MICR5831 L7: DNA Cloning II 8/5/25 NEEDS SAQ
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
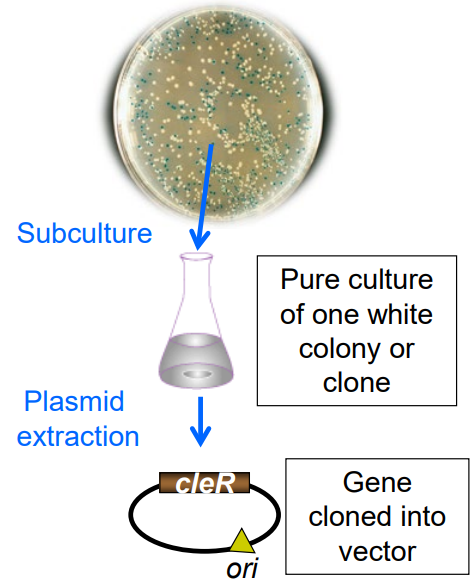
What are the steps for screening for a gene of interest/to isolate a plasmid?
1) Screen for genes with the same phenotype
2) Pick a colony
3) Grow pure culture
4) Alkaline lysis or column purification of plasmid
5) Analyze plasmid sequence or via restriction map
How do you identify cloning vectors that successfully underwent recombination?
-Insertional inactivation of phenotype present in plasmid
-Blue → white
Name two examples of insertional inactivation of a phenotype expressed by the plasmid
1) Antibiotic resistance marker on PBR322
2) Blue-white screening using pUC vectors
What is this?
-Tripartite replicon, first example of a modified vector
-Contains 3 segments:
-pMB1, R6-5, and R1
pBR322
What segments are found in pBR322, a tripartite replicon/the first modified vector?
1) pMB1
2) R6-5
3) R1
What does this segment of PBR322 contribute?
pMB1:
-Segment from ColE1 plasmid
-Medium copy number
oriV (Origin of Replication)
What does this segment of PBR322 contribute?
R6-5:
-Segment from R plasmid
Tetracycline resistance (TetR)
What does this segment of PBR322 contribute?
-R1:
-Segment from R plasmid R1
Ampicillin resistance (AmpR) from Tn3
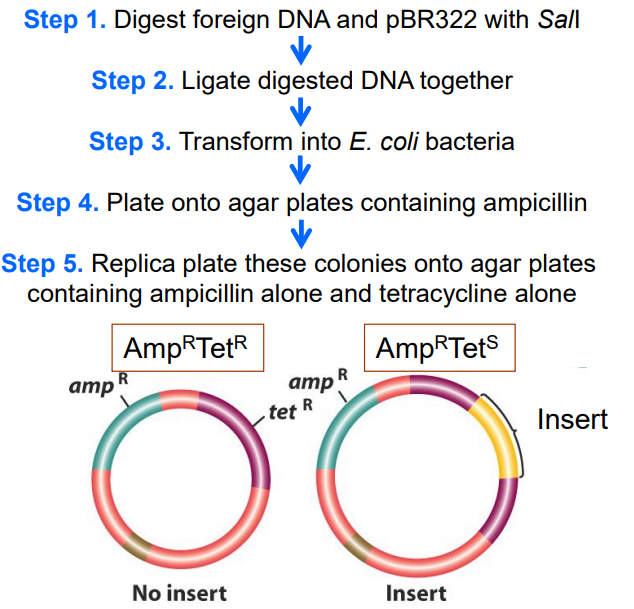
Name the steps for identifying recombinant vectors by using insertional activation (EX: pBR322)
1) Digest foreign DNA and pBR322 with Sal1
2) Ligate digested DNA together
3) Transform into E. coli bacteria
4) Plate onto agar plates containing ampicillin
5) Replica plate colonies onto agar with only ampicillin or only tetracycline
What is this recombinant vector used for Blue-White Screening?
