Biology Final (E3) Practice
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
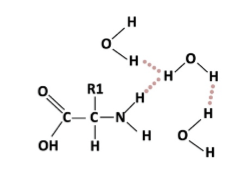
How many correct hydrogen bonds are indicated in this picture?
a. Two
b. Three
c. Nine
d. Sixteen
e. Zero
e. Zero
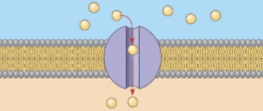
Which statement is true about the aquaporin protein, shown on the right?
a. It is categorized as a peripheral membrane protein.
b. Aquaporins only allow the flow of CO2 and O2 in and out of the cell.
c. Aquaporins are made up of amino acids with a mixture of polar AND nonpolar functional groups.
d. Aquaporins are highly charged, especially in its interior portion that interacts with fatty acids
e. None of the above is correct.
c. Aquaporins are made up of amino acids
with a mixture of polar AND nonpolar functional groups.
A solution with a pH=2 indicates which of the following?
a. The solution has a very high concentration of oxygen ions
b. The solution has a very low concentration of protons
c. The solution has a very high concentration of hydroxide ions
d. The solution has a very low concentration of hydrogen ions
e. The solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ions
e. The solution has a very high concentration of hydrogen ions
Which of the below reactions could lead to the formation of a nonpolar covalent bond?
a. adding one oxygen atom to another oxygen atom
b. adding one sodium atom to a chlorine atom
c. adding two water molecules together
d. adding one oxygen atom to two hydrogen atoms
e. Any of the above reactions could lead to the formation of a nonpolar covalent bond.
a. adding one oxygen atom to another oxygen atom
Which molecules have hydrophobic portions that could be partially or fully inserted into interior of the phospholipid bilayer?
a. peripheral proteins
b. starch
c. cholesterol
d. cellulose
e. trisaccharide
c. cholesterol
Carbon can form ________.
a. hydrocarbons by bonding covalently to oxygen
b. polar bonds to other carbon atoms
c. polar bonds to hydrogen atoms
d. bonds with up to four different atoms
e. None of the above is true.
d. bonds with up to four different atoms
Protons _____.
a. often vary in numbers within an atom, causing different isotopes
b. exist in different shells (orbitals) that vary in their distance from the atomic nucleus
c. have extremely little mass, compared to neutrons and electrons
d. can absorb or lose energy when they shift from one orbital to another
e. are positively charged
e. are positively charged
In DNA, how are nucleotide bases on the same strand held together?
a. The nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds
b. The nucleotides are held together by ionic bonds
c. The nucleotides are held together by hydrophobic interactions
d. The nucleotides are held together by covalent bonds
e. None of the above is true.
d. The nucleotides are held together by covalent bonds
Which of the following processes is consistent with anabolism?
a. Three fatty acid chains become covalently bonded to glycerol.
b. DNA is broken down into nucleotides.
c. Starch is digested into monosaccharides.
d. Salt is dissolved in water.
e. Hydrolysis reactions occur.
a. Three fatty acid chains become covalently bonded to glycerol.
The nucleus _____________.
a. has a membrane similar to the cell membrane (a single lipid bilayer)
b. contain membrane-bound organelles with specialized functions
c. is the site of ribosome production
d. contains circular chromosomes, that encode genetic information
e. All of the above are correct.
c. is the site of ribosome production
What are the functions of lysosomes?
a. They carry out synthesis of lipids and metabolism of carbohydrates
b. They carry out production of proteins that will be secreted from the cell
c. They modify proteins and package them into vesicles
d. They merge with damaged organelles and digest them
e. All of the above are true
d. They merge with damaged organelles and digest them
Proteins can have four different levels of structure, including primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary levels. What kinds of bonds are responsible for driving primary structure of proteins?
a. hydrogen bonds
b. ionic bonds
c. phosphodiester bonds
d. peptide bonds
e. a mixture of bonds, including sulfhydryl bridges, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic interactions
d. peptide bonds
Some atoms carry no electric charge because ________.
a. they do not have any protons
b. they do not have any electrons
c. they have uncharged neutrons in their nuclei
d. they have equal numbers of protons and electrons
e. they have an equal number of protons and neutrons
d. they have equal numbers of protons and electrons
Where would you typically find DNA in a eukaryote?
a. The nucleus
b. The mitochondria
c. The chloroplast
d. All of the above are correct.
e. None of the above is correct.
d. All of the above are correct.
