DSA13 - Pathology of Heartburn and Dyspepsia
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Condition in which the muscles of the lower part of the esophagus fail to relax, preventing food from passing into the stomach
Define Achalasia
Difficulty swallowing due to impaired transport of liquids, solids, or both from the pharynx to the stomach
Define Dysphagia
Pain when swallowing
Define Odynophagia
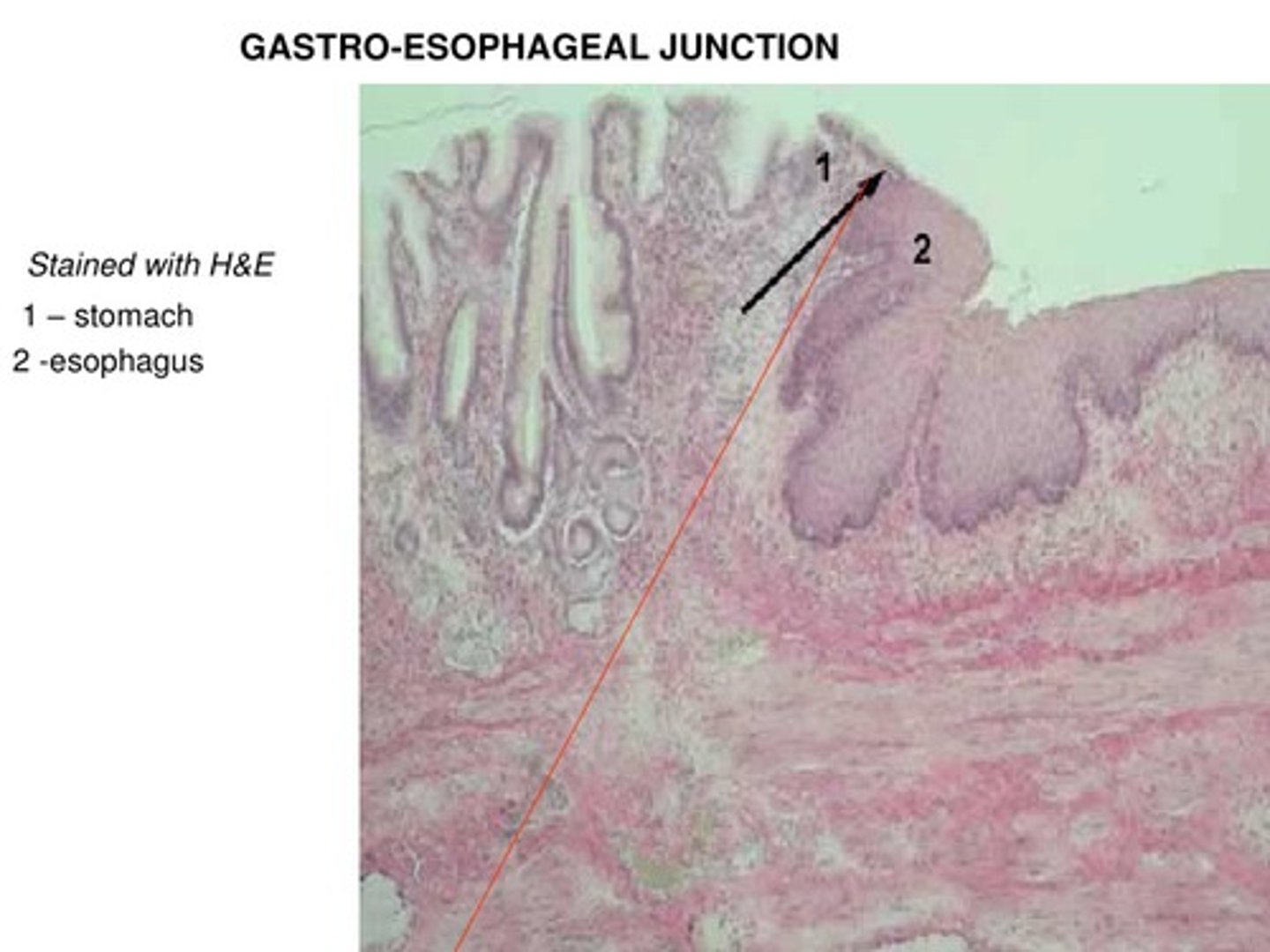
Stratified squamous --> Simple Columnar/Glandular
How does the Gastroesophageal Junction appear histologically (between the distal esophagus and the proximal stomach/cardia)?
Pill-induced (TCA, Doxy, Clinda, NSAIDs)
Reflux/Erosive (MC - STOMACH ACID)
Infex (HSV, CMV, Candida)
Corrosive (suicide attempt/accidental ingestion in peds)
Eosinophilic
What are the Causes of Esophagitis (think "PRICE")?
Sensation of pain/discomfort in upper abdomen - often recurrent; described as indigestion, gassiness, early satiety, postprandial fullness, gnawing or burning
Define Dyspepsia
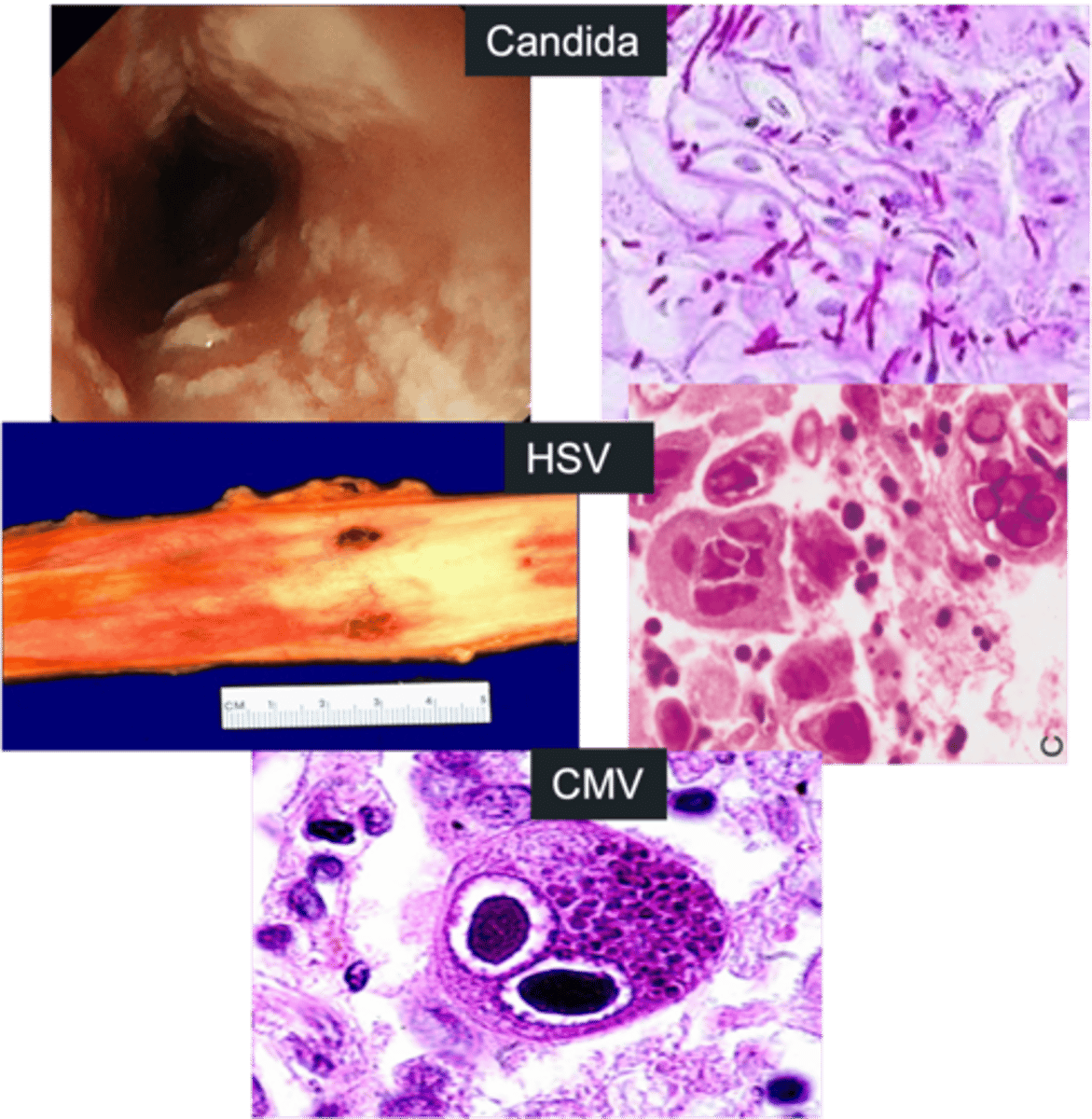
Infectious Esophagitis
Define Condition:
Inflammation of esophagus d/t INFECTION; AKA "heart burn
-Hx:
> Impaired Host Defenses (HIV. Immunocompromised)
> Infex
>> Candida albicans
>> HSV
>> CMV
-Sx:
> Difficulty swallowing saliva
> Odynophagia
> Chest Pain
-Dx: Endoscopy
> Candida
>> White or yellow patches ("cottage cheese")
>> Fungal pseudohyphae PAS (+)
> HSV
>> Ulcers = "Punched Out holes"
>> Multinucleated squamous cells w/ nuclear inclusions + margination of chromatin + nuclear molding
> CMV
>> Linear ulcers
>> Owl's Eye Inclusions (cytoplasmic & nuclear inclusions w/ peripheral clearing)
