1.2.3 Price, income and cross elasticity of demand
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define PED
A measure of responsiveness for quantity demand after a price change
What is the formal for PED
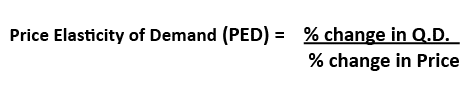
What does a PED of 0 mean
Perfectly inelastic demand. A change in price leads to no change in demand.
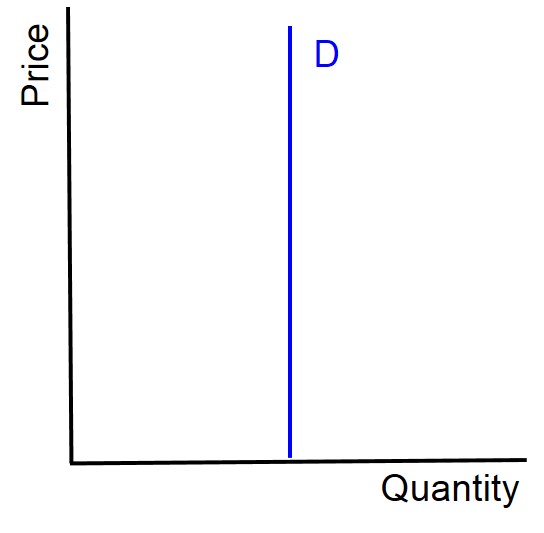
What does PED between between 0 and -1 mean
Price inelastic demand. A change in price leads to a proportionally smaller change in demand
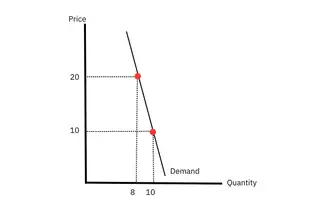
What does a PED on -1 mean
Unitary elasticity of demand. A change in price leads to proportional change in demand. this also means a change in price doesn’t lead to a fall in revenue.
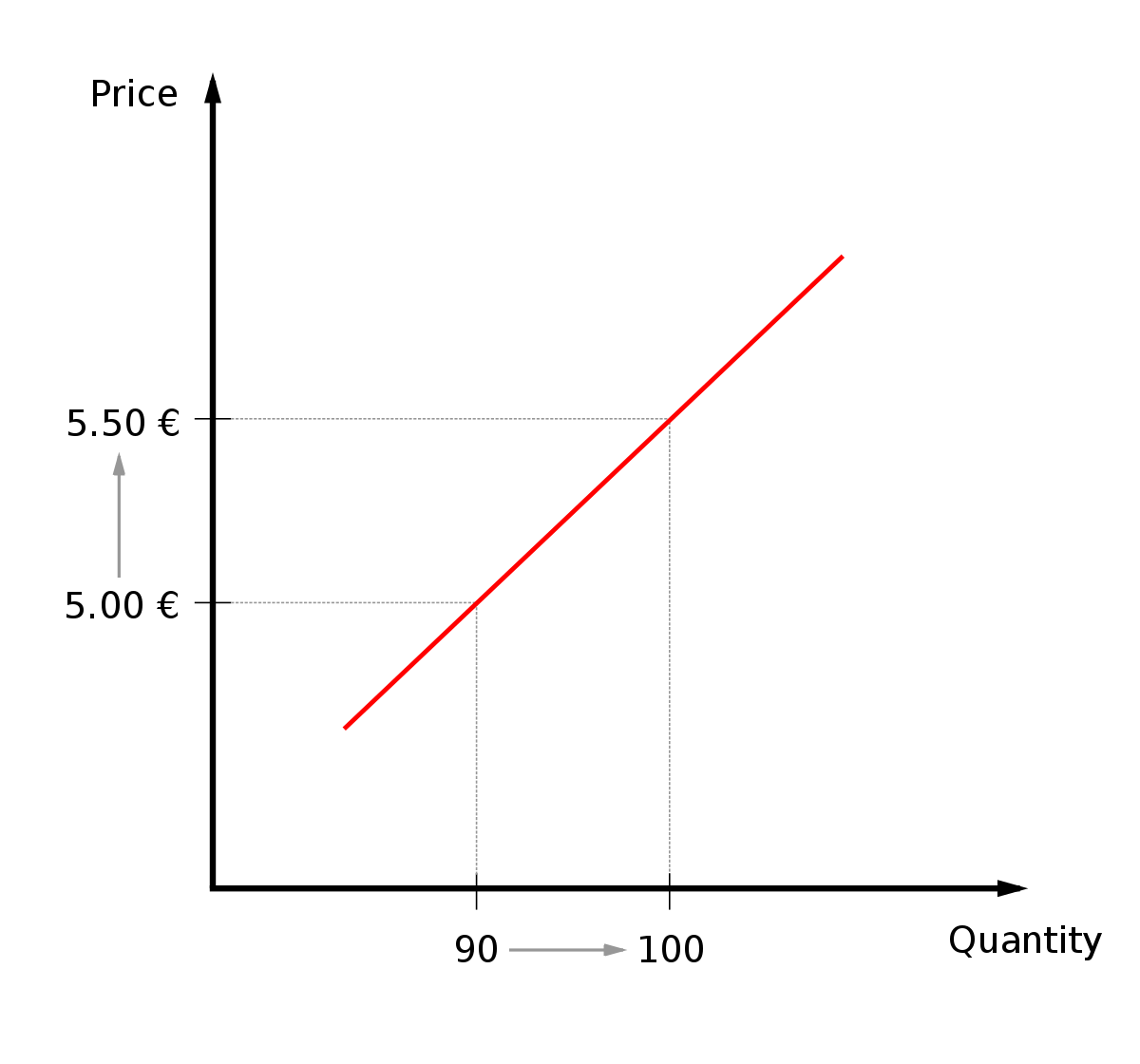
What does a ped of between -1 and infinity mean
Price elastic demand. A change in price leads to a proportionally larger change in demand.