Which statements are true about the mitochondrion and chloroplast?
a. Both have their own genetic material in its own nucleus (DNA)
b. Plants only have chloroplasts, and animals only have mitochondria
c. Both have their own ribosomes
d. Both have their own linear chromosomes
e. All of the above are correct.
c. Both have their own ribosomes
Which of the following statements is true about cell membranes?
a. Phospholipids in membranes are bound to each other by networks of covalent bonds.
b. Phospholipids cannot move laterally within each layer of the cell membrane.
c. The presence of saturated fats tends to make membranes more fluid.
d. Phospholipid bilayers get destabilized by extreme heat.
e. Phospholipids frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other.
d. Phospholipid bilayers get destabilized by extreme heat.
Classical cell theory, developed in the 1800s, includes which of the following ideas?
a. Atoms, such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, are required for life.
b. All living things are made of cells.
c. Water is required for cellular life.
d. All cells are negatively charged, because of overabundance of electrons.
e. All cells are made up of water, proteins, and fats.
b. All living things are made of cells.
Which of the below statements is true about water?
a. Water has a low specific heat.
b. Ionic bonds form between different water molecules.
c. Covalent bonds form between different water molecules.
d. Hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atoms of different water molecules.
e. Water has one atom that is highly electronegative.
e. Water has one atom that is highly electronegative.
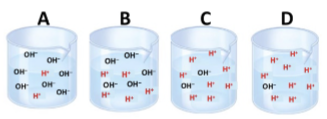
Which of the below statements is correct about the four water solutions pictured at the right?
a. Solution A has the lowest pH
b. Solution B has the lowest pH
c. Solution D is the most BASIC
d. Solution A has a pH of 2
e. Solution D is the most ACIDIC
e. Solution D is the most ACIDIC
Adding one hydrogen atom to another hydrogen atom causes:
a. a strong hydrogen bond in which electrons move to a new orbital
b. a strong ionic bond in which an electron shifts from one atom to another
c. a double covalent bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between atoms
d. a single covalent bond in which a pair of electrons is shared between atoms
e. none of the above, since hydrogen is an inert gas (it is not reactive)
d. a single covalent bond in which a pair of electrons is shared between atoms
A solution has a pH of 2. What is the concentration in terms of hydroxide ions in this solution?
a. [OH-]= 10-12 M
b. [H+] = 10-12 M
c. [OH-]= 10-2 M
d. [OH-] = 1010 M
e. [OH-] = 102 M
a. [OH-]= 10-12 M
Enzymes are polymers of ______________that assist with catalyzing reactions in the cell.
a. monosaccharides
b. steroids
c. fatty acids
d. amino acids
e. None of the above is correct.
d. amino acids
A nitrogenous base ___________.
a. is the variable portion of the DNA molecule
b. is attached to the phosphate in DNA
c. is attached to the amine group to build proteins
d. cannot form hydrogen bonds
e. is needed to build fatty acids
a. is the variable portion of the DNA molecule
Plant cells, animal cells, and bacterial cells all have _____________.
a. nuclear pores -- which are critical for movement of mRNAs
b. membrane-bound organelles with specialized functions
c. linear chromosomes, that vary in number
d. mitochondria, to power the reactions of the cell
e. None of the above is true.
e. None of the above is true.
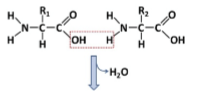
The reaction on the right ________.
a. shows a covalent bond being formed by hydrolysis
b. shows an ionic bond being formed by hydrolysis
c. shows the formation of a disaccharide
d. shows a dehydration reaction
e. None of the above is correct.
d. shows a dehydration reaction
Saturated hydrocarbon molecules are _________.
a. hydrophilic
b. common storage molecules in the cell
c. lacking in double bonds between carbons
d. made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
e. made up of polar covalent bonds
c. lacking in double bonds between carbons
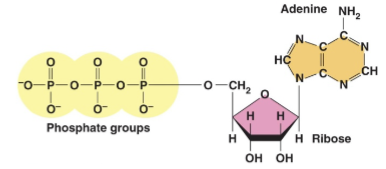
The molecule at the right ____________.
a. is polar
b. contains a monosaccharide
c. contains hydroxyl groups
d. contains at least one amine group
e. all of the above are true
e. all of the above are true
Which molecules or functional groups are nonpolar?
