How markets work 1.2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
underlying assumptions of rational economic decision making
consumers aim to maximise utility- utility is the satisfaction gained from consuming a product
Firms aim to profit maximise- to keep shareholders happy
Governments aim to maximise social welfare- governments are voted in by the public and work for the public
Demand
the ability and willingness to buy a particular good at a given price and at a given moment
movements and shifts along the demand curve
change in price or qty of the good
conditions of demand
population- demand would increase
income- if income increases demand increase as they can afford to buy more
related goods- complements or substitutes
advertising
seasons
taste
Diminishing marginal utility
the satisfaction derived from the consumption of an additional unit of good will decrease as more of a good is consumed
demand slopes downwards, if more of a good is consumed, there is less satisfaction derived from the good, consumers are less willing to pay high prices at high quantities since they are gaining less satisfaction
elasticity of demand
An attempt to measure the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in price
PED formular
% change in qty demanded/ % change in price
value of unitary
PED=1
a change in price does not affect total revenue
value of relative elastic PED
PED>1
relatively inelastic PED
PED<1
perfectly elastic PED
infinity
A decrease in price leads to an increase in revenue
An increase in price leads to a decrease in revenue
perfectly inelastic PED
0
A decrease in price leads to a decrease in revenue
An increase in price leads to an increase in revenue
Factors affecting PED
substitutes
time - st, lt
necessity
income
addictive
Significance of PED
Determine the effects of the imposition of direct taxes and subsidies
more elastic demand is = the lower the incidence of tax on the consumer
more inelastic demand= tax is passed onto consumer, higher tax revenue to government
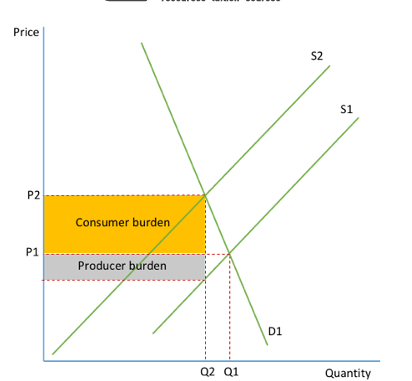
inelastic demand on diagram (subsidy)
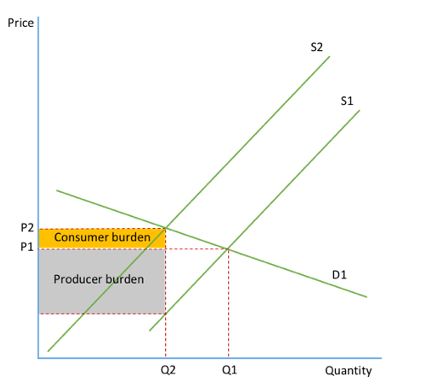
elastic demand on diagram (subsidy)
inelastic demand diagram (tax)
Shift from S1 to S2 is a result of the imposition of indirect tax
Income elasticity of demand
the responsiveness of demand to a change in income
YED formular
% change in qty demanded/ % change in income
value of an inferior good
YED<0
a rise in income will lead to a fall in demand for the good
Value of a normal good
YED>0
a ride in income will lead to a rise in demand for good
value of luxury good
YED>1
Significance of YED
Important for businesses to know if their sales will be affected by changes in the income for the population
Impact the of good that a firm produces
Cross elasticity of demand
the responsiveness of demand for one good to a change in price for another
% change in qty demanded of A/ % change in price of B
Substitutes
XED>0
An increase in the price of good B will increase demand for good A
Complementary
XED<0
An increase in the price of good B will decrease demand for good A
Unrelated goods
XED=0
change in the price of good B has no impact on good A
Significance of XED
Firms need to be aware on their competition and how changes by other firms will impact them
Supply
