Glencoe Biology - Chapter 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 : Chemistry in Biology
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Acid
Has a ph less than 7. Stomach HCL, vinegar, tomatoes
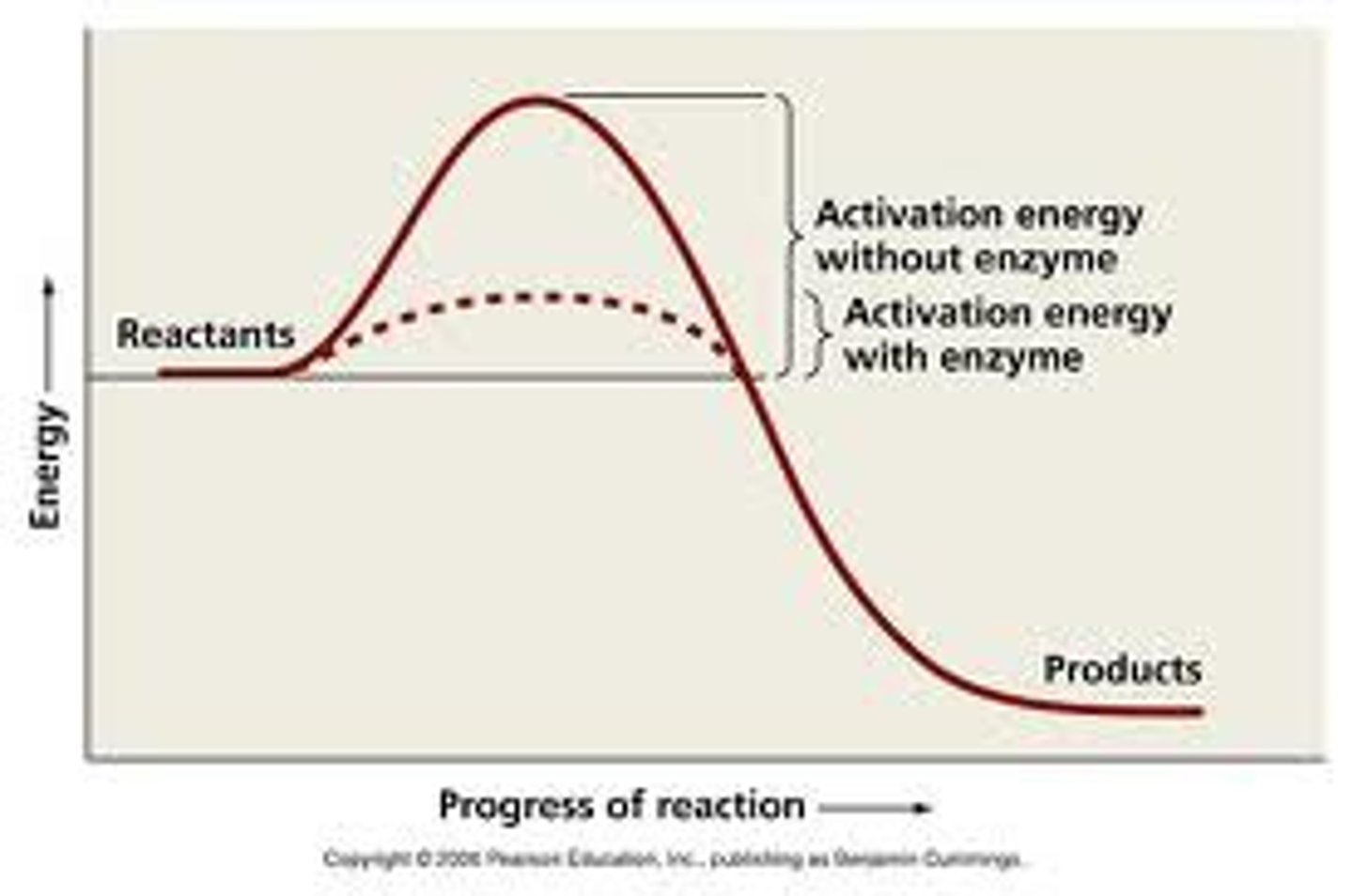
Activation energy
Minimum amount of energy needed for reactants to form products in a chemical reaction.
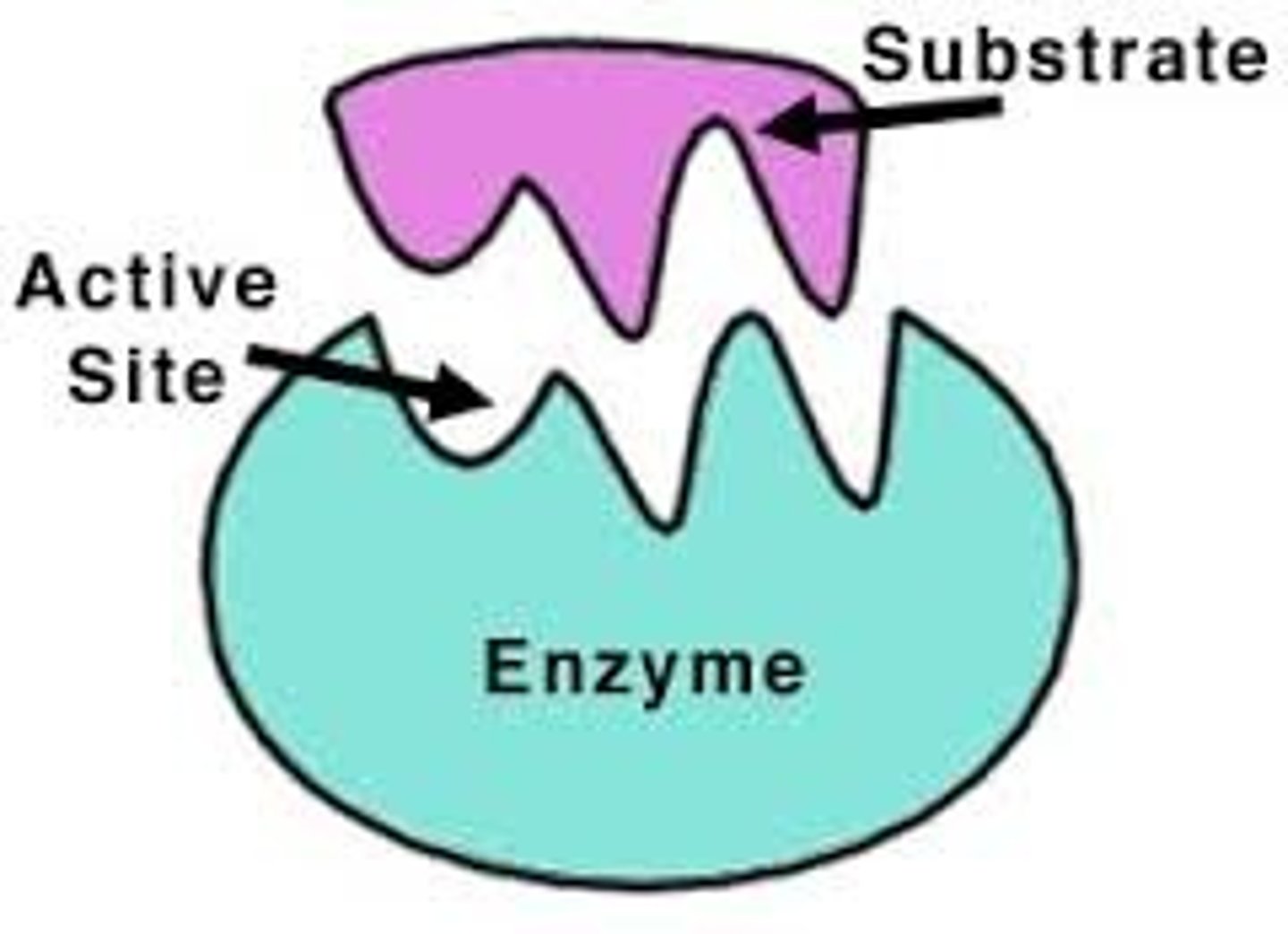
