Psychology 12 Brain
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Neuron
Cells that have specialized extensions for the reception and transmission of electrical signals.
Motor neurons
Send messages from the brain to the muscles, organs and glands Also know as Efferent Neuron. Helps your brain complete task and do actions.
sensory neurons
Carries information from our sense(vision, taste, smell, pain, hearing, touch) receptors to the spinal cord and up to brain. Also known as Afferent Neurons
Dendrite
Branchlike extension that arise from the cell body; they receive signals from other neutrons. Front of the Neuron, the receiver. Made out of fibres.
Soma/cell body
Keeps the cell working properly and maintains the cell health. Analyzes messages the cell receives and passes on the appropriate information to the axon.
Nucleus
The control center of the neuron, housing the cell's genetic material and important for cell growth/maturing.
Axon
A long, thin structure that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles. It is often covered by myelin to speed up signal transmission.
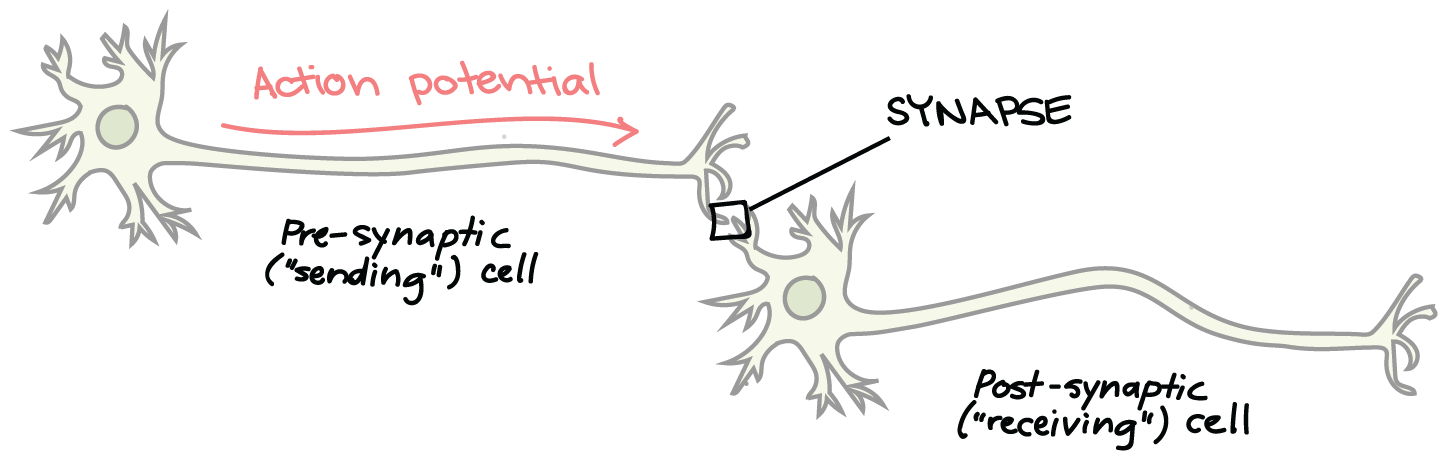
Synapse
The places where neurons connect and communicate with each other are called synapses.
End bulbs (axon terminal)
End of the neuron • Produces & releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap. • Electrical message converted to chemical messaging to transmit signals to other neurons.
Myelin sheath
Protective coating of the axon and helps insulates the electric signal
Neurotransmitter/ cell body
the chemical message (neurotransmitters) floats across the synaptic gap to other neurons
Receptor sites
Helps receive information top of dendrites
Respond to the information by triggering a specific action in the cell
Regulate the amount and type of information that gets through
Interpret the information and help the cell make decisions
Think of receptor sites like a messenger service:
They receive messages (chemicals)
They decode the message and figure out what it means
They respond to the message by triggering a specific action in the cell
Action potential
Electrical signal traveling down the axon
Refractory period
a period of time during which a cell is incapable of repeating an action potential
Re-uptake
Re-uptake is when neurotransmitters (chemical messengers) are absorbed back into the neuron that released them.
Cerebral cortex
is the outermost layer of the brain, responsible for processing sensory information, controlling movement, and facilitating thought, perception, and memory. (outer skin of the brain)
Share info
Connected to each hemispheres the fibers connecting the two halfs
Transfer of sensory, motor and cognitive info
Plasticity
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain's ability to reorganize, adapt, and change throughout life in response to new experiences, environments, and learning.
ability of the brain tissue to take on new functions or recover lost functionality.
Reorganization of neural pathways
The greatest in childhood reduces as you age
Repair damage or slow the weakening of the brain
Left brain specialization
Speech, Symbolic thinking
Language
Detail
Analysis
Math/numbers
logic/reasoning
Problem solving
Right side control
Right brain specialization
Controls life side of the body
Spatial perception
Organization
Creativity
Music
Emotions & relationships
Face recognition
Left side control
Reuptake
Reabsorbs the information sent
the process by which a brain cell "takes back" a chemical messenger (neurotransmitter) after sending a signal, regulating its amount and strength.
all-or-none principle
the axon either “fires” or it does not similar to a gun
The same level of electricity is utilized independent of the intensity of the stimulus. • How do we detect a gentle graze from a stubbing our toe? • A strong stimulus, like hitting our foot hard, can trigger more neurons to fire, more often, but not any stronger.
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging)
display anatomic structure in high-resolution
Helps to find & diagnose brain abnormalities
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the brain’s soft tissue.
Non-invasive, no radiation way to examine organs, tissues, brain & skeletal system
Used for: structural imaging, injuries, cancers, neurological disorders
provide information about structures and tissues at one point in time.
Electroencephalography (EEG)
measures brain waves
Measures brain electrical activity
Non-invasive, painless
electrodes detect electrical activity in the brain and the computer creates a graph-like image.
In real time
EEG can detect issues such as: anxiety, head injuries, epilepsy, sleep disruption
fMRI (Functional MRI)
shows the physical structure, activity, and function of the brain in real time.
determine which part of the brain controls thought, speech, movement and sensation (brain mapping)
The patient interacts with stimuli during the scan to show that activity
Measures brain activity, blood flow, and oxygenation in the brain
Non-invasive, no radiation
Used for: brain function, cognitive processes, neural activity
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
uses a small amounts of radioactive form of glucose(sugar) to visualize brain function
As your brain/body uses the glucose, the scanner shows areas of varying intensity depending on brain activity.
Can see trouble spots where glucose isn’t moving correctly.
Minimally invasive, low radiation
PET scans can evaluate: seizures, Alzheimer’s, tumors
Computerized Tomography (CT)
Uses X-rays to produce detailed images
combined to form cross-sectional slices or 3-D models of the brain.
provide more detail than a standard X-ray.
CT scans can:
find certain types of brain injuries
identify cancer
locate brain swelling or bleeding
reveal structural brain changes from schizophrenia
MEG (Magnetoencephalography)
measures the magnetic field from neuron activity.
can locate & identify malfunctioning neurons in your brain.
Measures magnetic fields generated by brain electrical activity
MEG can help to assess:
epilepsy sources
motor areas
sensory areas
language and vision
Glial Cells
Helper cells in the brain and nervous system that:
Keep neurons healthy
Provide nutrients and oxygen
Remove waste
Insulate and protect neurons
Help fight infections
Think of glial cells like the pit crew for neurons, keeping them running smoothly and efficiently!