molecular bio exam 4 Ch. 18
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what are the 4 phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
M phase
G1 phase
S phase
G2 phase
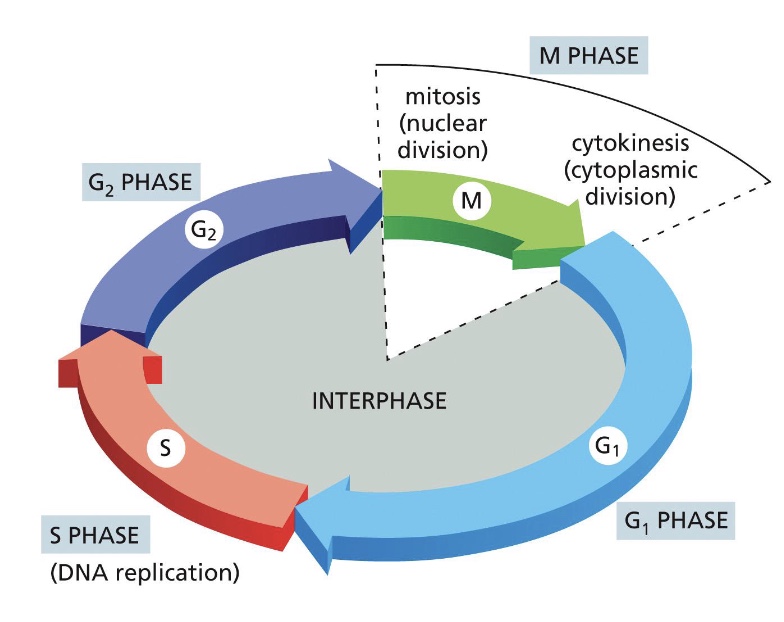
what is the cell cycle control system?
Network of regulatory proteins that govern the orderly progression of a eukaryotic cell through the stages of cell division
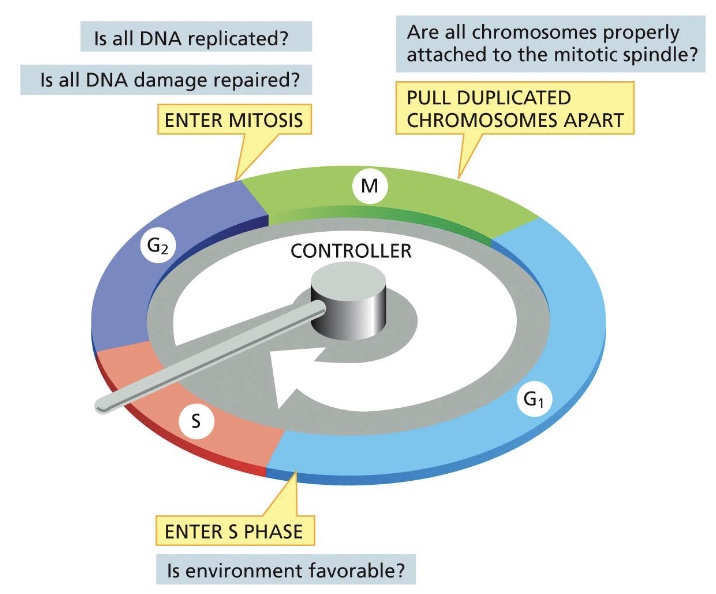
what does the cell cycle depend on?
Cyclically Activated Protein Kinases. Called Cdks
what do cdks do in the cell cycle system?
A Cdk must bind a regulatory protein called a cyclin before it can become enzymatically active. This activation also requires an activating phosphorylation of the Cdk
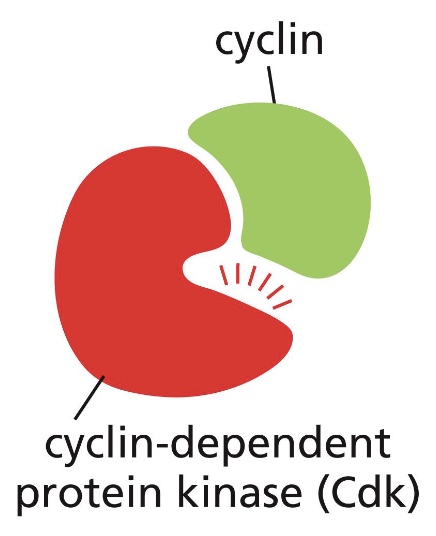
what happens once a cdk is activated?
