Topic 2 - Organisation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
How is an organism organised?
Cells are the building blocks and make up all living organisms.
A group of the same or similar cells that work together is a tissue.
A group of different tissues that work together is an organ.
A group of organs that work together is an organ system.
Organ systems work together to make entire organisms.
What are 3 types of tissue?
Muscular tissue - Allows food to be churned around the stomach.
Glandular tissue - Produces digestive juices.
Epithelial tissue - Covers the outside and the inside of the stomach.
What is a catalyst?
A substance which increases the speed of a reaction, without being changed or used up in the reaction.
What is an enzyme?
They are catalysts produced by living things. They reduce the need for high temperature and we only have enzymes to speed up the useful chemical reactions.
What is the lock and key model?
An enzyme has an active sight which is a unique shape that fits onto the substance involved in a reaction. They only work if the substrate matches the active sight. Then the enzyme will break down the substrate and release it from the active sight.
Substrate - Protein
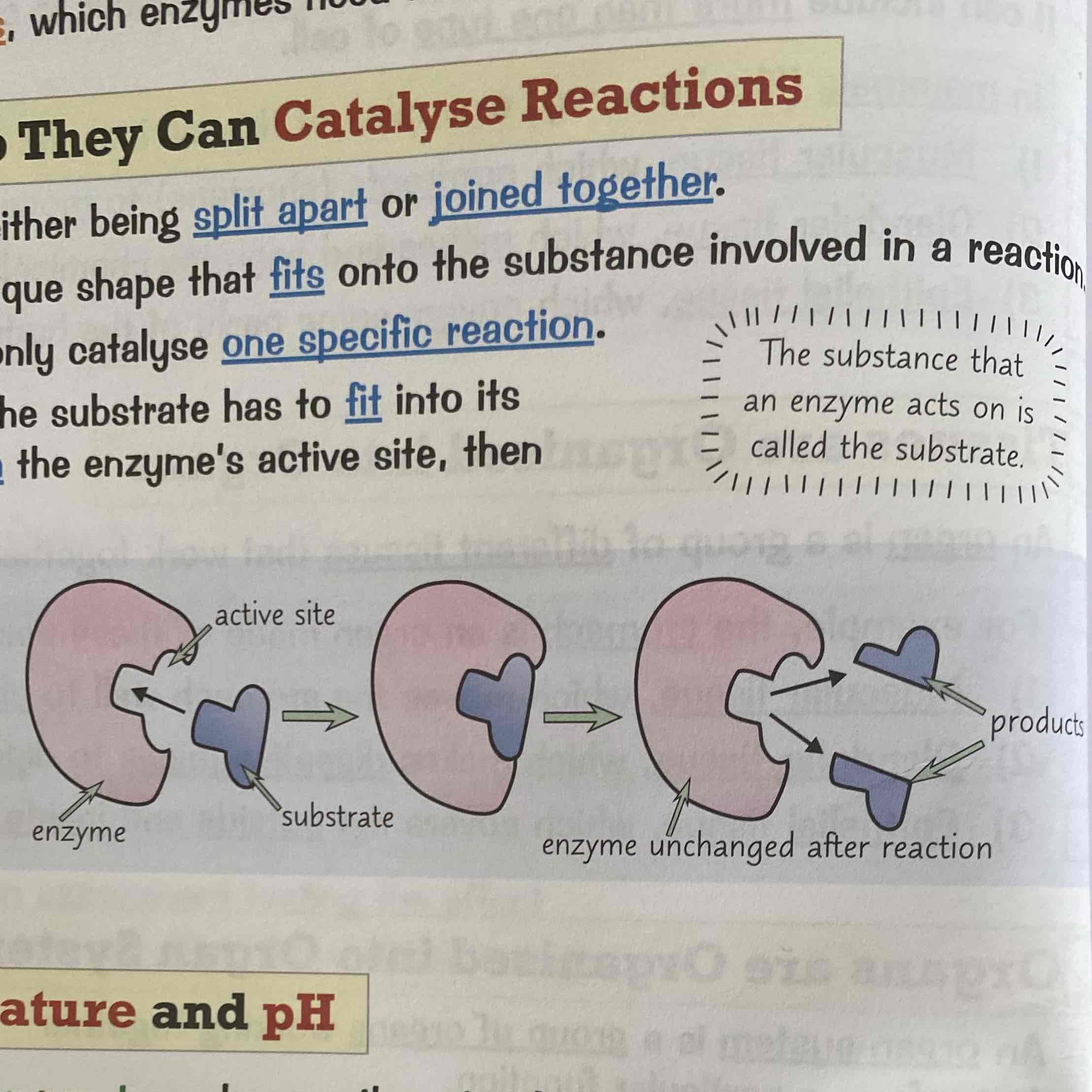
How does temperature and pH affect enzymes?
