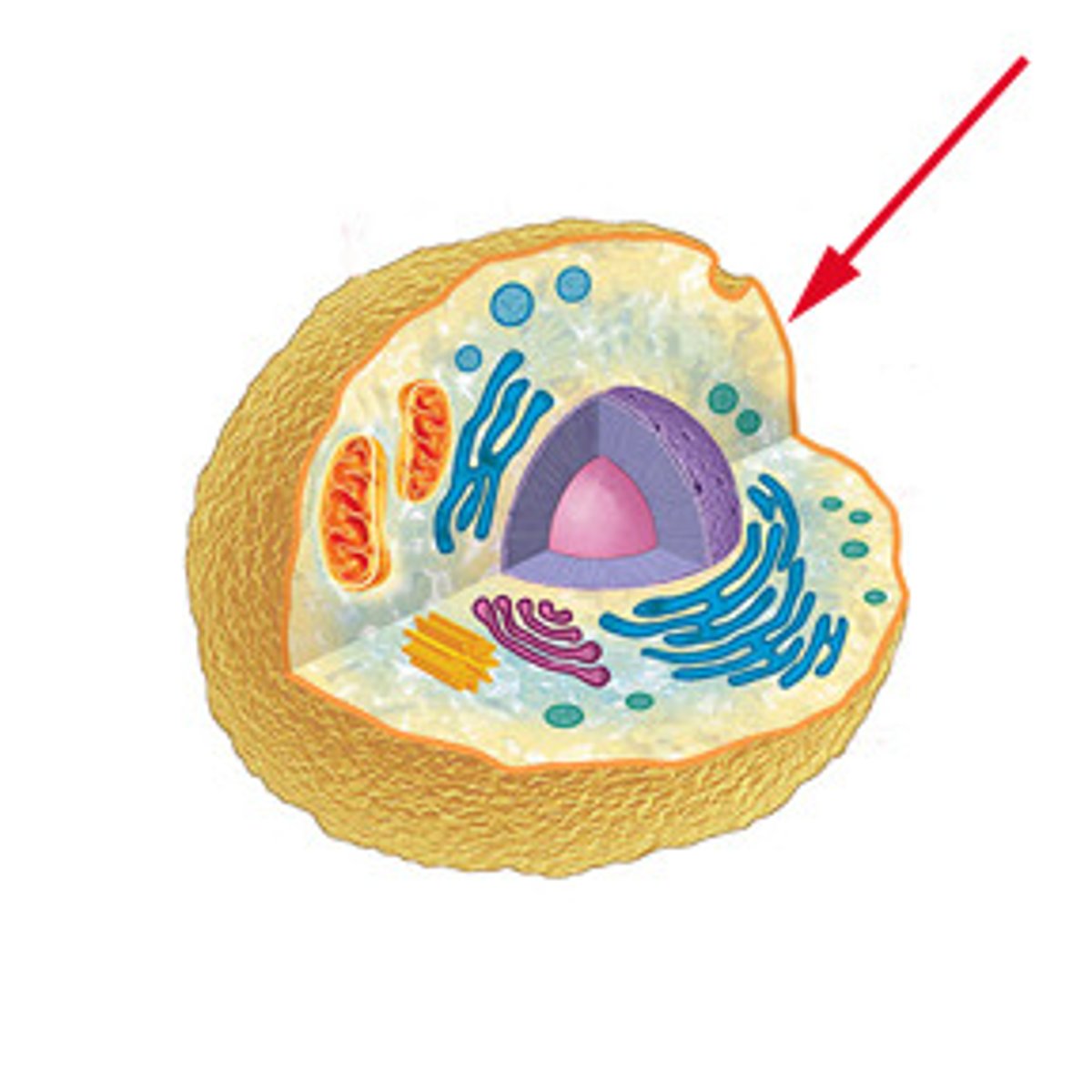
Protoplasm
What does the cell wall surround?
Protoplasm
Consists of all living cell components, including the cytoplasm and the nucleus itself
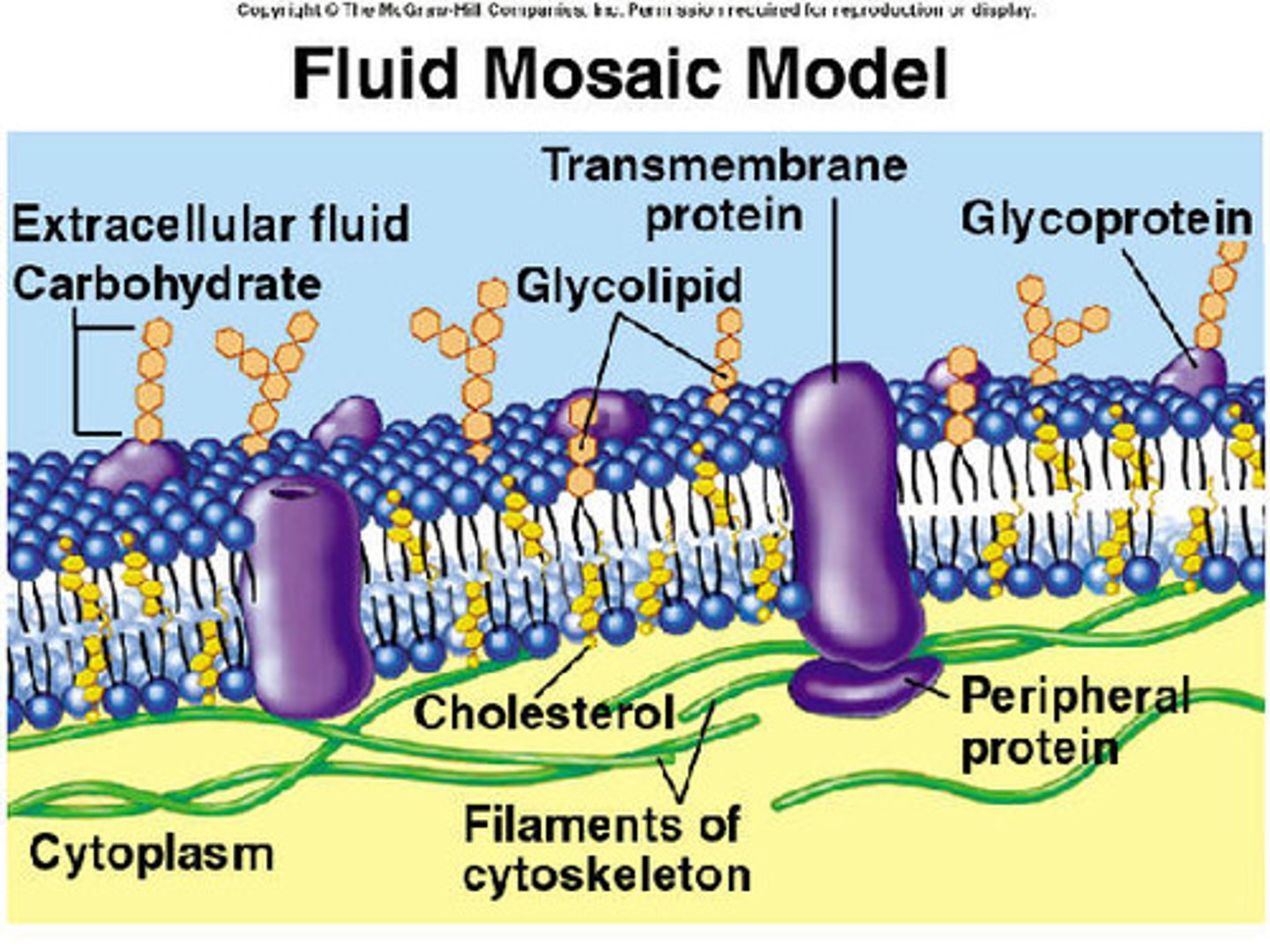
Plasma membrane
The membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier, thereby regulating the cell's chemical composition
Cytoplasm
Consists of all cellular components between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
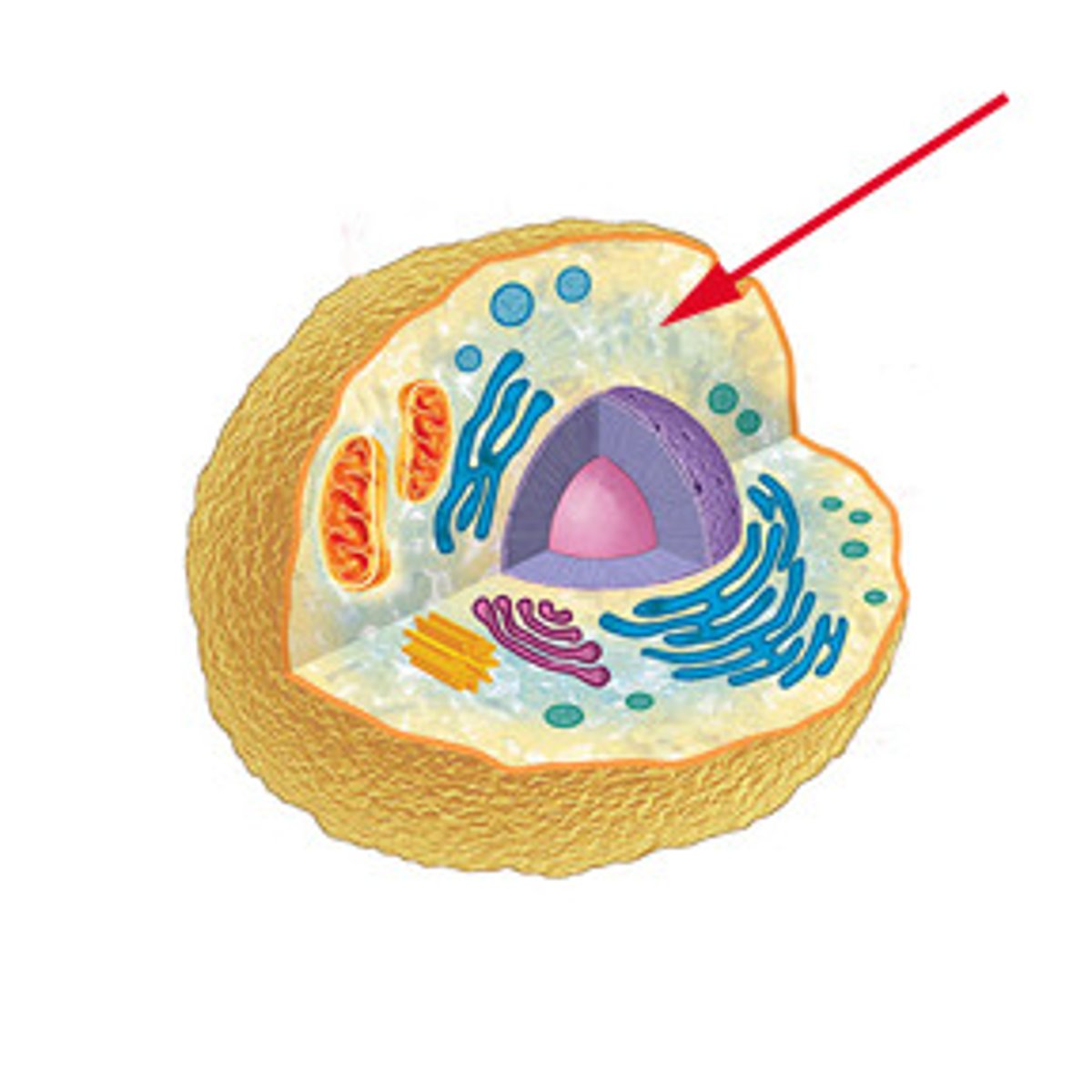
Cytosol
Fluid within cytoplasm containing organelles
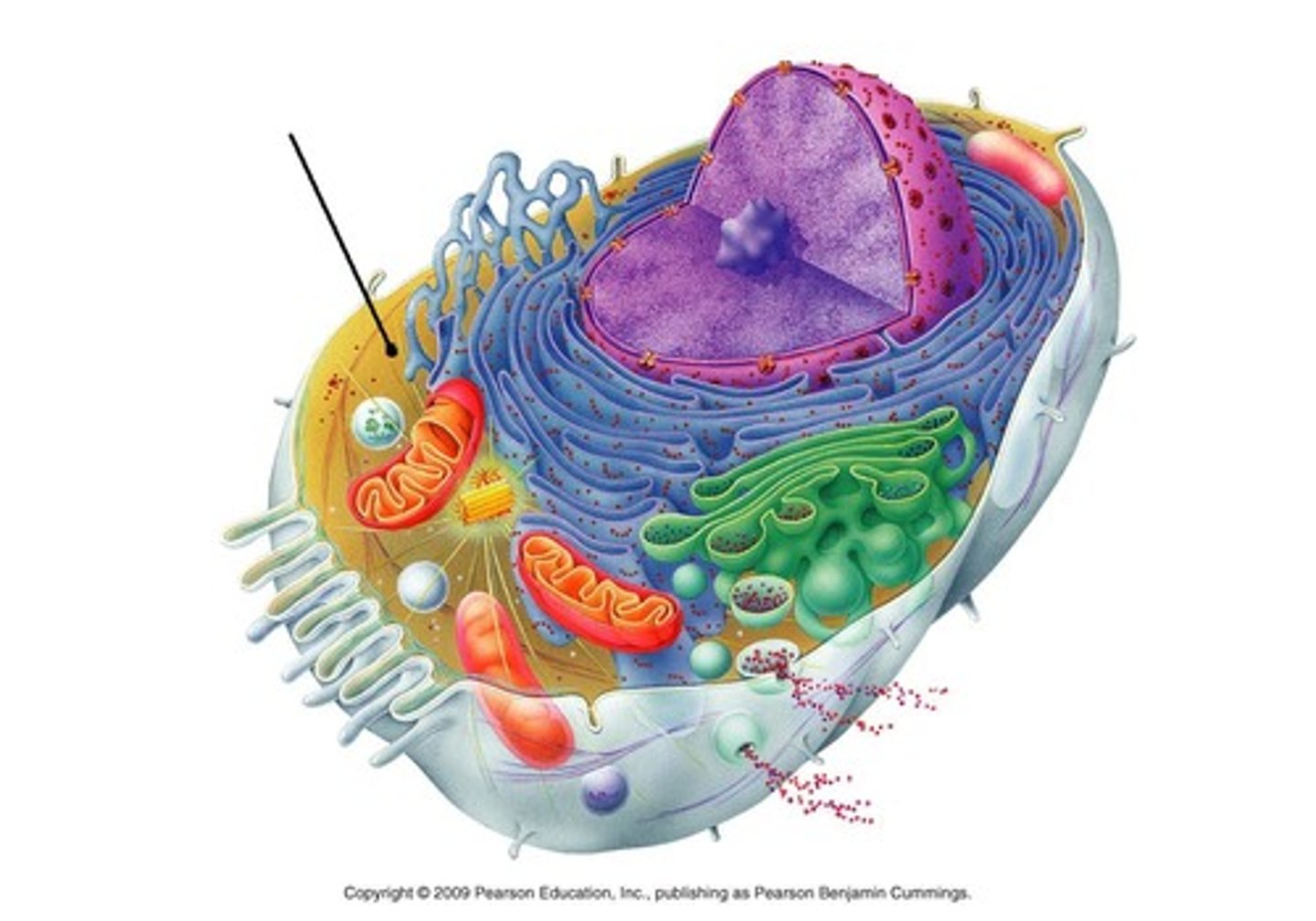
Why do smaller cells grow faster?
Smaller cells have relatively large surface to volume ratios enabling faster and more efficient cellular communication
What is the main structural component of cell walls?
Cellulose (long chains of glucose monomers)
Hemicellulose
Holds cellulose fibrils together inside the cell wall
Pectin
Gives stiffness (like in fruit jellies) inside of cell wall
Glycoproteins
Proteins with associated sugars found inside cell wall
