Glomerular Filtration and Clearance Part 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
A nephron consists of …?
a glomerulus and a tubule
t/f: The nephron forms an ultrafiltrate of the blood plasma and then selectively reabsorbs the tubule fluid or secretes solutes into it
true
Kidneys regulate the ________ of the plasma and extracellular fluid
composition and volume
Kidneys control the level of solutes in the body by carefully regulating the amount of their __________ followed by …?
filtration rate
reabsorption and secretion
renal function ensures that excretion and uptake of solutes and water from the diet are _______
balanced
how do the kidneys accomplish its homeostatic role?
Filters blood to generate fluid (in renal tubule) free of cells and most proteins
Reabsorbs certain solutes (i.e., Na+, Cl-, glucose, etc.) and water from tubular fluid
Secretes other solutes (i.e., uric acid) into tubular fluid
Excretes in the urine the water and solutes that remain in the tubular fluid after passing through the renal tubule
what is the site of formation of the glomerular filtrate?
renal corpuscle
the renal corpuscle comprises of…?
glomerulus, Bowman’s space, and Bowman’s capsule
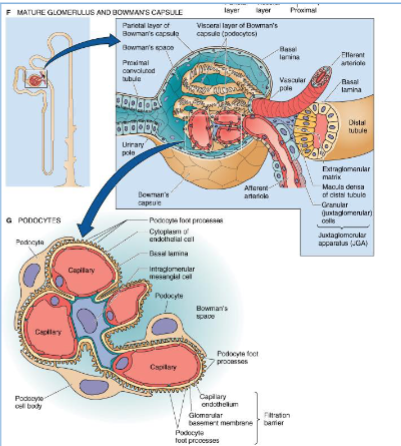
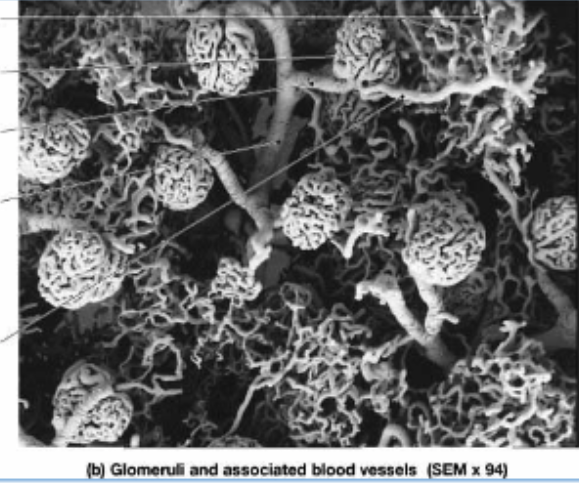
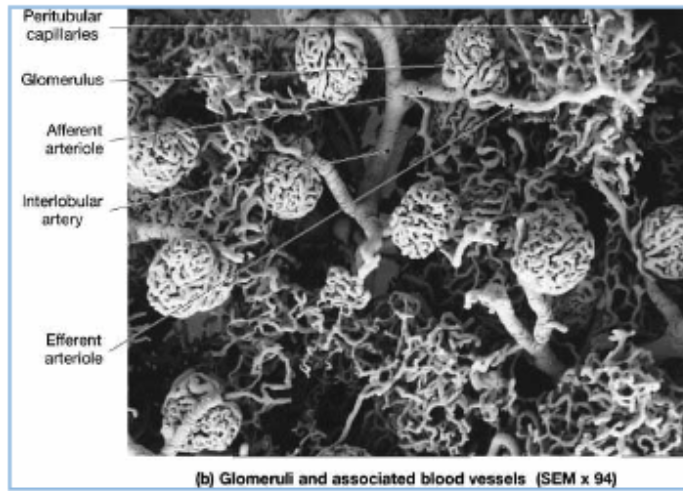
The glomerular filtration barrier between the glomerular capillary lumen and Bowman’s space comprises four elements with different functional properties:
glycocalyx covering the luminal surface of endothelial cells,
endothelial cells,
glomerular basement membrane,
epithelial podocytes
what is clearance of a solute?
the virtual volume of plasma that would be totally cleared of a solute in a given time
All solutes excreted into the urine ultimately come from the…?