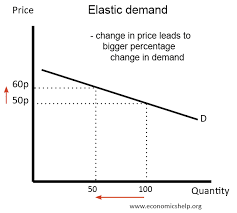
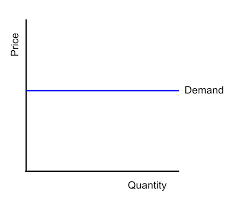
What does a PED of infinity mean
Perfectly elastic demand. A change in price leads to an infinite change in supply. A change in price causes revenue to fall to zero.
What factors influence the PED of a good or service
PLANTS
Proportion of income-The higher the prop proportion of income a good or service take up the more elastic it will be.
Loyalty-The stronger loyalty the more inelastic good will be.
Addictiveness-The goods that are more addictive or habitual are more inelastic.
Necessities- Necessities are more inelastic
Time- The longer since a price rise the more elastic
Substitutes-The stronger the substitutes the more elastic.
Define income elasticity of demand
The responsiveness of demand to a change in income.
What is the formula for income elasticity of demand
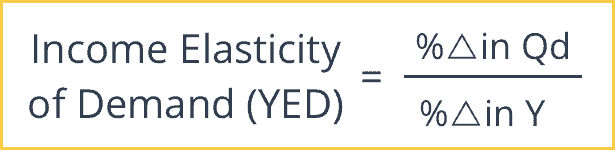
What YED values would normal goods have
Positive as when income rise demand rises as well
What YED values would inferior goods have
Negative as when income rise demand falls
What YED values do necessities have
Values between 0-1 as they are more inelastic
What YED values do luxuries have
Values greater than 1 as they are more elastic
What does the relationship between income and quantity demanded for a normal good
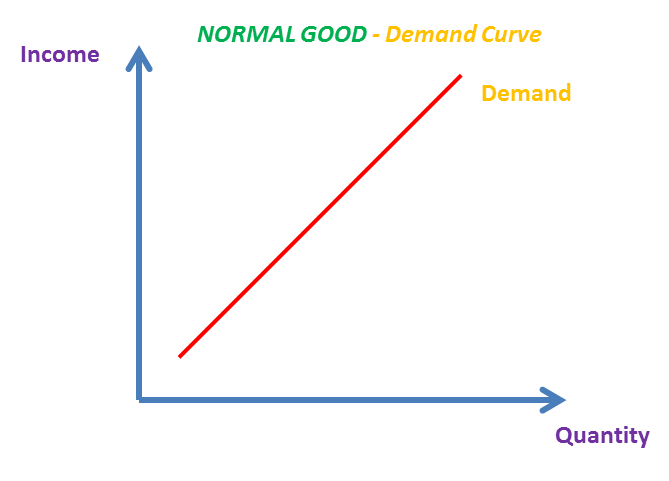
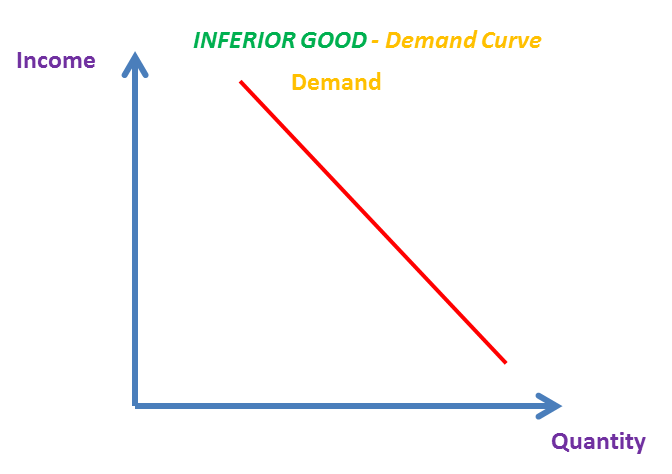
What does the relationship between income and quantity demanded for an inferior good
Define cross elasticity of demand
The responsiveness of demand for one product to a change in the price of another product
What is the formula for cross elasticity of demand
XED=
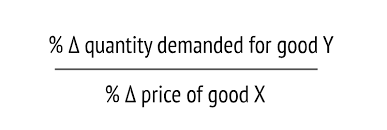
What XED values do substitute goods have
Positive as the price of one good rise the demand for the substitute good increases
What XED values do complementary goods have
Negative as the price of one good rise demand for the complementary good falls