-Derived from pBR322
-MCS starts after lacZ gene
-Plac promoter for inducible expression
-VERY high copy number (~1000 copies/cell)
pUC series
How is pUC derived from pBR322?
Replacing TetR-gene with lacZ' gene
Where is the MCS (Multi-Cloning Site) of pUC found?
Starts after Nucleotide 15 or Amino Acid 5 of the lacZ' gene
What does the Plac promoter of pUC do?
1) Binds LacI repressor
2) Induces LacZ transcription via allolactose or IPTG
True or False: Plac promoter of pUC can be turned on and off via inducible expression
True, it is induced by allolactose and IPTG
Which produces more copies of genes, pUC or pBR322?
pUC
What does the B-galactosidase LacZ do?
-Cleaves Lactose → galactose + glucose
-Cleaves X-gal → blue precipitate
What peptides is LacZ cleaved into?
1) lacZ Delta-M15
2) lacZ Prime (Alpha peptide)
True or False: The peptides formed by LacZ being cleaved (lacZ Delta-M15 and lacZ') are both inactive
True
True or False: Coexpression of both lacZ Delta-M15 and lacZ' will restore ẞ-galactosidase activity via alpha-complementation
True
What is this?
-F' plasmid
-Contains lacZAM15 (inactive B-galactosidase)
-Contains lacl repressor
E. coli host JM109
What two genes does the JM109 E. coli host contain?
1) lacI (repressor)
2) lacZAM15 (inactive B-galactosidase)
True or False: The pUC vector's origin of replication is compatible with the F' one in JM109
True
Where would you find the MCS (Multiple Cloning Sites) inside the pUC vector?
1) pLac (promoter)
2) lacZ' (inactive alpha peptide)
True or False: If the MCS of the pUC vector contains a fragment of DNA, the alpha complementation will be disrupted and appear as white (recombinant) instead of blue (wild type)
True
True or False: If 10 extra amino acids are added to lacZ', yet the translational frame is maintained and it can complement lacZ Delta-M15, it will not show up as recombinant (white) but rather the wild-type (blue-green)
True
What is the first step in Blue White screening for UC18?
1) Digest foreign DNA and pUC18 with Sal1
What happens during Blue White screening after this?
1) Digest foreign DNA and pUC18 with Sal1
Ligate digested DNA together
What happens during Blue White screening after this?
2) Ligate digested DNA together
Transform digested DNA into E. coli host JM109
What happens during Blue White screening after this?
3) Transform digested DNA into E. coli host JM109
Plate onto agar plates containing ampicillin, IPTG and X-gal
What happens during Blue White screening after this?
4) Plate onto agar plates containing ampicillin, IPTG and X-gal
White colonies contain recombinant vector
Blue/green colonies contain self-ligated vector (wild type)
How do you screen a library for a specific gene?
1) Synthesize a labelled probe that binds nucleotide sequence of gene
2) Raise an antibody that binds protein
How do you design a nucleotide sequence probe?
-Produce degenerate nucleotide sequence probe (conserved motif with 90-100% identity)
1) Take homologous gene from a related organism
2) Purify protein, sequence it and back-translate it
How do you design a probe for a protein?