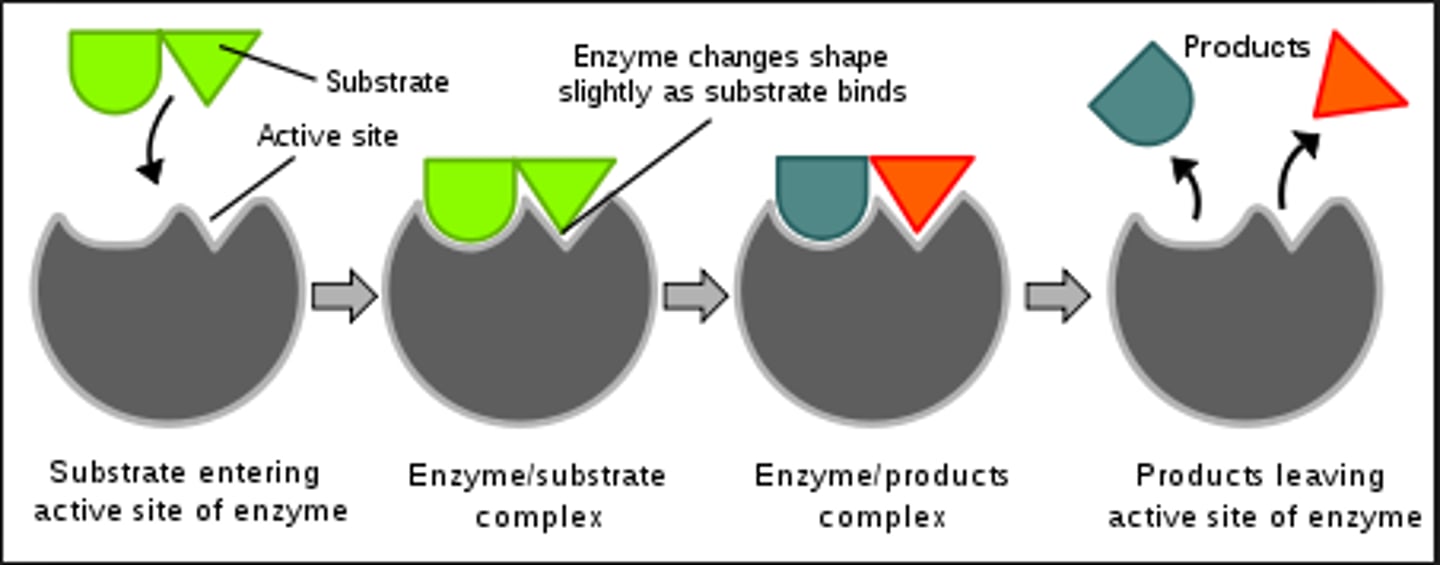
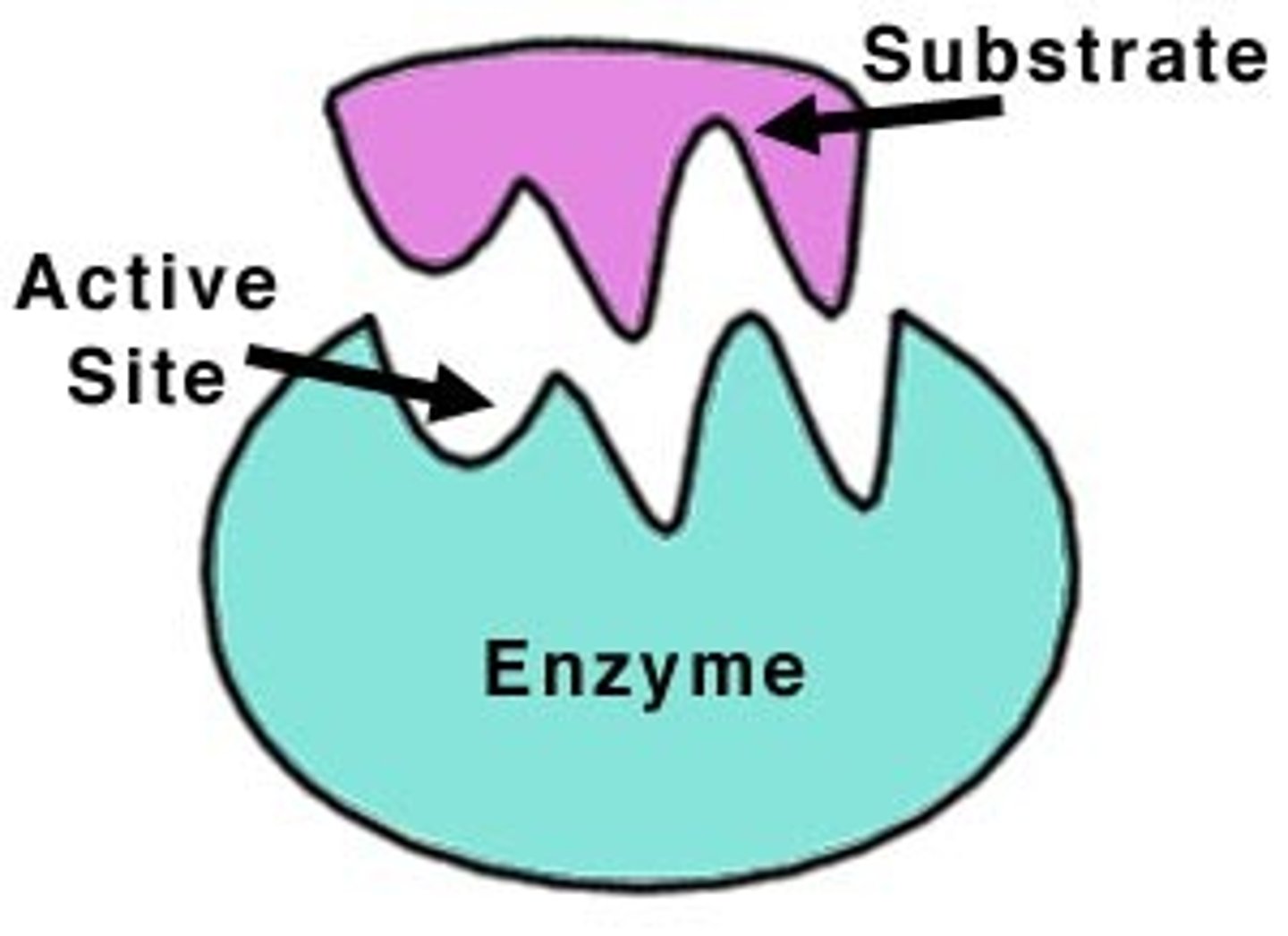
Active site
Specific place where a substrate binds on an enzyme.
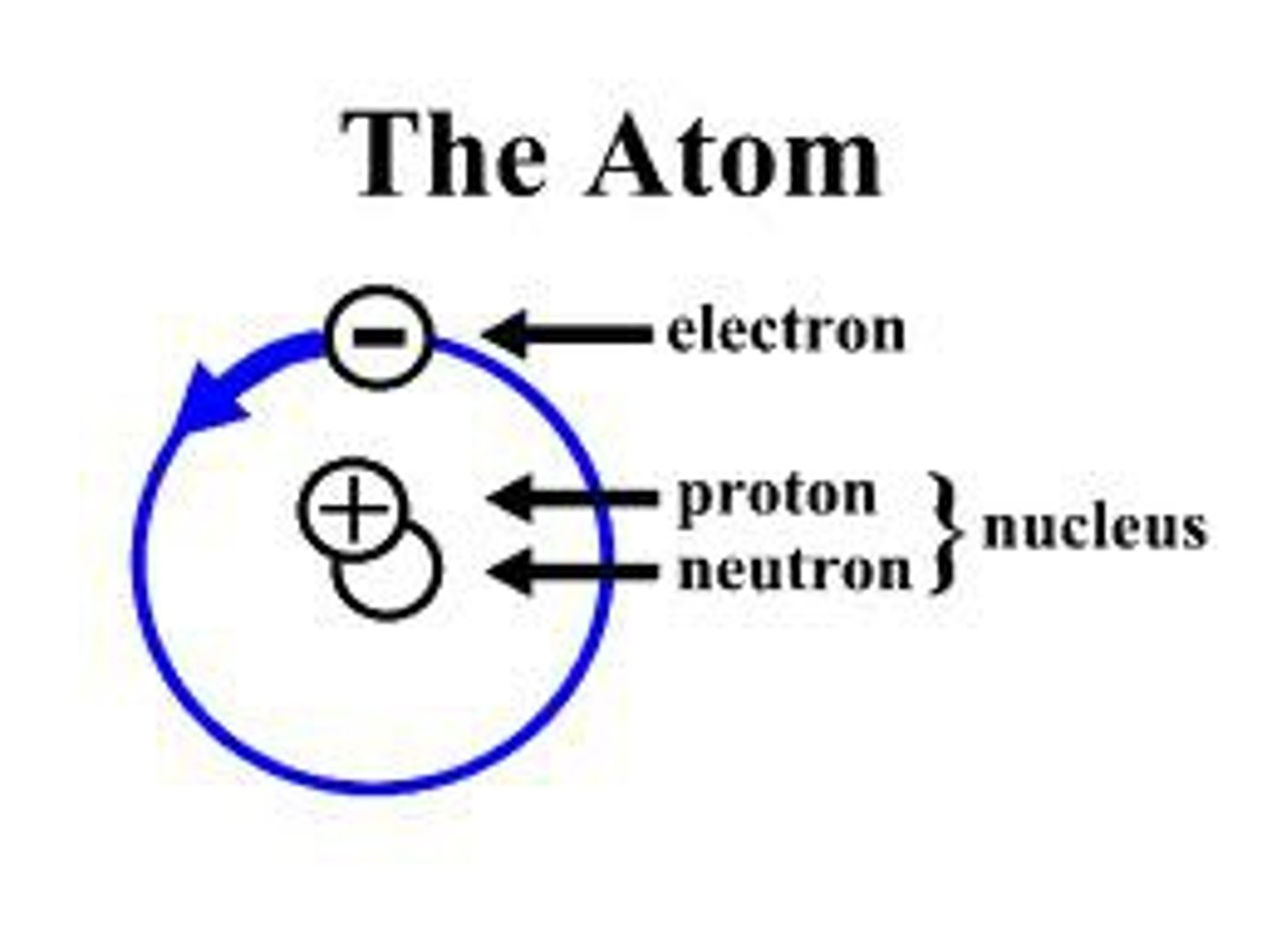
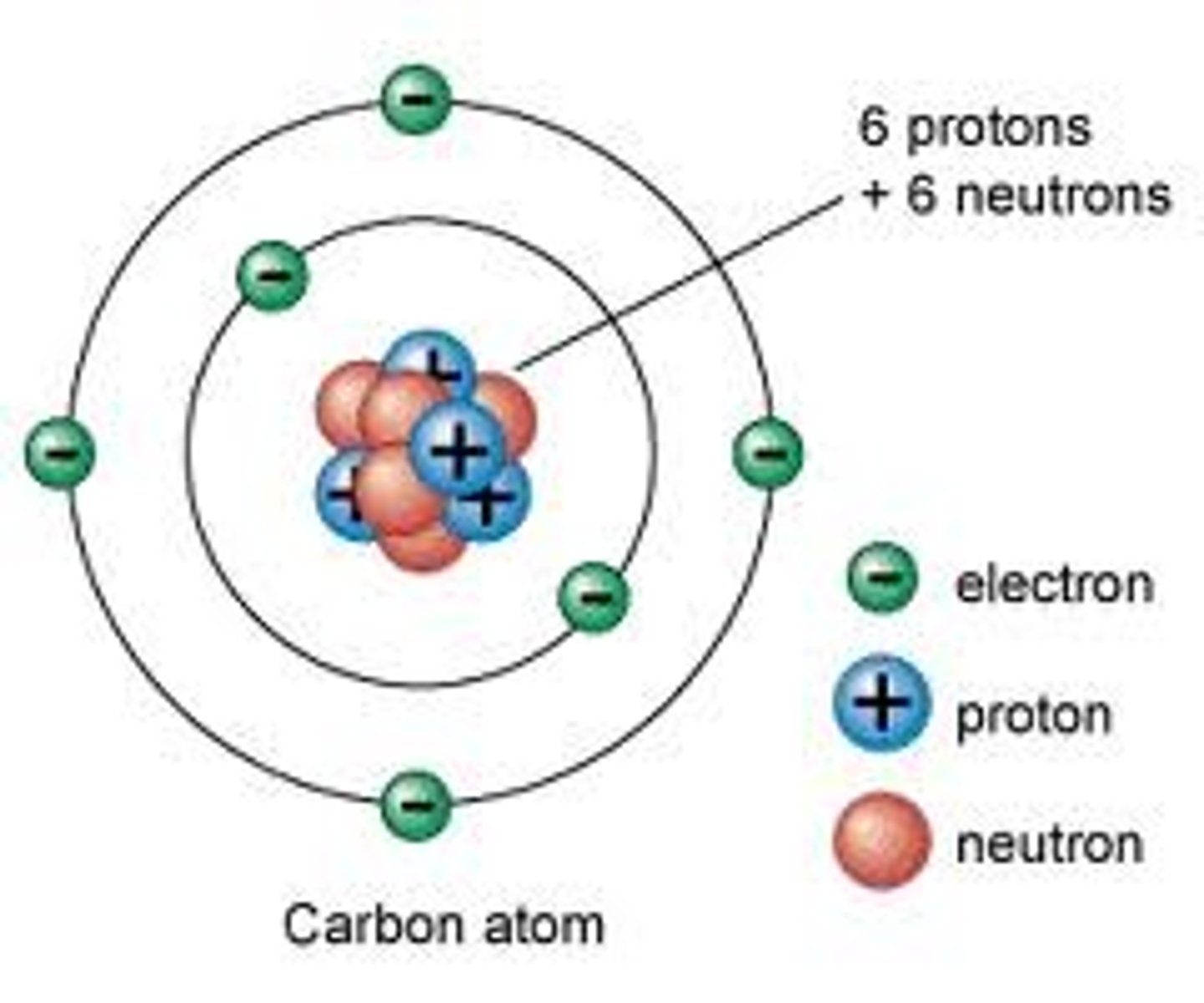
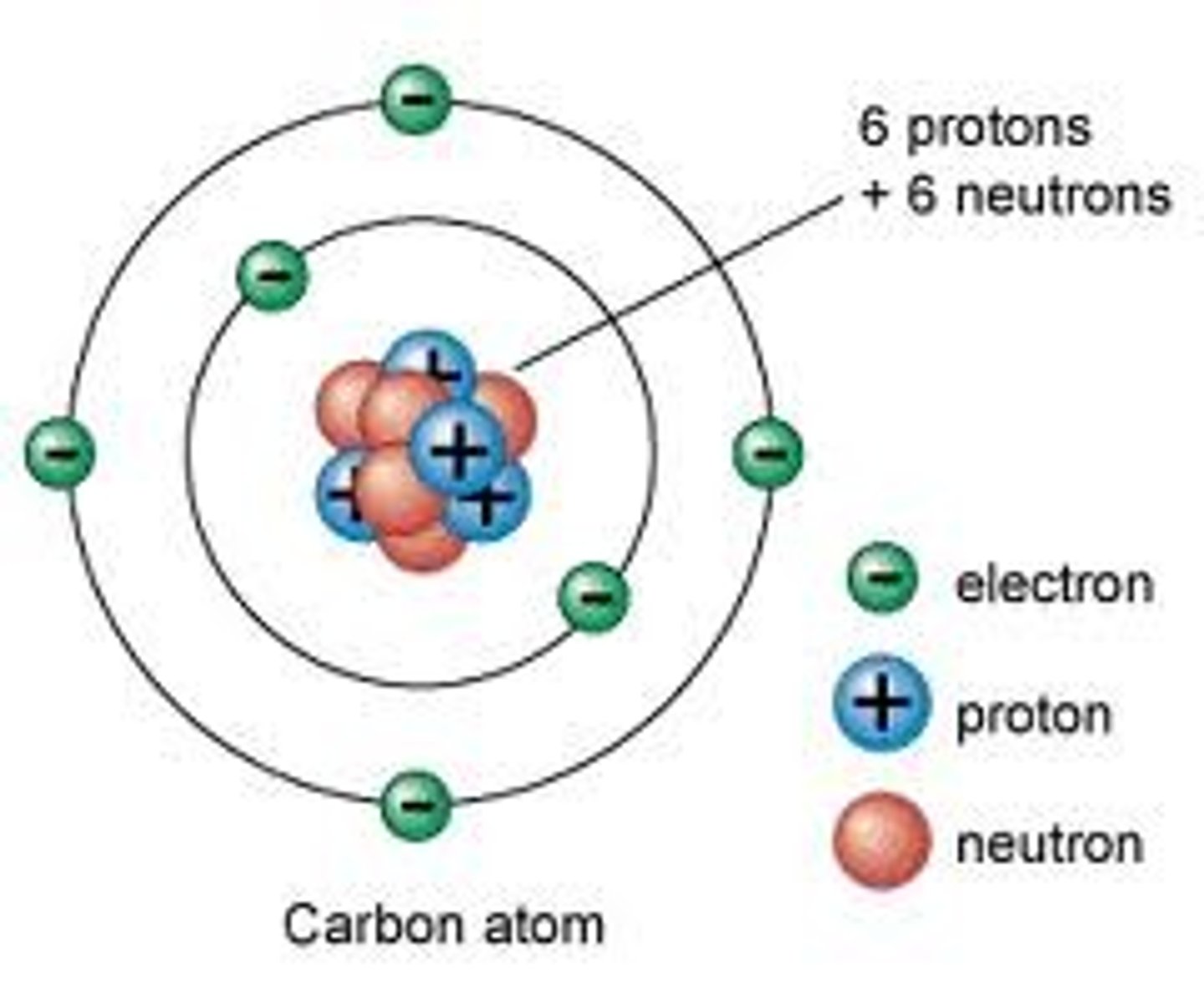
Atom
Building block of matter; contains subatomic particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons.
Base