Middle lamella
Sheets that hold cells together, first produced when new cell walls are formed (shared by two adjacent cells)
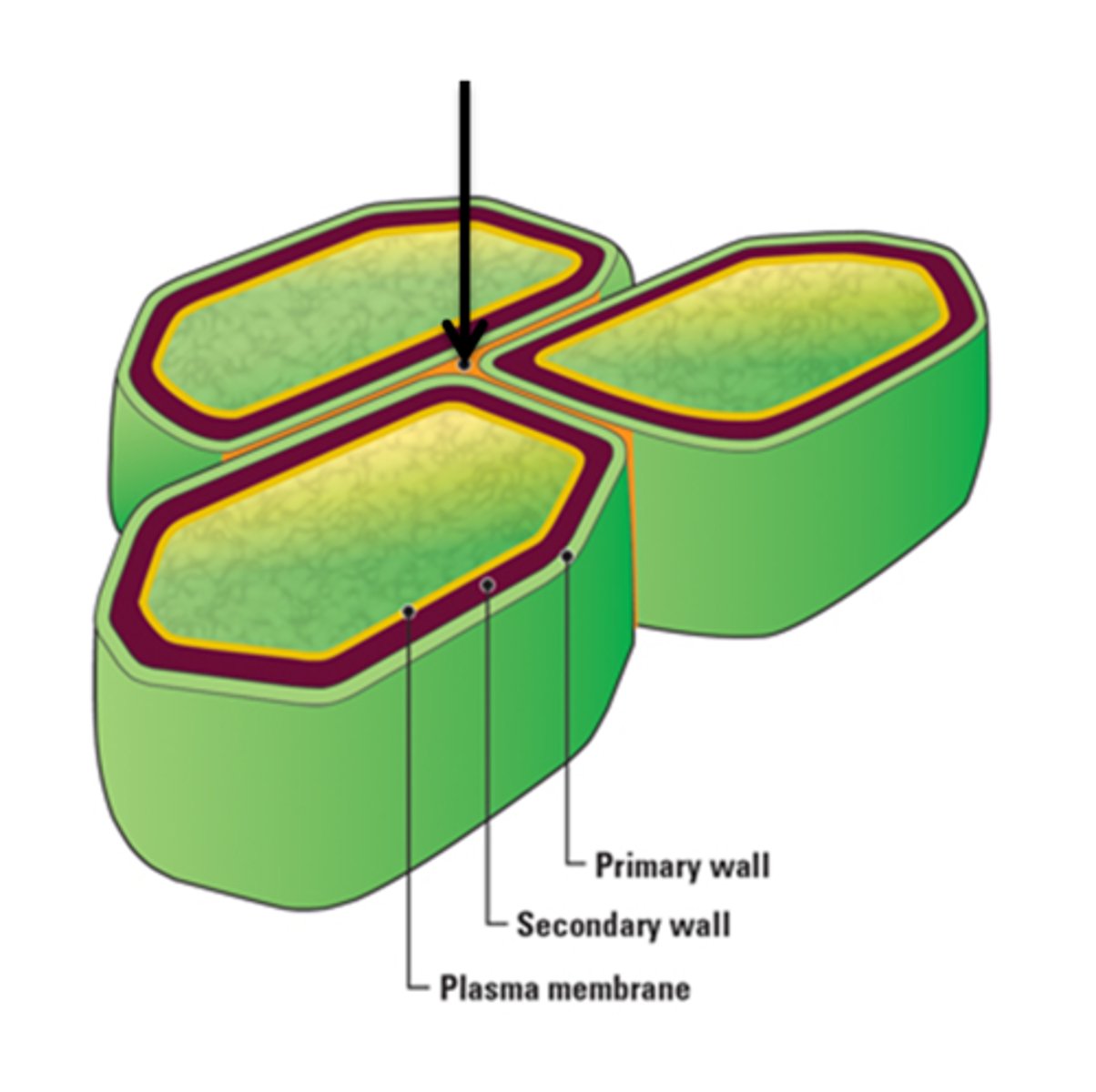
Primary walls
Laid down on either side of middle lamella

Secondary walls
Produced inside primary walls
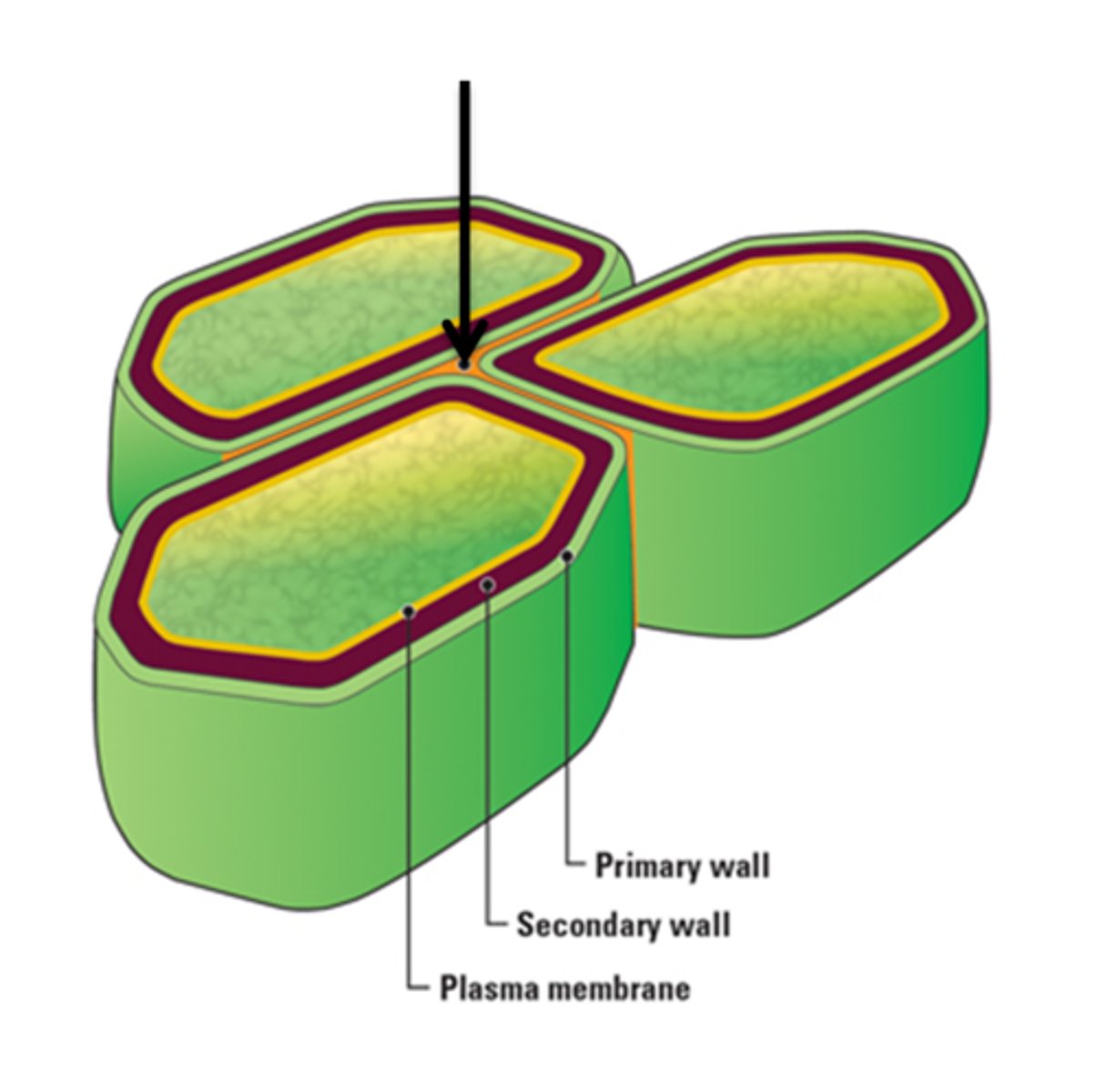
Lignin
A complex organic polymer that gives structure to plants, especially wood and bark
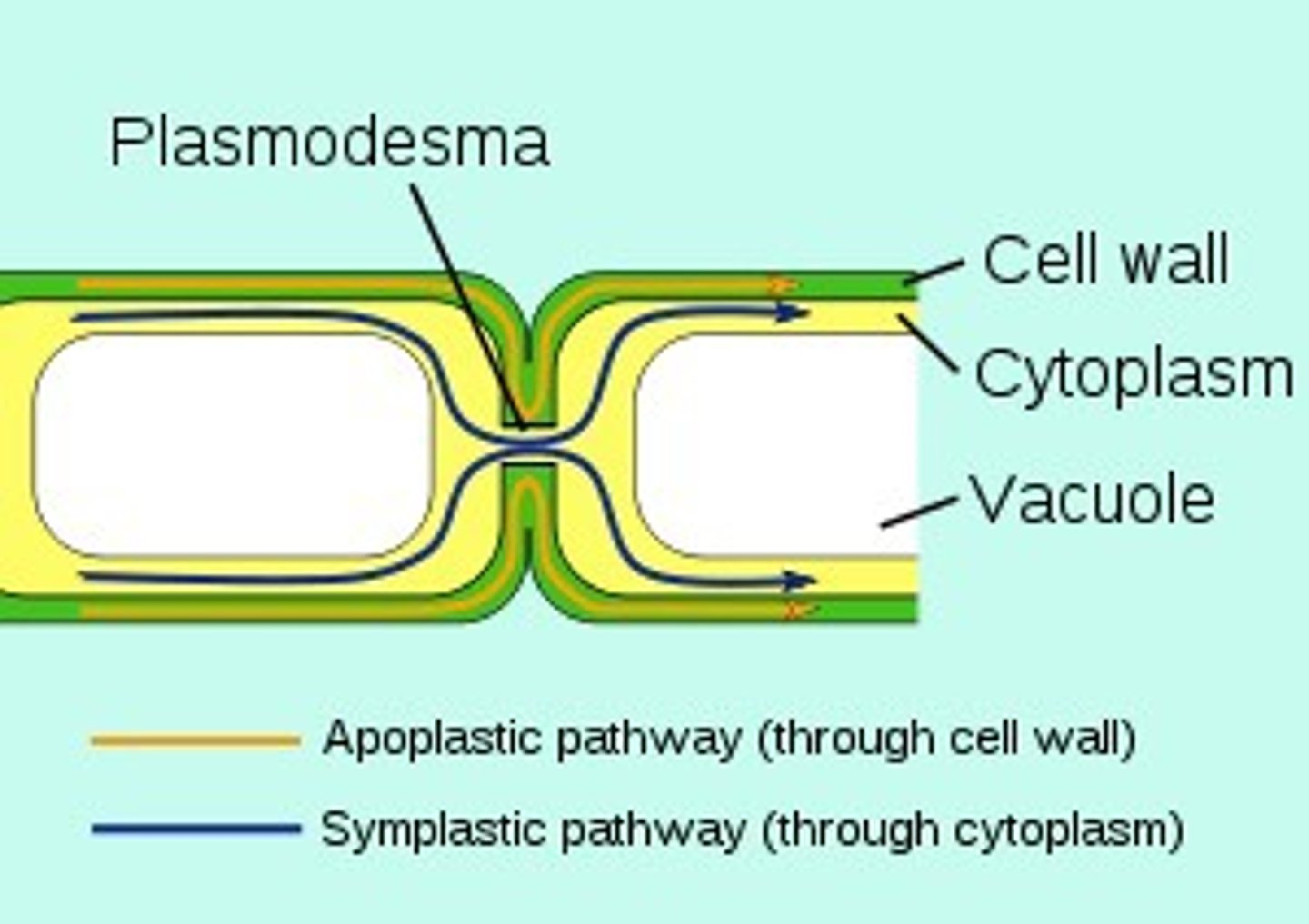
Plasmodesmata
Are cytoplasmic strands that extend between cells through minute openings
Fluid mosaic model
Plasma membrane is dynamic structure (always changing)
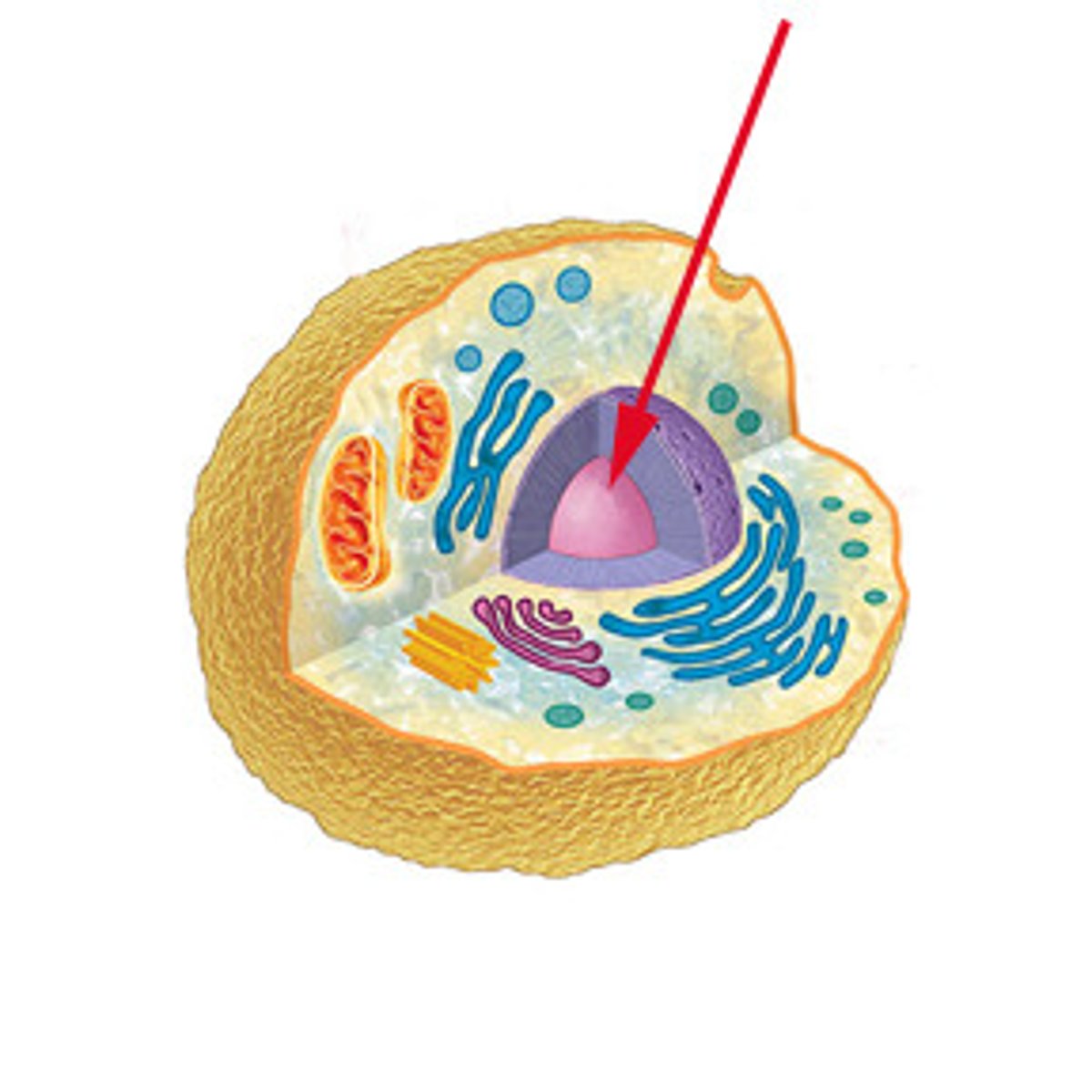
Nucleus
Control center of the cell and contains DNA
Nuclear envelope
Layer of two membranes that surrounds the nucleus of a cell
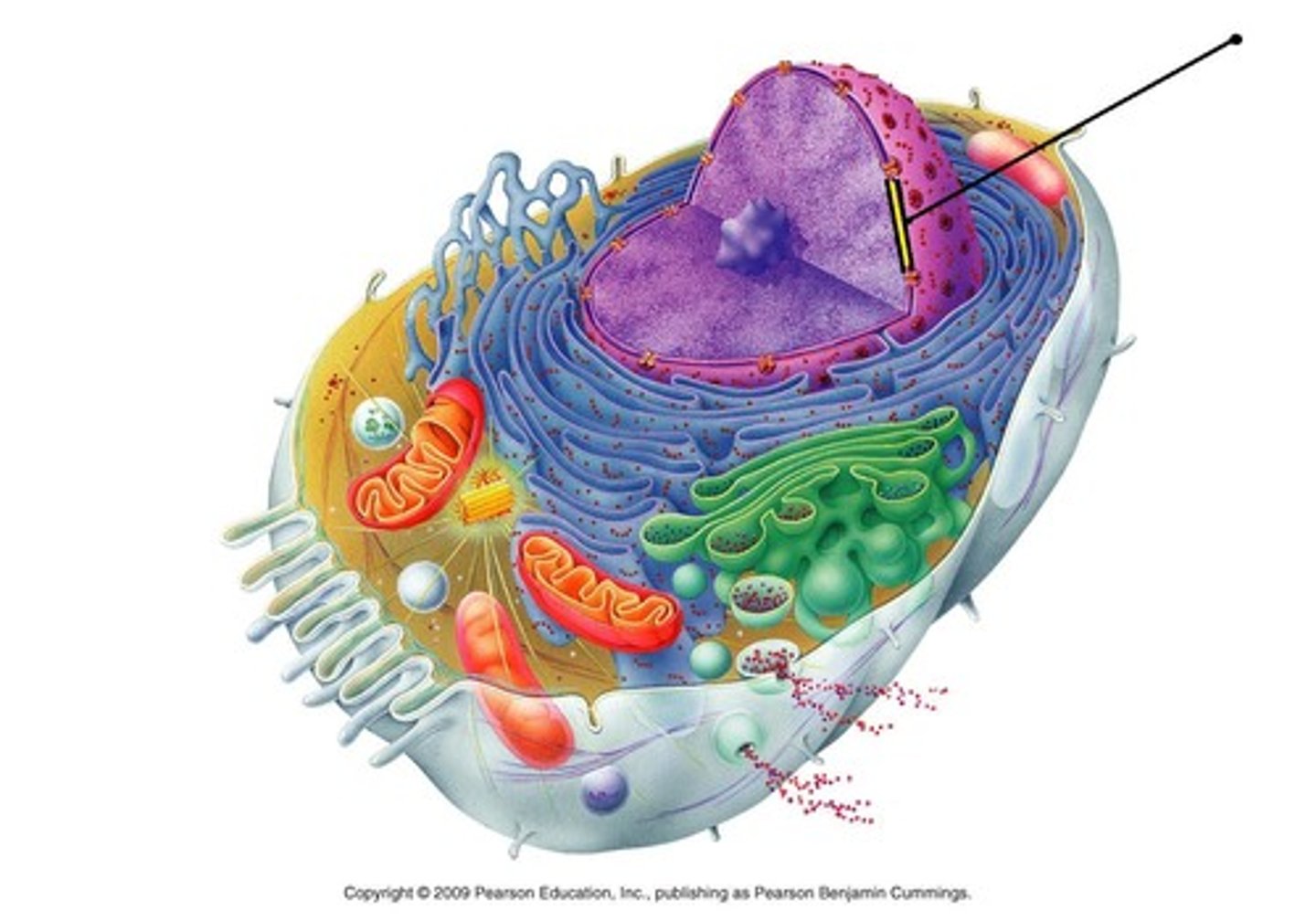
Nucleoli
Composed primarily of RNA
Chromatin strands
Composed of DNA and proteins; coil and become chromosomes
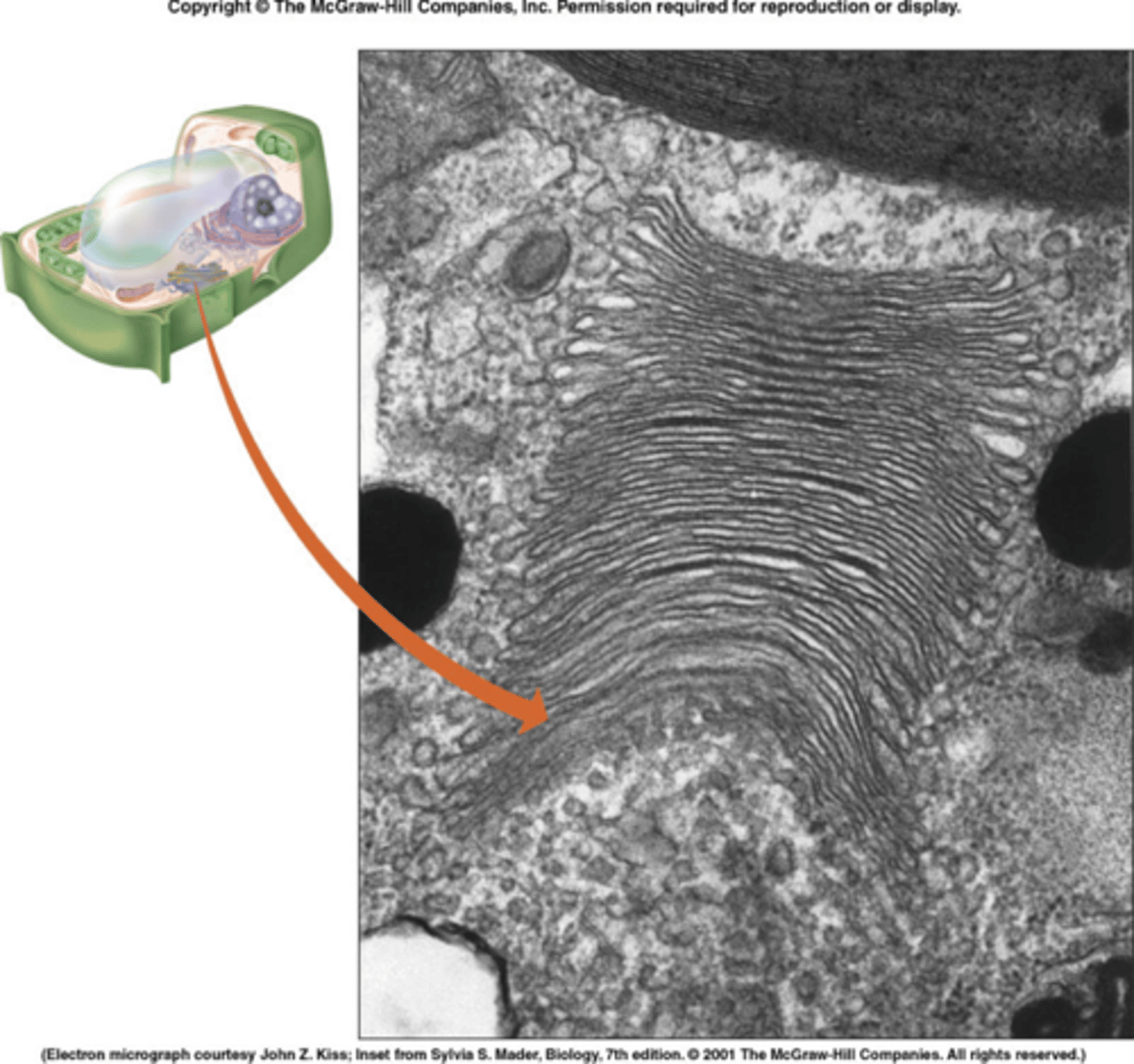
Endoplasmic reticulum
An enclosed space consisting of a network of flattened sacs and tubes forming channels throughout the cytoplasm