1) Purification of protein encoded by the gene
2) Raise antibodies that will detect protein expressed by the clones
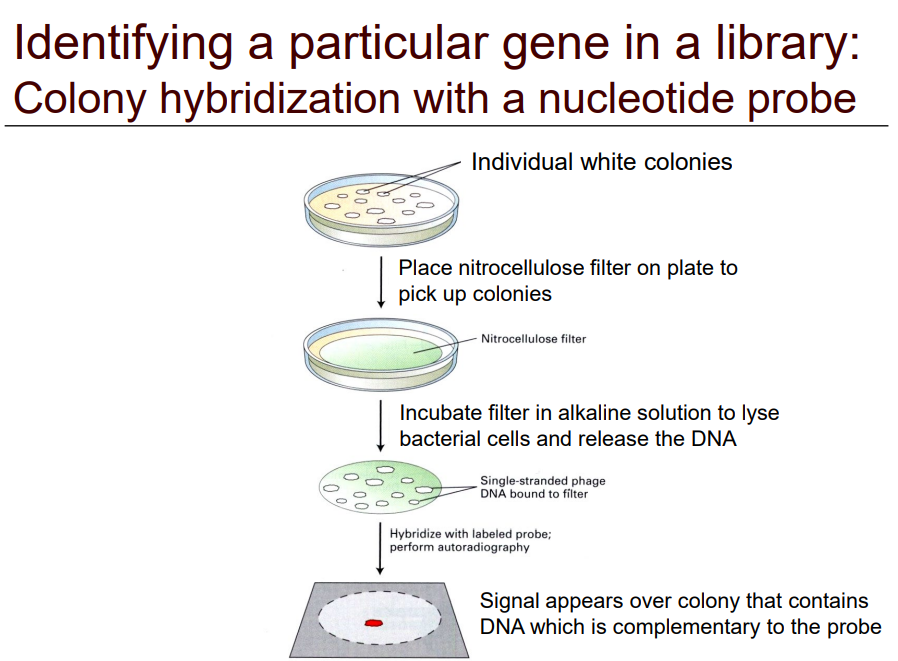
How do you identify a particular gene using this method?
Create a hybrid colony with a nucleotide probe
1) Take individual white colonies
2) Place nitrocellulose filter on plate to pick up colonies
3) Incubate filter in alkaline solution to lyse bacterial cells and release the target DNA
4) Hybridize with labeled probe
5) Perform autoradiograph
6) Signal appears over colony that contains DNA which is complementary to the probe

How do you identify a particular gene using this method?
-Immunoblot a colony with antibodies
1) Overlay nitrocellulose filter
2) Break open bacteria with SDS and NaOH, then neutralize
3) Proteins from Master plate bind to nitrocellulose
4) Incubate filter with primary antibody then wash and incubate with radiolabeled secondary antibody
5) Fusion protein binds → nitrocellulose
Primary antibody/secondary antibody bind → protein
6) Perform autoradiography via X-ray film to confirm protein's presence thanks to attached radiolabelled secondary antibody
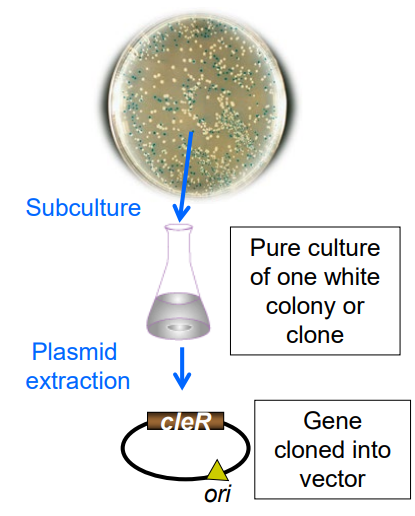
Using a flow chart describe the steps you would use to isolate a gene of interest. (slide 27)
1) Screen for same phenotype (ex: Haemolysis)
2) Pick a colony
3) Grow a pure culture