A basic solution has a ph greater than 7. Drain cleaner, bleach, NaOH
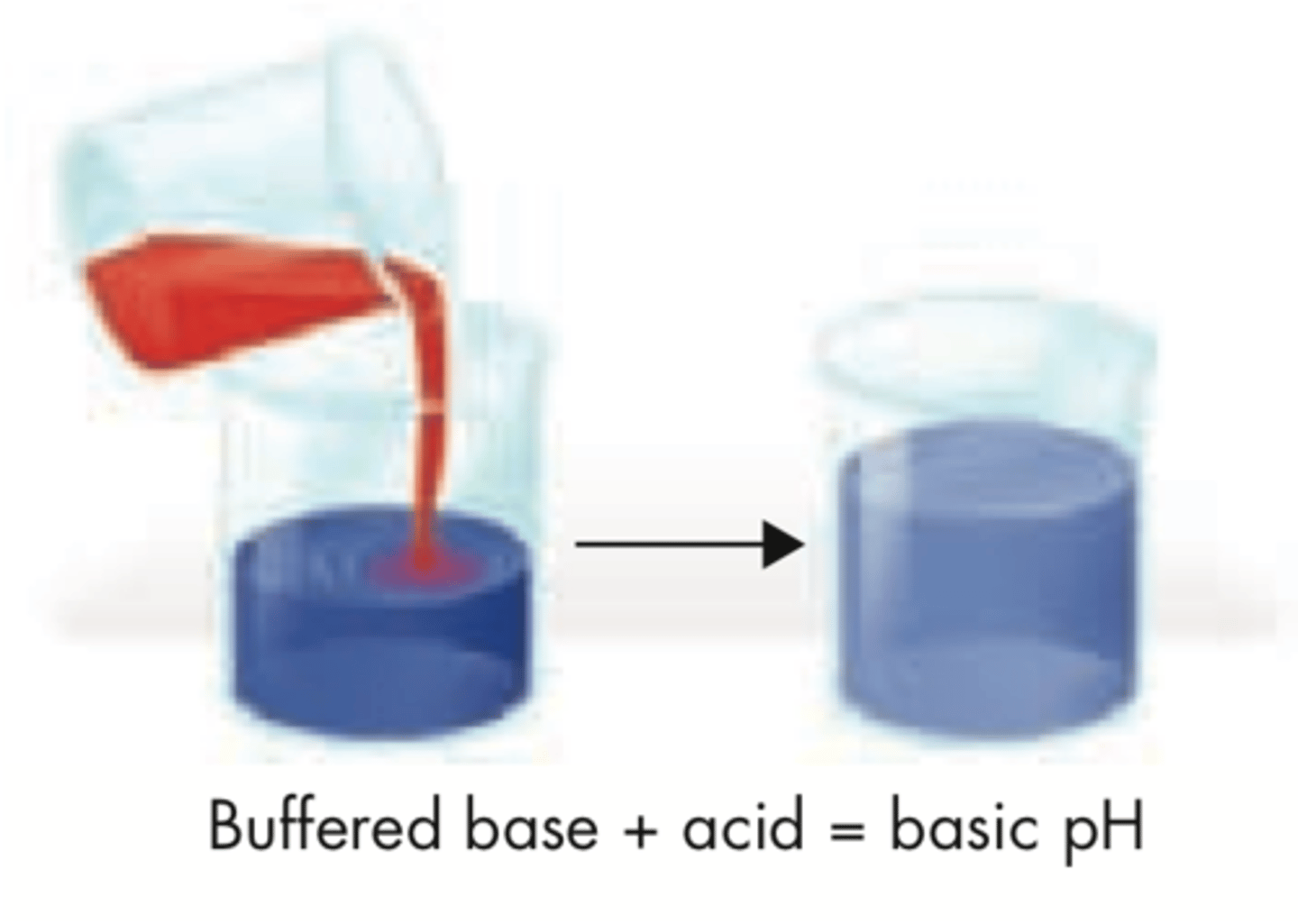
Buffer
Mixture that can react with an acid or a base to maintain the ph within a specific range. important for homeostasis so your bodily fluids don't get out of whack
Catalyst
Substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by reducing the needed amount of activation energy.