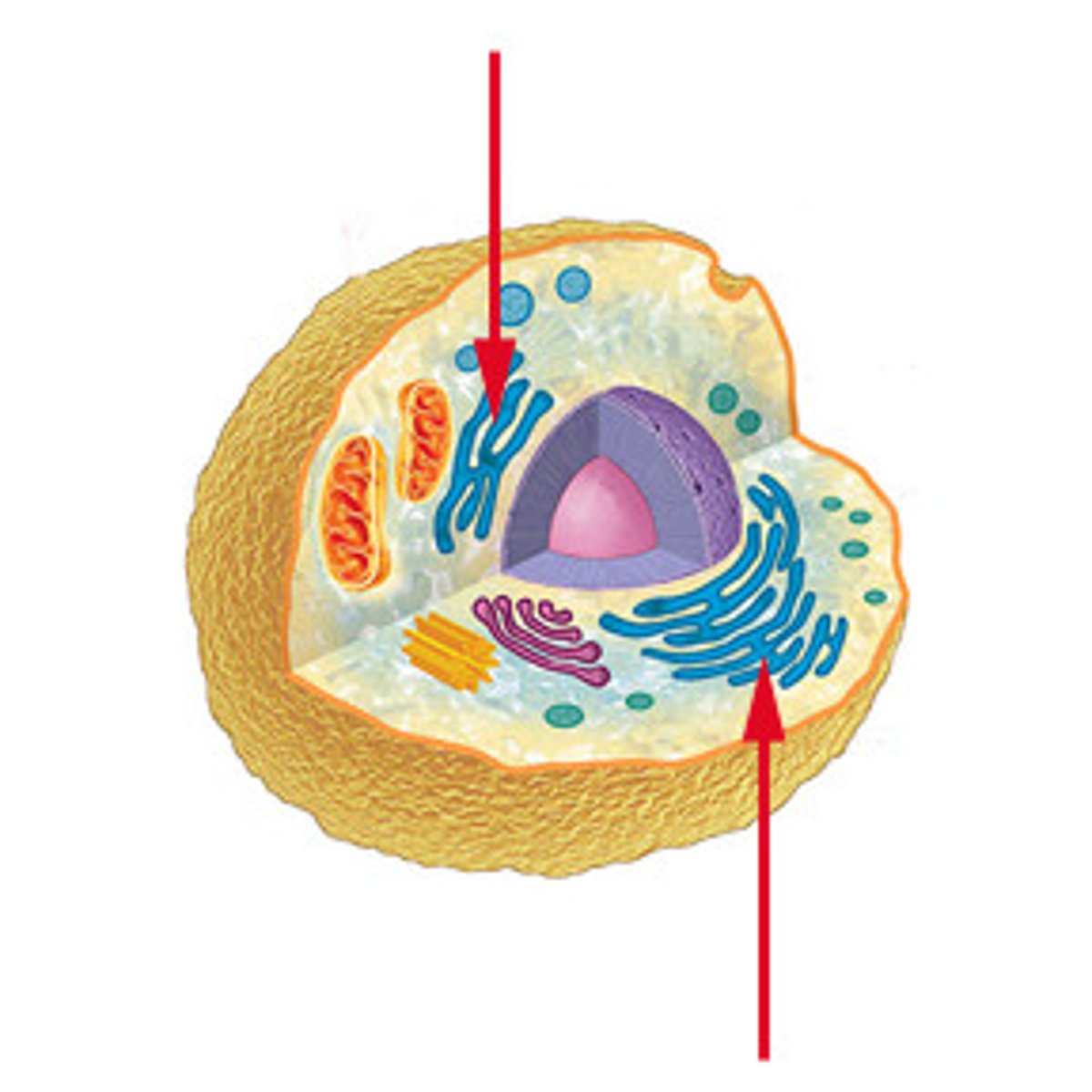
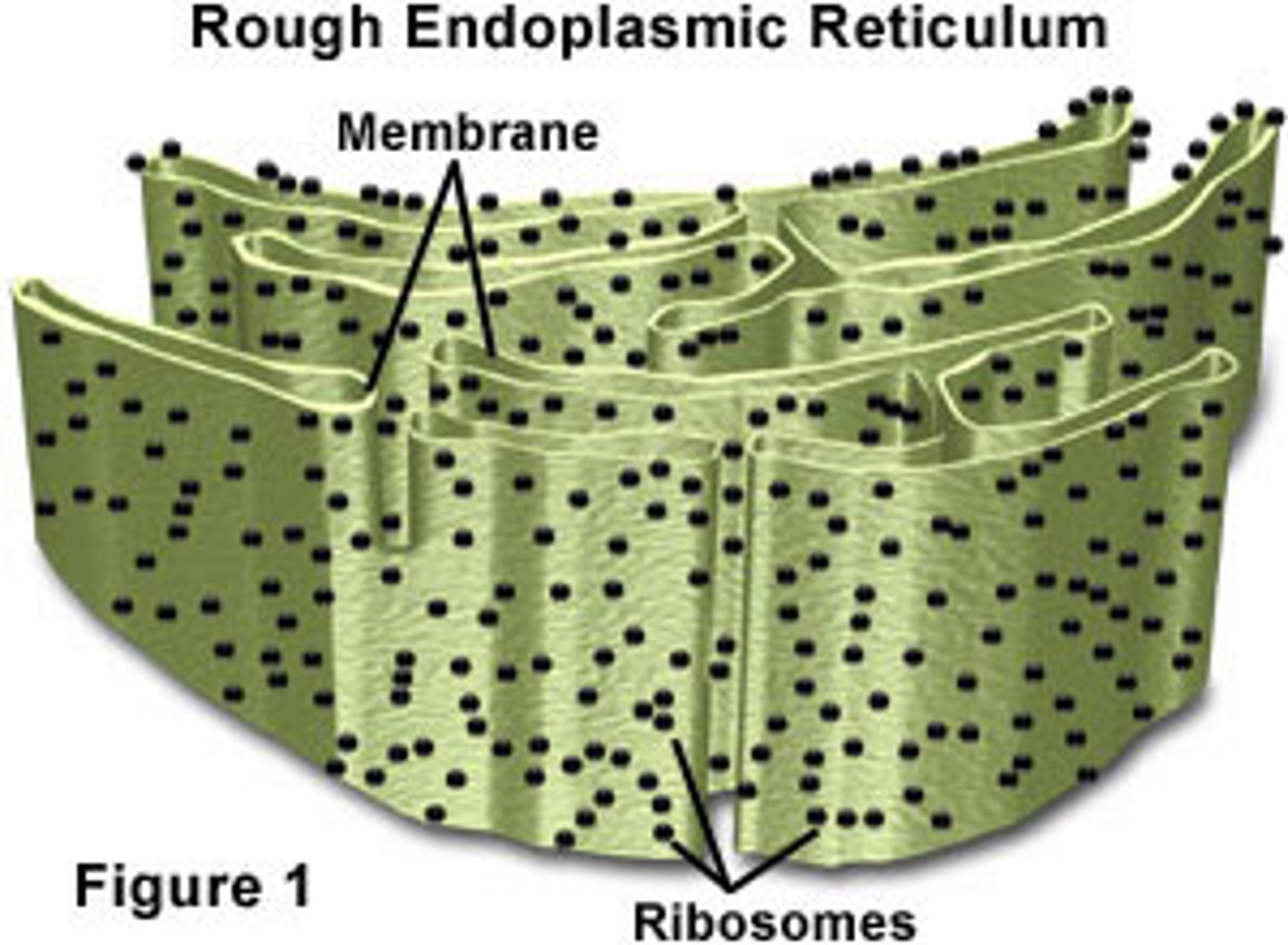
Rough ER
Ribosomes distributed on outer surface of ER and associated with protein synthesis and storage
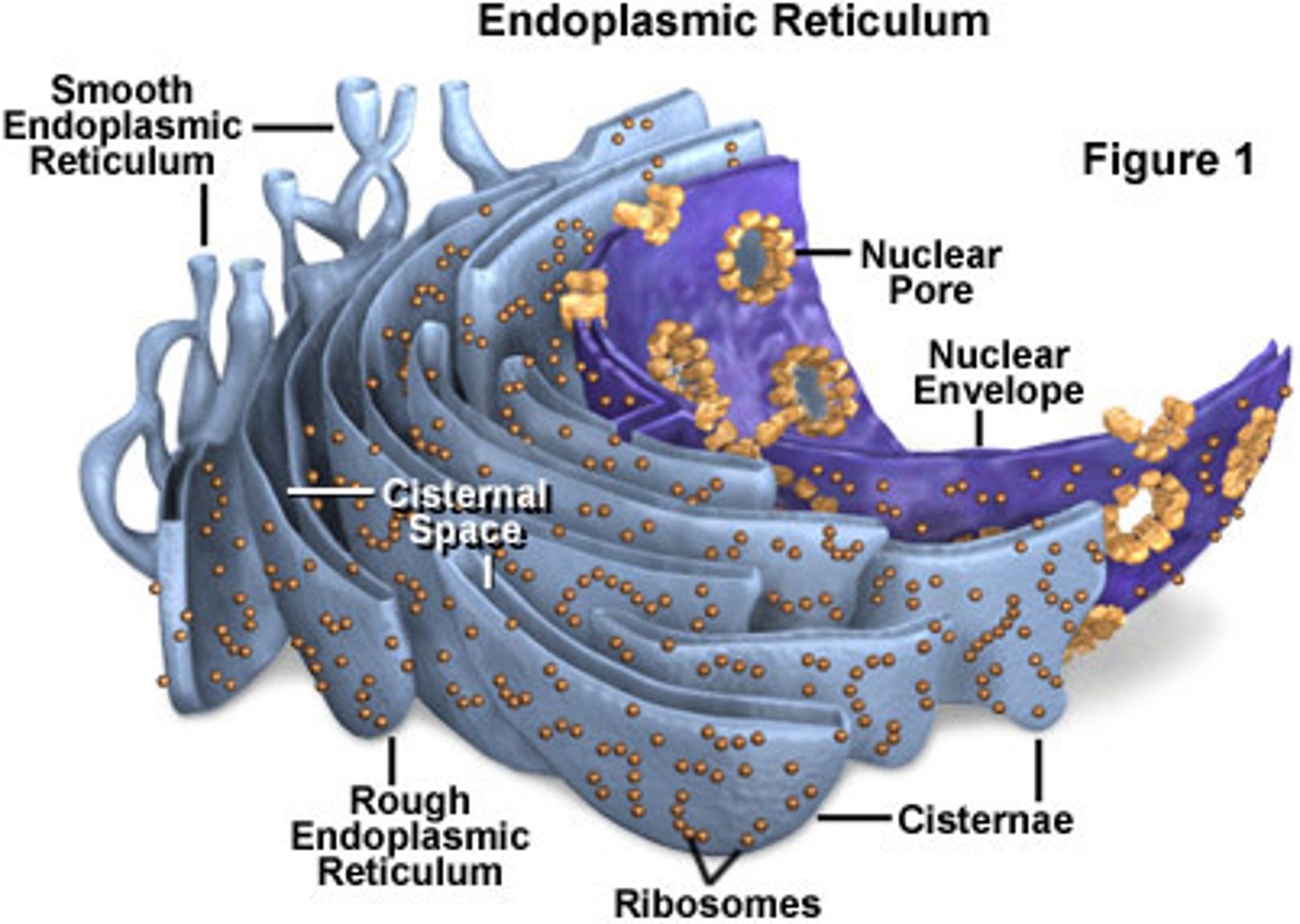
Smooth ER
Devoid of ribosomes and associated with lipid secretion
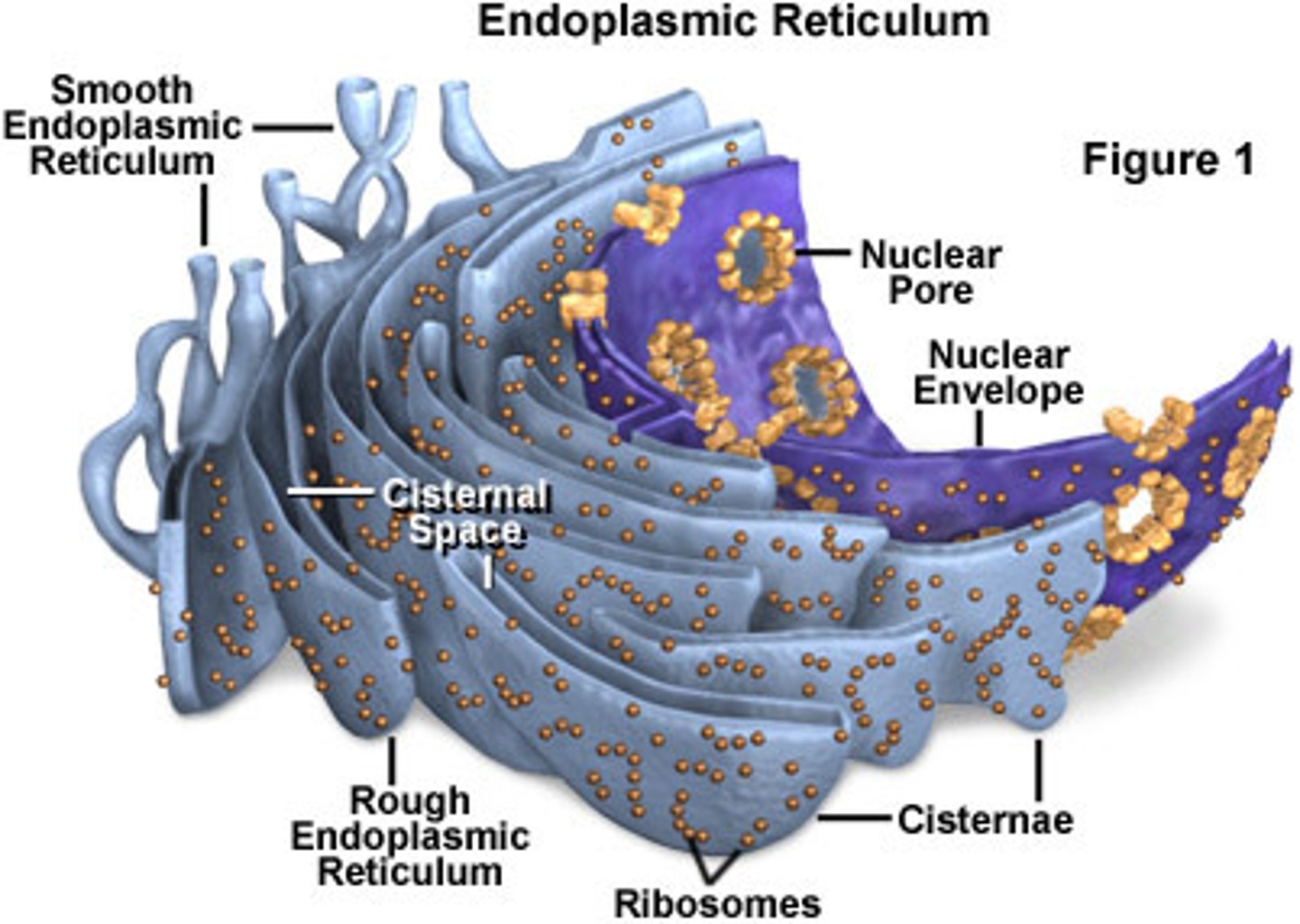
Ribosomes
Consist of two subunits that are composed of RNA and proteins
Dictyosomes
Stacks of flattened discs or vesicles
What are the functions of dictyosomes?
•To modify carbohydrates attached to proteins that are synthesized and packaged in the ER.
•To assemble polysaccharides (sugars) and collect them in small vesicles.
Plastids
organelles found in plant and algae cells that perform photosynthesis and other functions
They are membrane-bound and contain their own DNA and ribosomes
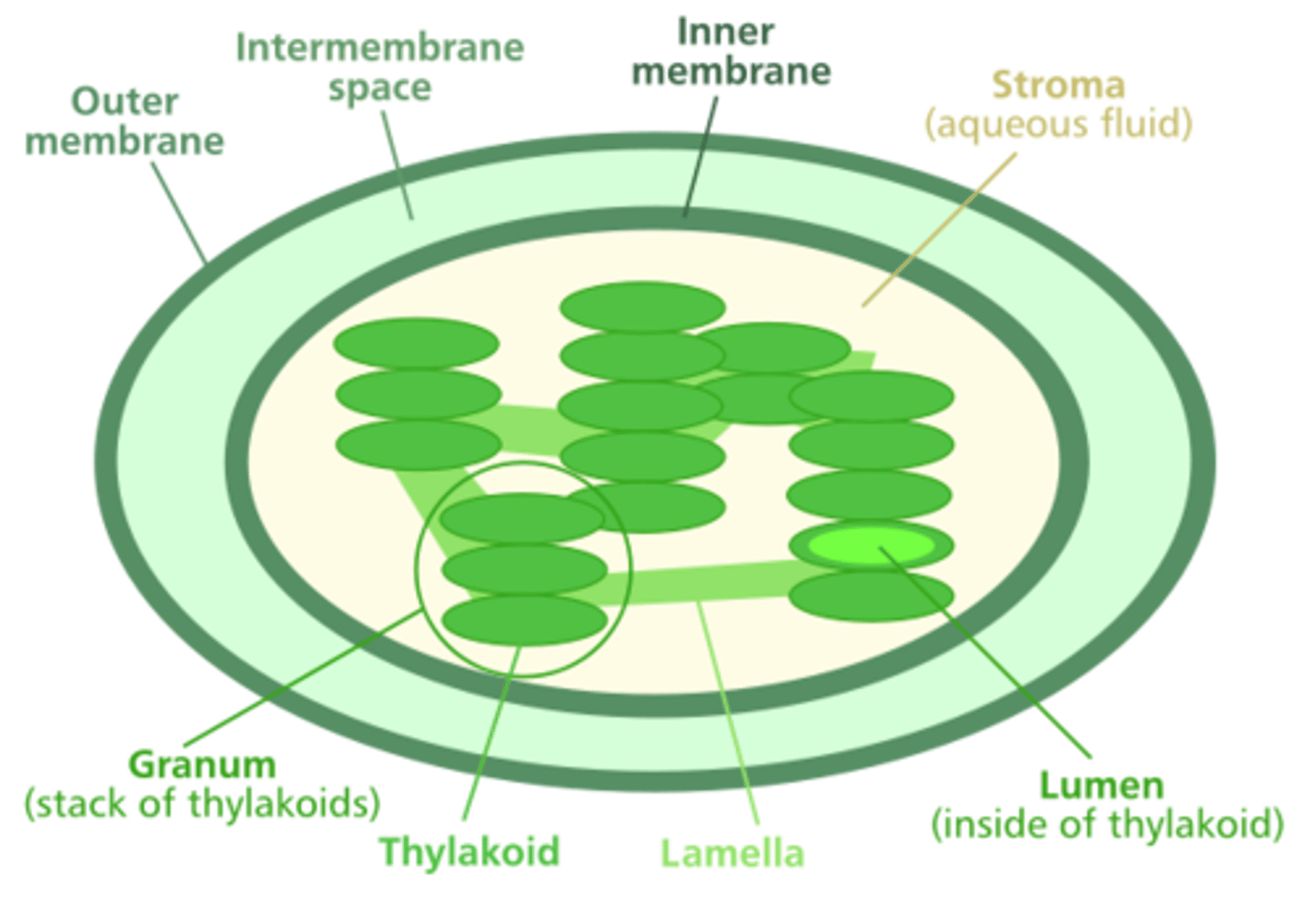
Grana
Stacks of thylakoids
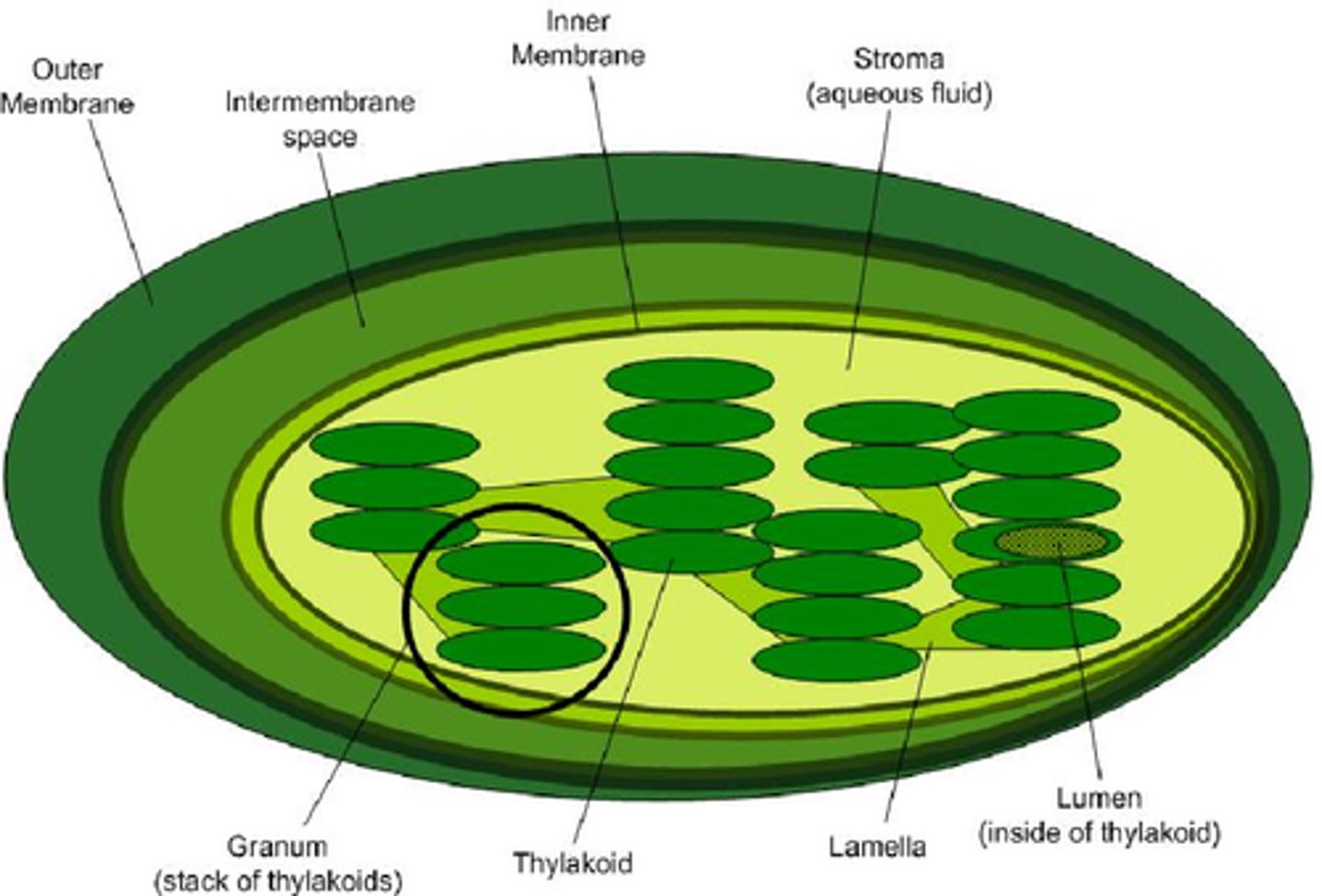
Thylakoid
First steps of photosynthesis occur in ______ membranes (contain chlorophyll)