The willingness to provide a good or service at a particular price at a given moment
Movement of supply
caused by a change in the price of a good
Shift in supply
The amount of goods being supplied
Conditions of supply
cost of production
Price of other goods
Weather
Technology
subsidies ad tax
Why is supply upward sloping
If prices are higher, firms will increase production to take advantage of the high profits they can make
Higher prices will encourage new firms to enter
Price elasticity of supply
The responsiveness of supply to a change in price of the good
% change in qty supplied/ % change in price
Factors affecting PES
Time
Stocks
Availability of factors of production
Availability of substitutes
Price determinism
The equilibrium point is the point in which there are no forces bringing about change
supply is equal to demand
Excess demand
if price is set below equilibrium there is excess demand
will lead to a contraction in demand
Excess Supply
If price is set higher than the equilibrium there is excess supply
firms have unsold goods
Price mechanism
Allocates resources
Price is determined by the interactions of demand and supply
Adam smith described the invisible hand
Rationing
the price system is a way of rationing goods because when price increases some people may not be able to afford the product
limiting resources for those who can afford them and value them the most highly
Signalling
Where resources should be used
Price indicates to suppliers and consumers that market conditions have changed so they should change the qty bought and sold
Incentive
Acts as an incentive for people to work hard
more money more goods they can buy
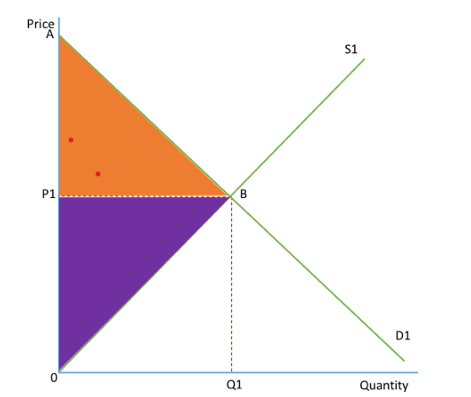
Consumer surplus
the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay
(top part of diagram)
Producer surplus
The difference between the price that the supplier is willing to produce their product at and the price they actually produce at
( bottom part of diagram)
CS and PS diagram
show economic gain from buying and selling of goods
Indirect taxes
tax on expenditure where the person who is ultimately charged the tax is not the person responsible for paying the sum to the government
ad valorem
specific tax
Ad valorem
where the tax payable increases in proportion to the good
VAT
Specific tax
where an amount is added to the price
excise duties
Impacts of tax
increase in the cost of production
consumer sees higher prices and sufferes from a tax burden
producer sees a rise in costs and a fall in output
CB and PB of tax
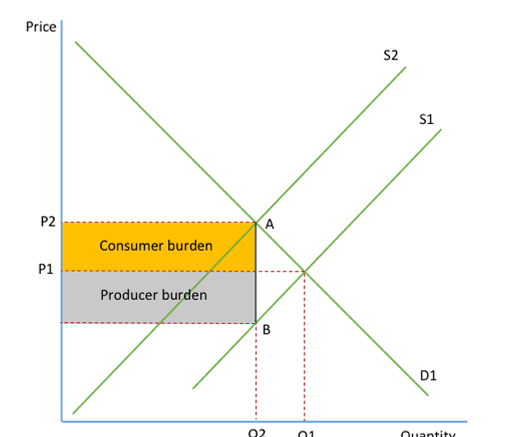
CB and PB ad valorem
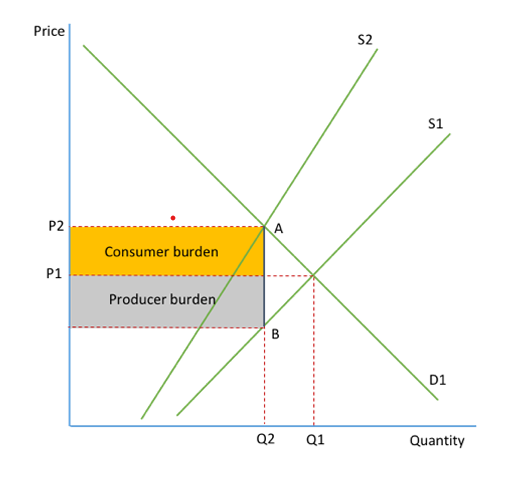
Incidence of tax
the tax burden on the tax payer
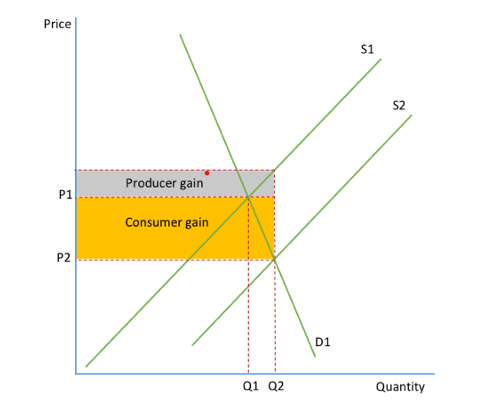
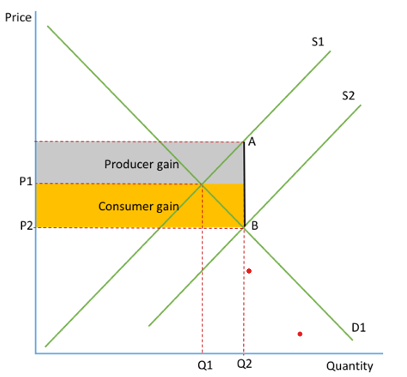
Subsidies
A grant given by the government and is the opposite of a tax
An extra payment to encourage production/ consumption of a good/ service
Subsidy on a diagram
increase in supply
producer sees a fall in production costs
rise in output
total shaded area is gov spending
consumer behaviour
aim to maximise utility
companies aim to maximise profit
governments aim to maximise welfare of citizens
influences of other people
influence of habitual behaviour
consumer weakness at computation- consumers arent willing or able to make comaprisons between prices and so they will buy more expensive goods than needed