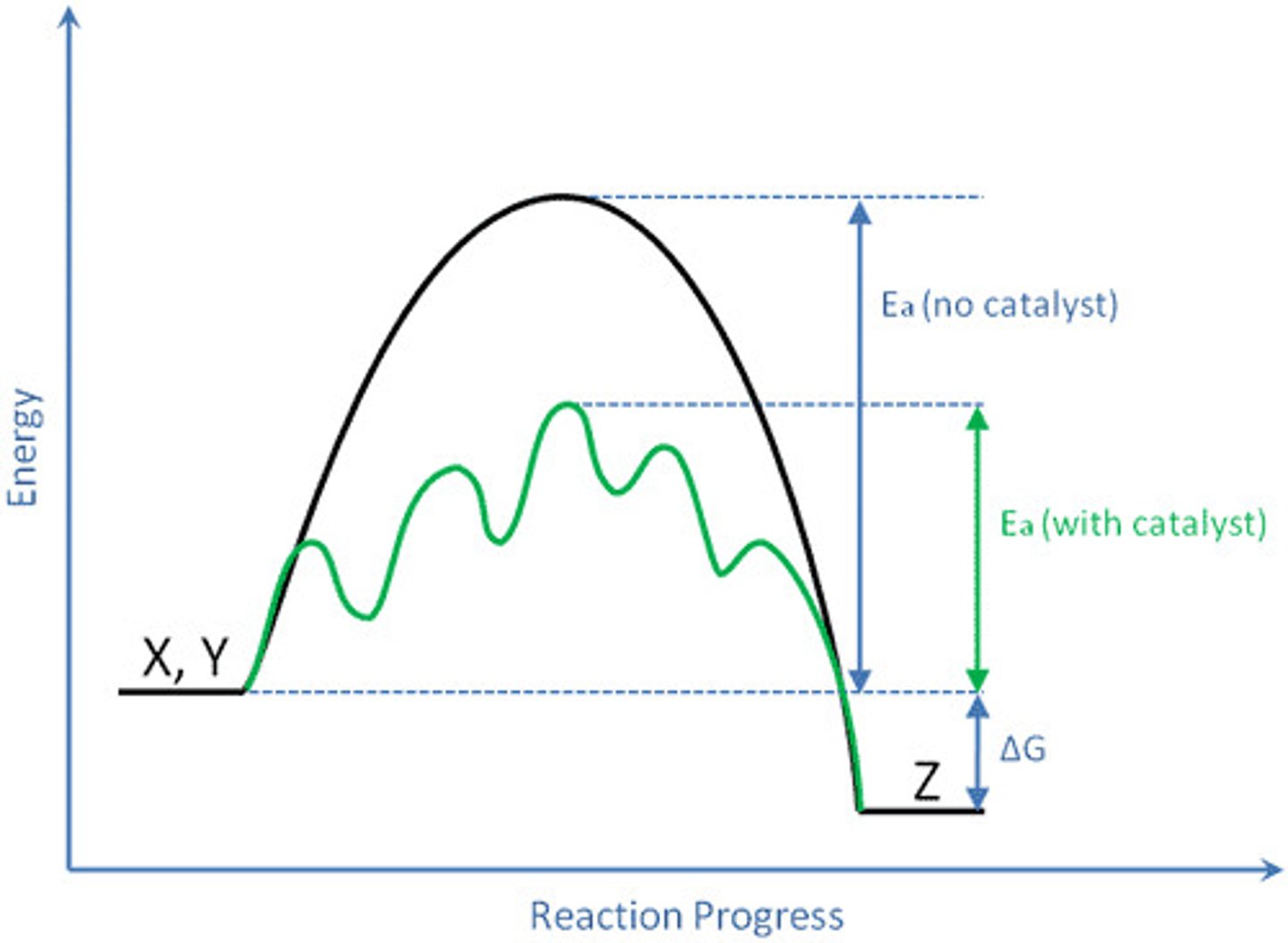
Chemical reaction
Energy-requiring process by which atoms or groups of atoms are changed into different substances.
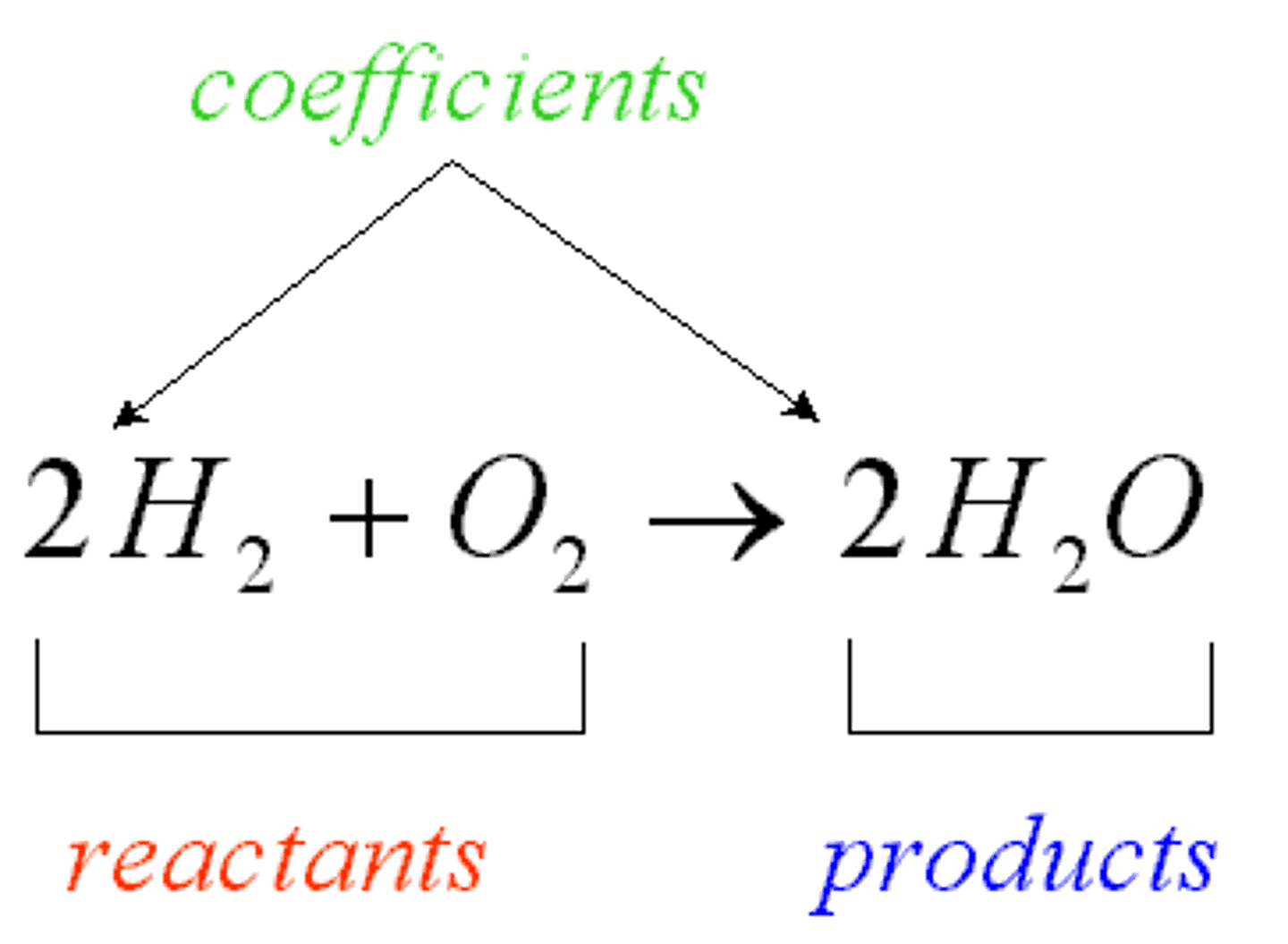
Electron
Negatively charged particle that orbits an atom's nucleus.
Element
Pure substance composed of only type of atom; cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means.
Enzyme
A biological catalyst that speeds up a reaction by lowering the amount of activation energy needed to start the reaction. It is a special protein.
