SLR07 - Types of Programming Languages
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Programming Paradigm
Describes a way of doing things
Expect languages to include facilities
Turing complete
Languages that can solve all the problems a computer can solve
Why are different programming paradigms needed?
Some problems are better suited to being solved using a certain paradigm
Machine code
Least abstract
Closest to what actually happens on computer
Programs directly to OS
Translated into matching electrical signals
Assembly language
Uses mnemonics, each having specific sequence 1s & 0s
One-to-one relationship with machine code
Translated by assembler
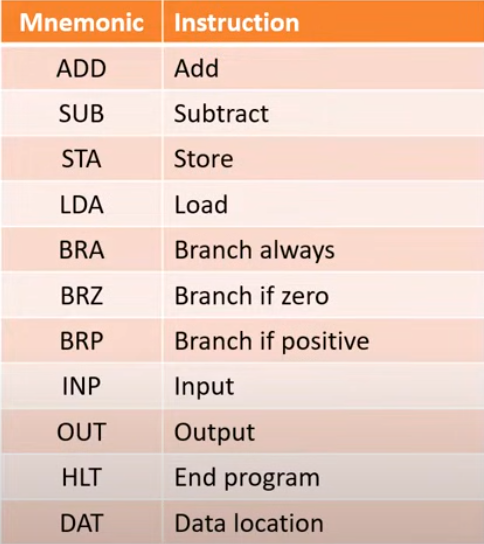
Eg: LMC
High level language
One-to-many relationship for code to machine code
More complex
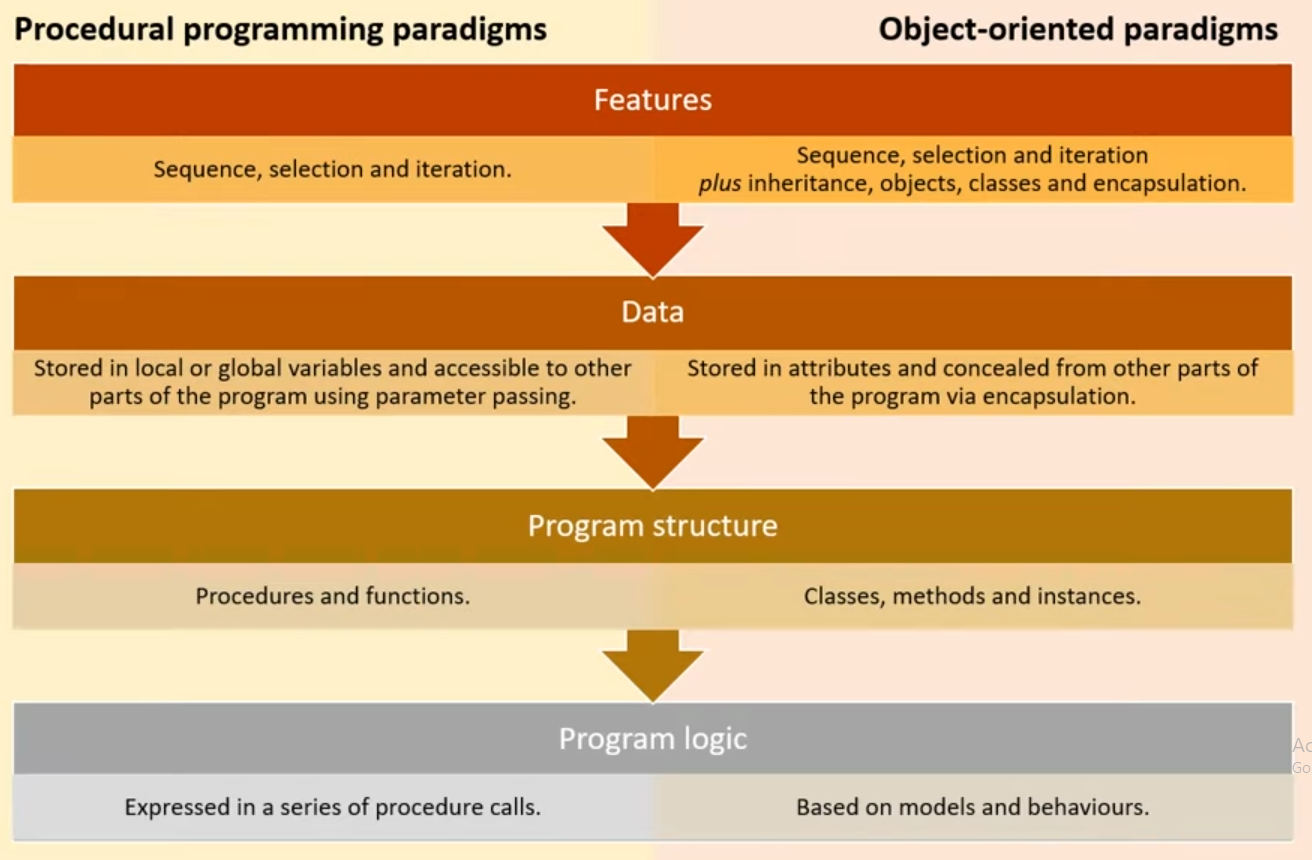
Imperative Language
Uses sequence, selection, iteration statements that change a program’s state
Focus on describing how a program operate
Contains Procedural and Object Orientated Programming
Procedural programming
Program is built from one or more subroutines
Statements in procedural programming
Sequence
Selection
Iteration
Object orientated programming
Focuses on a modular approach to programming
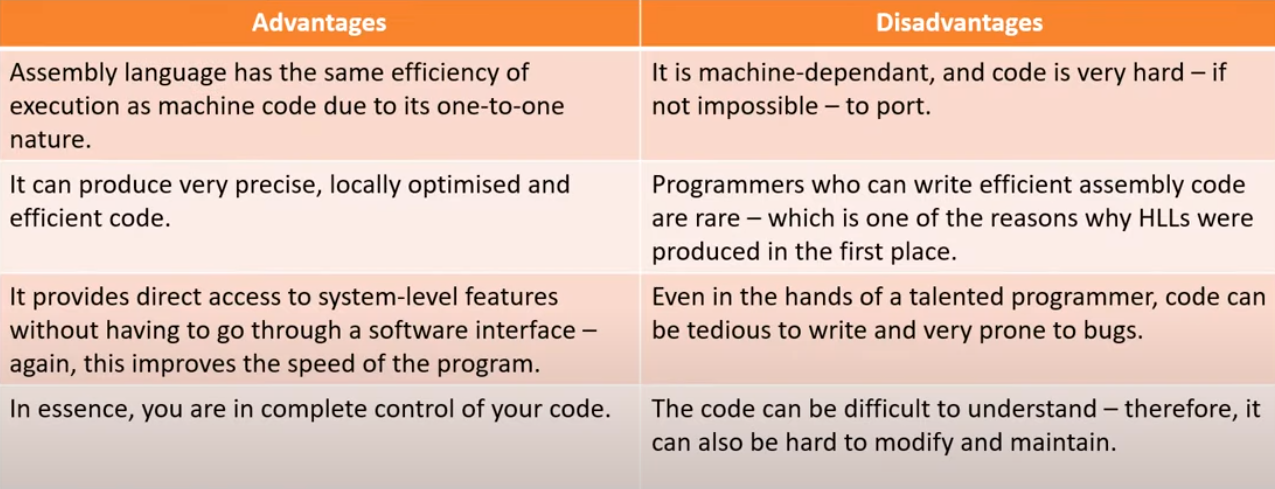
Advantages & Disadvantages of machine code & assembly language
Feature comparison of procedural & object orientated
LMC mnemonics
Opcode & Operand
Opcode: Instruction
Operand: Data instruction is carried out on
Immediate addressing
Value in address part of instruction is actually the value to be used, memory is not searched
ADD 10 means “add 10” not add value held in memory position 10
Direct addressing
Value in address part of instruction is a reference to the address in memory where required value is located
ADD 10 means “find whatever is in memory location 10 and add it to accumulator”
Indirect addressing
Value in addressing part references a memory location that contains the address in memory where required value is located
ADD 10 = “Find memory address 10, there you will find another address, go to this address and add what is found there to accumulator”
Useful as for larger address range as operand has only 4 bits available
Indexed addressing
Eg. contents of an array of 100 items long has to be added together
Need to use Index Register
IR set to 0, so first value taken from 10 + 0
IR incremented and same instruction = uses address 10 + 1
This is why array needs to be stored in contiguous memory locations
“ADD 10” = find memory address 10 plus value of IR