a cyclin–Cdk complex phosphorylates key proteins in the cell that are required to initiate particular steps in the cell cycle. The cyclin also helps direct the Cdk to the target proteins
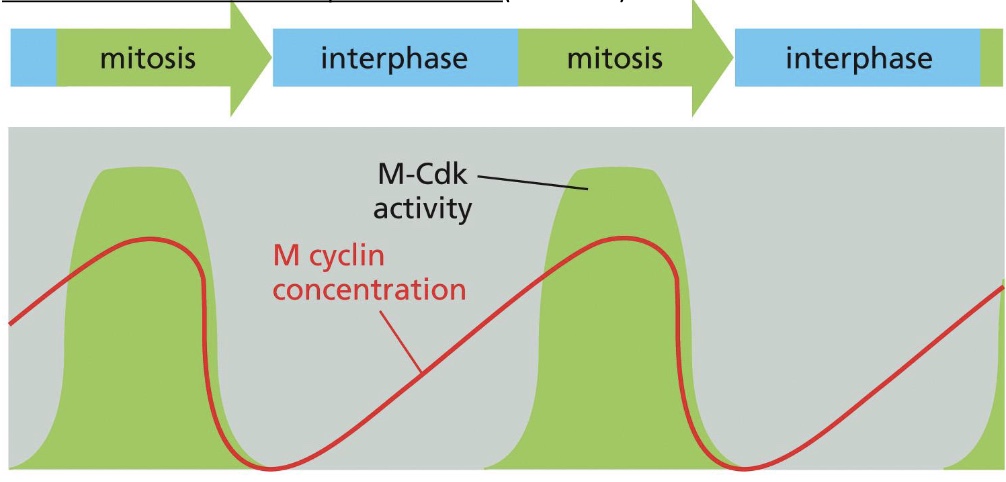
how does the accumulation of cyclins help regulate the activity of Cdks?
Increasing concentration of the relevant cyclin (called M cyclin) helps direct the formation of the active cyclin–Cdk complex (M-Cdk) that drives entry into M phase. Although the enzymatic activity of each type of cyclin–Cdk complex rises and falls during the course of the cell cycle, the concentration of the Cdk component does not
what happens during interphase (G1, S, G2)?
G1: “first gap”, cell growth
S: “synthesis”, cell growth and DNA duplication
G2: “second gap”, cell growth
what happens during the mitotic phase?
cytokinesis
mitosis
prophase
prometaphase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase (overlaps with cytokinesis)
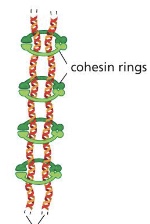
what are cohesins?
protein complex that holds sister chromatids together after DNA has been replicated in the cell cycle
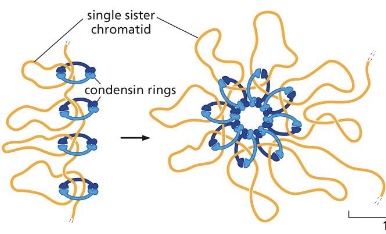
what are condensins?
protein complex that helps configure duplicated chromosomes for segregation by making them more compact. Condensins assemble along each individual sister chromatid, helping each of these double helices to coil up into a more compact form
what are sister chromatids?
copy of a chromosome, produced by DNA replication, that remains bound to the other copy
what are centromeres?
Regions of specialized chromatin
what are kinetochores?
Assemble at centromeres. Link centromeres to mitotic spindle. They are composed by many different types of proteins
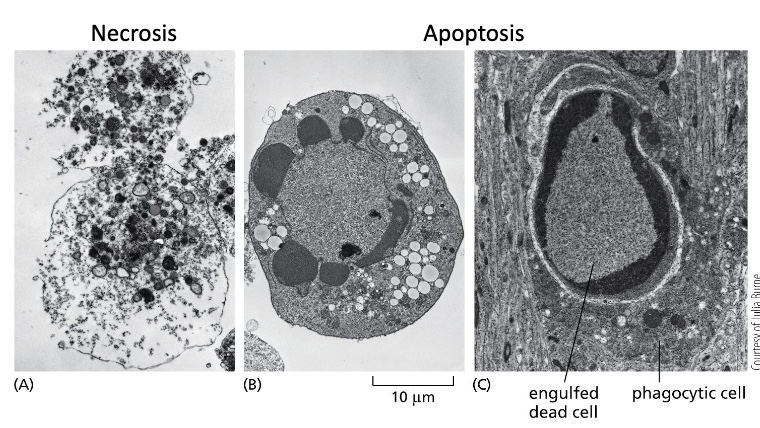
what happens during apoptosis?
Cytoskeleton collapses
Nuclear envelope disassembles
Nuclear DNA breaks up into fragments
Plasma membrane alters to attract phagocytic cells (macrophages) to engulf and remove the apoptotic cell before it leaks out and recycle the organic components
of the apoptotic cell
what are caspases?
one of a family of proteases that, when activated, mediates the destruction of the cell by apoptosis
what are procaspases?
the inactive precursors of caspases
what are executioner substrates?
example lamin proteins, breaking the nuclear lamina and allowing nucleases to enter and break down the DNA (Initiator caspases cleave executioner caspases)