4) Purify plasmid via alkaline lysis or column purification
5) Analyze plasmid via restriction map or sequence
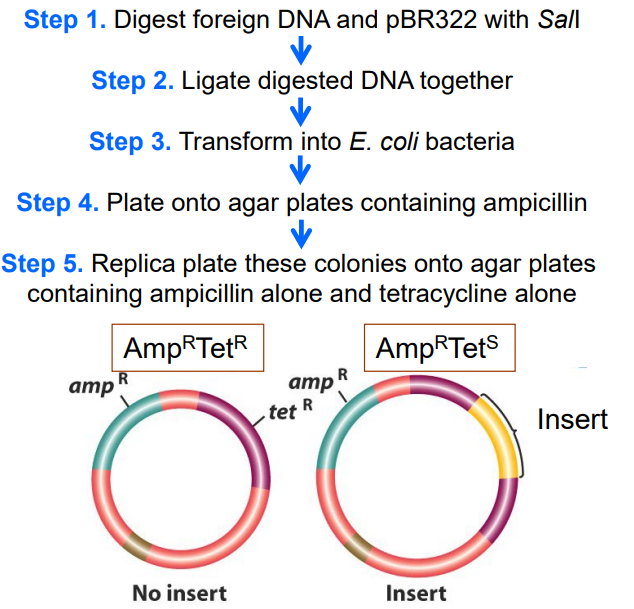
Describe the process of insertional inactivation of a phenotype expressed by the plasmid and how this can identify your gene of interest. (slide 30-31)
1) Digest foreign DNA and pBR322 with Sal1
2) Ligate digested DNA together
3) Transform into E. coli bacteria
4) Plate onto agar plates containing ampicillin
5) Replica plate these colonies onto agar plates containing ampicillin alone and tetracycline alone
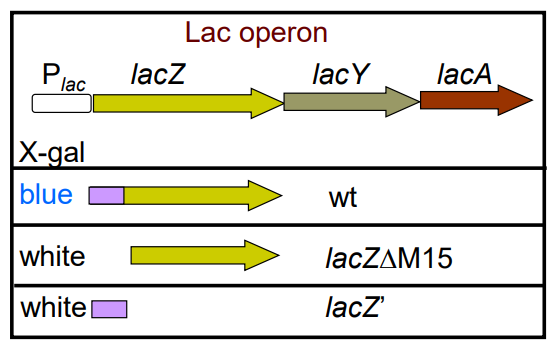
How does blue white screening work? (slide 34-35)
-B-galactosidase LacZ cleaves Lactose -> galactose + glucose and X-gal -> blue precipitate
-Repressor LacI binds to Plac promoter and represses LacZ gene (white colonies)
-LacZ is cleaved → lacZ Delta-M15 and lacZ’ (white colonies)
-If both lacZ Delta-M15 + lacZ’ are expressed, B-galactosidase (LacZ) activity is restored (blue colonies)
-E. coli host JM109 has an F' plasmid that contains lacZ Delta-M15 (no lacZ’) and LacI repressor (white/AmpR)
-pUC vector has lacZ’ and is compatible with JM109 F' plasmid (blue colonies restored when combined)
-If pUC vector has extra DNA fragment in MCS, disrupts complementation of pUC lacZ’ and JM109 F’ plasmid Delta-M15 (white colonies)
Name the compounds and their role in the media used for blue white screening (slide 34-35)