-Tx: Antifungal or Antiviral Drugs
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Define Condition:
Inflammation of esophagus d/t CHRONIC IMMUNE REACTION; AKA "heart burn
-Hx:
> Refractory to PPIs
> A/w:
>> Atopic Dermatitis
>> Allergic Rhinitis
>> Asthma
>> Peripheral Eosinophilia
-Path: Chronic Immune Rxn to environmental and food allergens --> deficient esophageal mucosal barrier
-Sx:
> Children = Feeding intolerance & GERD-like Sx
> Adults = Food Impaction/Dysphagia
-Dx:
> Biopsy: Eosinophilic Infiltration (> 15 eos per hpf) FAR from GE Junction
> Endoscopy: RINGS in upper esophagus
-Tx: Restrict food (allergies) + Steroids
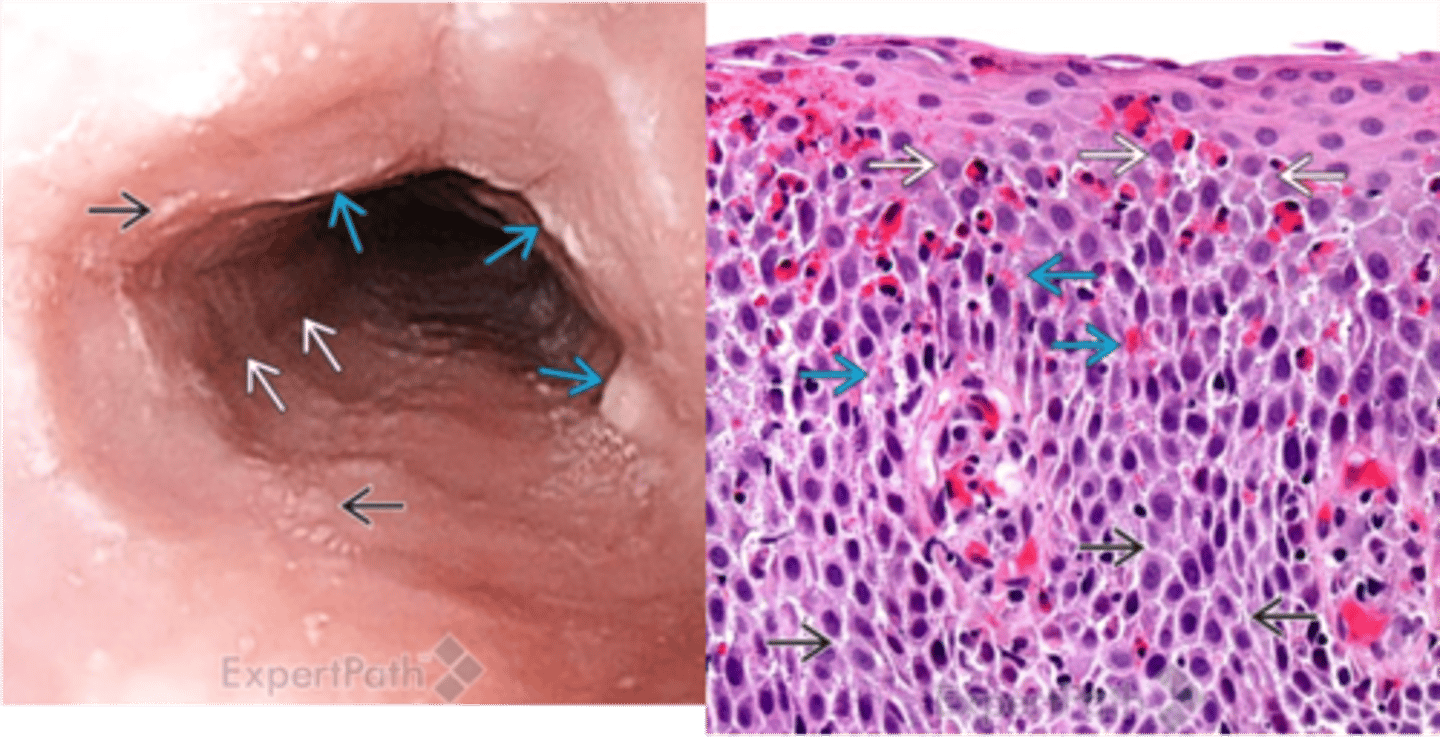
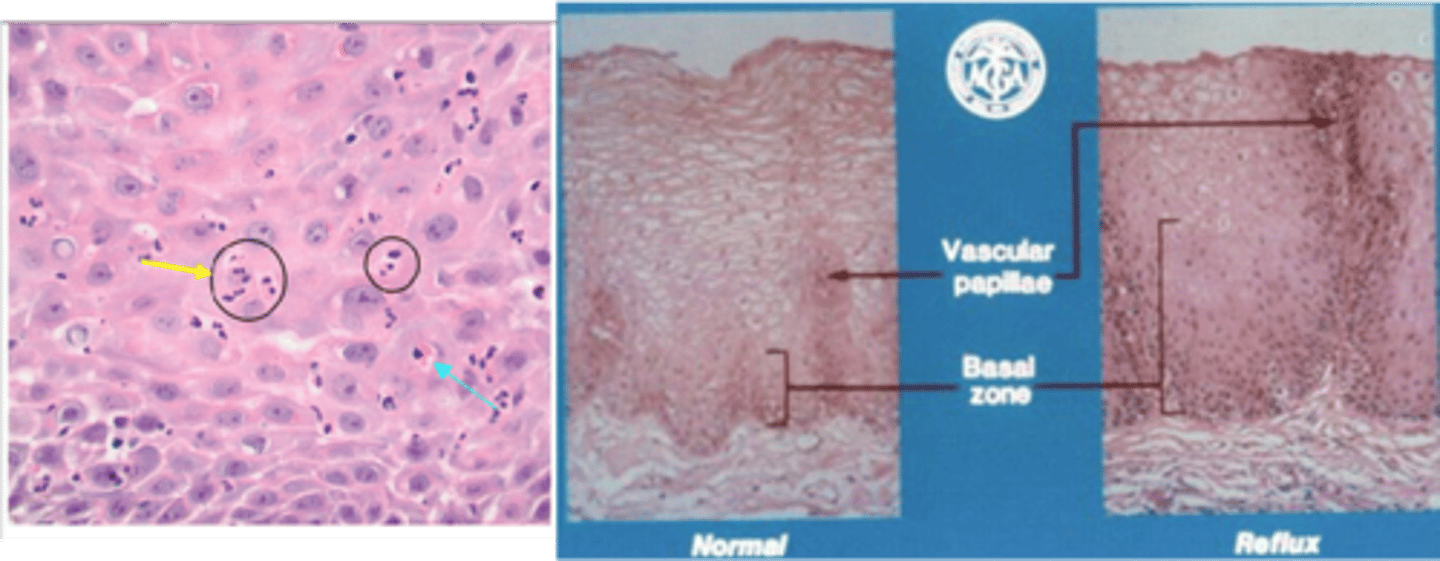
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)/Reflux Esophagitis
Define Condition:
Reflux of gastric juices causing mucosal injury d/t transient decreases in lower esophageal sphincter (LES) tone
-Hx: Increase frequency of transient LES relaxations
> Foods (Fat, Chocolate, Spicy)
> Habits (EtOH, Caffeine, Smoking)
> Obesity (stretching & applied pressure to LES --> less LES tone)
> Hiatal Hernia
>> Changes GE Junction
>> Loosens LES
>> Increase transient LES relaxations
> Pregnancy (prolongs intra-abdominal pressure)
-Sx:
> Heartburn
> Dysphagia
> Regurgitation of Sour-tasting gastric contents
> Asthma-like Sx (Aspiration of acid in trachea --> Coughing, Wheezing, Pneumonia)
> Retrosternal Chest Pain
-Dx:
> Biopsy:
>> Eosinophils & Neutrophils scattered in epithelium
>> HYPERPLASTIC on reflux side
-Prog: (most have no complications)
> Erosive Esophagitis
> Strictures
