Dual-Credit Econ: Quiz 2
1/263
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
264 Terms
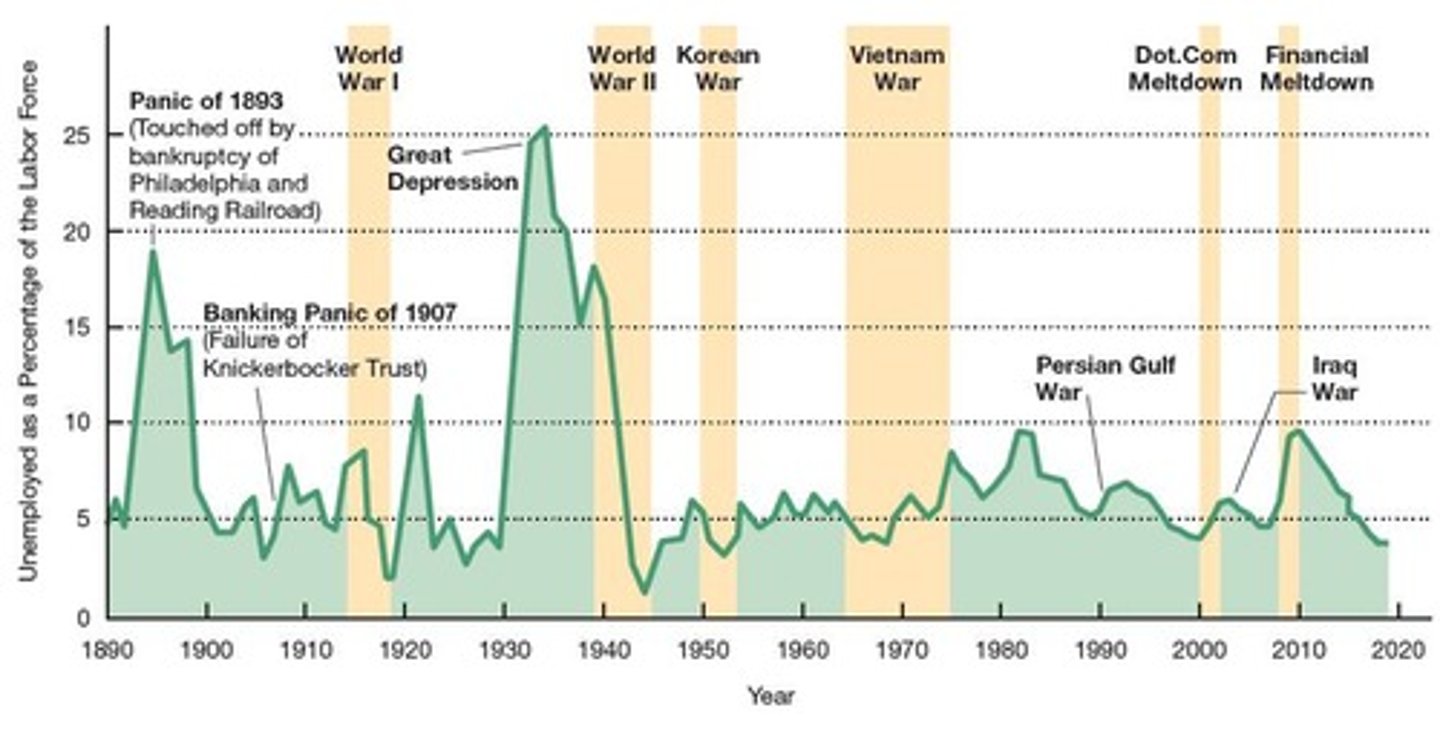
Unemployment rate
The percent of people deemed eligible to be employed but who currently do not have a formal job.
Informal work
Work that is not officially recognized or recorded, with about one out of every five U.S. residents engaging in it. Not accounted for in GDP.
Price indexes
Statistical measures that track changes in the price level of a basket of consumer goods and services.
Nominal interest rates
Interest rates that have not been adjusted for inflation.