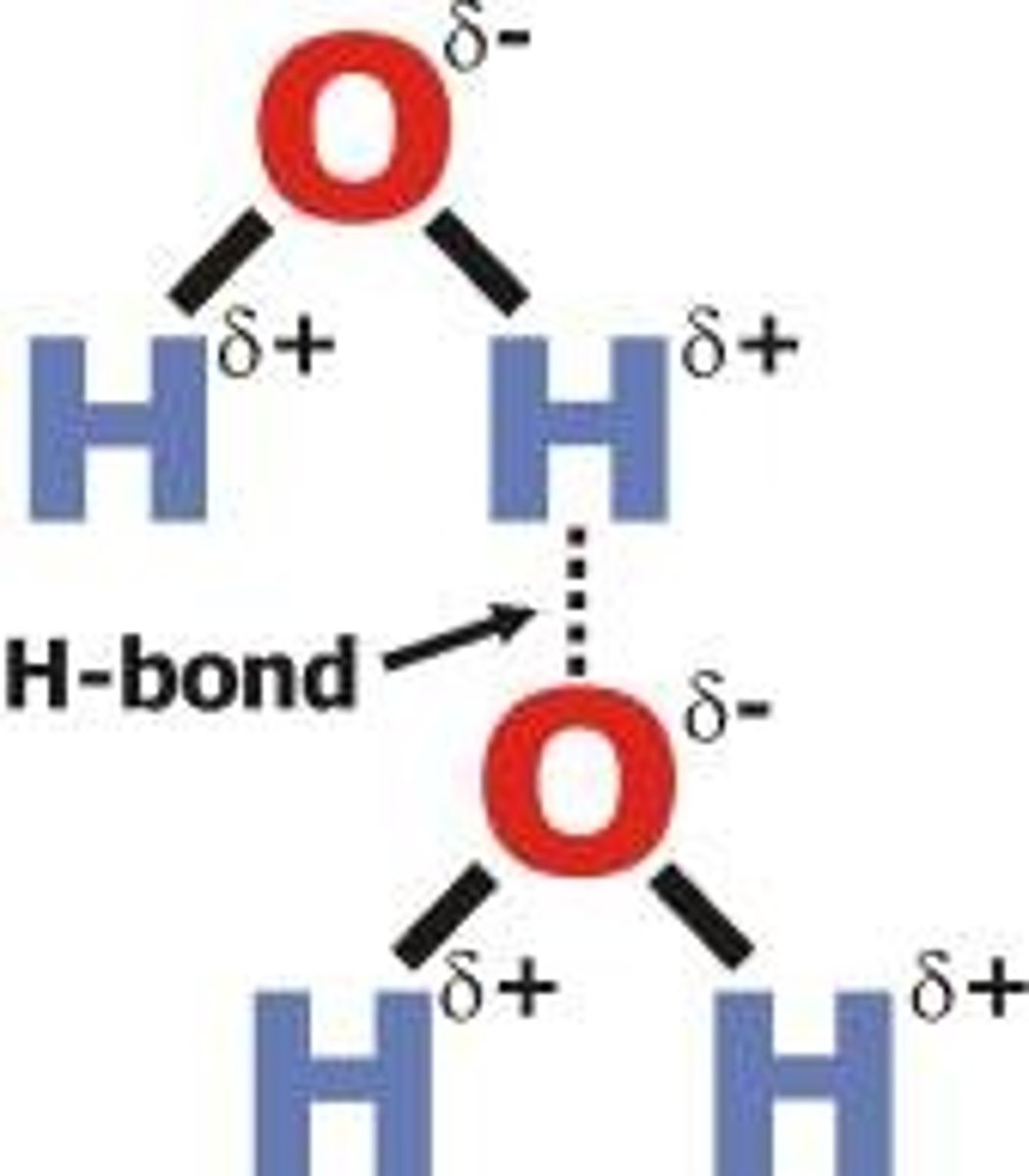
Hydrogen bond
Weak electrostatic bond formed by the attraction of opposite charges between a hydrogen atom and an oxygen, fluorine, or nitrogen atom.
Neutron
Particle without a charge in an atom's nucleus.
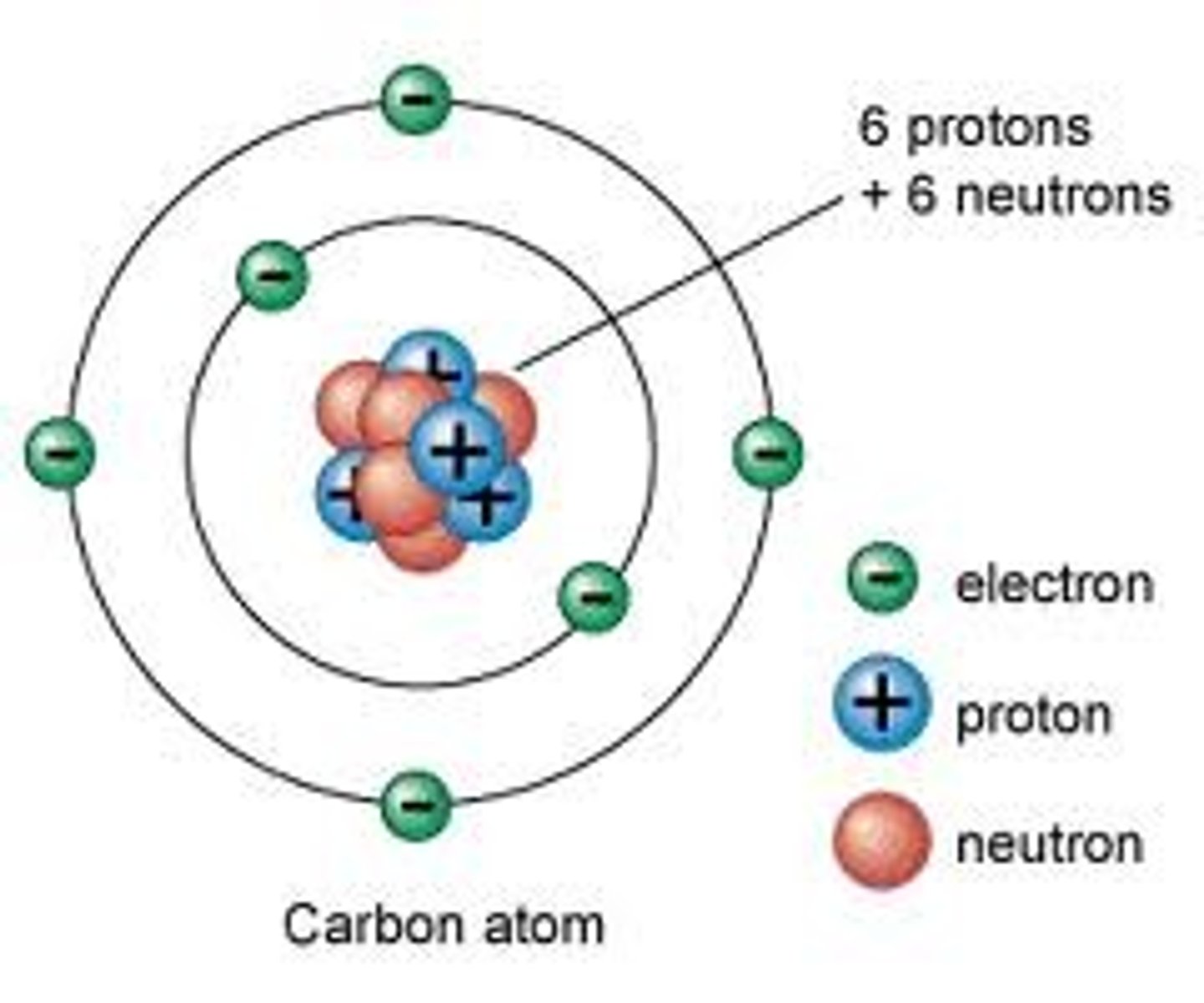
Nucleus
Center of an atom; contains neutrons and protons.
pH
Measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions (h+) in a solution; indicates the relative strength of an acid or a base: an acidic solution has a ph value less than 7, a basic solution has a ph value greater than 7, and pure water is neutral with a ph value

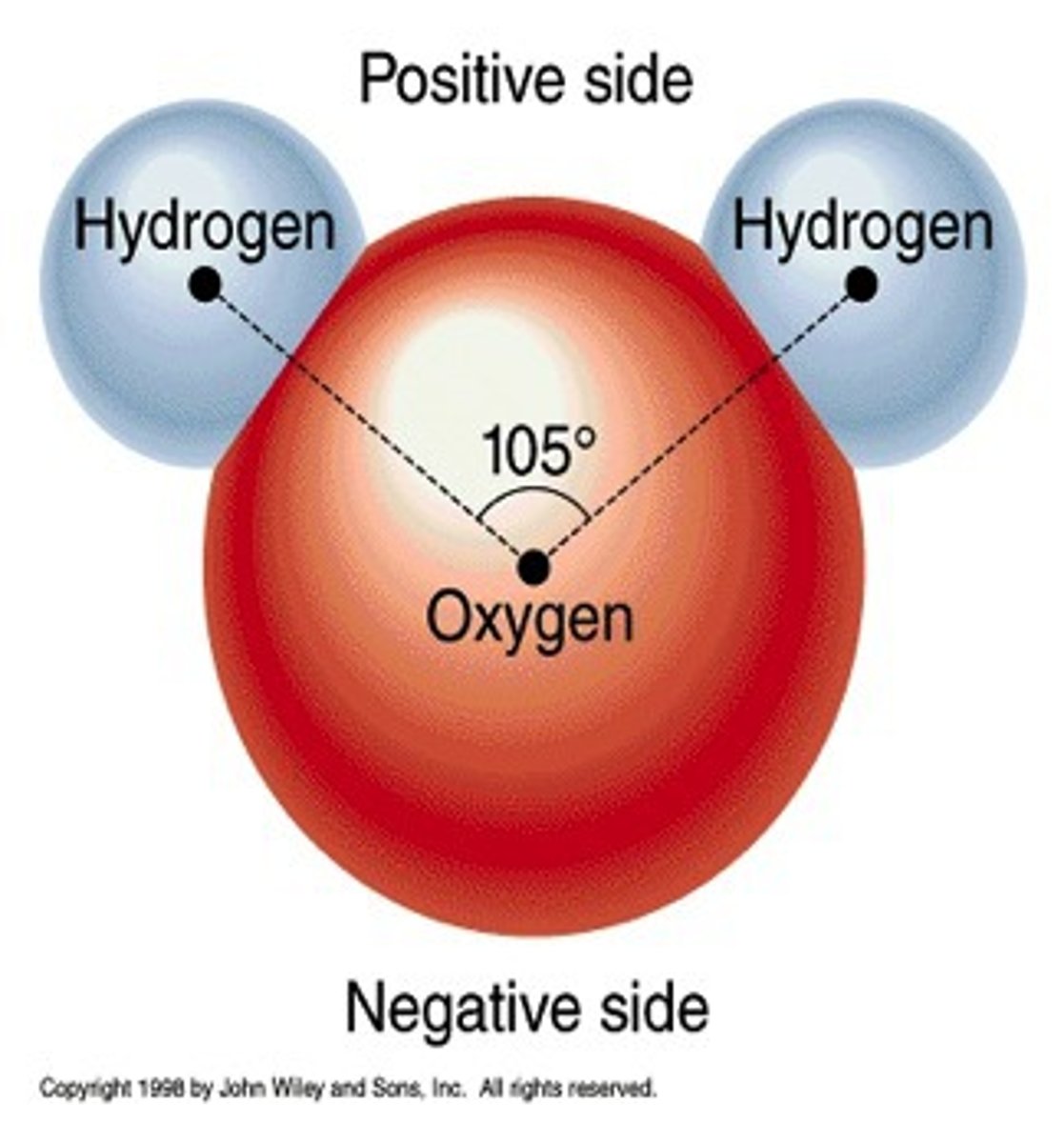
Polar molecule
Molecule with oppositely charged regions.