1) X-gal:
-Cleaved by β-galactosidase
-Form a blue precipitate/blue colonies
2) IPTG:
-Triggers the lac operon and expression of the lacZ gene
-lacZ gene is transcribed, β-galactosidase is produced
-Forms blue colonies
4) Ampicillin:
-Antibiotic that selects for AmpR gene
What are the natural and synthetic substrates of B-galactosidase? What are the products of the cleavage reaction of beta-galactosidase? (slide 34)
Lactose (Natural Substrate) → Galactose +Glucose
X-gal (Synthetic Substrate) → Blue precipitate
Beta-galactosidase → lacZ Delta-M15 + lacZ’ (Prime)
What is the role of IPTG in blue white screening? (slide 34)
-LacZ gene expression is induced
-Results in blue colonies
Using LacZ as an example describe alpha-complementation (slide 34)
-Nonfunctional β-galactosidase enzyme = (white colonies)
-lacZ Delta-M15 is found in JM109
-lacZ’ is found in pUC
-Co-expression restores ẞ-galactosidase = blue colonies
-Disrupted by DNA fragments in MCS = (white colonies)
Describe the features of the E. coli JM109 strain that makes it ideal for blue white screening (slide 35)
F´ plasmid includes a functional lacZ Delta-M15 gene
Describe the features of the pUC vectors that make them ideal for blue white screening (slide 36)
MCS encodes for lacZ’ gene
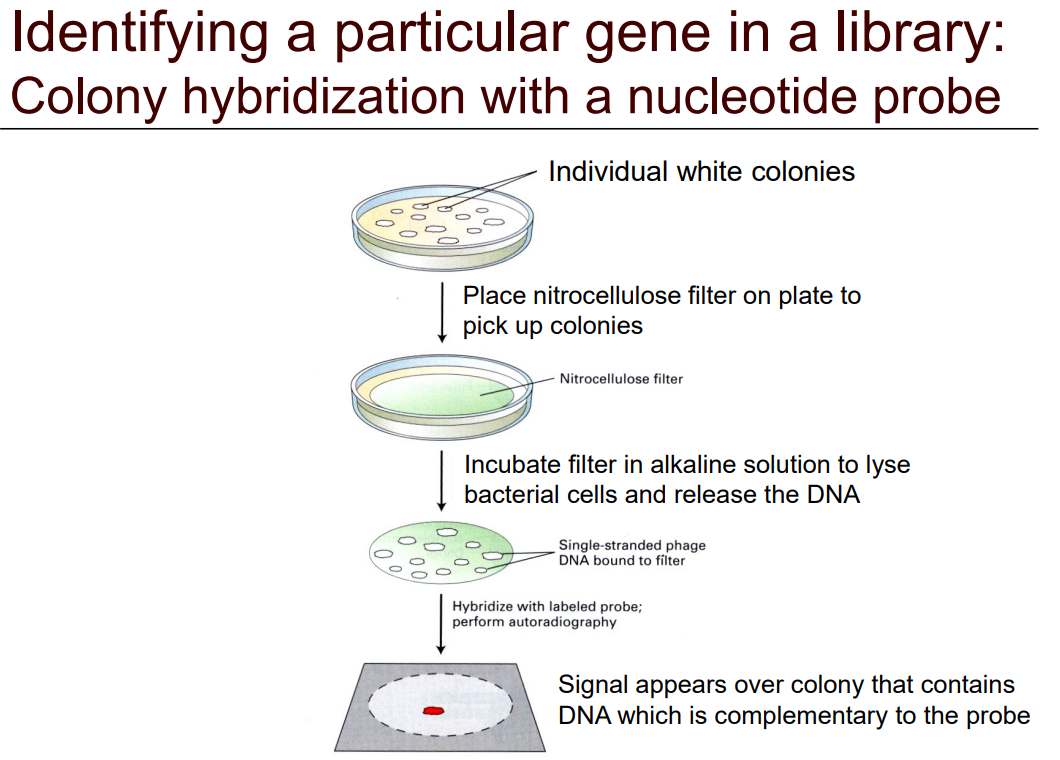
Describe colony immunoblotting with a nucleotide probe (slide 38)