a. carbonyl groups
b. carbohydrates
c. hydrocarbons
d. sulfhydryl groups
e. amino groups
c. hydrocarbons
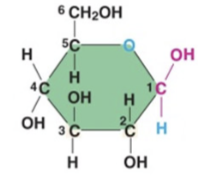
The molecule at the right is a monomer of a__________.
a. protein
b. nucleic acid
c. hydrocarbon
d. polysaccharide
e. steroid
d. polysaccharide
Which of the following is correct about the structure of DNA.
a. Ionic bonds are important to building the molecule into the correct shape.
b. Dehydration reactions, resulting in the loss of a water molecule, are needed to build the DNA monomers.
c. Hydrogen bonds are required between the phosphate and sugars.
d. Covalent bonds occur between the nitrogenous bases of different DNA strands.
e. None of the above is correct.
b. Dehydration reactions, resulting in the loss of a water molecule, are needed to build the DNA monomers.
The following reaction C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ___________.
a. Involves the breakdown of a fatty acid chain
b. Involves the breakdown of a triglyceride
c. has a positive DG (Gibbs Free Energy)
d. is not a spontaneous reaction
e. is exergonic
e. is exergonic
electron shells _____.
a. can carry charged or uncharged particles
b. vary in the numbers of neutrons that they carry
c. vary in their distance from the atomic nucleus
d. can only carry one proton at a time
e. can carry different numbers of neutrons
c. vary in their distance from the atomic nucleus
For every carbon atom in a carbohydrate there is __________?
a. one oxygen atom
b. one hydrogen atom
c. one carbonyl group
d. one hydroxyl group
e. one amine group
a. one oxygen atom
Phosphate and carboxyl ________.
a. are functional groups that repel water
b. are nonpolar
c. are hydrophobic groups
d. are important to carbohydrates
e. None of the above is correct
e. None of the above is correct
A long molecule that has an amino terminus (end) and a carboxyl terminus, and 243 monomers in between. This molecule ________.
a. was formed by 243 hydrolysis reactions
b. is a protein
c. has 242 phosphodiester bonds
d. is a polysaccharide
e. is a type of DNA
b. is a protein
Watson and Crick’s 1953 model for the structure of DNA provided an explanation for what previous mystery?
a. Previously, scientists were not sure if proteins or nucleic acids were the genetic material.
b. Previously, scientists were not sure if DNA or RNA was the genetic material.
c. Previously, scientists were unsure why nitrogenous bases came in predictable frequencies, such as G = C and A = T.
d. Previously, scientists were not sure how DNA was transcribed into RNA.
e. None of the above is correct.
c. Previously, scientists were unsure why nitrogenous bases came in predictable frequencies, such as G = C and A = T.
Apply Chargaff’s rules to solve the following problem. The nitrogenous base adenine (i.e., ‘A’) makes up 20% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an organism Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this sample will be made up of guanine?
a. 10%
b. 20%
c. 30%
d. 40%
e. Not enough information is provided.
c. 30%
During cellular respiration, energy released by ______________is used to pump protons into the ____________, in eukaryotic cells. Ultimately, these protons will flow down their own electro-chemical gradient back into the ______________________?
a. the electron transport chain, mitochondrial intermembrane space, mitochondrial matrix
b. the electron transport chain, mitochondrial matrix, cytoplasm
c. the electron transport chain, stroma, cytoplasm
d. glycolysis, mitochondrion, cytosol
e. photosynthesis, chloroplast intermembrane space, cytosol
a. the electron transport chain, mitochondrial intermembrane space, mitochondrial matrix
During which parts of cellular respiration is CO2 NOT released?
a. Pyruvate oxidation
b. Glycolysis, Electron transport chain, Chemiosmosis
c. Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
d. Krebs cycle and pyruvate oxidation
e. Krebs cycle only
b. Glycolysis, Electron transport chain, Chemiosmosis
What is the primary way that chemical energy gets generated during the Krebs cycle?
a. ATP is generated via the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
b. Electron carriers get reduced.
c. NADH and FADH 2 get oxidized.
d. CO2 is allowed to go down its own concentration gradient.
e. Electron carriers donate their high energy electrons to oxygen.
b. Electron carriers get reduced.
During the light reactions of photosynthesis ________.
a. protons are released from water into the thylakoid space
b. both ATP and NADPH are generated
c. a proton gradient is generated across the thylakoid membrane
d. two electrons are released from water via oxidation
e. All of the above are correct.
e. All of the above are correct.