Real interest rates
Interest rates that have been adjusted for inflation.
Unemployment
The total number of adults (aged 16 years or older) willing and able to work and who are actively looking for work but have NOT found a job.
Labor force
Individuals aged 16 years or older who either have jobs or who are looking and available for jobs; the number of employed plus the number of unemployed.
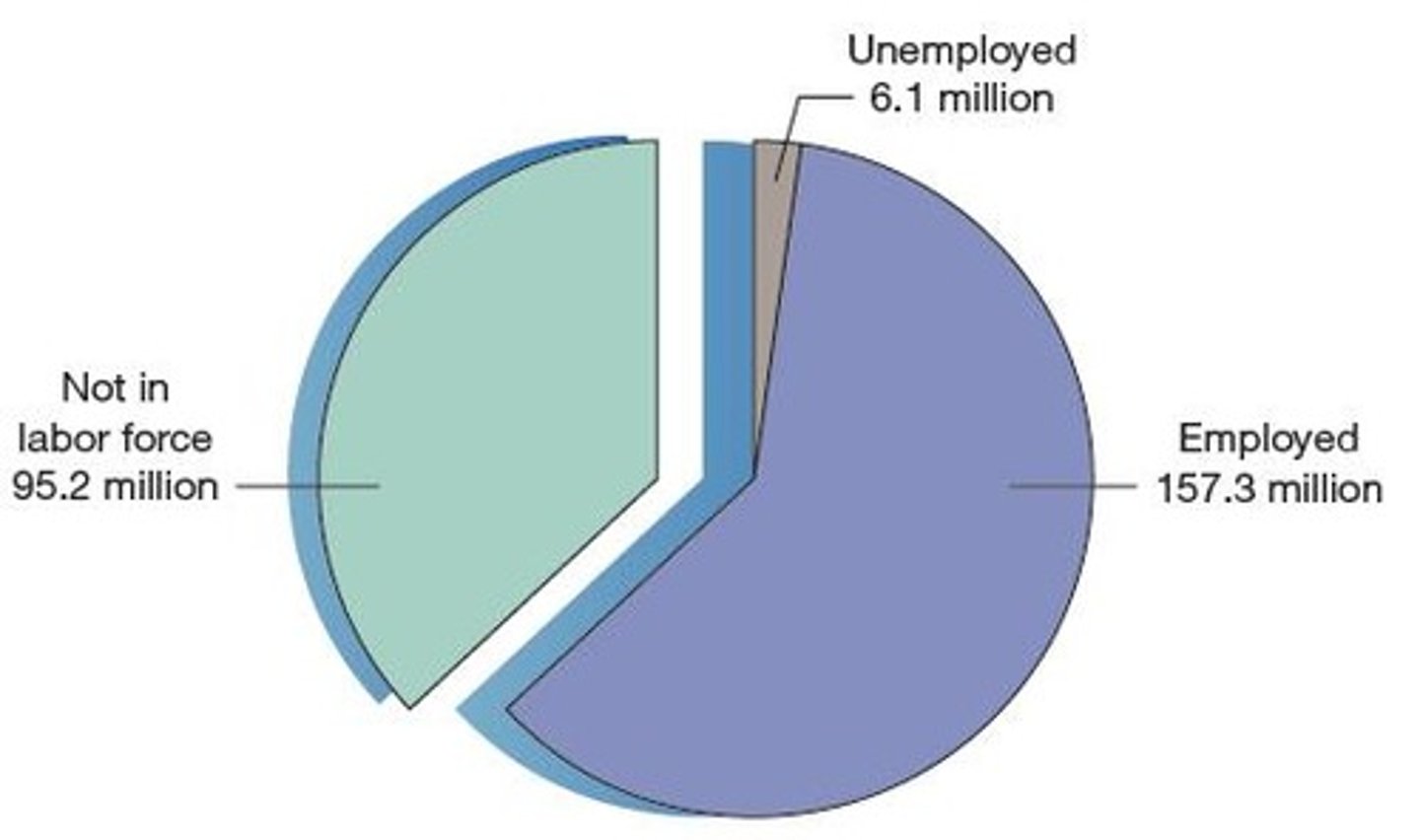
Unemployment rate (definition)
The percentage of the measured labor force that is seeking a job but does not have one.
