Fractional Distillation.
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Crude oil is heated and vaporised. The vapour enters a fractionating column which is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top. Fractions condense at different heights based on boiling points.Smaller molecules with lower boiling points rise to the topand condense there. Larger molecules with higher boiling points condense near the bottom. Gases come out at the top, bitumen is collected at the bottom.
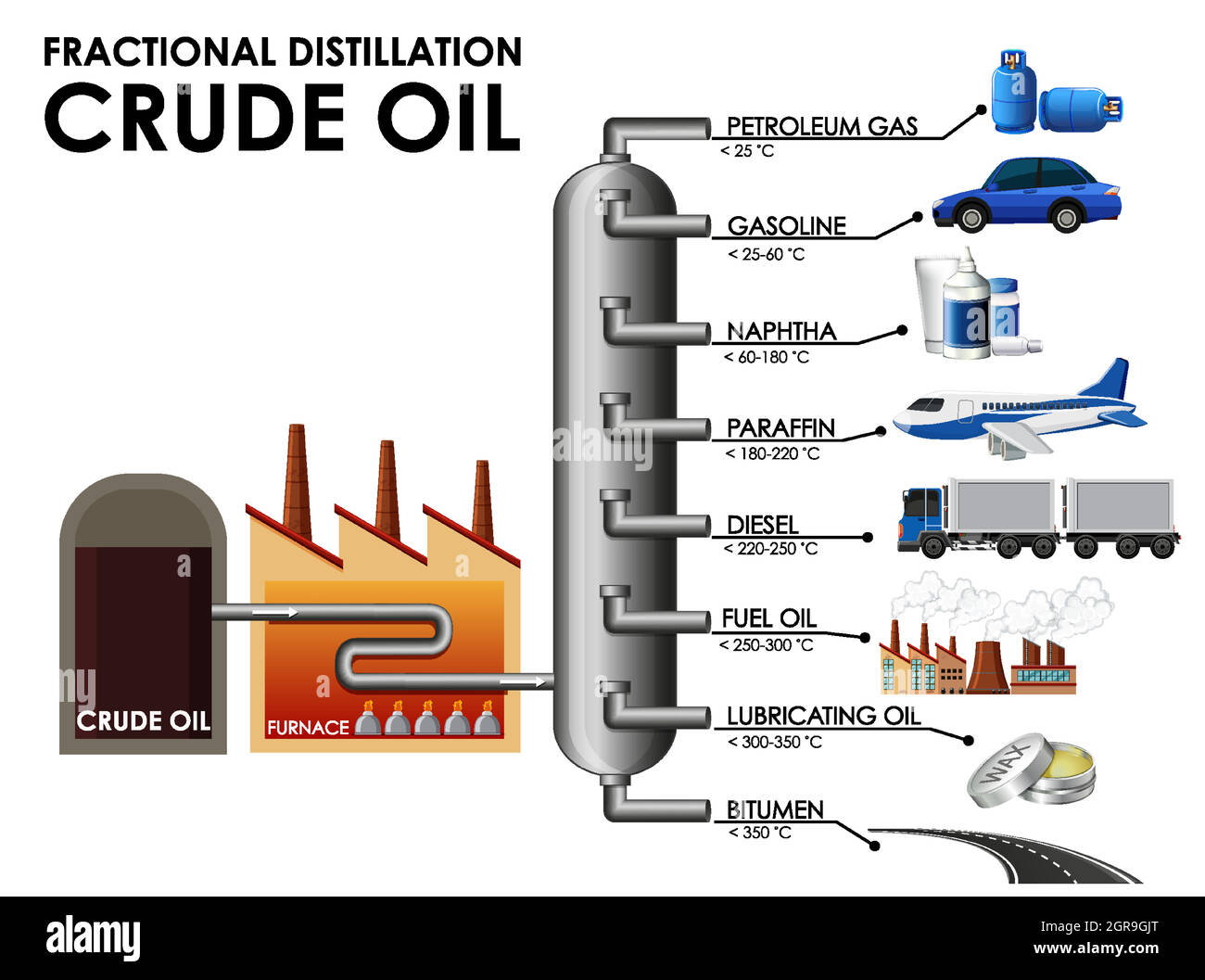
Used as bottled gas for heating and cooking; has the **lowest boiling point**, exits at the **top** of the column. Temperature: 30C
Used as **fuel for cars**; low boiling point, collected **near the top** of the column. Temperature: 100C
Used as **jet fuel**; collected in the **middle** of the column. Temperature: 250C
Used as **fuel for buses, trucks, and some cars**; collected **below kerosene**. Temperature: 350C
Used in **ship engines and power stations**; has a **high boiling point**, collected near the **bottom**. Temperature: 550C
Used for road surfacing and roofing; has the highest boiling point and largest molecules; collected at the very bottom. Temperature: 600C