Product
Substance formed by a chemical reaction; located on the right side of the arrow in a chemical equation.
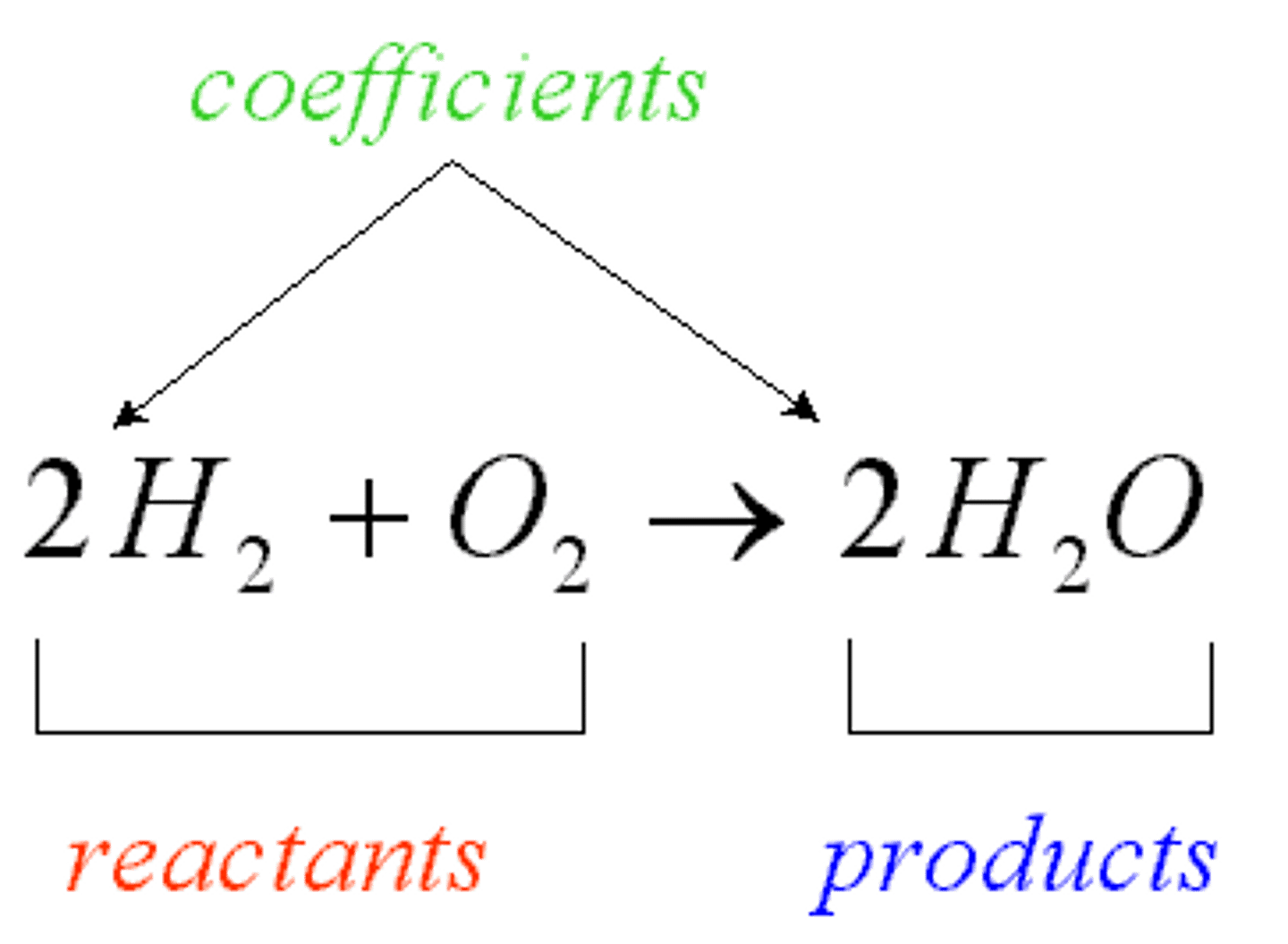
Proton
Positively charged particle in an atom's nucleus.
Reactant
Substance that exists before a chemical reaction starts; located on the left side of the arrow in a chemical equation.
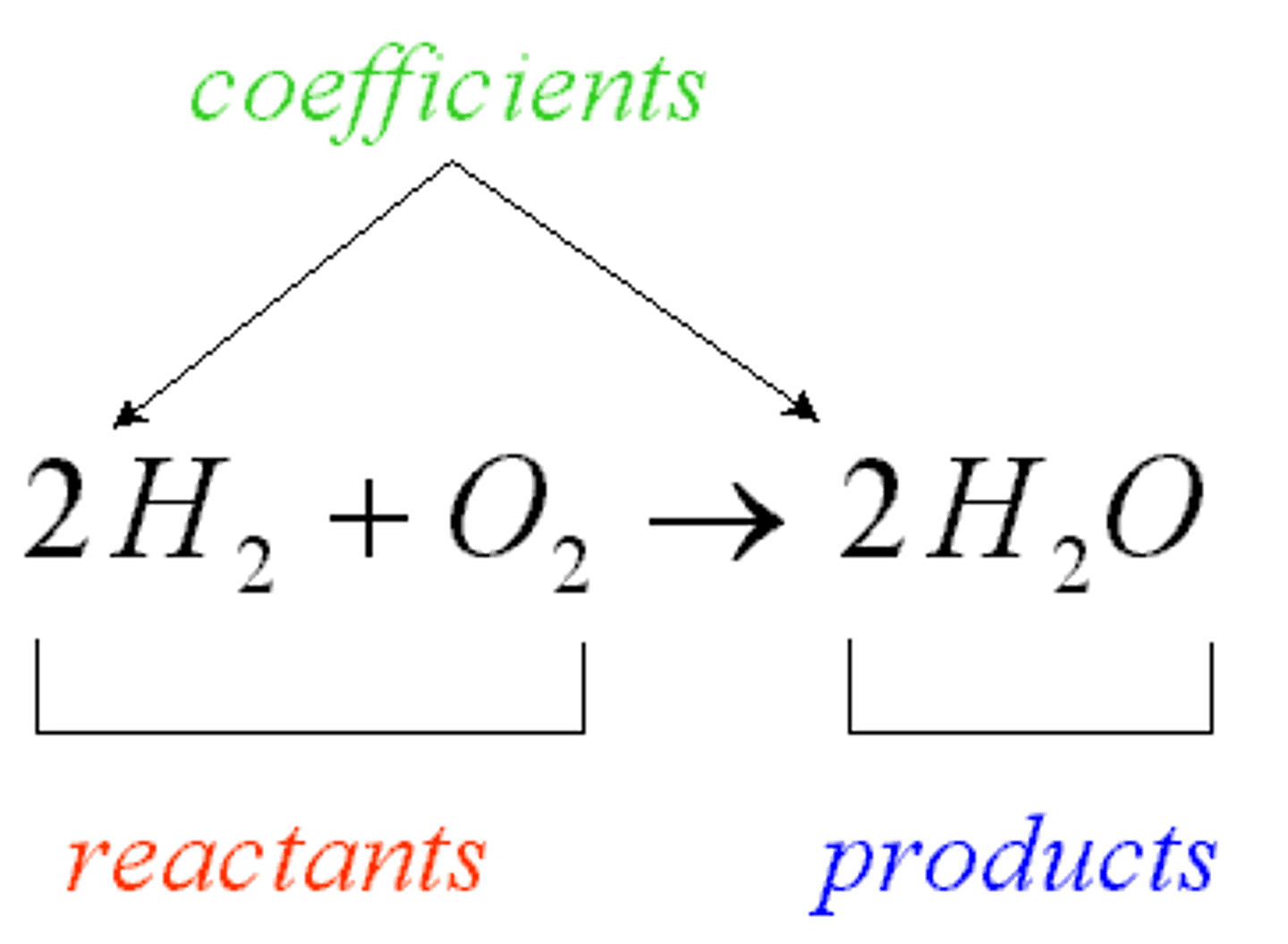