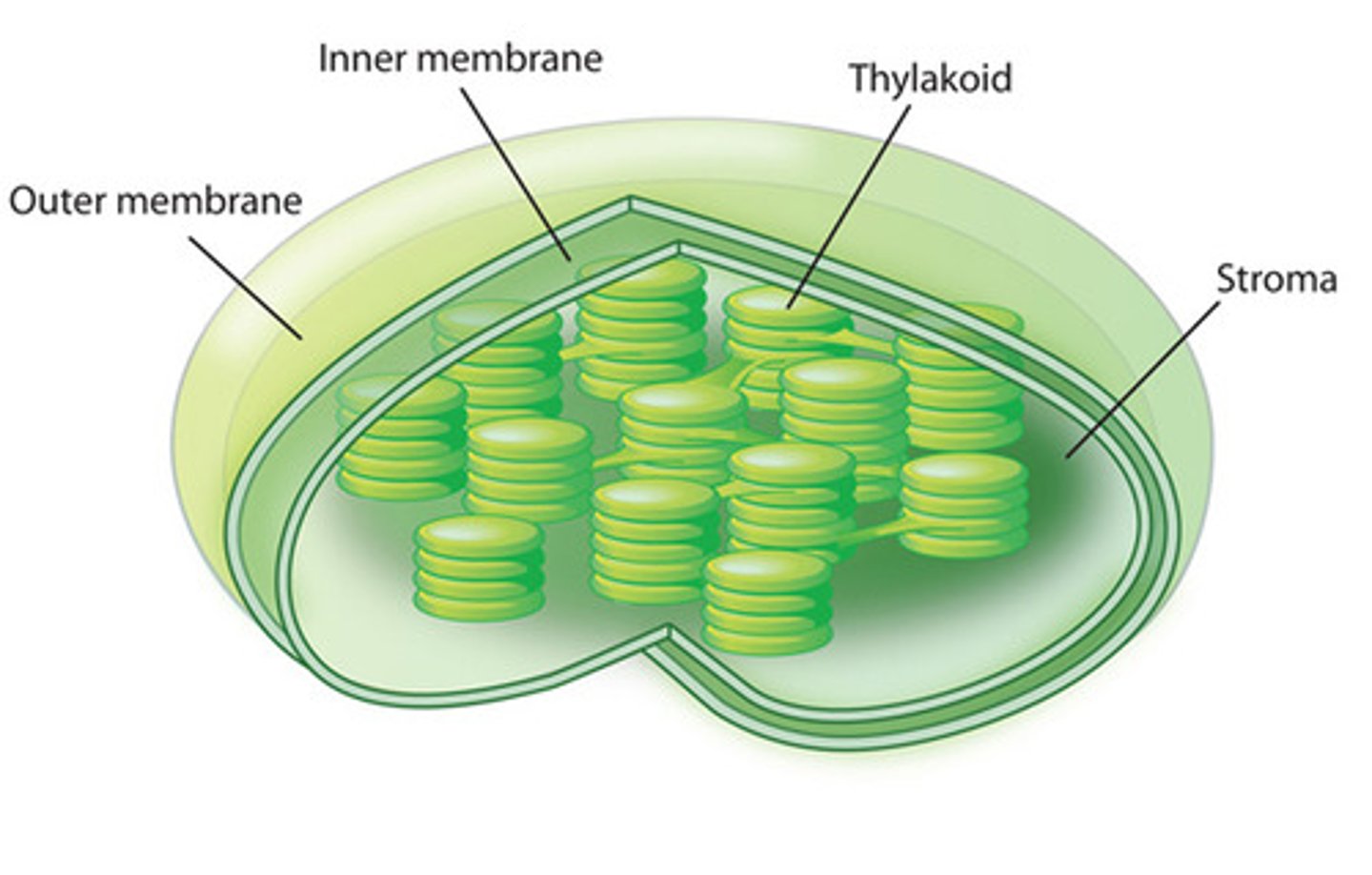
Stroma
Matrix of enzymes involved in photosynthesis

Chromoplasts
Synthesize and accumulate carotenoids (yellow, orange, red)
Leucoplasts
Colorless, may synthesize starches (amyloplasts) or oils (elaioplasts)
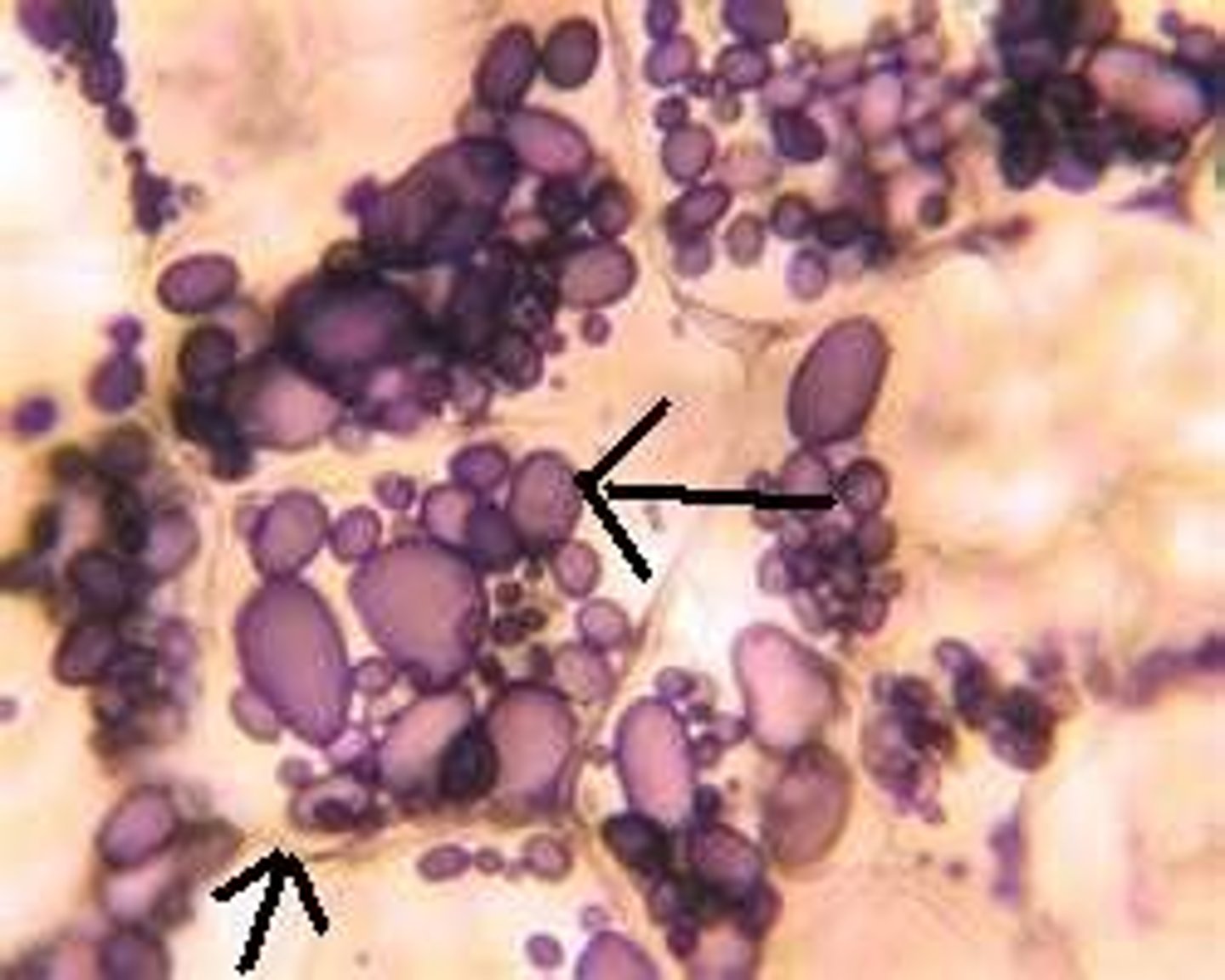
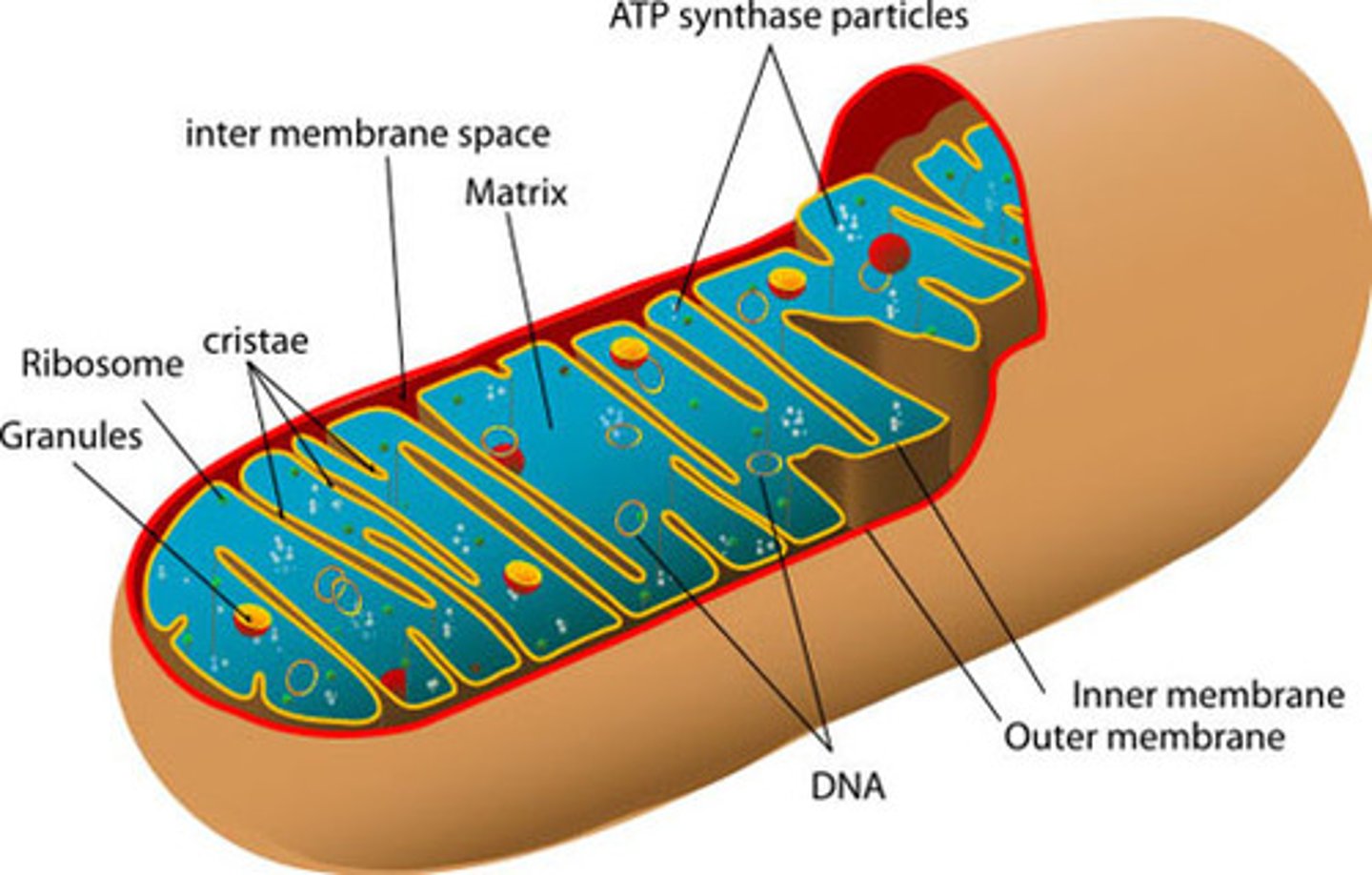
Mitochondria
Releases energy produced from cellular respiration
Microbodies
Small, spherical bodies distributed throughout the cytoplasm that contain specialized enzymes
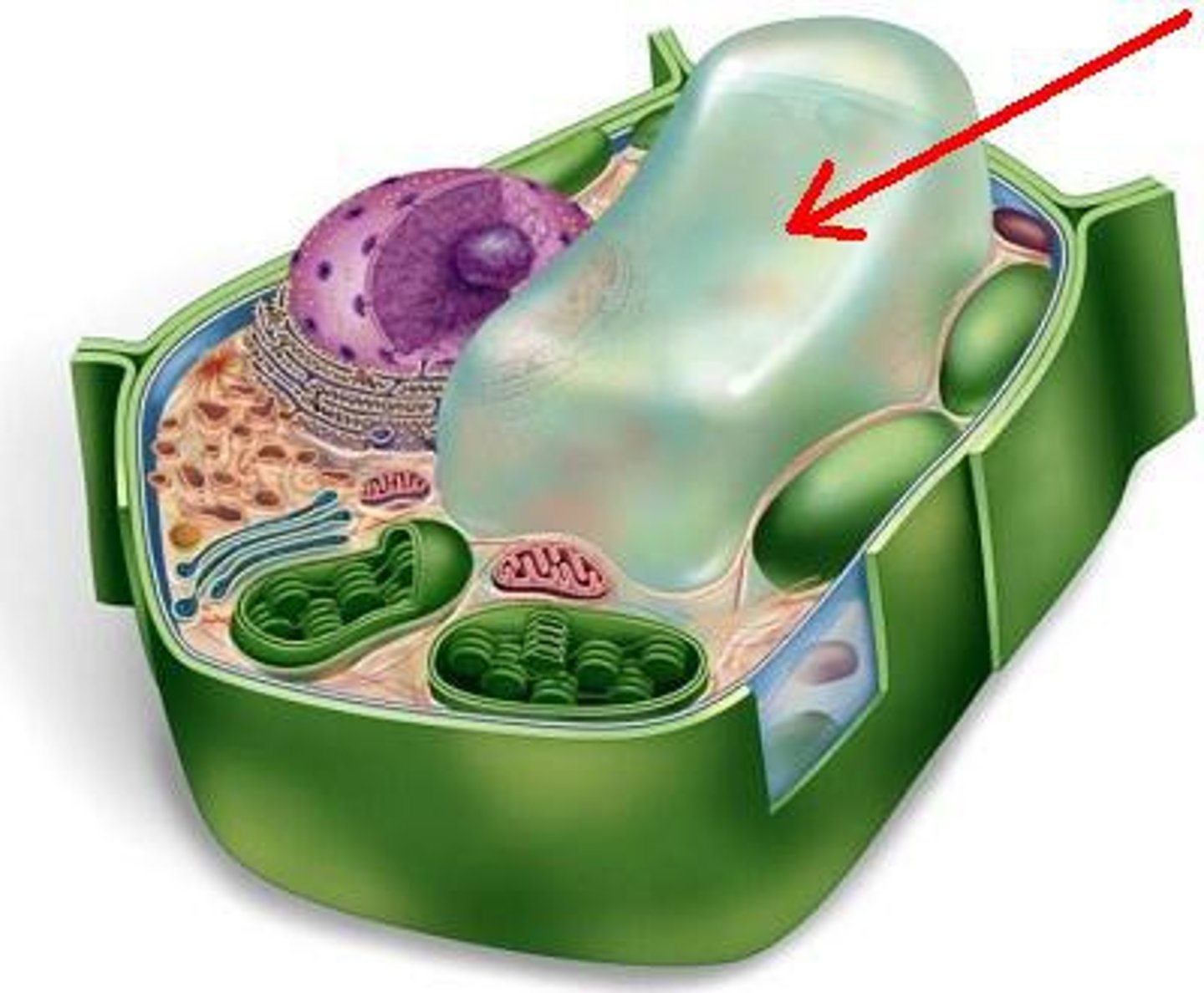
Central vacuole
A membranous sac that takes up 90% of volume in a plant cell
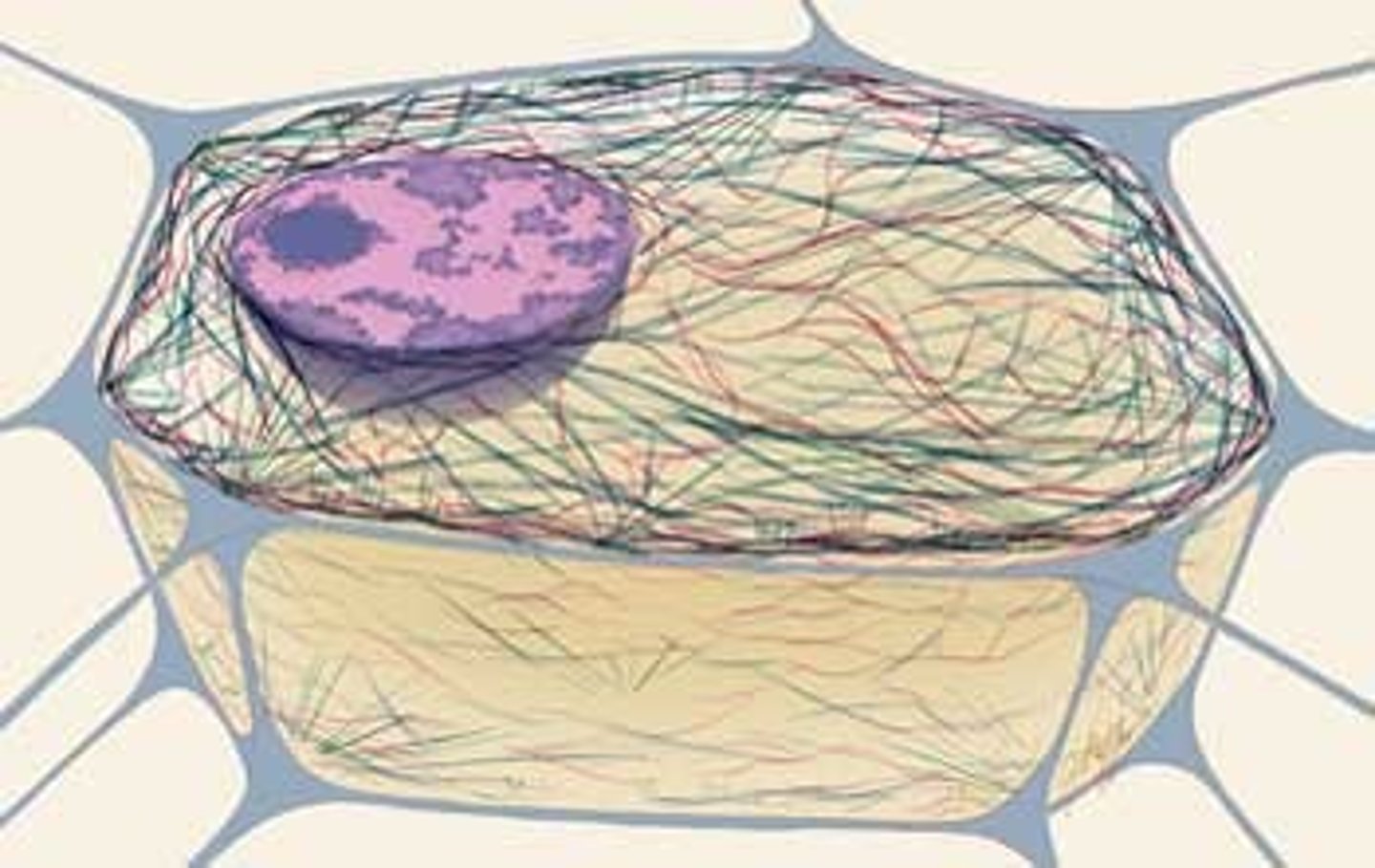
Cytoskeleton
Involved in movement within cell and in cell's architecture
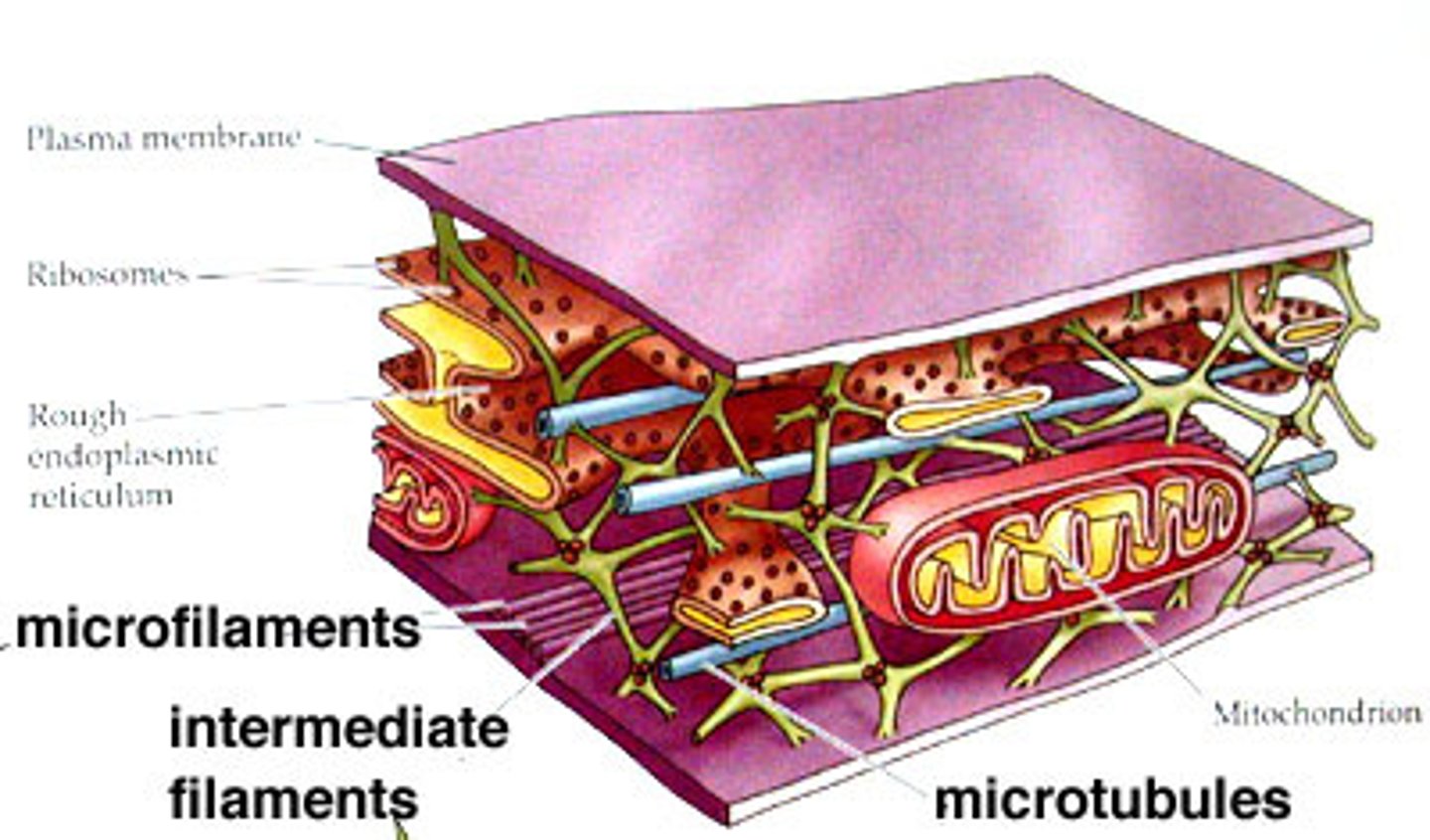
Microtubules
Control addition of cellulose to cell wall
Are thin, hollow, tubelike and composed of tubulins (proteins)
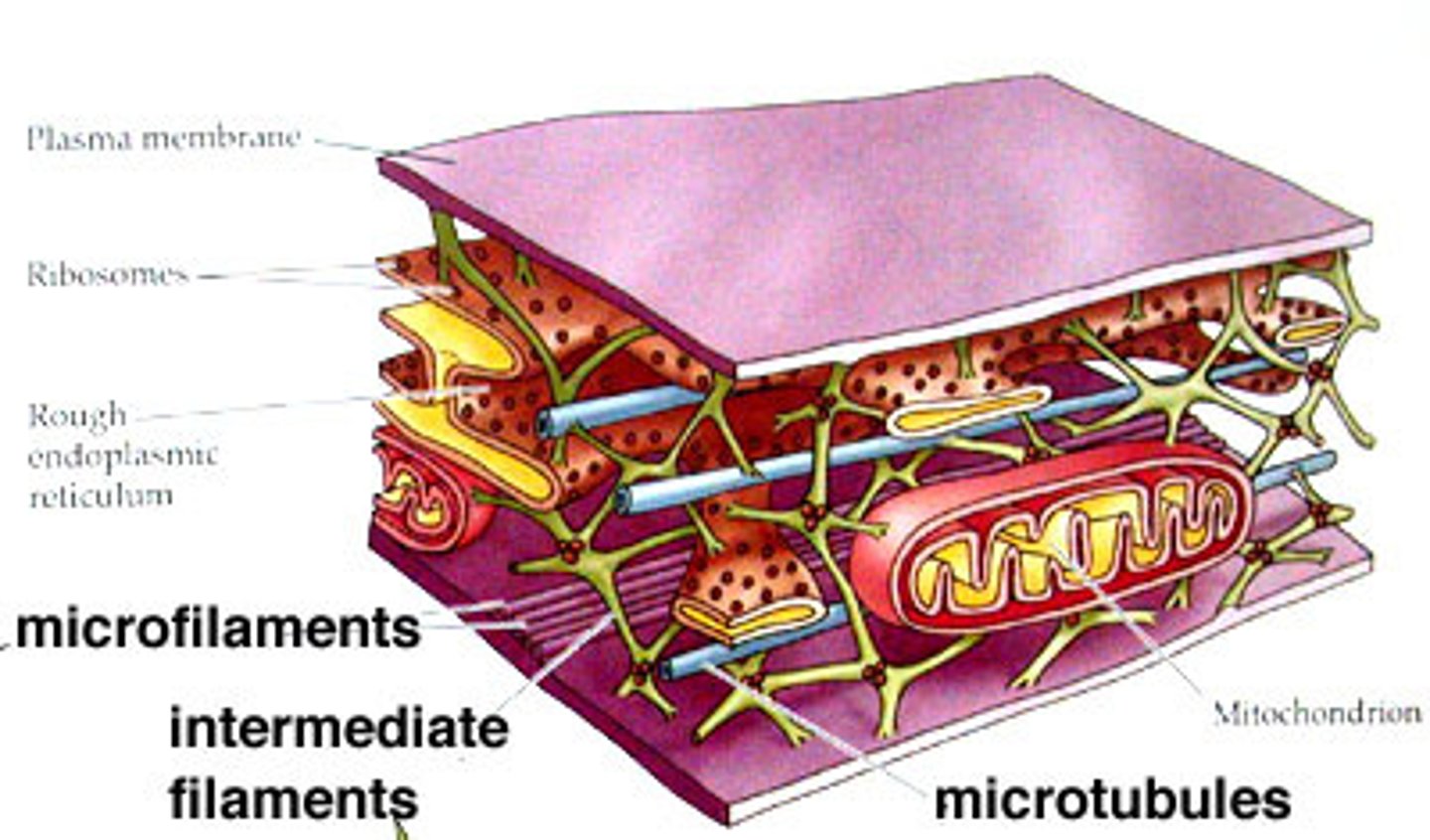
Microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
Traits of plant cells
•Cell walls
•Cell plate and plasmodesmata