> Barrett esophagus
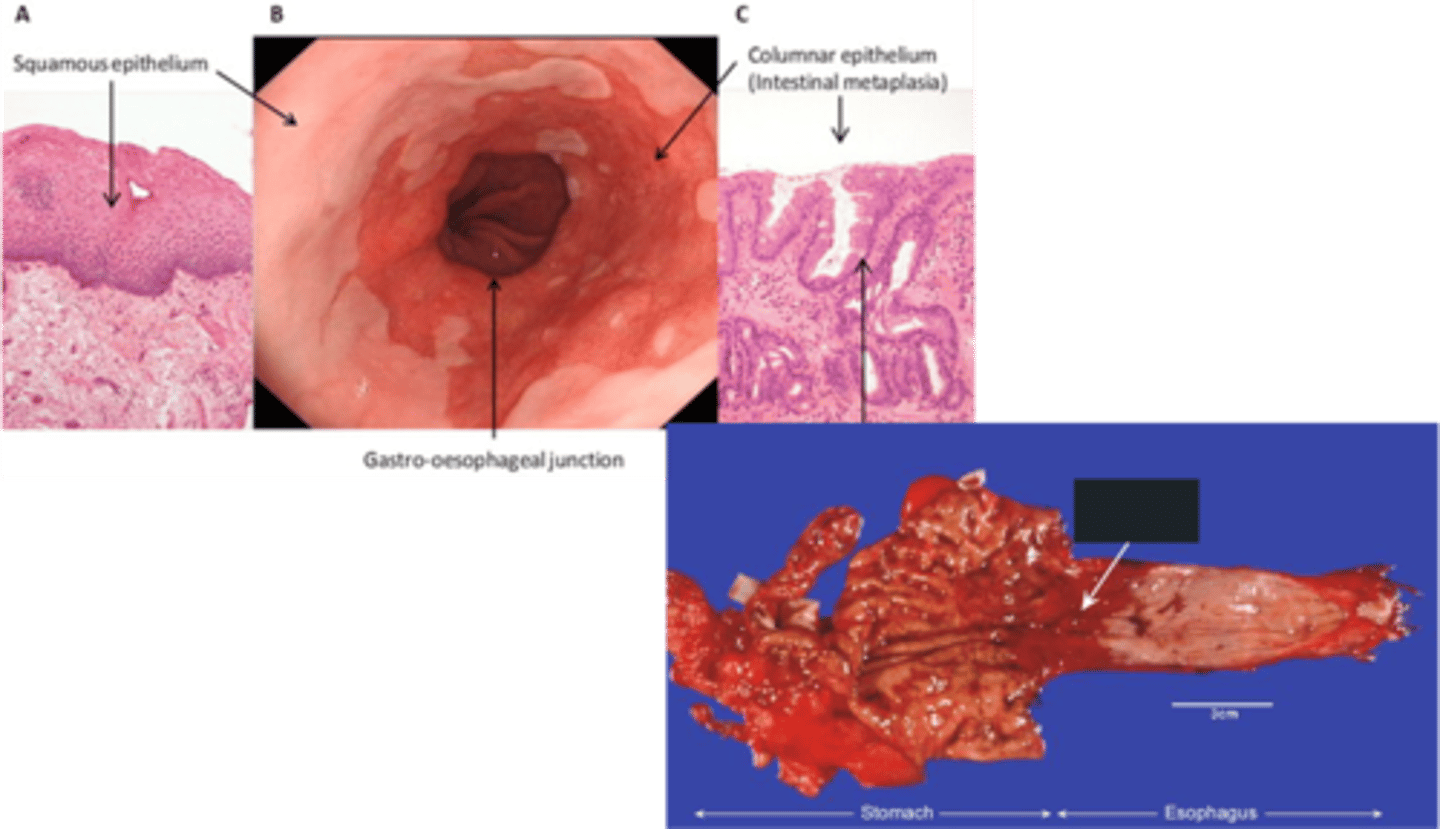
Barrett Esophagus
Define Complication of GERD:
Metaplasia of the lower esophageal mucosa from stratified squamous epithelium to nonciliated columnar epithelium with goblet cells
-Hx:
> Prolonged & Untreated GERD
> More in MALES < 50 y/o (if > 50, then Dxed in 60-70)
> More Caucasians
> Central Obesity
> Cigarrete Smoking
> FHx of this OR Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
-Path: Lower Esophageal Mucosa turns from Squamous to GLANDULAR METAPLASIA into COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM to protect itself from harsh reflux of gastric juices (Goblet cells secrete mucus)
-Dx:
> Gross: Red & Velvety areas
> Endoscopy: "Salmon Pink Patches"
Hiatal Hernia
Define Condition:
Abnormal protrusion of any abdominal structure/organ, most often a portion of the stomach, into the thoracic cavity through a lax diaphragmatic esophageal hiatus
-Hx:
> Congenital
> Secondary
>> Aging
>> Obesity
>> Smoking
-Path: Loss of Diaphragm Reinforcement (LES incompetence) --> Stomach Acid Reflux
> Sliding Type (MC) = Stomach immediately below GE Junction PROLAPSES through diaphgramatic hiatus into chest/mediatstinum - Creates GERD Sx
> Paraesophageal Type = Fundus of stomach herniates upward through hole in diaphragm ADJACENT the esophagus
-Sx: (< 10% - resemble GERD b/c MC = Sliding Type)
> Heartburn
> Dysphagia
> Regurgitation of Sour-tasting gastric contents
> Asthma-like Sx (Aspiration of acid in trachea --> Coughing, Wheezing, Pneumonia)
> Retrosternal Chest Pain
Foveolar Cells
What cells (A) secrete protective mucus in the cardia of stomach?