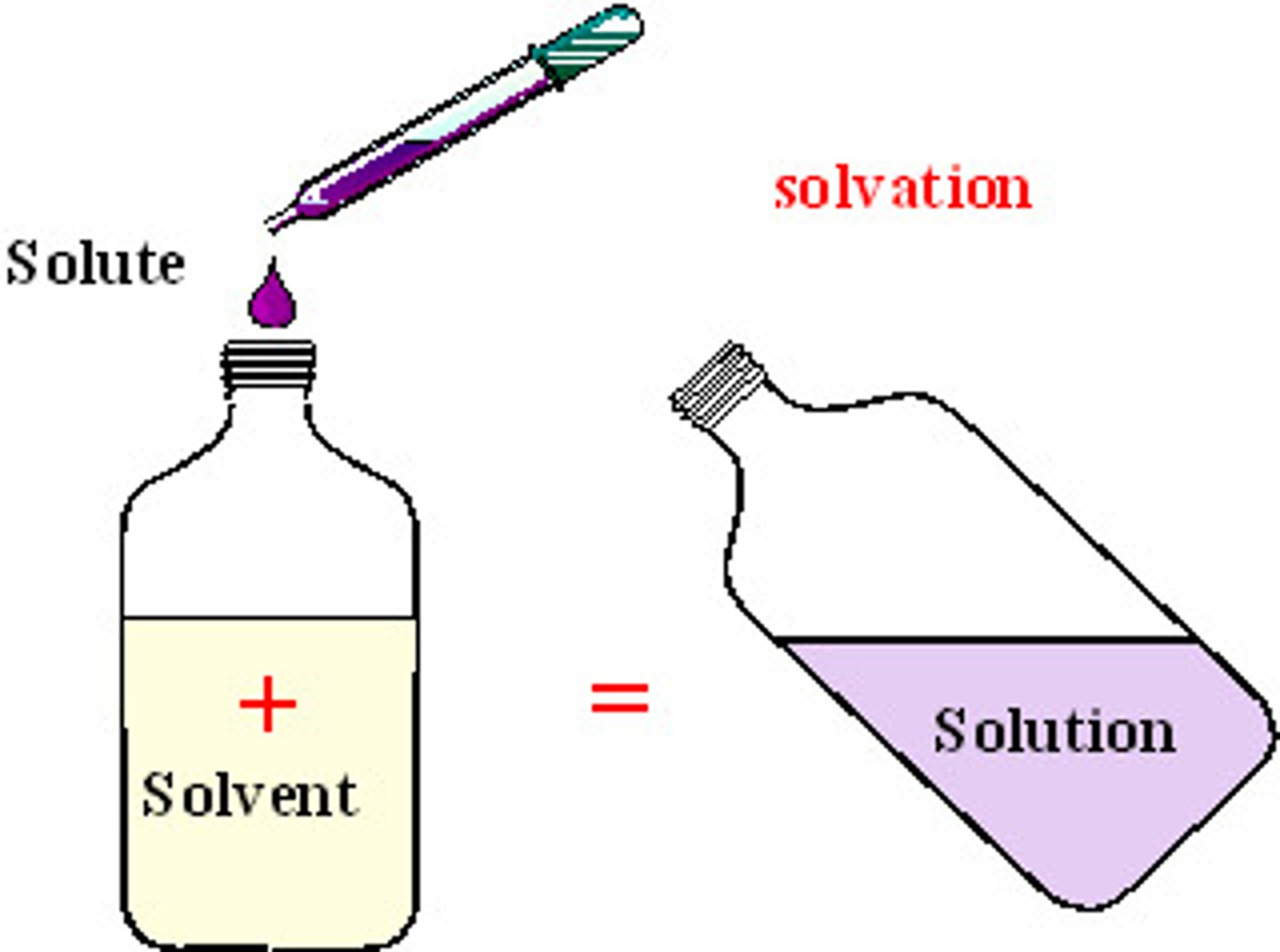
Solute
Substance dissolved in a solvent.(salt, koolaid)
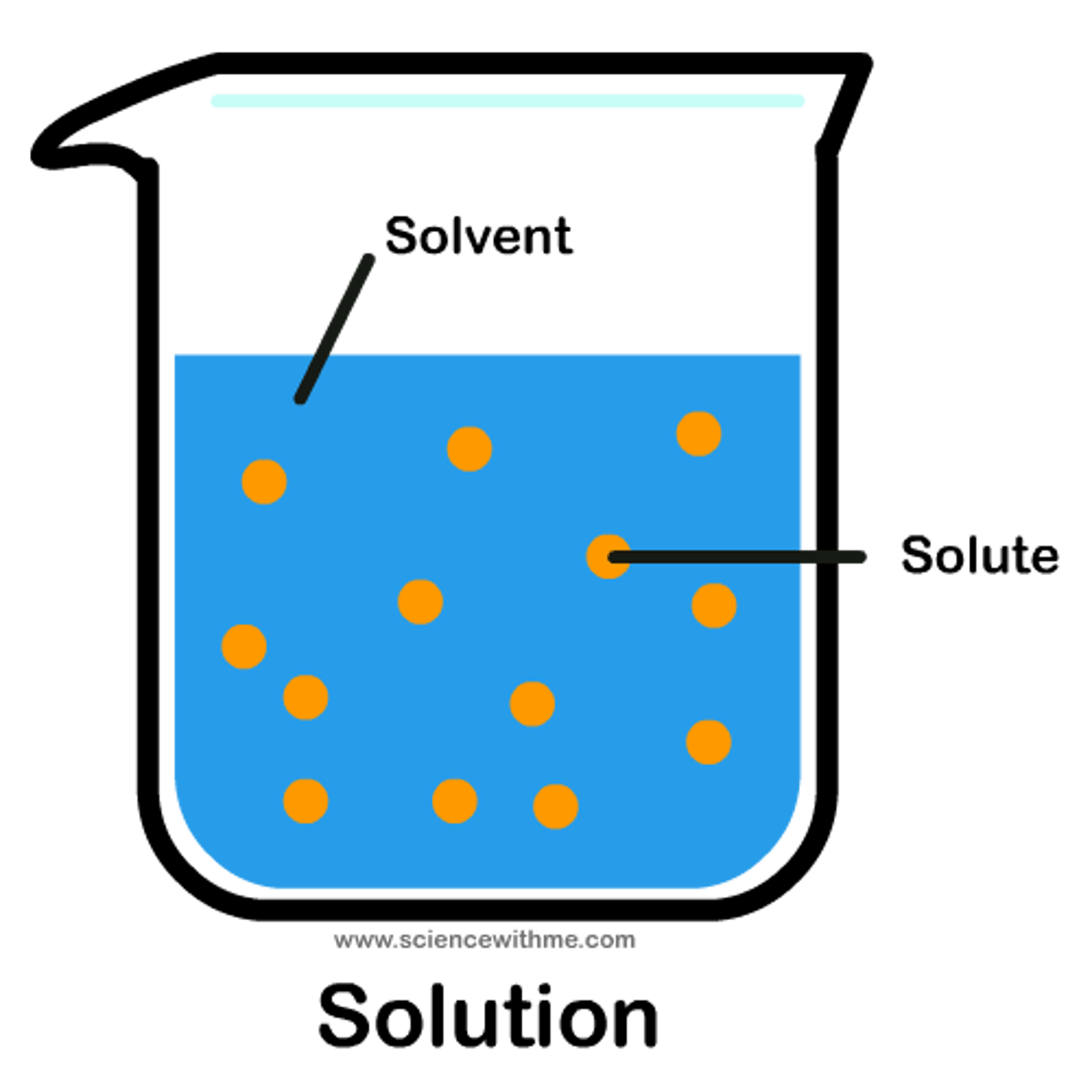
Solution
Homogeneous mixture formed when a substance (the solute) is dissolved in another substance (the solvent).
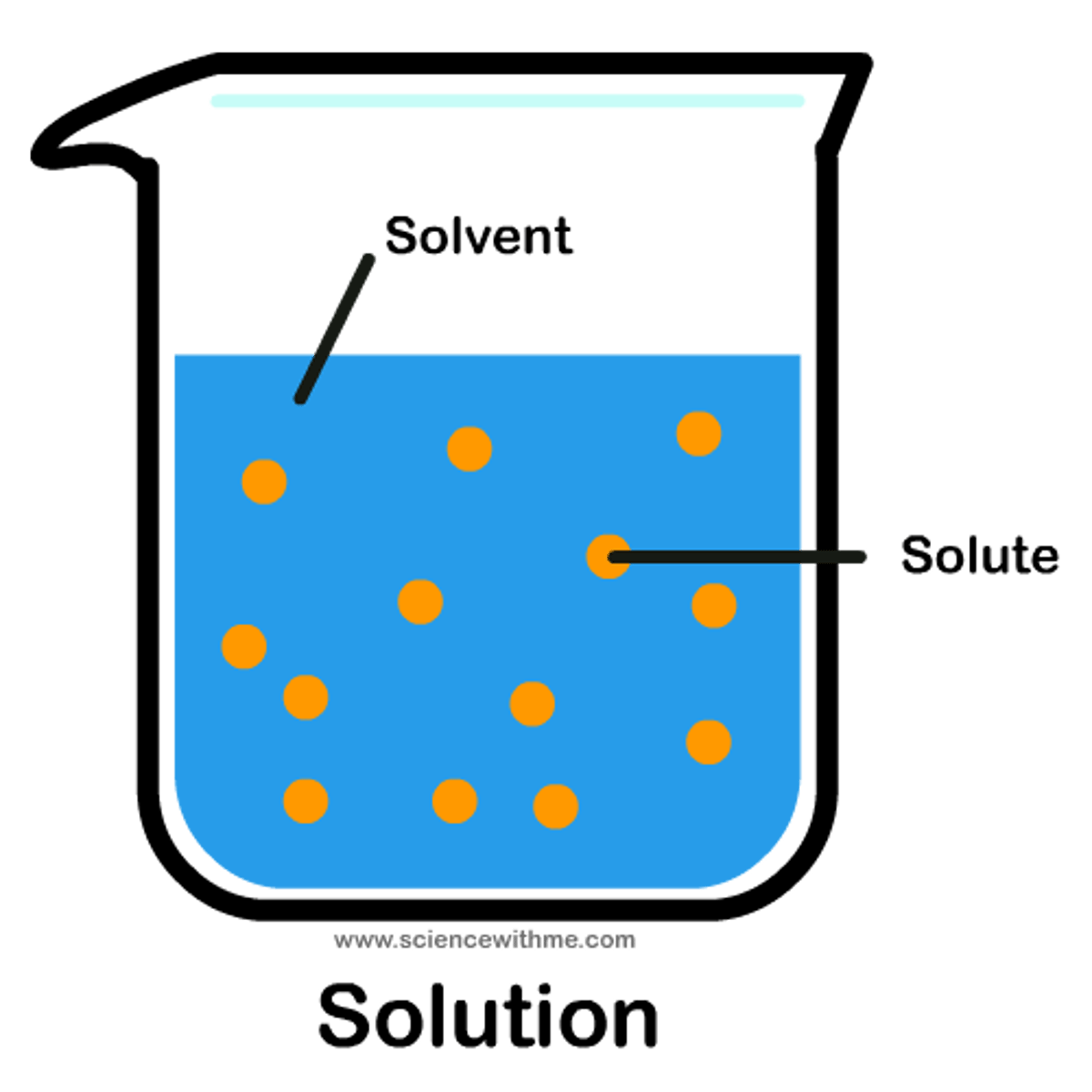
Solvent
Substance in which another substance is dissolved.(water)
Substrate
Reactant to which an enzyme binds.