•Plastids and vacuoles
Traits of animal cells
•Internal or external skeletons; no cell walls
•Plasma membrane called cell membrane.
•Divide by pinching in two; no cell plate nor plasmodesmata
•Centrioles present during cell division.
•No plastids nor vacuoles
Dictyosomes function
To modify carbohydrates attached to proteins that
are synthesized and packaged in the ER.
• To assemble polysaccharides and collect them in small vesicles.
• Vesicles pinched off from margins of dictyosomes.
• Vesicles migrate to plasma membrane, fuse with it, and secrete contents
to the outside of cell.
• Contents may include cell wall polysaccharides, floral nectars, and
essential oils in herbs.
Radicle
root-like part of a developing plant embryo
Root cap
Thimble-shaped covering of parenchyma cells that protects a growing root tip from abrasion
Region of cell division
Area adjacent to the root cap where cell division occurs
Protoderm
primary meristem that gives rise to epidermis
Ground meristem
primary meristem that gives rise to pith and cortex
(i.e., inner tissues of the stems and roots)
Procambium
primary meristem that gives rise to vascular Cambium
Region of elongation
Area where cells grow longer
• Located just behind the region of cell division
Secondary tissues
Layers of tissues added after primary tissues
Region of differentiation
Area where cells differentiate into distinct types that form various tissues
Root hair
Thread-like extensions along the root that increase surface area for better absorption
Cortex
• A thick area of parenchyma cells between the epidermis and inner tissues used to store food
Endodermis
A one-cell layer boundary between the cortex and inner tissues
Casparian strip
Bands of cell wall material in endodermis that are made of suberin, which is water-resistant
• Force materials entering or exiting the inner tissues to pass thru plasma membranes or plasmodesmata of the endodermis
Passage cells
Thin-walled cells in the endodermis that lack suberin and which allow fluids to pass w/o going thru plasma membrane
Pericycle
A one-cell layer just inside the endodermis from which lateral roots arise