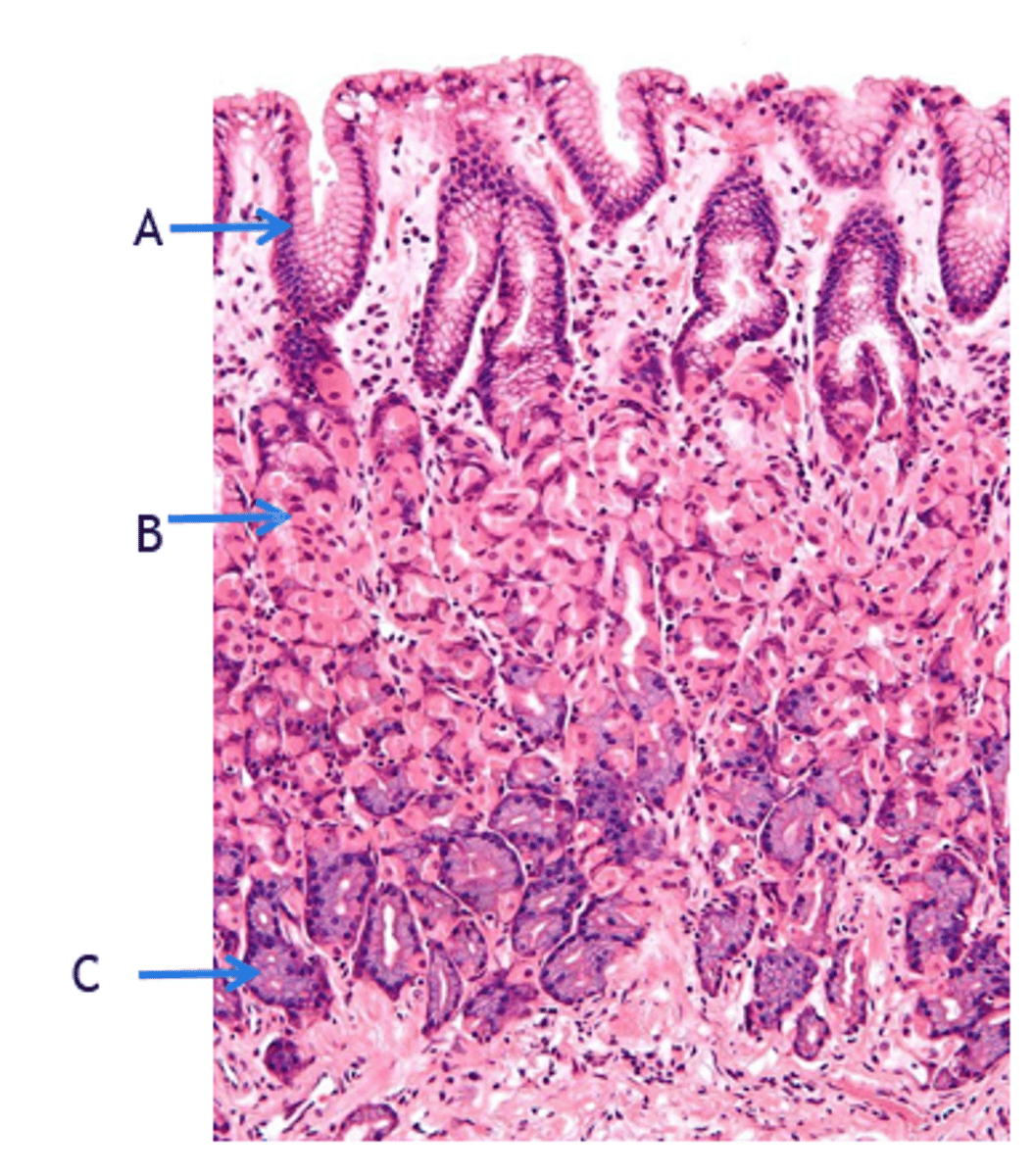
Parietal/Oxyntic Cells
What cells secrete acid & IF in the fundus/body of stomach?
> ACh
> Gastrin
> Histamine
What chemicals STIMULATE parietal cell acid production (bad)?
Prostaglandins
What chemical INHIBITS parietal cell acid production (good)?
Chief Cells (Basophilic)
What cells secrete Digestive Enzymes (ex: Pepsinogen, Lipase) in the fundus/body of stomach?
G-cells
What cells secrete Gastrin in the antrum of stomach?
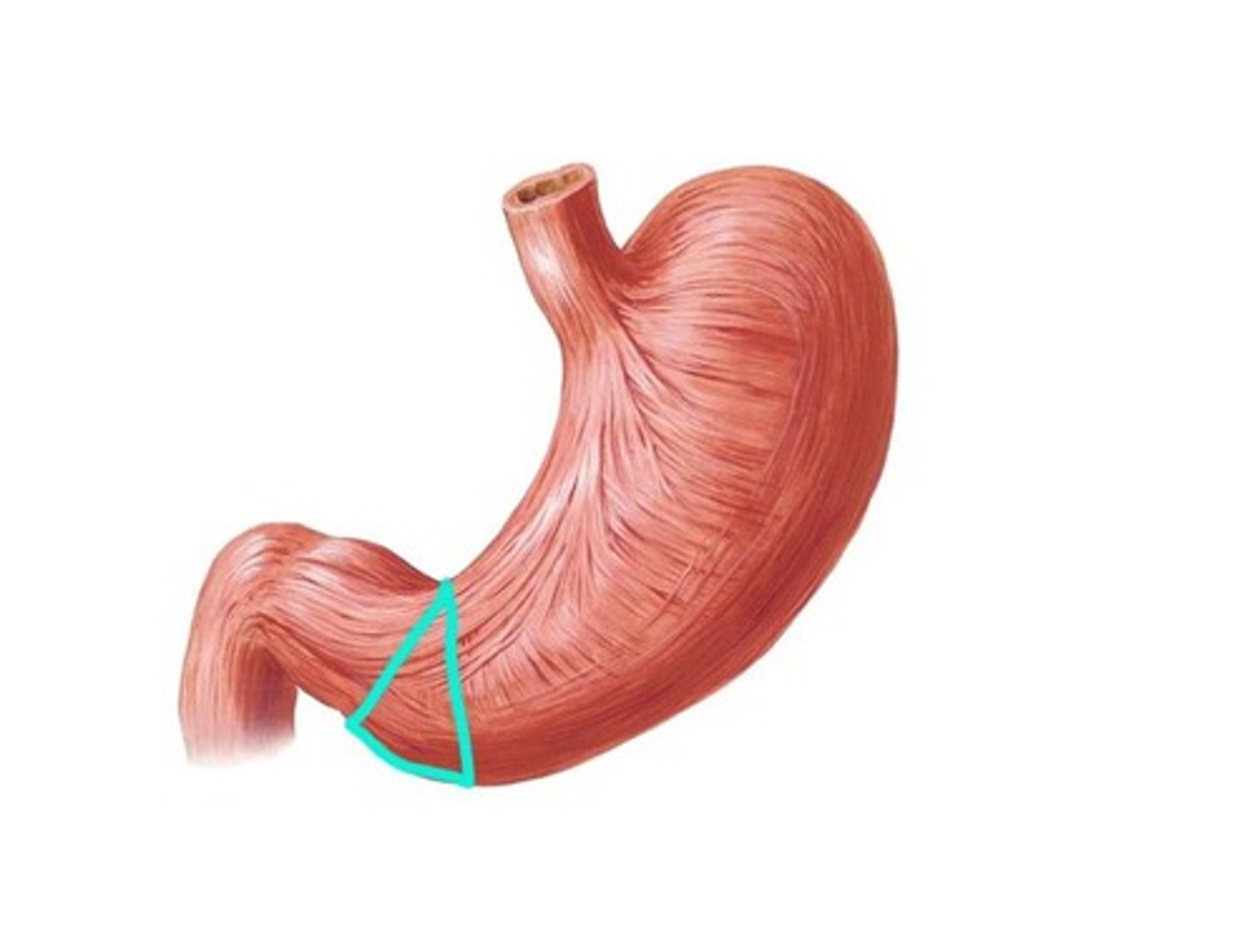
Gastropathy
Define Condition:
Does NOT involve inflammation - just changes of repair and regeneration
-Hx:
> NSAIDs (More acid secretion, less mucus secretion d/t less PGs)
> Alcohol (Induce Cellular/DNA damage)
> Bile
> Stress
-Sx:
> Epigastric Pain
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-PE: (If Severe)
> Ulceration
> Hematemesis
> Melena
> Massive Hemorrhage
-Prog: Gastritis if untreated
Acute Gastritis
Define Condition:
ACUTE Inflammation
-Hx:
> NSAIDs (More acid secretion, less mucus secretion d/t less PGs)
> Alcohol (Induce Cellular/DNA damage)
> Older Age (less mucus/bicarb produced)
> High Altitudes/Hypoexmia (less O2 --> impair gastric defenses)
> Harsh Acids/Bases ingestion
> STRESS
> Severe Illness/H pylori infex
-Sx:
> Epigastric Pain
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-PE: (If Severe)
> Ulceration
> Hematemesis
> Melena
> Massive Hemorrhage
-Dx:
> Biopsy: NEUTROPHILS
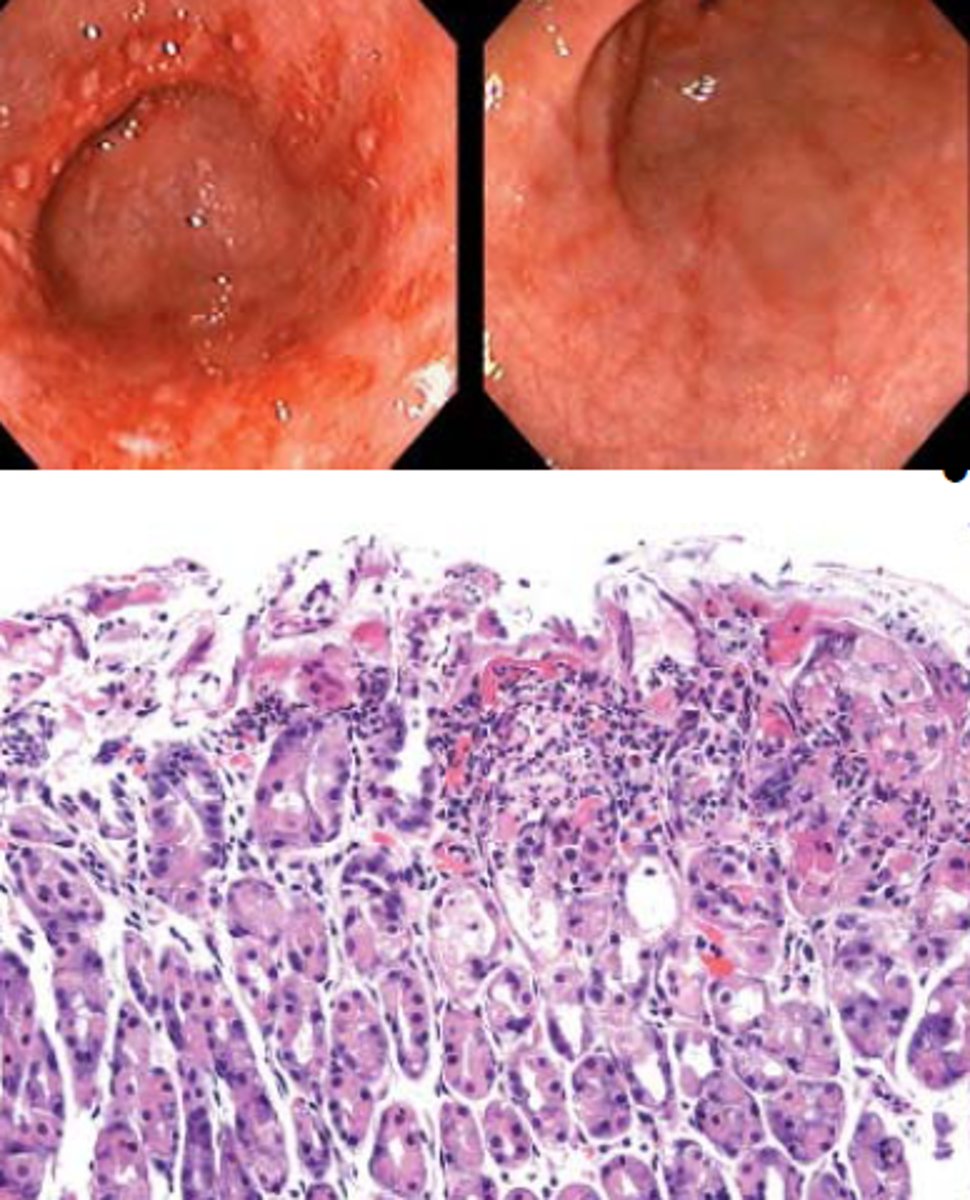
Chronic ACTIVE Gastritis
Define Condition:
Long-term condition in which the gastric mucosa, is inflamed or irritated over a longer period of time
-Hx:
> Autoimmune gastritis (Type A)
> MC = H pylori infex (Type B)
> Type C = Chronic NSAID use (More acid secretion, less mucus secretion d/t less PGs), Chronic Bile Reflux, Radiation
> Older Age (less mucus/bicarb produced)
> High Altitudes/Hypoexmia (less O2 --> impair gastric defenses)