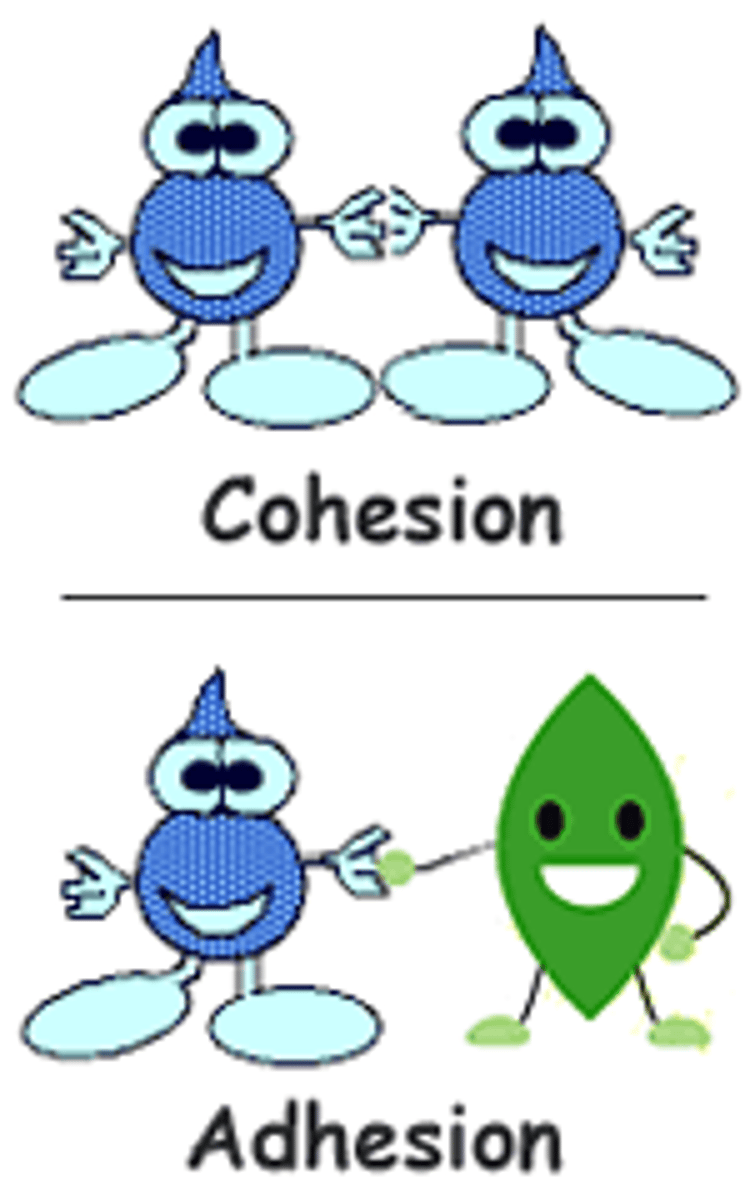
adhesion
Water molecules sticking to other surfaces.
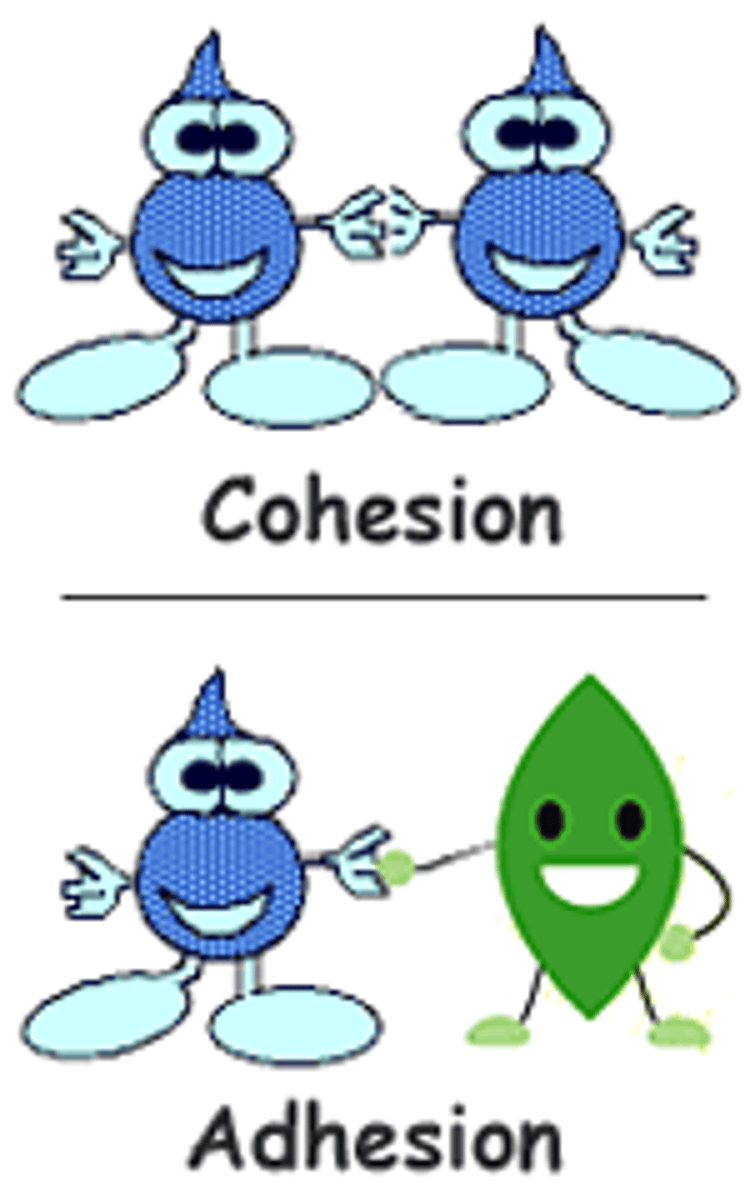
cohesion
Water molecules sticking to each other.
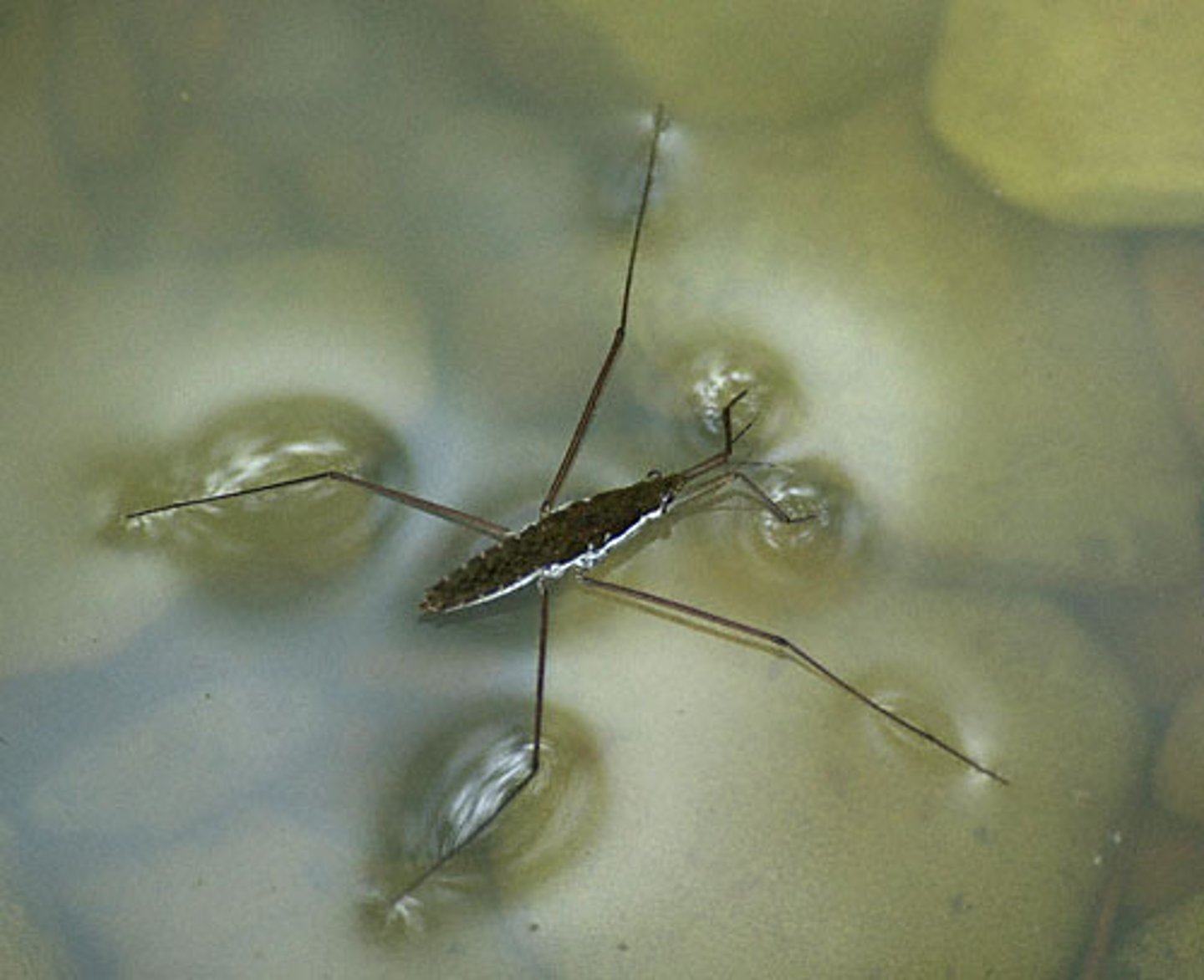
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

Denature
To render(make) an enzyme useless. Enzyme is destroyed usually by a change in pH or high temperature
CHONCaP
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Ca and Phosphorous. Main elements in living things.
Universal Solvent
Water- due to its polarity and ability to dissolve many different solutes. (salt, sugars...)
endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat
exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
High Heat Capacity
absorbs and releases large amounts of heat before changing temperature. Important for homeostasis and climate.
Capillary action
the combined force of attraction among water molecules and with the molecules of surrounding materials. Allows water to travel up small tubes and spaces (like between the fibers of a paper towel)