blood plasma
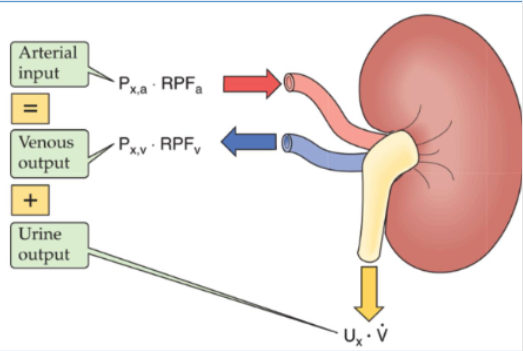
the rate at which the kidney excretes a solute into the urine equals …?
the rate at which the solute disappears from the plasma
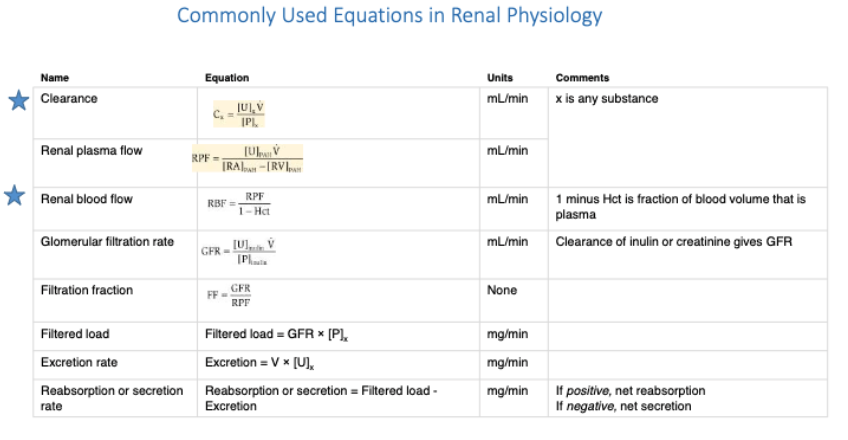
what is the formula for calculating renal clearnace?
arterial input = venous output + urine output
what are the 3 basic functions of the kidney?
glomerular filtration,
tubule reabsorption,
tubule secretion—determine the renal clearance of a solute
what is the clearance equation that describes the volume of plasma that would be totally cleared of a solute in a given time? (important one)

If the kidneys completely clear X from plasma during a single passage, the renal clearance of X equals
Renal Plasma Flow (RPF)
the clearance of what substance is a good estimate of renal plasma flow (RPF) because it is just that solute?
p-aminohippurate (PAH)
what is the volume of fluid filtered into Bowman’s capsule per unit time?
glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
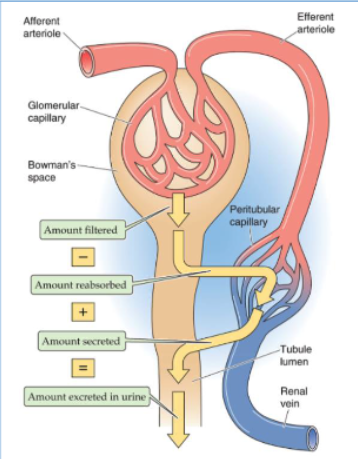
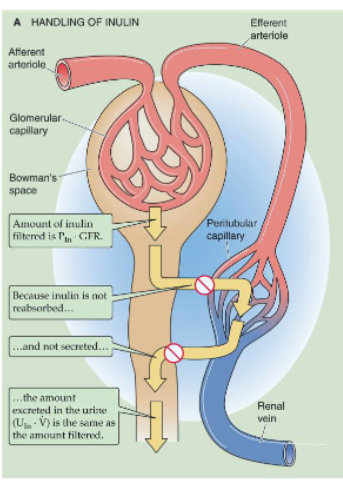
The amount of X that appears in the urine per unit time (UX · V̇) is the same as
the amount of X that the glomerulus filters per unit time (PX · GFR) when there is no reabsorption or secretion.
what is the formula for glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
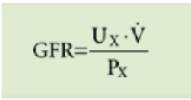

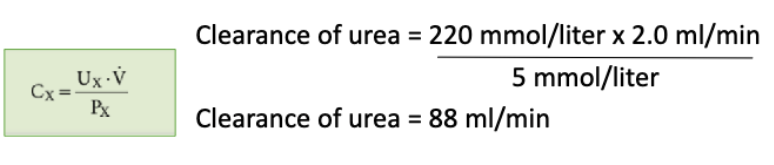
A low/high GFR is essential for maintaining stable and optimal extracellular levels of solutes and water
high
Under normal conditions, what is the GFR of the two kidneys?