Vascular cylinder
The collective core of tissues inside the endodermis that are involved in transport of fluids
• i.e., the xylem and phloem
Food storage roots
Roots specially adapted to store large amounts of food
Water storage roots
Roots specially adapted to store large amounts of
water
• Found especially in arid regions
Propagative roots
Roots specially adapted to grow into individual new plants
Adventitious buds
Buds located in places other than the stem
Easier to propagate
Pneumatophore
Specialized roots that extend above ground and above water to aid in gas exchange
Aerial roots
Roots extending above ground
Contractile roots
Roots that pull the plant deeper into the soil for thermal stability
Buttress roots
Above-ground roots that add to stability
Parasitic roots
Roots on plants that lack chlorophyll and which depend on photosynthesizing plants for nutrients (needs host)
Ex. Beech drops, squaw root
Haustoria
Projections that connect parasitic roots to their host plant
Saprophyte
Organisms that lack chlorophyll and obtain nutrients from decaying organic matter
Fungi!
Epiphyte
Plants that grow on other plants. Have aerial roots
Ex. Orchids
Epiparasite
A parasite of a parasite
Mycorrhizae
Fungi associated with/ plant roots that aid the plant in uptake of nutrients
Root nodule
Swellings in roots that contain a large # of nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Node
The area of a stem where a leaf attaches
Internode
The region between nodes
Blade
The broad, flat part of a leaf (recognizable)
Petiole
The stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the plant steM (leaves the leaf scar on twigs)
Axil
The angle between the petiole and the stem
that contains a bud
Deciduous
Trees that lose their leaves in autumn, regrow in spring
Leaf scar
A mark left on a twig from where a leaf grew
USUALLY HEART-SHAPED
Bundle scar
Tiny holes within a leaf scar caused by the
xylem and phloem that was within the leaf that
previously grew there
Protoderm
Becomes epidermis
Procambium
Becomes vascular cambium
Leaf primordial
Become leaves
Horn shaped under microscope