Which of the following statements describes what happens to the molecule that acts as an electron donor in an oxidation-reduction reaction (redox)?
a. It gets oxidized and gains potential energy.
b. It loses electrons but has no net change in potential energy.
c. It gets oxidized, and it loses some potential energy.
d. It gets reduced and gains potential energy.
e. It gains electrons and loses potential energy.
c. It gets oxidized, and it loses some potential energy.
Which of the below is NOT a critical step during DNA replication?
a. the elongation of DNA in the 5' → 3' direction
b. the breakage of hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
c. the formation of hydrogen bonds between DNA strands
d. the polymerization of RNA in the 5' → 3' direction
e. the breakage of covalent bonds by helicase
e. the breakage of covalent bonds by helicase
Which of the statements below describes the results of the following reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O6 → 6 CO2 + H2O + Energy
a. During the above reaction, oxygen becomes reduced and carbon dioxide becomes oxidized.
b. In the above reaction, pyruvate becomes covalently bonded to oxygen which releases water and energy.
c. In the above reaction, glucose becomes oxidized, and oxygen becomes reduced.
d. During the above reaction, oxygen becomes oxidized, and water becomes reduced.
e. In the above reaction, carbon dioxide becomes reduced, and oxygen becomes oxidized.
c. In the above reaction, glucose becomes oxidized, and oxygen becomes reduced.
In his transformation experiments on Streptococcus, what did Griffith find?
a. He demonstrated that strains of Streptococcus varied in the effects on hosts and that some strains could transfer their capacity to harm hosts to other strains.
b. He showed that mice could transform each other through the transfer of specific proteins.
c. Mixing a heat-killed non pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain become harmless.
d. Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
e. None of the above are correct.
a. He demonstrated that strains of Streptococcus varied in the effects on hosts and that some strains could transfer their capacity to harm hosts to other strains.
Plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis. What is the source of the oxygen during this process?
a. The oxygen comes from the atmosphere (air).
b. The oxygen is released during the reduction of carbon dioxide.
c. The oxygen diffuses from photosystem II after the oxidation of water.
d. The oxygen is released during the oxidation of carbon dioxide.
e. The oxygen is released as a byproduct of the Calvin Cycle.
c. The oxygen diffuses from photosystem II after the oxidation of water.
Why are plants green?
a. The Calvin cycle is unable to utilize green light wavelengths.
b. The Calvin cycle produces green light during carbon fixation (i.e., Calvin fluorescence)
c. The thylakoid membrane uses green light for photosynthesis.
d. Plant cells are packed with mitochondria with RuBisCo, a green colored molecule.
e. None of the above is correct.
e. None of the above is correct.
What is the role of ATP synthase during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
a. The ATP synthase fixes CO2 onto RuBP to generate a glucose precursor.
b. It synthesizes ADP from ATP powered by carbon fixation.
c. It synthesizes ATP from ADP powered by a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
d. It synthesizes ATP within photosystem I.
e. It synthesizes ATP within photosystem II.
c. It synthesizes ATP from ADP powered by a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
During photosynthesis, the enzyme RuBisCo is responsible for what process?
a. RuBisCo catalyzes the splitting of water in the light reactions of photosynthesis.
b. RuBisCo oxidizes water to generate two high energy electrons.
c. RuBisCo catalyzes the production of ATP and NADPH from the photosystems.
d. dRuBisCo catalyzes carbon fixation and reduction of carbon molecules, leading to the production of Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (G3P)
e. All of the above are correct.
d. dRuBisCo catalyzes carbon fixation and reduction of carbon molecules, leading to the production of Glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (G3P)
Where in the chloroplast does water become oxidized?
a. In the inner chloroplast membrane
b. In the stroma
c. In the matrix
d. In the thylakoid
e. Photosystem
d. In the thylakoid
In most plants, which of the following reactions REQUIRE molecular oxygen (O2)?
a. only the light reactions
b. only the splitting of CO2 by RuBisCO
c. only the reduction of electron carriers in photosystem I
d. only the reduction of electron carriers in photosystem II
e. only the electron transport chain in the mitochondrion
e. only the electron transport chain in the mitochondrion
Chargaff studied key features of DNA before its full structure was understood. Which of the below statements is consistent with one of Chargaff’s rules?
a. Bacteria have circular DNA, but eukaryotes have linear DNA.
b. The proportions of the different nitrogenous bases in DNA are unique to each species.
c. All animals and plants have the same frequencies of the four types of nitrogenous bases in their genomes.
d. The proportions of the sugars and phosphates in the DNA are unique to each species.
e. None of the above is correct
b. The proportions of the different nitrogenous bases in DNA are unique to each species.