125 mL/min or 180 L/day
Under normal conditions, the GFR of the two kidneys is 125 mL/min or 180 L/day.
Such a large rate of filtrate formation is required to ..?
expose the entire extracellular fluid frequently (>10 times/day) to the scrutiny of the renal tubule epithelium
If it were not for such a high turnover of the extracellular fluid, only small volumes of blood would be “cleared” per unit time of certain solutes and water
Low levels of GFR would cause:
delayed excretion of material
(in the presence of a sudden increase in the plasma level of a toxic material—originating either from metabolism or from food or fluid intake)
The clearance of Inulin, or Creatinine is a measure of
GFR
t/f: Although the inulin clearance is the most reliable method for measuring GFR, it is not practical for clinical use
true *(needs to be administered IV)
Although the inulin clearance is the most reliable method for measuring GFR, it is not practical for clinical use. What should be used instead to calculate GFR?
creatinine (endogenous substance)
what is the source of plasma creatinine?
normal metabolism of creatine phosphate in muscle
why is insulin or creatinine a good measure of GFR?
insulin is not reabsorbed or secreted so the amount excreted in the urine is the same as the amount filtered into the Bowman’s space
when pts lose kidney function, what happens to creatinine levels?
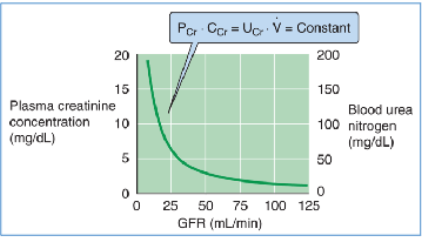
creatinine levels keep increasing in blood circulation (kidneys can’t filter it causing inverse correlation)
Creatinine as a marker of renal function is often unreliable in what pt populations?
those with decreased muscle bulk such as the elderly, amputees and in individuals affected by muscular dystrophy.
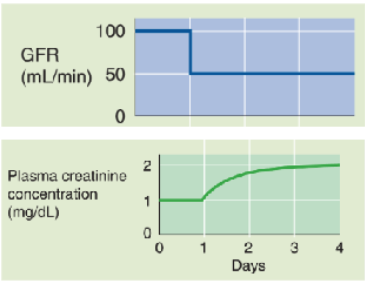
In a healthy person whose GFR is 100 mL/min, plasma creatinine is ∼1 mg/dL.
If GFR suddenly drops to 50 mL/min, the kidneys will initially filter and excrete less creatinine, although the production rate is unchanged.
As a result, the plasma creatinine level will rise to a new steady state, which is reached at a PCr of 2 mg/dL
The sieving coefficient (filterability) for of a solute, depends on
molecular weight and effective molecular radius
Substances of low molecular weight (<5500 Da) and small effective molecular radius (e.g., water, urea, glucose, and inulin) appear in the filtrate in the same concentration as in plasma
Larger macromolecules are restricted from passage, so that only traces of plasma albumin are normally present in the glomerular filtrate.
In cases of glomerulonephritis, what happens to the glomerular barrier and how does this affect permeability?
glomerular barrier loses its negative charge
permeability of barrier to negatively charged macromolecules is enhanced
Proteins leak into ultrafiltrate, may appear in the urine
what factors influence permselectivity of the glomerular barrier?
electrical charge and shape
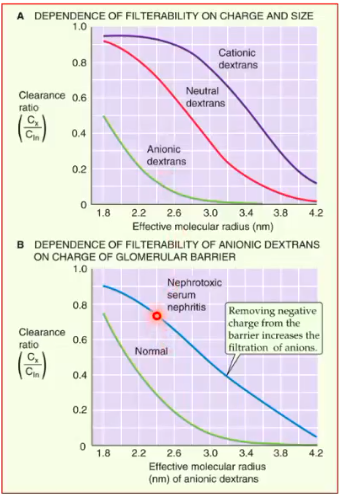
how does electrical charge affect permselectivity of glomerular barrier?