Stock
The quantity of something, measured at a given point in time—for example, an inventory of goods.
Flow
A quantity measured over time, such as the income you make per year or the number of individuals fired every month.
Job loser
An individual who has lost their job.
Job leaver
An individual who voluntarily leaves their job.
New entrant
An individual who is entering the labor force for the first time.
Work disincentives
Factors that discourage individuals from seeking employment, such as those generated by the Affordable Care Act.
Affordable Care Act
The 2010 national health care law that has been estimated to reduce the number of people seeking jobs by about 200,000 per year.
Macroeconomics
The branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole.
Average price level
A measure of the overall level of prices in the economy.
Total production of goods and services
The total output of an economy, encompassing all goods and services produced.
Reentrant
An individual who has worked a full-time job before but left the labor force and has now reentered it looking for a job.
Duration of unemployment
More than a third of job seekers find work within one month. Approximately another third find employment within a second month. About a sixth are still unemployed after six months. The average duration of unemployment has varied between 10 and 20 weeks since the mid-1960s.
Discouraged workers
Individuals who have stopped looking for a job because they are convinced they will not find a suitable one.
Frictional unemployment
Frictional unemployment results from the fact that workers must search for appropriate job offers. This takes time, so they remain temporarily unemployed.
Structural unemployment
This type of unemployment over lengthy intervals results from skill mismatches with position requirements of employers and from fewer jobs being offered by employers constrained by governmental business regulations and labor market policies.
Cyclical unemployment
Unemployment that results from economic downturns or recessions.
Government labor market policies
Policies that influence how many jobs businesses wish to create, thereby affecting structural unemployment.
Temporary Work
A situation where workers are employed on a short-term basis, which can contribute to structural unemployment problems.
Youth unemployment rates
High rates resulting from companies providing little training or skill-building tasks to young workers.
Full employment
An arbitrary level of unemployment that corresponds to 'normal' friction in the labor market.
Natural rate of unemployment
The unemployment rate estimated to prevail in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium, excluding cyclical unemployment.
Inflation
A sustained increase in the average of all prices of goods and services in an economy.
Deflation
A sustained decrease in the average of all prices of goods and services in an economy.
Purchasing power
The value of money for buying goods and services, which varies with prices and income.
Nominal value
Price expressed in today's dollars.
Real value
Value expressed in purchasing power, adjusted for inflation.
Market basket
A representative bundle of goods and services.
Base year
The point of reference for comparison of prices in other years.
Price index
The cost of today's market basket of goods, expressed as a percentage of the cost of the same market basket during a base year.
Price index formula
Price index = (cost of market basket today / cost of market basket in base year) × 100.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
A real-world price index that measures the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
A real-world price index that measures the average change over time in the selling prices received by domestic producers for their output.
Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Index
A real-world price index that measures the prices paid by consumers for goods and services.
Market basket of goods and services
A typical collection of goods and services used to measure consumer spending.
Short-run leading indicator
An economic indicator that predicts future movements in the economy, used before the Consumer Price Index.
Broadest measure of prices
A measure that reflects both price changes and the public's market responses to those price changes.
Primary inflation indicator
The main measure used by the Federal Reserve to gauge inflation.
Anticipated inflation
The inflation rate that we believe will occur.
Nominal rate of interest
The market rate of interest, expressed in today's dollars.
Real rate of interest
The nominal rate of interest minus the anticipated rate of inflation.
Real interest rate calculation
If nominal interest rate = 5% and expected inflation rate = 3%, then real interest rate = 5% - 3% = 2%.
Average price of a new house in 1968
$25,300.
Average price of a new house today
About $350,000.
Inflation-adjusted price of a new house in 1968
$115,000.
Bias in CPI
The reported value of the CPI fails to reflect changes in the quality-adjusted prices of new products, tending to bias the value of the CPI upward.