Which of the below statements is true about Watson & Crick’s 1953 model of DNA structure?
a. They suggested that the two DNA strands were bonded to each other by covalent bonds between nitrogenous bases.
b. They suggested that the two DNA strands were bonded to each other by covalent bonds between phosphate groups.
c. They suggested that the two DNA strands were bonded to each other by covalent bonds between ribose groups.
d. They suggested that the two DNA strands were bonded to each other by ionic bonds between ribose groups.
e. None of the above is correct.
e. None of the above is correct.
When a new DNA strand is created during DNA replication, where does each new nucleotide attach to?
a. It attaches to the carboxyl end of the previous nucleotide.
b. It attaches to the 5’ phosphate group of the previous nucleotide.
c. It attaches to the 3’ OH of the ribose sugar of the previous nucleotide.
d. It attaches to the amino end of the previous nucleotide.
e. It attaches to the helicase enzyme, which directs it to the newly growing DNA strand.
c. It attaches to the 3’ OH of the ribose sugar of the previous nucleotide.
In Meselson & Stahl’s experiment, their goal was to test models of how DNA replicated. How were they able to differentiate the template strand (the ‘old’ strand) from the synthesized strand (the ‘new’ strand)?
a. The old strand was replicated in the 5’3’ direction, but the new one was replicated in the 3’5’ direction.
b. The old strand was replicated in the 3’5’ direction, but the new one was replicated in the 5’3’ direction.
c. The old strand was heavier, since it contained extra neutrons in its nitrogen atoms (15N).
d. The old strand required a helicase, but the new one does not.
e. The old strand was lagging, whereas the new strand was leading
c. The old strand was heavier, since it contained extra neutrons in its nitrogen atoms (15N).
The oxygen molecule (O2) is a required reagent for cellular respiration. During which step is oxygen specifically involved in the process?
a. Oxygen gets consumed during glycolysis.
b. Oxygen gets consumed during the citric acid cycle.
c. Oxygen is needed for the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
d. Oxygen is required as a final step in the electron transport chain.
e. Oxygen must be released as a waste product from the breakdown of glucose.
d. Oxygen is required as a final step in the electron transport chain.
One of the end products of cellular respiration is carbon dioxide (CO2). Where does this molecule come from?
a. Carbon dioxide (CO2) comes from the covalent bonding of molecular oxygen (O2) to free carbons.
b. Carbon dioxide (CO2) comes from the organism breathing in.
c. The cells supply the CO2 as an electron acceptor, such as pyruvate (oxidative phosphorylation).
d. Carbon dioxide (CO2) comes from the covalent bonding of water to free carbons.
e. None of the above is correct.
e. None of the above is correct.
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a new DNA strand in the 5' → 3' direction?
a. Primase
b. RNA ligase
c. DNA polymerase
d. Helicase
e. Ligase
c. DNA polymerase
A female student in Biol005a (Sex chromosomes = XX) finds out through her genetic counselor that she carries a sex-linked allele associated with muscular dystrophy (a disease that causes progressive weakness and muscle loss). Which of her future offspring would inherit this allele from her?
a. You would need to know the father’s genotype to make any predictions.
b. All her sons would inherit the allele from her.
c. Half of her daughters and half of her sons would inherit the allele from her.
d. All her daughters and none of her sons would inherit the allele from her.
e. Half of her daughters and all her sons would inherit the allele from her.
c. Half of her daughters and half of her sons would inherit the allele from her.
Which of the following items would NOT be present in a cell undergoing metaphase of mitosis? (17)
a. Fully condensed chromosomes
b. Centrosomes that connect to the chromosomes with microtubules
c. Sister chromatids attached to each other at the centromere
d. Sister chromatids, lined up in the middle of the cell
e. All of the above are present
e. All of the above are present.
Gregor Mendel stated that alleles of two (or more) different genes always get assorted into gametes independently of each other. Based on current knowledge, what would be the most accurate update of his ‘Law of independent assortment’?
a. Alleles of different genes never assort independently.
b. Alleles of different genes always assort independently.
c. Alleles of different genes very rarely assort independently.
d. Alleles of different genes often assort independently.
e. Alleles of different genes only assort independently if they are on the same chromosome.
d. Alleles of different genes often assort independently
How does DNA content vary among cells of the human body?
a. Somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, but gametes have 23 chromosomes.
b. Every cell in the human body has 46 chromosomes (2n=46).
c. Every cell in the human body has 23 chromosomes (1n=23)
d. Somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, but new zygotes (fertilized egg) start off life with 23 chromosomes.
e. DNA content varies among tissue types, because different genes are expressed depending on the cell’s function.
a. Somatic cells have 46 chromosomes, but gametes have 23 chromosomes.