Neutral dextrans with an effective molecular radius < 2 nm pass readily across the glomerular barrier.
anionic (-) dextrans are restricted from filtration,
cationic (+) dextrans pass more readily into the filtrate
how does shape affect permselectivity of glomerular barrier?
Rigid or globular molecules have low clearance ratios
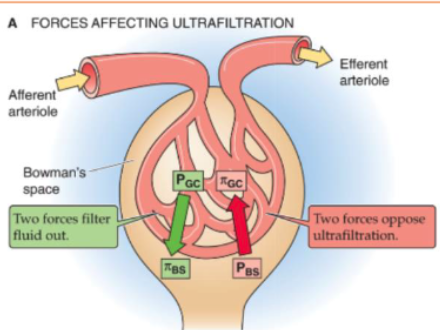
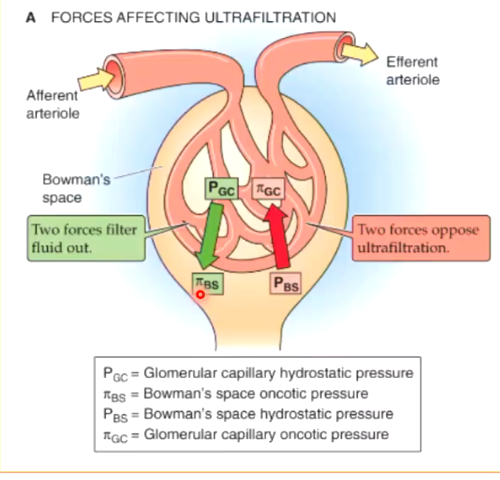
what forces affect ultrafiltration?
2 hydrostatic pressure forces
2 oncotic pressure forces
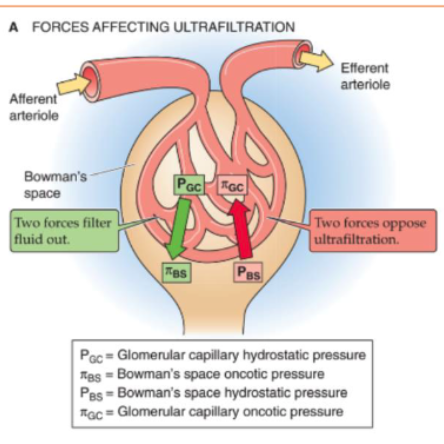
which forces FAVOR glomerular ultrafiltration?
hydrostatic pressure in capillary
oncotic pressure in Bowman’s Space
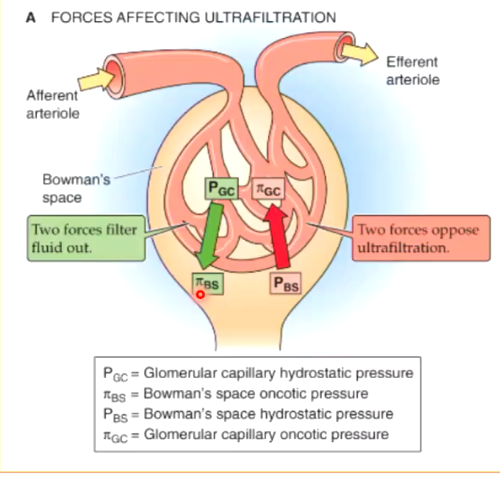
which forces OPPOSE glomerular ultrafiltration?
hydrostatic pressure in BOWMAN’S SPACE
oncotic pressure in capillary
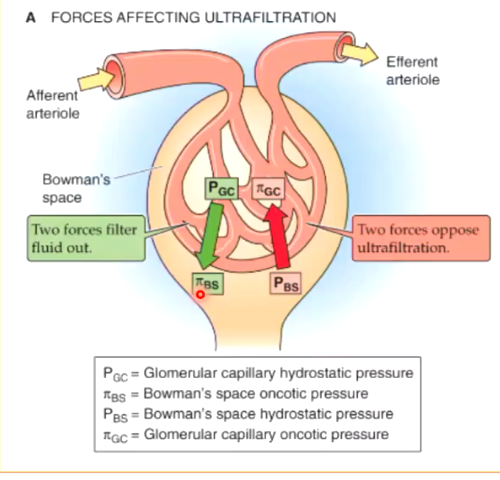
oncotic pressure in the Bowman’s space should normally always be ZERO. why?
oncotic presure comes from proteins. if no proteins were filtered into bowman’s space, there should be no oncotic pressure.