> Harsh Acids/Bases ingestion
> STRESS
-Path: Mucosal inflammation --> Atrophy (Hypochlorhydria --> Hypergastrinemia) and Intestinal Metaplasia
-Sx:
> Epigastric Pain
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-Dx:
> Biopsy: MANY Inflammatory cells in Lamina Propria
-Prog: Increased risk of Gastric Cancer
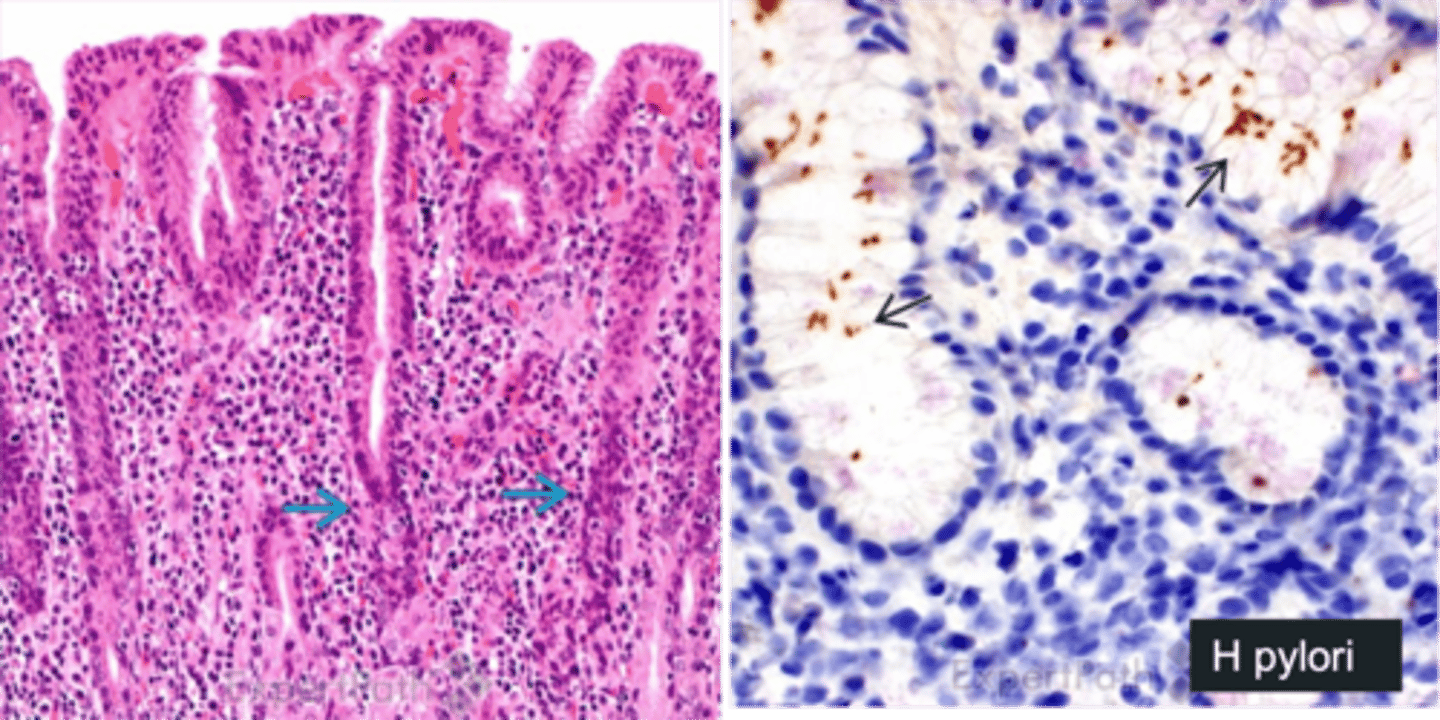
Chronic Gastritis
Define Condition:
Long-term condition in which the gastric mucosa, is inflamed or irritated over a longer period of time
-Hx:
> Autoimmune gastritis (Type A)
> MC = H pylori infex (Type B)
> Type C = Chronic NSAID use (More acid secretion, less mucus secretion d/t less PGs), Chronic Bile Reflux, Radiation
> Older Age (less mucus/bicarb produced)
> High Altitudes/Hypoexmia (less O2 --> impair gastric defenses)
> Harsh Acids/Bases ingestion
> STRESS
-Path: Mucosal inflammation --> Atrophy (Hypochlorhydria --> Hypergastrinemia) and Intestinal Metaplasia
-Sx:
> Epigastric Pain
> Nausea
> Vomiting
-Dx:
> Biopsy: LYMPHOCYTES/PLASMA CELLS
-Prog: Increased risk of Gastric Cancer
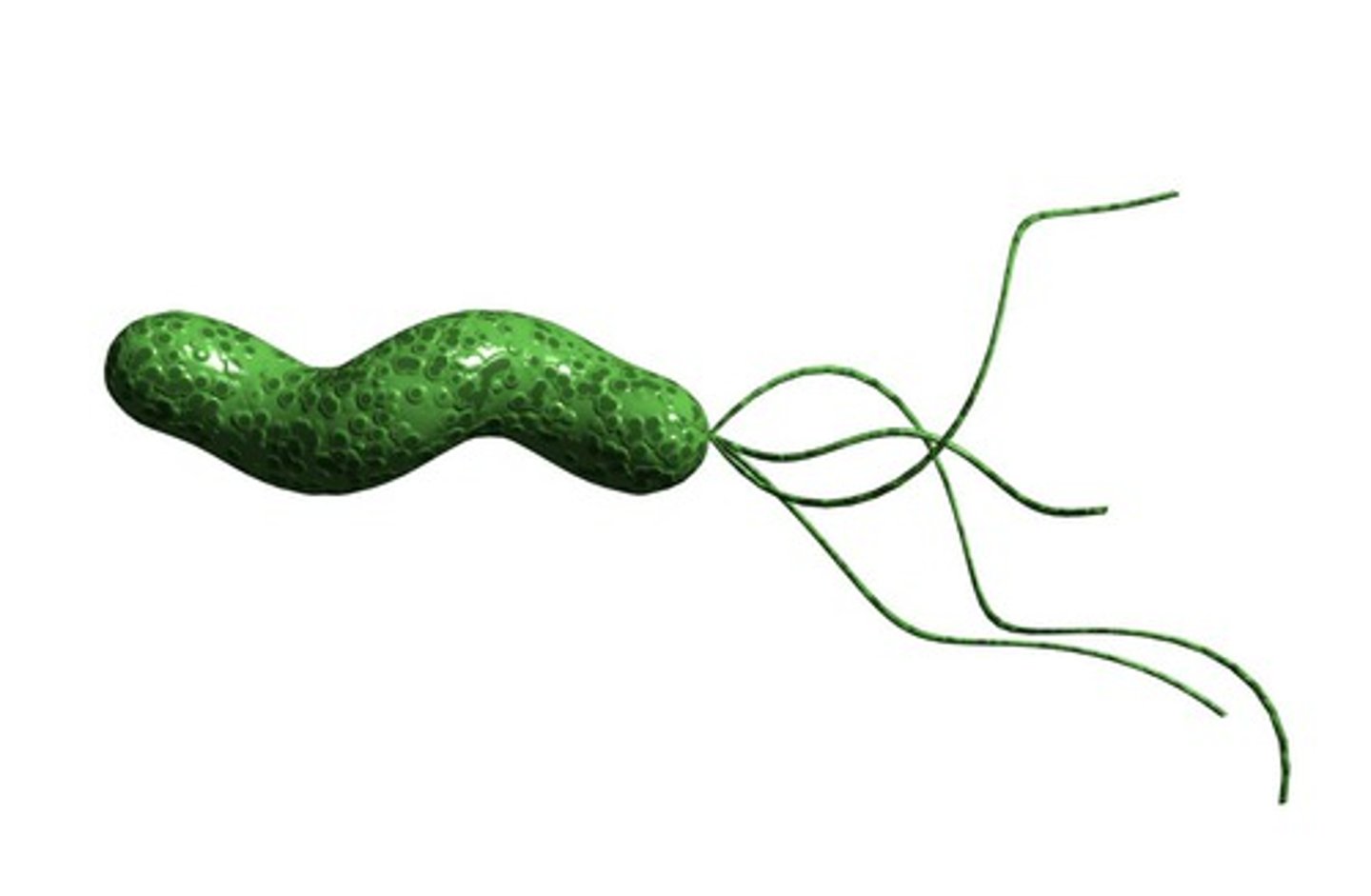
Helicobacter pylori
Identify Causative Organism:
Small gram(-), Comma-shaped, curved, spiral rod
-Hx:
> Acute Gastritis
> MCC = Chronic Gastritis (TYPE B)
> Peptic Ulcers
-Path:
> Lives in antrum and locally destroys the mucus layer of gastric foveolar cells --> mucosa vulnerable to injury by acid
> Usually presents as antral gastritis w/ increased acid produciton ==> Stomach or Duodenal Ulcers
-Dx:
> UREASE (+) (increases Stomach pH by hydrolyxing urea to produce ammonia --> protects bacteria from stomach acid); Increased pH ==> Gastrin Release --> Increased Acid by Parietal Cells ==> INJURY
> Urea Breath Test
> Stool Antigen Test
-Tx: PPIs & Abx (Use breath test/stool antigen test to confirm eradication)
-Prog:
> MALT Lymphoma
> Gastric Adenocarincoma (Infex may extend from antrum to fundus/body --> less Acid and Too much Gastrin --> Atrophic Gastritis/Intestinal Metaplasia)