Inflation-expectation surveys
Surveys that people respond to by thinking in terms of prices of a small set of items of most immediate importance to them instead of the overall price level.
Bias in inflation expectations
Constraints on the ability of people to consider all relevant aspects of the problem of predicting the relevant inflation rate cause the expectations obtained by polltakers to be biased.
Unanticipated inflation
Inflation that affects creditors negatively while benefiting debtors.
Cost-of-living adjustments (COLAs)
Clauses in contracts that allow for increases in specified nominal values to account for changes in the cost of living.
Repricing cost of inflation
The cost associated with recalculating prices and printing new price lists when there is inflation.
Business fluctuations
The ups and downs in business activity throughout the economy.
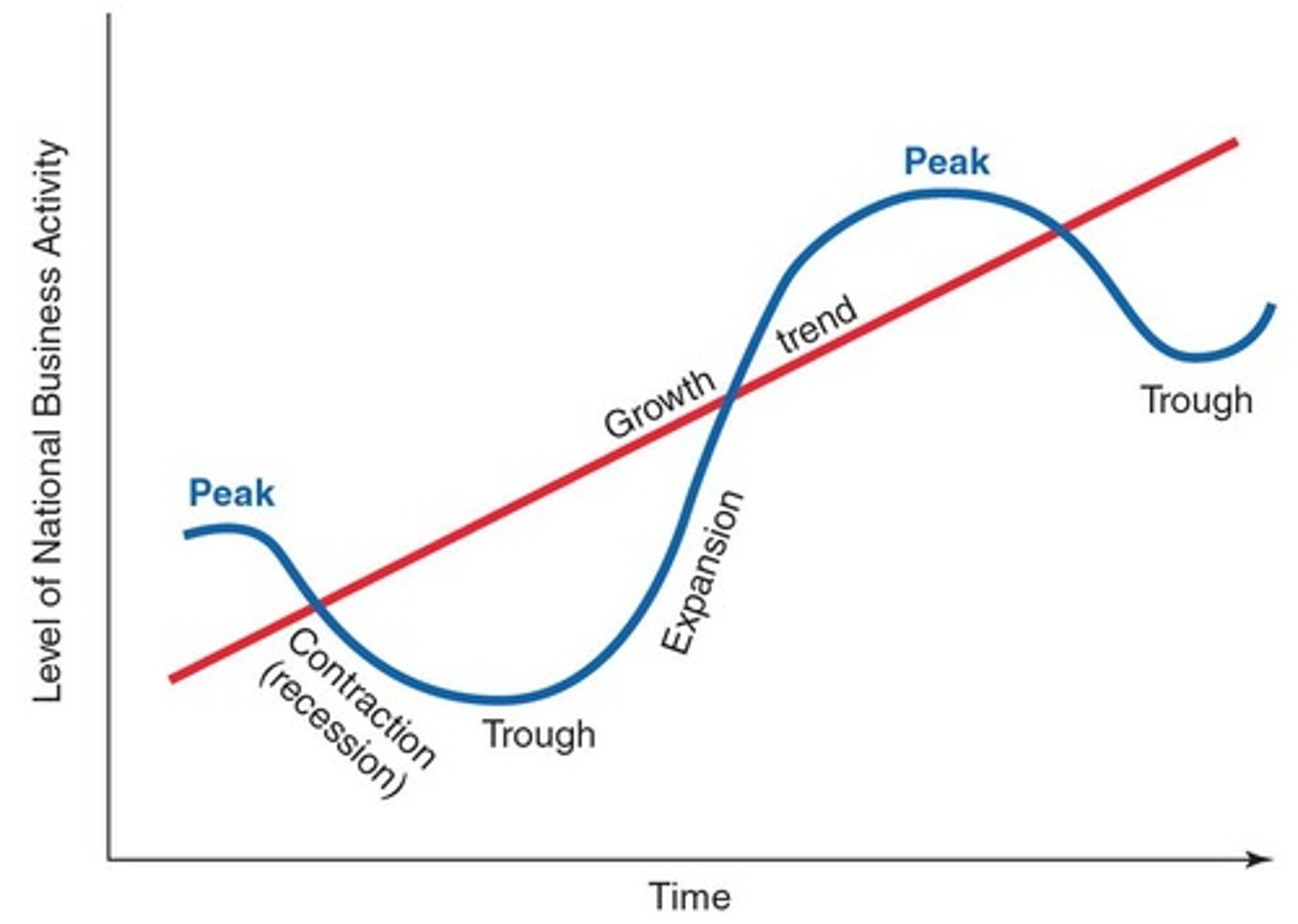
Expansion
A business fluctuation in which the pace of national economic activity is speeding up.