1) Pick individual white colonies
2) Place nitrocellulose filter on plate to pick up colonies
3) Incubate filter in alkaline solution to lyse bacterial cells and release the DNA
4) Hybridize with labelled probe
5) Use autoradiography to screen
6) Signal appears over colony that contains DNA that is complementary to the probe
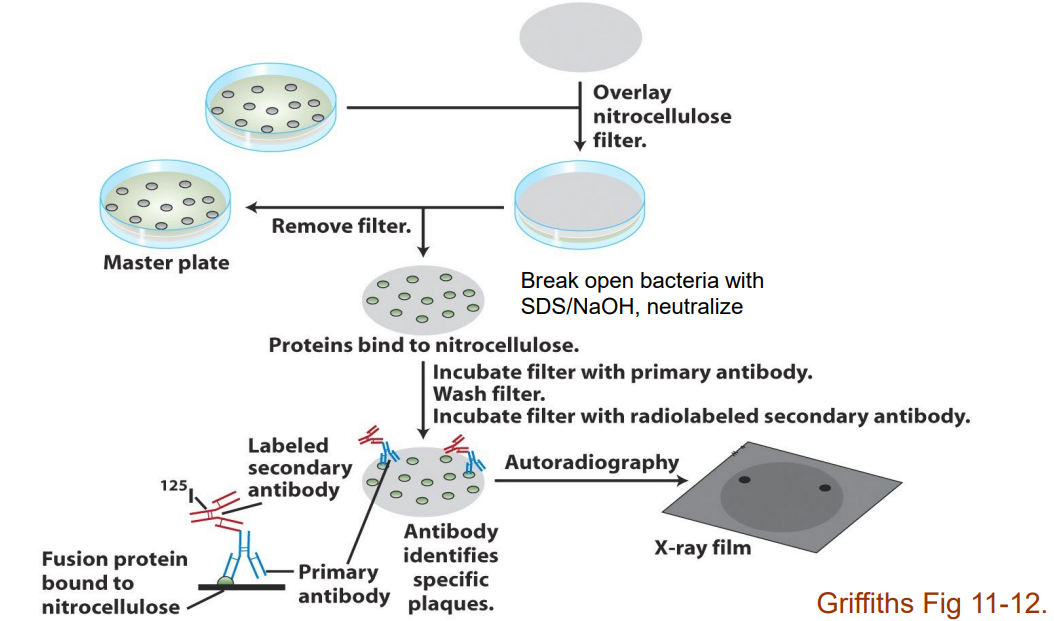
Describe colony immunoblotting with an antibody (slide 39)
1) Overlay nitrocellulose filter
2) Break open bacteria with SDS and NaOH, then neutralize
3) Proteins from Master plate bind to nitrocellulose
4) Incubate filter with primary antibody then wash and incubate with radiolabeled secondary antibody
5) Fusion protein binds → nitrocellulose
Primary antibody/secondary antibody bind → protein
6) Perform autoradiography via X-ray film to confirm protein's presence thanks to attached radiolabelled secondary antibody
Describe the enzymatic activity of restriction endonucleases, bacterial enzymes that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences (aka restriction sites)
Type II:
-Cut at a fixed position within sequence
-Sticky/cohesive ends or blunt ends
-Used in cloning experiments
Type I and III:
-Cut at random sites outside recognition sequence
-Not used in cloning experiments
Calculate the frequency of cutting exhibited by restriction enzymes that recognize 4bp, 6bp, 8bp