Sister chromatids are___________.
a. each double stranded
b. genetically identical to each other (other than rare mutations)
c. attached to each other at the centromere
d. copies of the same chromosome that arise from replication
e. All the above are correct
e. All the above are correct
What are the products of meiosis?
a. Meiosis produces two diploid (2n) gametes from each diploid meiocyte (2n).
b. Meiosis produces two haploid (1n) gametes from each diploid meiocyte (2n).
c. Meiosis produces three haploid (1n) gametes from each diploid meiocyte (2n).
d. Meiosis produces four haploid (1n) gametes from each diploid meiocyte (2n).
e. Meiosis only produces haploid meiocytes, not gametes
d. Meiosis produces four haploid (1n) gametes from each diploid meiocyte (2n).
Which of the following statements is true about a diploid species that has a chromosome number of 1n = 16?
a. The species has 16 chromosomes per somatic cell.
b. The species has 8 pairs of chromosomes per somatic cell.
c. Each diploid cell has eight homologous pairs of chromosomes.
d. A gamete from this species has 16 chromosomes.
e. None of the above is correct.
d. A gamete from this species has 16 chromosomes.
How is it possible to produce a human zygote with 46 chromosomes?
a. fertilization of an egg by one sperm
b. failure of the egg nucleus to be fertilized by the sperm
c. failure of a fertilizing sperm to complete meiosis I
d. incomplete cytokinesis during spermatogenesis after meiosis I
e. an error in meiotic anaphase 1 occurring in either an egg or sperm
a. fertilization of an egg by one sperm
Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants demonstrated that________.
a. traits are inherited in small stretches of coding DNA, which he called genes
b. recessive traits are always visible in the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross
c. traits blend with each other in the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross
d. traits are inherited as distinct heritable units
e. All of the above are correct
d. traits are inherited as distinct heritable units
Mendel mated true-breeding purple flowered plants with true-breeding white flowered plants to produce___________ in the F1 generation.
a. a 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowered offspring
b. a 1:1 ratio of purple to white flowered offspring
c. a 3:1 ratio of heterozygous to homozygous offspring
d. heterozygote offspring
e. all homozygous offspring
d. heterozygote offspring
How did Mendel describe the patterns of inheritance of different genes?
a. independent assortment
b. dominant genes block the expression of recessive ones
c. segregation of alleles
d. hybridization
e. heritable units
a. independent assortment
Why are females LESS OFTEN affected by sex-linked mutations, compared to males?
a. Females pass on both X chromosomes to their daughters whereas males only pass on one X chromosome.
b. Females have two X chromosomes, and thus are unlikely to have the sex-linked mutation on both.
c. Female hormones (estrogen) block the expression of key traits that do not get expressed in females.
d. Female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
e. X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
b. Females have two X chromosomes, and thus are unlikely to have the sex-linked mutation on both.
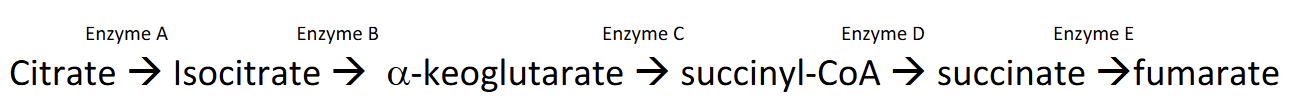
The flow chart below shows a simple metabolic pathway. According to Beadle and Tatum's hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
a. Less than 5
b. 5
c. 6
d. More than 6
e. It cannot be determined from the pathway.
b. 5
What is the reason that transcription and translation cannot be coupled in eukaryotes?
a. These processes cannot be coupled because transcription is much too slow compared to translation.
b. These processes cannot be coupled because translation is too error prone compared to transcription.
c. There are too many genes to transcribe in eukaryotic genome.
d. Eukaryotic genes are very long and must be transcribed by many RNA polymerase enzymes at the same time. This does not leave any room for ribosomes to do their work.
e. None of the above is correct
e. None of the above is correct
Which of the following statements best describes the termination step of transcription?
a. The ribosome transcribes up to a stop codon, causing the transcription machinery to stop advancing through the gene and release the mRNA.
b. RNA polymerase transcribes up to the poly-A signal, causing proteins to associate with the transcript and cut it free from the polymerase.
c. RNA polymerase transcribes up to the terminator sequence, causing the polymerase to separate from the DNA and release the transcript.
d. Once transcription has initiated, RNA polymerase transcribes until it reaches the end of the chromosome.
e. RNA polymerase transcribes up to a stop codon, causing the polymerase to stop advancing through the gene and release the mRNA.
c. RNA polymerase transcribes up to the terminator sequence, causing the polymerase to separate from the DNA and release the transcript.