Autoimmune (Atrophic) Gastritis
Define Condition:
Autoimmune destruction of gastric parietal cells & Chief Cells (fundus & body)
-Hx:
> MC in WOMEN
> A/w HLA-DR Antigens
-Path:
> AutoAbs (T-Cell mediated) destruction to parietal cells & IF
> Destroyed parietal cells (Fundus/Body - Spares Antrum) --> Less acid secretion --> MORE GASTRIN SECRETION ==> Neuroendocrine Hyperplasia & Possible Carcinoid Tumors
> Destroyed Chief Cells --> Less Pepsinogen
-Dx:
> Biopsy: (LOOKS LIKE ANTRUM - No Oxyntic Mucosa)
>> Lymphocytes & Plasma Cells
>> Enterochromaffin-like Cell Hyperplasia ==> Carcinoid Tumor
>> Atrophic-appearing mucosa
>> Intestinal Metaplasia
-Tx:
-Prog:
> Pernicious Anemia (Vit B12 deficiency)
> Increased risk of Gastric Adenocarcinoma
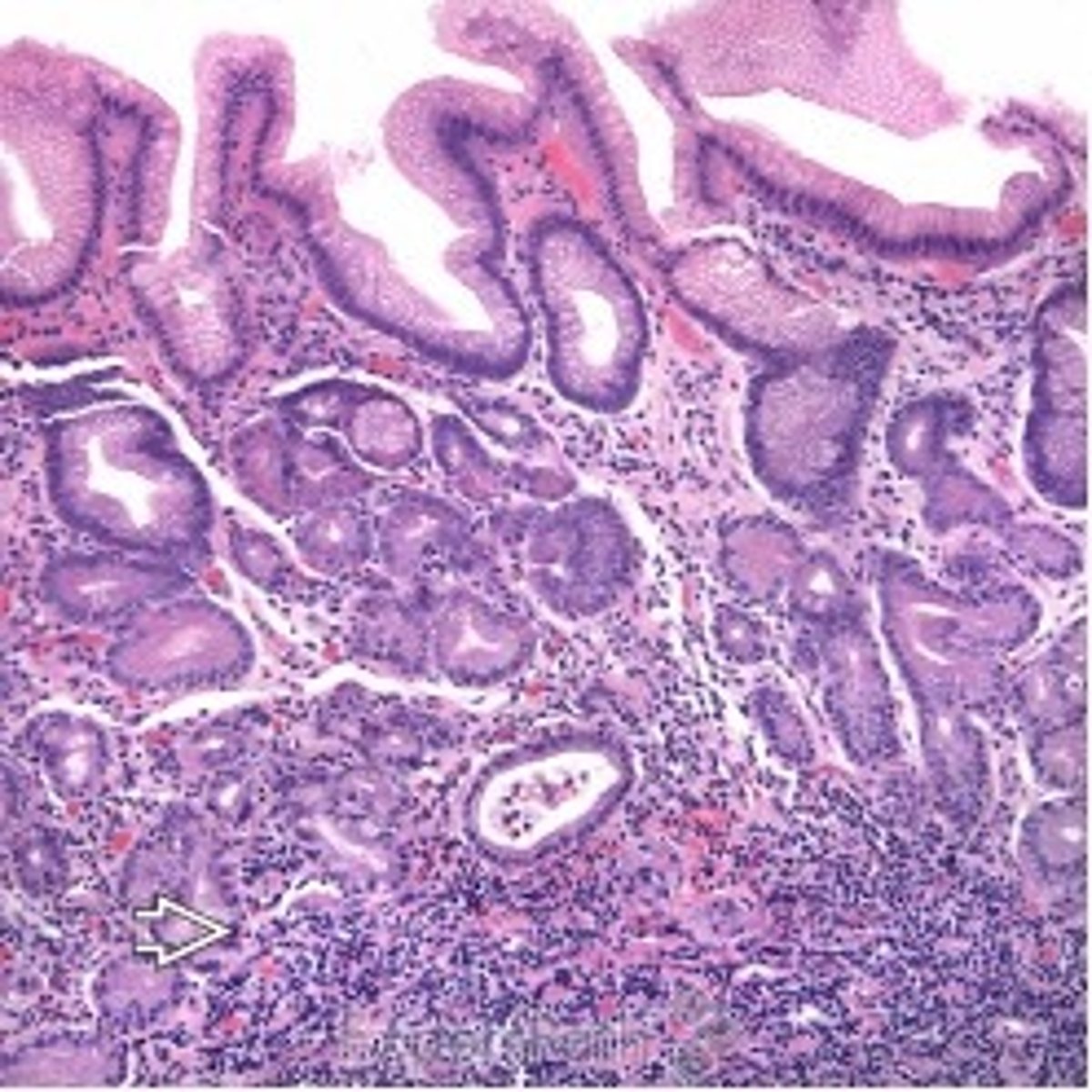
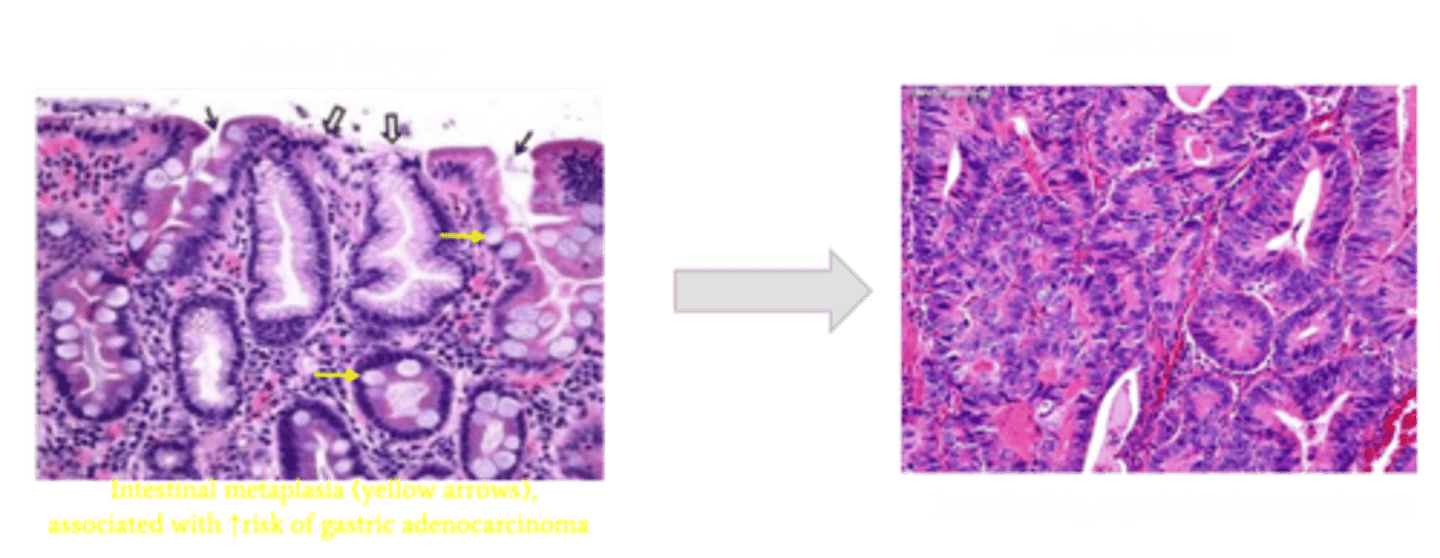
Intestinal Metaplasia
Define Complication of Chronic Gastritis:
Precursor lesion to intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma
-Hx:
-Path: Chronic inflammation can also expose the gastric epithelium to constant regenerative change which can render it vulnerable to genetic alterations and then cancer
DUODENAL Peptic Ulcer Disease (Acid-Induced Tissue Injury)
Define Complication of Chronic Gastritis:
Solitary Ulcer in Duodenum
-Hx:
> MCC = H. pylori
> Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (gastrinoma --> More acid secretion)
> Smoking
> Meckel Diverticulum (congenital outpouching of the small intestine --> Heterotropic gastric tissue secretes acid, aka "Gastric Heterotopia")
-Sx:
> Epigastric pain (worse 1-3 hrs postprandial, may radiate to back, worse at night on empty stomach - relieved by antacid/food since meal stimulates bicarb)
-PE:
-Dx:
> Endoscopy
>> "Cookie-Cutter" Defects in mucosa or extending into submucosa/deeper
> Biopsy
>> Hypertrophy of Brunner glands
-Tx: Eradicate H pylori via Abx & PPIs to reduce acid