4bp: (1/4)^4 = 1/256. 1 every 256 bp
6bp: (1/4)^6 = 1/4096. 1 every 4096 bp
8bp: (1/4)^8 = 1/65536. 1 every 65,536 bp
Explain DNA electrophoresis
-DNA molecules are separated according to length
-At pH = 8, DNA is negatively charged
-Electric current makes DNA migrate -> positive electrode
-Concentration determines porosity
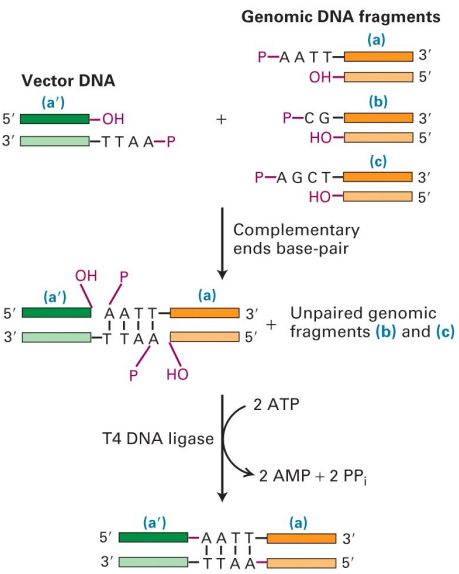
Explain how DNA ligase or alkaline phosphatase or T4 DNA polymerase works (add diagram)
-Forms phosphodiester bond between 5' phosphate and 3' OH
-T4 DNA ligase uses ATP to connect blunt/sticky ends
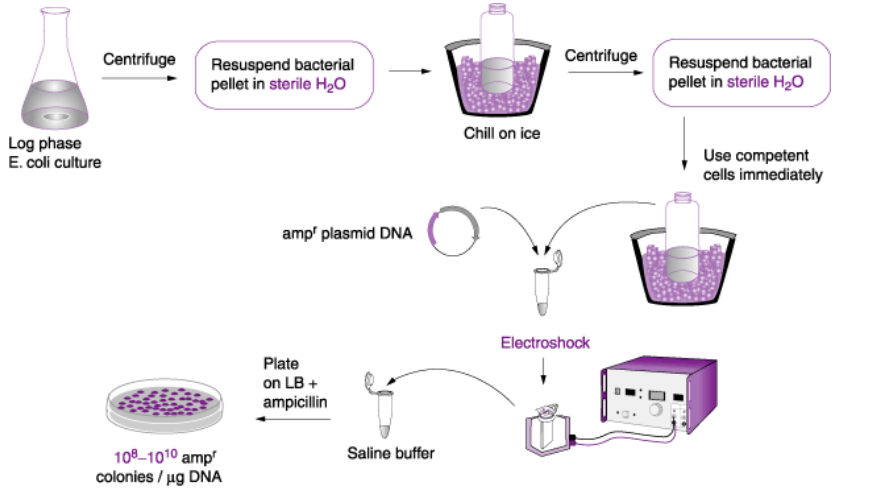
Describe the methods of bacterial transformation
1) Chemical Method: Cloning small fragments
-Centrifuge, resuspend in CaCl2 solution
-Chill on ice, aliquot competent cells
-Heat shock, then plate on LB Agar + Ampicillin
-10E6 to 10E8 AmpR colonies/ug DNA
2) Electroporation: Cloning big fragments
-Centrifuge, resuspend in sterile water
-Chill on ice, centrifuge and electroshock
-Place in saline buffer
-Plate on LB Agar + Ampicillin
-10E8 to 10E10 AmpR colonies/ug DNA
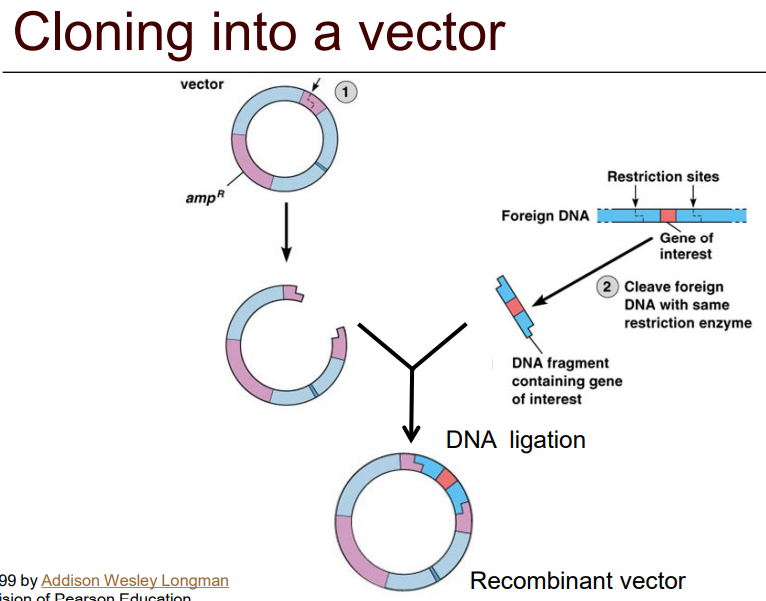
Describe, using a diagram, the steps taken to clone gene.
1) Isolation
2) Selecting/cutting vector w/restriction enzyme
3) Ligation
4) Transformation (adding recombinant DNA to host)
5) Selection and screening of AmpR vector plasmids
6) Amplification and expression to confirm gene