The genetic code is ___________.
a. read in the 5’ → 3’ direction
b. universal
c. degenerate
d. made up of three letter words called codons
e. all of the above are correct
e. all of the above are correct
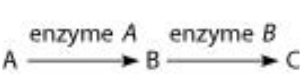
Refer to the metabolic pathway illustrated below, wherein nutrient A undergoes a reaction, changing it to B, and nutrient B undergoes a reaction, changing it to C. If nutrient C is required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on medium supplemented with which of the following nutrient(s)?
a. nutrient A only
b. either nutrient B or C
c. nutrient C only
d. nutrients A and C
e. none of the above is correct
b. either nutrient B or C
A particular triplet of bases in the template strand of DNA is 5ʹ AGT-3ʹ. What would be the corresponding codon for the mRNA that is transcribed?
a. 3ʹ-UCA-5ʹ
b. 3ʹ-UGA-5ʹ
c. 5ʹ-TCA-3ʹ
d. 3ʹ-AGU-5ʹ
e. None of the above is correct
a. 3ʹ-UCA-5ʹ
Which molecular structures contain codons?
a. DNA
b. mRNA
c. tRNA
d. rRNA
e. mRNA and tRNA
b. mRNA
In humans, there are 61 mRNA codons that are used specify the twenty required amino acids, but there many fewer tRNAs (i.e., <61). Which of the following statements explains this fact?
a. Some tRNAs have anticodons that recognize multiple amino acids.
b. Many codons are never used, so the tRNAs that recognize them are dispensable.
c. The DNA codes for all 61 tRNAs, but some are then destroyed.
d. The anticodon on a tRNA can often recognize multiple codons via “wobble pairing”
e. None of the above is correct
d. The anticodon on a tRNA can often recognize multiple codons via “wobble pairing”
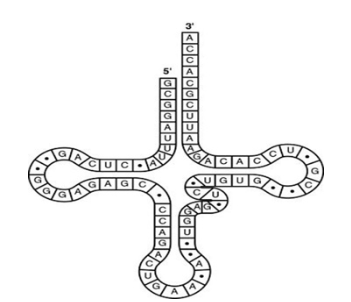
What type of bonding is responsible for maintaining the shape of the tRNA molecule shown in the figure?
a. phosphodiester covalent bonds between RNA strands
b. ionic bonding between phosphates
c. hydrogen bonding between base pairs
d. van der Waals interactions between the RNA strands
e. peptide bonding between amino acids
c. hydrogen bonding between base pairs
The genetic code is redundant. What is meant by this statement?
a. tRNAs can encode for multiple amino acids.
b. A single codon can specify the addition of more than one amino acid.
c. The genetic code is different for different domains of organisms.
d. The genetic code is universal (the same for all organisms).
e. More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid.
e. More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid.
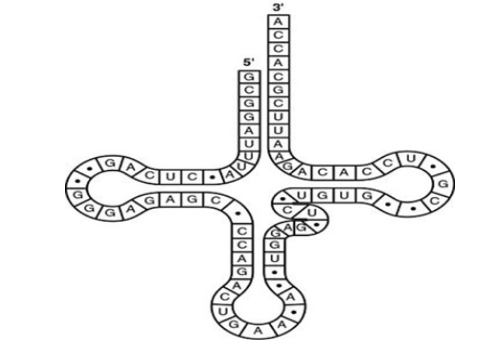
The tRNA shown below has its 3ʹ end projecting beyond its 5ʹ end. Which of the following processes will occur at this 3ʹ end?
a. A poly-A tail will be synthesized at the 3’ end.
b. The amino acid binds covalently.
c. The excess nucleotides (ACCA) will be cleaved off at the ribosome.
d. The small and large subunits of the ribosome will attach to it.
e. The 5ʹ cap of the mRNA will become covalently bound.
b. The amino acid binds covalently.