A higher temperature will increase the rate but if it gets too hot then the bonds holding the enzyme together break changing the shape of the active sight. The enzyme is then said to be denatured.
If the pH is too high or low then it can also change the shape of the enzyme making it denatured.
How do you calculate the rate of reaction?
Rate = 1000/Time
What are 3 enzymes and what do they do?
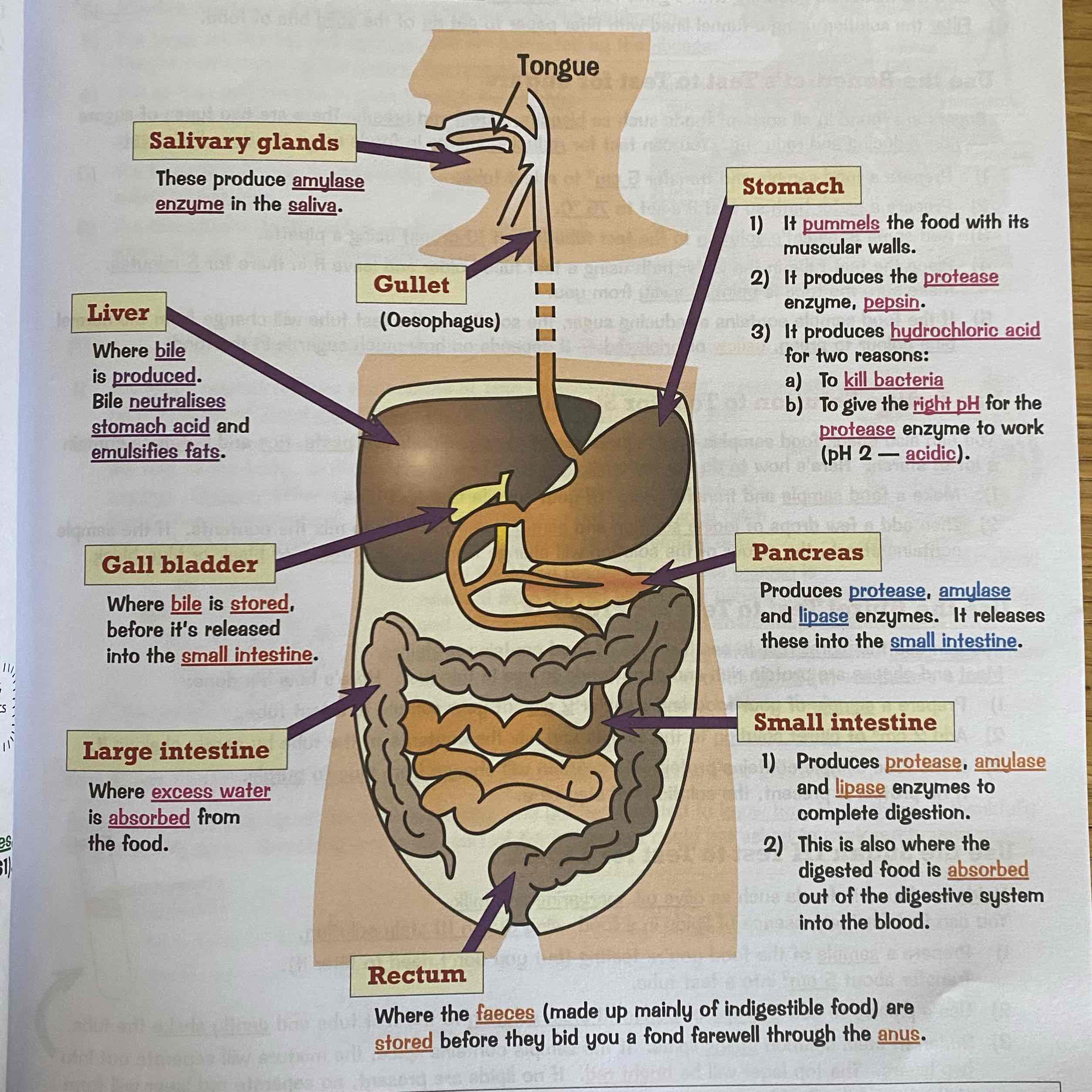
Amylase - Breaks down starch into simple sugars - Made in the salivary glands, pancreas and small intestine
Protease - Breaks down proteins into amino acids - Made in the stomach, pancreas and small intestine.