Contraction
A business fluctuation in which the pace of national economic activity is slowing down.
Recession
A period of time during which the rate of growth of business activity is consistently less than its long-term trend or is negative.
Depression
An extremely severe recession.
Leading indicators
Events that have been found to occur before changes in business activity.
Economic downturns
Often follow a reduction in the average workweek, a rise in unemployment insurance claims, a decrease in prices of raw materials, and a drop in the quantity of money circulating.
Google trend indexes
Values reported by Google for specific search terms that predict unemployment rates.
Job search trend index
A trend index value for Google 'job' searchers that better predicts the unemployment rate than other commonly used leading indicators.
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the total number of adults who are willing and able to work and are actively looking for work but have not found a job of the total labor force (unemployed plus employed).
Teen Unemployment Rate
Dropped from approximately 27 percent in 2010 to nearly 13 percent today—the lowest level since 1969.
Informal Work
Work that government statisticians currently do not take into account when assessing whether a person is officially unemployed or part of the labor force.
Informal Work Participation
More than 35 percent of working-age adults engage in some form of informal work in addition to formal jobs.
Labor Force Participation Rate Adjustment
Accounting for informal work would boost the labor force participation rate by about 1.4 percentage points.
Unemployment Rate Adjustment
Accounting for informal work would reduce the unemployment rate by about 0.5 percentage point.
Frictional Unemployment
A type of unemployment that occurs when people are temporarily between jobs.
Structural Unemployment
A type of unemployment that occurs when there is a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the demands of the job market.
Cyclical Unemployment
A type of unemployment that results from economic recessions or downturns.
Natural Rate of Unemployment
Estimated to prevail in the long-run macroeconomic equilibrium.
Price Index Calculation
Multiply 100 by the ratio of the cost of a market basket of goods in the current year to the cost of the same basket in a base year.
CPI
Consumer Price Index, a key price index.
PPI
Producer Price Index, a key price index.
GDP Deflator
A key price index that measures the change in prices of all new, domestically produced, final goods and services in an economy.
PCE Index
Personal Consumption Expenditures Index, a key price index.
Nominal Interest Rate
The market rate expressed in current dollars.
Real Interest Rate
The nominal interest rate minus the expected inflation rate.
Creditors and Inflation
Creditors lose as a result of unanticipated inflation.
Borrowers and Inflation
Borrowers gain as a result of unanticipated inflation.
Business Fluctuations
Increases and decreases in business activity.
Real GDP per Capita
GDP adjusted for population, indicating average income.
Productivity Growth
Increase in output per unit of input used.
Economic Growth Rate
Rate of change in real GDP per capita.