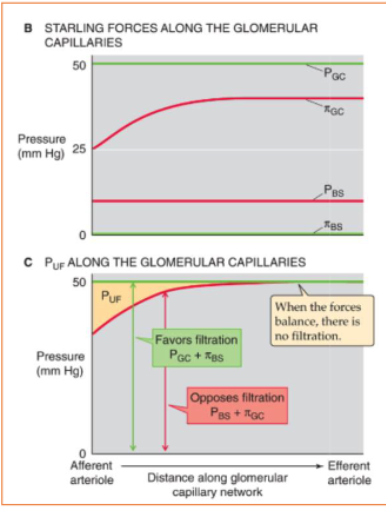


what is the formula for calculating net filtration pressure?
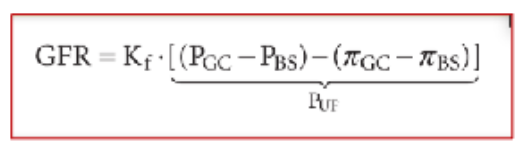
net filtration pressure = (difference in hydrostatic pressures) - (difference in oncotic pressures)
what is the formula for calculating renal blood flow?
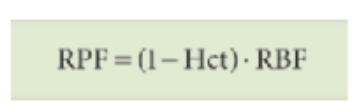
Renal blood flow (RBF) is ∼_ L/min out of the total cardiac output of _ L/min
1 L/min
5 L/min
Renal blood flow (RBF) is ∼1 L/min out of the total cardiac output of 5 L/min.
Given a hematocrit (Hct) of 0.40, the “normal” RPF would be…?
∼600 mL/min
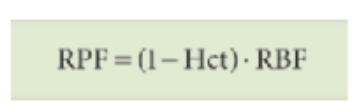
RPF = (1-0.4) x 1000 mL/min
RPF = 0.6 x 1000 mL/min
RPF = 600 mL/min
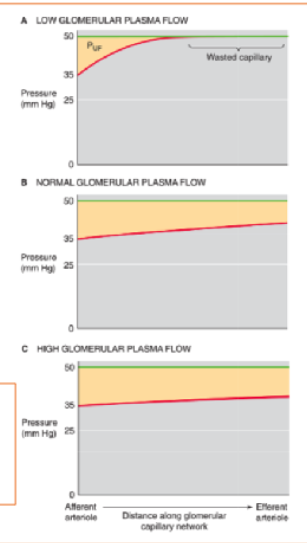
Increased glomerular plasma flow leads to an increase in glomerular filtration rate.
Thus, the end of the capillary that is “wasted” at low plasma flow rates really serves what function?
“in reserve” to contribute at higher rates..
Single nephron GFR increases with glomerular plasma flow. However, this increase is not linear. instead, what is the relationship?
the GFR summed for both kidneys increases only moderately with increasing RPF, but it decreases greatly with decreasing RPF (Fig. D)
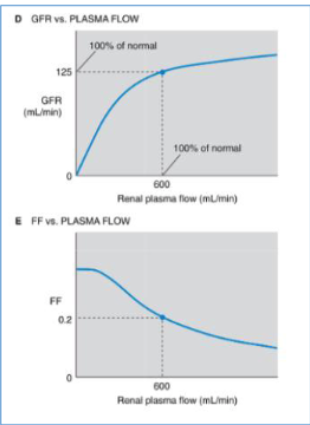
what is the volume of filtrate that forms from a given volume of plasma entering the glomeruli?
filtration fraction (FF)
(also defined by relationship between GFR and RPF)
what is the formula for filtration fraction?