-Prog:
> BLEEDING if ulcers are POSTERIOR (ruptures gastroduodenal arteries); MOST are Anterior
> Repair/Fibrosis --> Strictures --> Obstruction
> Pancreatitis
> Perforation
GASTRIC Peptic Ulcer Disease (Acid-Induced Tissue Injury)
Define Complication of Chronic Gastritis:
Solitary Ulcer in stomach
-Hx:
> MCC = H. pylori
> NSAIDs
> Smoking
> Meckel Diverticulum (congenital outpouching of the small intestine --> Heterotropic gastric tissue secretes acid, aka "Gastric Heterotopia")
-Sx:
> Epigastric pain IMMEDIATELY AFTER MEALS (Acid secretion)
-PE:
> Weight Loss from Eating Aversion (to avoid pain from eating)
-Dx:
> Endoscopy: "Cookie-Cutter" Defects in mucosa or extending into submucosa/deeper
> Biopsy: Ulcer located on lesser curvature of antrum
-Tx: Eradicate H pylori via Abx & PPIs to reduce acid
-Prog:
> Bleeding if ruptures left gastric artery
> Repair/Fibrosis --> Strictures --> Obstruction
> Mimics gastric adenocarcinoma (Do Biopsy of margins to rule out)
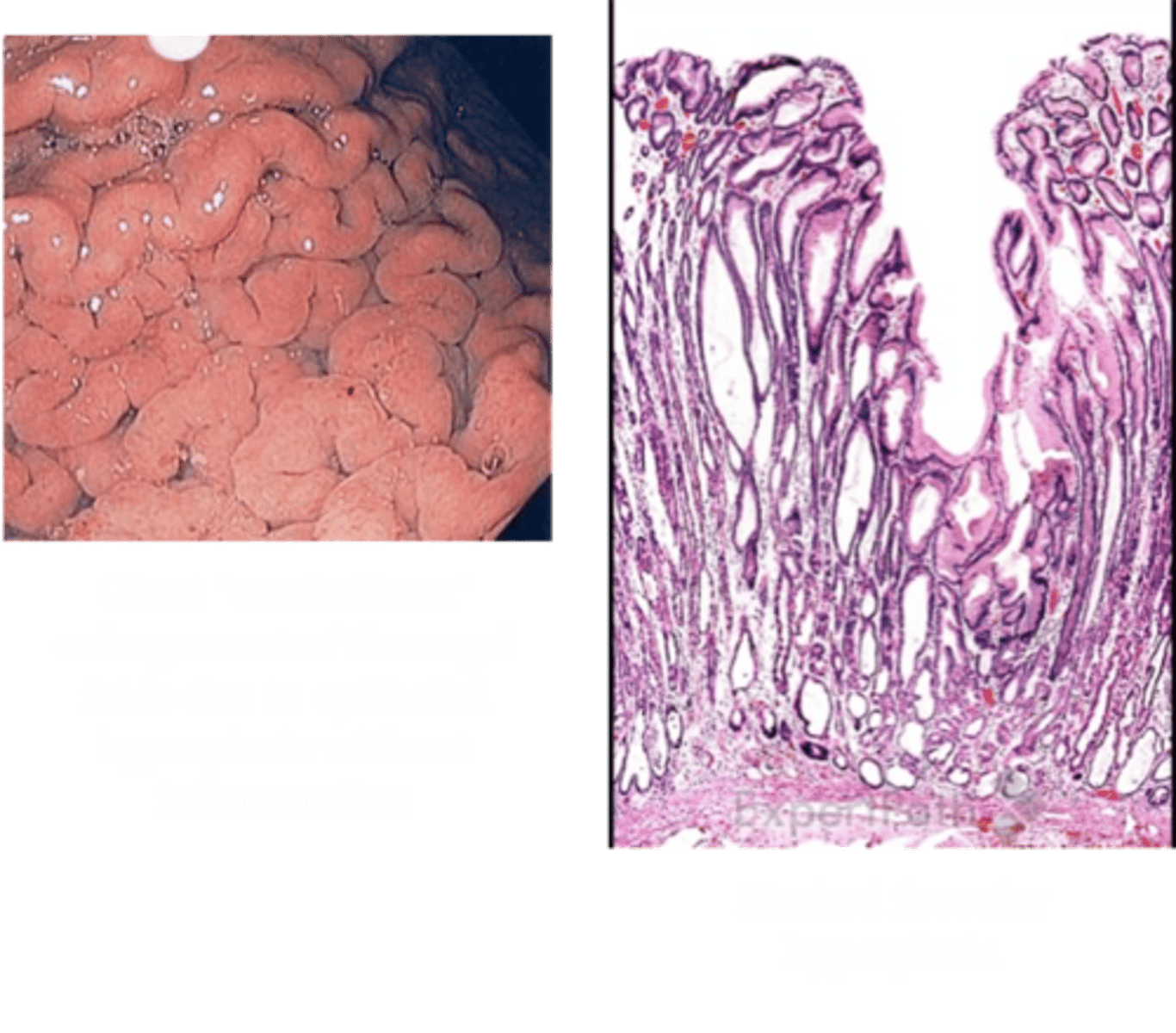
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES)
Define Condition:
(info)
-Hx:
> Duodenal/Pancreatic Islet Cell Tumor (Gastrinoma)
> MEN1 = Pancreatic Gastrinomas
-Path:
> HYPERPLASIA OF PARIETAL CELLS & Large Gastric Folds + PUD
> Multiple ulcers in the stomach, duodenum, and even jejunum
-Sx:
> GERD Like
>> Heartburn
>> Dysphagia
>> Regurgitation of Sour-tasting gastric contents
>> Asthma-like Sx (Aspiration of acid in trachea --> Coughing, Wheezing, Pneumonia)
>> Retrosternal Chest Pain
> PUD Like = Epigastric Pain around Meals
> Diarrhea (More acidity in duodenum --> Less pancreatic digestive enzymes ==> Fat malabsorption)
-Dx:
> Gross: Enlarged fundic mucosal folds with cerebriform pattern
> Biopsy: Hyperplasia primarily of parietal cells in fundic glands
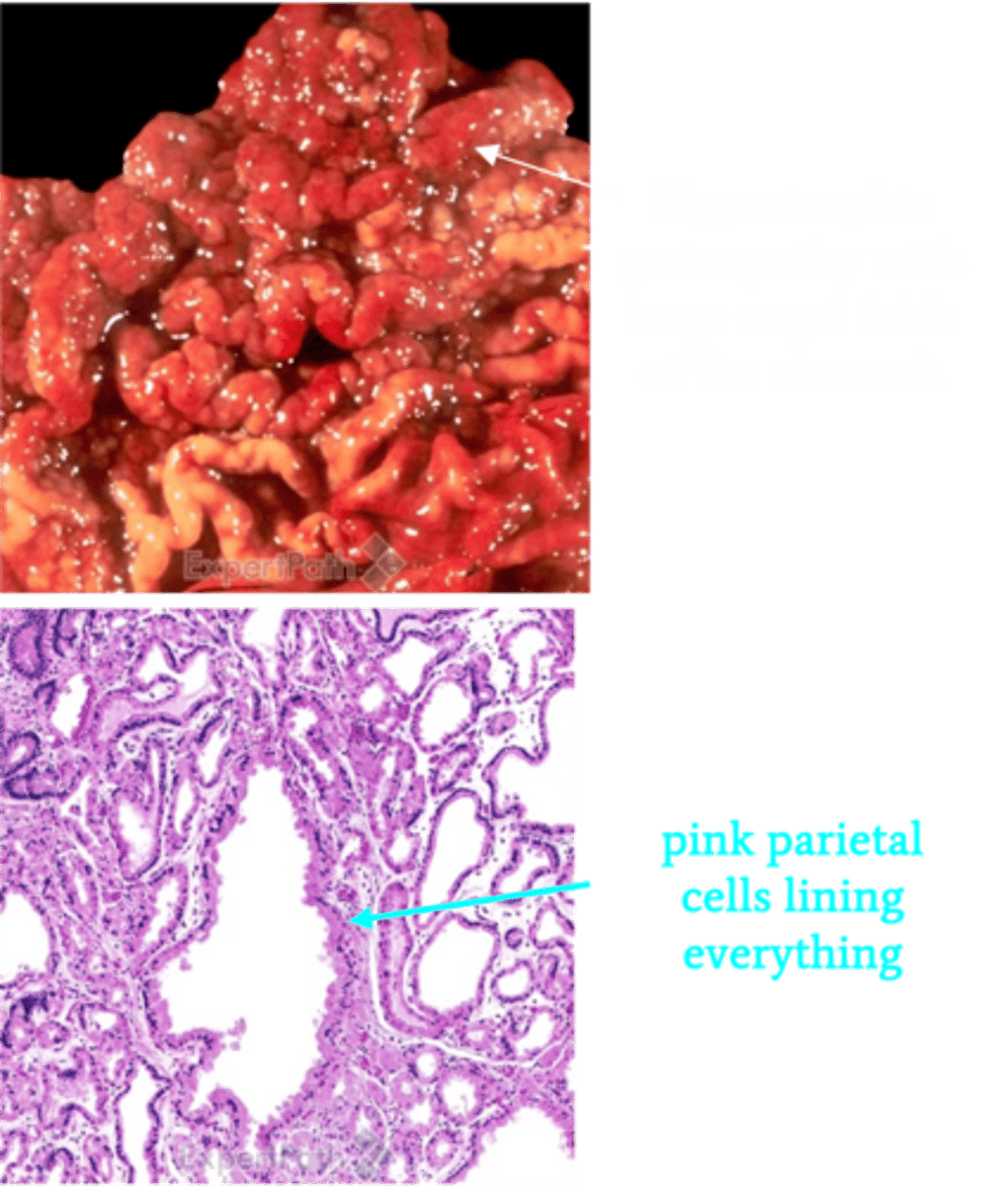
Ménétrier Disease
Define Condition:
