Groups and main characteristics of microorganisms belonging to medical microbiology. The main roles of microorganisms. Basic concepts related to pathogenicity and virulence.
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Louis Pasteur
Microbiology is the science of microbes, organisms too small to be seen by unaided eyes
Types of Microorganisms
Subcellular
Cellular
Multicellular
Subcellular
Viruses
Viroids
Prions
Cellular
• Prokaryotes: archaea, bacteria
• Eukaryotes: unicellular fungi,
• Protists: protozoa, algae
Multicellular
• Helminths and ectoparasites (can be classified among infectious agents of medical microbiology)
Microbes characteristics
yes
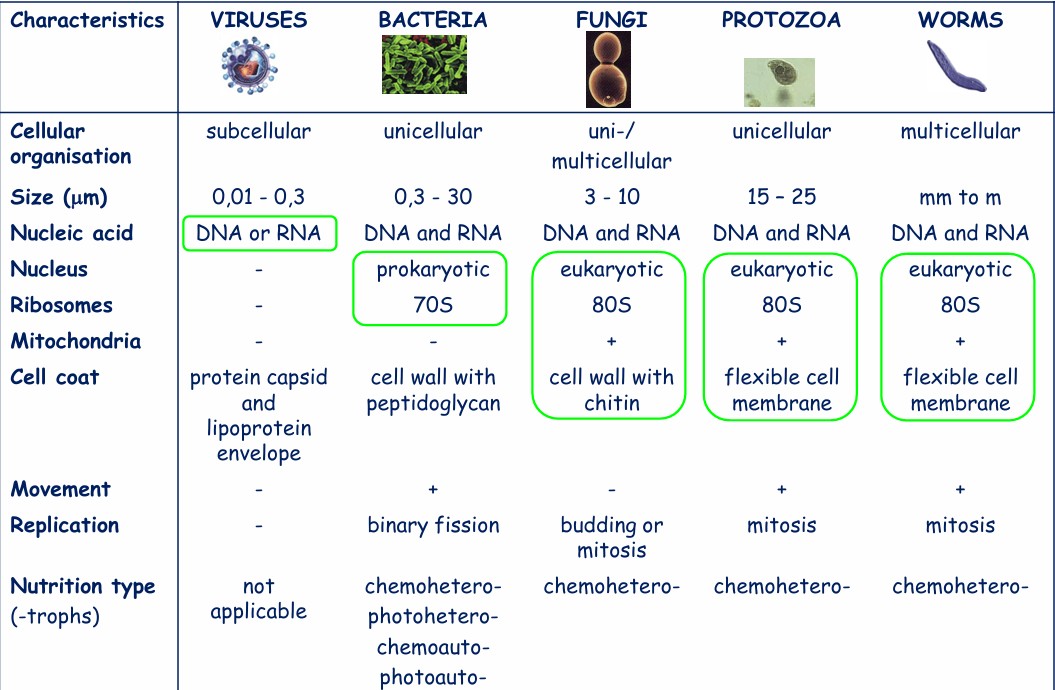
Relative sizes
yesss
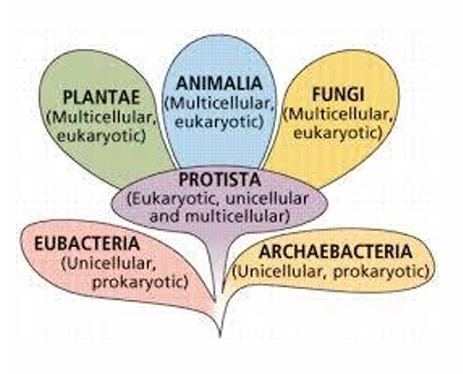
The domains of life
Eubacteria: Unicellular, prokaryotic
Plantae: Multicellular, eukaryotic
Protista: Eukaryotic, uni and multicellular
Archaebacteria: Unicellular, prokaryotic
Animalia: Multicellular, eukaryotic
Fungi: Multicellular, eukaryotic
The role of microorganisms
• The biogeochemical cycle of chemical elements
• The production of food and pharmaceuticals, as well as biotechnological products
• Microbes are capable of living in beneficial interactions with the host organism (microbiota, microbiome →)
• They can cause diseases (pathogens, pathogenicity →)
microbiome
the community of microbes—bacteria, archaea, eukaryotic microbes (e.g., fungi), and viruses—living in a given environment, together with the environment they inhabit. In contrast, the term microbiota refers exclusively to the microbes themselves