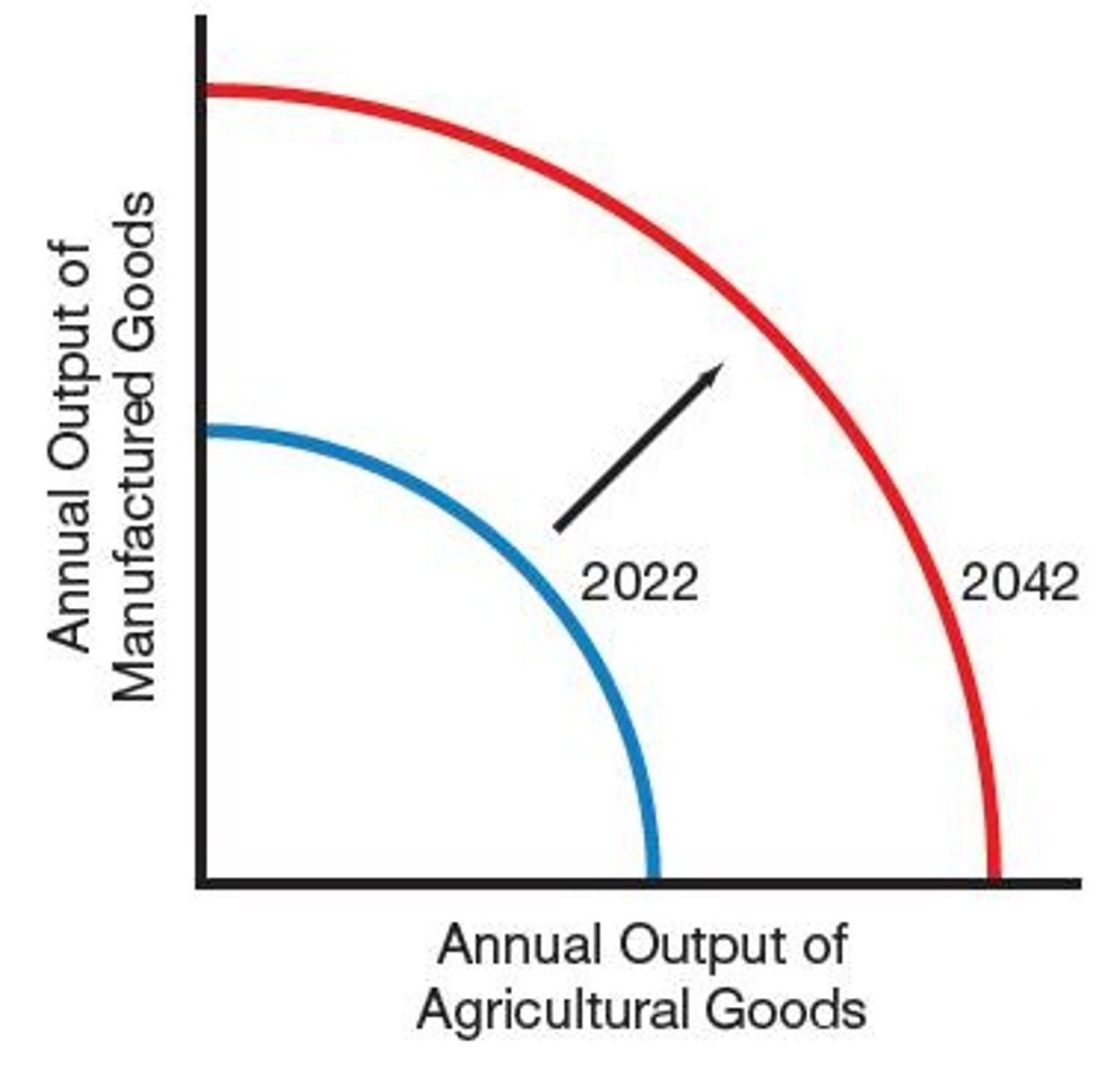
Production Possibilities Curve
Graphical representation of maximum output combinations.
Immigration
Movement of people affecting labor supply and growth.
Property Rights
Legal rights to own and use property.
Economic Development
Process of improving economic well-being and quality of life.
New Technologies
Innovations that enhance productivity and efficiency.
U.S. Economic Growth
Historically positioned in the middle range globally.
Average Annual Growth Rate
Percentage increase in GDP per capita yearly.
Historical Economic Growth
Trends observed in U.S. economic performance over time.
Costs of Economic Growth
Growth may worsen individual well-being according to some psychologists, increased traffic and overcrowding due to economic growth, degradation of natural resources from industrial activities.
Benefits of Economic Growth
reduction in illiteracy, reduction in poverty, improved health and longer lives, political stability