Hypertrophic gastropathy secondary to hyperplasia of mucus-producing cells in the stomach
-Hx:
> Excessive secretion of TGF-Alpha
> MEN Age 30-60 y/o
-Path:
> Increased mucin production --> leads to malabsorption of nutrients, electrolytes, and vitamins in the small bowel and protein loss (hypoproteinemic hypertrophic gastropathy)
> Little to no acid production
-Sx:
> Diarrhea
> Abdominal Pain
> Nausea
> Emesis
-PE:
> Anorexia
> Edema (d/t protein loss)
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> Low Albumin
>> Increased TGF-Alpha
> Endoscopy: Giant rugal folds in the body and fundus, but the antrum is generally spared
> Biopsy: DIFFUSE HYPERPLASIA OF FOVEOLAR EPITHELIUM of the body and fundus and atrophy of parietal cells
Stress-Related Mucosal Disease
Define Condition:
Shallow erosions caused by superficial epithelial damage, or deeper lesions that penetrate the depth of the mucosa
-Hx: Hospitalized Pts
> Severe Trauma
> Shock
> Sepsis
-Path:
> Healing with complete re-epithelialization occurs days or weeks after the inciting factors are removed without scarring
> D/t LOCAL ISCHEMIA
> ANYWHERE in stomach (often multiple)
-Sx:
> Asx
> Gnawing/Burning Epigastric distress
> N/V
-PE:
> Hematemesis
> Melena
-Dx:
> Endoscopy: STRESS ULCERS (Multiple dark brown, shallow erosions)
>> Curling Ulcers (BURNS/trauma --> Hypovolemia --> Ischemia in Proximal Duodenum)
>> Cushing Ulcers (BRAIN Injury --> High ICP --> Vagal Stimulation = ACH ==> H+ Production --> Seen in Stomach, Esophagus or Duodenum)
-Tx:
> Prophyl = PPIs
> Tx Underlying Illness
> Loss of SUPERFICIAL EPITHELIAL LAYERS of mucosa
> Can EXTEND to MUSCULARIS MUCOSAE
> A/w EROSIVE GASTRITIS
> Progress to Ulcer (if breaks through muscularis mucosae)
Describe characteristics of Erosion
> Loss of ALL EPITHELIAL LAYERS (THROUGH SUBMUCOSA)
> Usually FOCAL
> A/w PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD)
> Mainly in Stomach/Duodenum
Describe characteristics of Ulcer