Lipase - Breaks down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids - Made in the pancreas and small intestine.
What is bile?
Bile is a alkaline fluid produced in the liver which neutralises hydrochloric acid so it can work with the enzymes in the small intestine. It also emulsifies fats so it digests faster.
Describe the digestive system?
See image:
How can you test for foods?
Sugars - Add Benedict’s Solution - Blue to Green, yellow or red (Depends in how much sugar)
Starch - Iodine Solution - Orange to Black/Blue
Proteins - Biuret Solution - Blue to Purple
Lipids - Sudan III Solution- Normal to Red Layer
Describe the Respiratory System?
See Image:

Describe the Circulatory System?
See Image

What are the Pacemaker cells?
The pacemaker cells are located on the right atrium wall and produce a small electric impulse which causes surrounding muscle cells to contract. This is your resting heart rate.
An artificial pacemaker can be used if the patient had an irregular heartbeat.
What are the coronary arteries?
Arteries that give the heart its own supply of oxygenated blood. They branch off for the aorta.
What is the function of the arteries?
The carry blood away from the heart at high pressure meaning the walls are strong and elastic. They have elastic fibres and a thick wall.
Describe the capillaries?
They carry blood very close to every cell to exchange substances. They have permeable, one cell thick walls so they can supply food and oxygen easily.
Describe the veins:
Capillaries join up to form veins. The blood is at low pressure so the walls aren’t that thick. Large lumen for greater blood flow and valves so blood flows in the right direction.
What are the 4 main things that the blood carries?
Red blood cells - To carry Oxygen - Biconcave disc - No nucleus - Haemoglobin to hold oxygen.
White blood cells - Engulf unwelcome microorganisms - Produce proteins
Platelets - Small fragments of cells - No nucleus- Help clot wounds
Plasma - They carry everything else - All above, Nutrients, Carbon Dioxide, Urea, Hormones and proteins.
How does cardiovascular disease happen?
Its the term used to describe heart or blood vessel diseases (CHD).
What are 2 ways we can prevent things like Coronary Heart Disease?
Stents
Statings
What are stents and what do they do?
They are tubes inserted inside arteries. They push the fatty material into the wall and open up space in the artery again.
They lower the future risk of heart attack and are effective for a long time.
However there is a risk if the stent is infected or the operation goes wrong.
What are statins and how do they work?
They are a drug that reduces the amount of cholesterol present in your blood stream so fatty deposits don’t start forming.
They reduce heart risk and may prevent other diseases.
They can cause negative side effects and you must take the drug for a long time.
What are some plant tissues?
Epidermal Tissue - Covers the whole plant.
Meristem Tissue - Found at the tips of roots and can differentiate into lots of cells.
Xylem and Phloem - They transport water, food and ions around the plant.
Describe the diagram of a leaf?
See Image:

What is Translocation?
The phloem is a column of elongated living cells with holes to allow cell sap to flow through. They transport food from the leaves in both directions of the tube. This process is called translocation.
What is Transpiration?
It is the loss of water from evaporation and diffusion. As it leave a shortage water is drawn up from the rest if the plant through the xylem to replace it. This leads to a constant transpiration stream (The movement of water from the roots to the leaves).
What 4 things affect transpiration?
Light Intensity - The brighter, the greater rate
Temperature- The warmer, the greater rate
Air Flow - The better, the greater rate
Humidity- The drier, the greater rate