Which of the following processes is the first event to take place in translation?
a. base pairing of activated arginine-tRNA to AUG of the messenger RNA
b. binding of the larger ribosomal subunit to smaller ribosomal subunits
c. the ribosome reaches a promoter sequence in DNA and assembles there
d. the small subunit of the ribosome reaches a promoter sequence in DNA and then assembles to an initiator tRNA
e. the small subunit of the ribosome recognizes a sequence near the 5ʹ end of the mRNA
e. the small subunit of the ribosome recognizes a sequence near the 5ʹ end of the mRNA
What is the function of the release factor during translation in eukaryotes?
a. It causes the activated tRNA to move from the A site to the P site to the E site
b. It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of an activated tRNA.
c. It releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form a peptide bond.
d. It releases the ribosome from the ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol.
e. It binds to the terminator sequence in the DNA, stopping production of the transcript
b. It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of an activated tRNA.
During the elongation phase of translation, which site in the ribosome represents the location where a codon is being read?
a. the small ribosomal subunit
b. E site
c. P site
d. C site
e. A site
e. A site
Which one of the following structures is required for the start of translation?
a. intron
b. 5ʹ cap
c. AUG codon
d. poly-A tail
e. all of the above are correct
c. AUG codon
Which of the following processes increases the efficiency of gene expression in prokaryotes but not in eukaryotes?
a. post-transcriptional removal of introns
b. transcription and translation occur simultaneously
c. translation in the absence of a ribosome
d. formation of polyribosomes
e. addition of 5’ cap and 3’ poly- tail
b. transcription and translation occur simultaneously
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in a change in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product?
a. a deletion of a codon
b. an insertion of a codon
c. a deletion of two nucleotides
d. a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
e. a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
c. a deletion of two nucleotides
Which of the following statements correctly describes the effect a nonsense mutation would have on a gene?
a. It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
b. It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
c. It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
d. It alters the reading frame of the mRNA.
e. None of the above is correct
c. It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
A single base substitution mutation is likely to have a less deleterious effect when the base change introduces which of the following characteristics?
a. a stop codon
b. a codon that specifies a perfect match to an anticodon
c. a codon that specifies the same amino acid as the original codon
d. an amino acid substitution that alters the tertiary structure of the protein
e. an amino acid substitution at the active site of an enzyme
c. a codon that specifies the same amino acid as the original codon
How might a single base substitution in the sequence of a gene affect the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by the gene?
a. A single base substitution cannot affect the amino acid sequence, because at least three bases have to change for this to occur.
b. Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame would be unaffected.
c. The amino acid sequence would be substantially altered, because the reading frame would change with a single base substitution.
d. All amino acids following the substitution would be affected, because the reading frame would be shifted.
e. None of the above is correct.
b. Only a single amino acid could change, because the reading frame would be unaffected.
Which of the following statements are true about the types of mutations that are responsible for sickle cell anemia?
a. Sickle-cell anemia is not a genetic disorder, but is instead caused by persistent blood loss after infection by the Malaria parasite
b. Sickle-cell anemia is not a genetic disorder, but is instead caused by toxins released after infection by the Malaria parasite
c. Sickle-cell anemia is caused by major changes in hemoglobin structure driven by a minimum of six different mutations that alter quaternary structure
d. Sickle-cell anemia is caused by major changes in hemoglobin structure driven by poor diet
e. None of the above is correct
e. None of the above is correct
How many levels of protein structure does Hemoglobin have?
a. Primary
b. Secondary
c. Tertiary
d. Quaternary
e. All of the above are correct
e. All of the above are correct
Plasmids are _________.
a. useful in cloning because they can rapidly cut DNA into small portions
b. useful in cloning because they can differentiate into a whole organism
c. small sections of DNA with ‘sticky ends’
d. palindromic sites in the sequence of DNA
e. small circular DNA molecules
e. small circular DNA molecules
Palindromic sites are DNA sequences that______.
a. initiate transcription
b. promote the binding of helicase
c. must be repaired before DNA replication is complete
d. are spelled the same way in either direction (or in this case strand)
e. must be spliced out of a plasmid before gene cloning can occur
d. are spelled the same way in either direction (or in this case strand)
Plant cloning________.
a. is still in the early phases of research but will soon be available to farmers
b. requires the extraction of a single, actively growing cell from the embryo
c. has been developed but leads to developmental plant disorders
d. has been going on for more than a century
e. requires the creation of a triploid ancestor
d. has been going on for more than a century