COMM 1ST TERM (2ND SEM)
4.2(6)Studied by 80 people
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
coverage: 1.1 -1.8 ( I did not include 1.6 since wala namn mga important terms don)
Last updated 7:05 AM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
DEFINING THE COMMUNICATION
“sending” or “receiving” AND “sharing”
2
New cards
is the art and process of creating and sharing ideas.
COMMUNICATION
3
New cards
imparting or exchange of thoughts, opinions, or information by speech, writing, or signs.
COMMUNICATION
4
New cards
ACCORDING TO KINCAID AND SCHRAMM:
* Not all communication has to be human communication.
\
* Communication does not always require two or more participants.
\
* Communication can take place over large distances of space and time.
\
* Not all communication takes place in words.
\
* Not all participants in a communication process have to be present at the same time
\
* Thinking is a form of communication.
\
* Communication does not always require two or more participants.
\
* Communication can take place over large distances of space and time.
\
* Not all communication takes place in words.
\
* Not all participants in a communication process have to be present at the same time
\
* Thinking is a form of communication.
5
New cards
Communication as a process and its four attributes:
* SYSTEMATIC
* DYNAMIC
* MEANING IS PERSONALLY CONSTRUCTED
* SYMBOLIC INTERACTION
\
* DYNAMIC
* MEANING IS PERSONALLY CONSTRUCTED
* SYMBOLIC INTERACTION
\
6
New cards
Consist of group of elements which interact to influence each other and the system as a whole
SYSTEMATIC
7
New cards
On-going; ever-changing, with no clear beginnings and endings
DYNAMIC
8
New cards
Meanings are in people, not in words.
MEANING IS PERSONALLY CONSTRUCTED
9
New cards
Language is a form of symbol. “The medium shapes the message “
SYMBOLIC INTERACTION
10
New cards
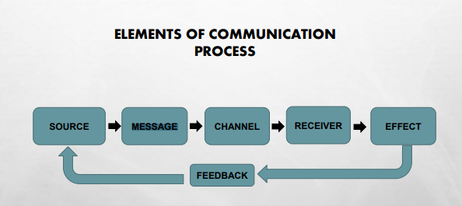
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION PROCESS
\
11
New cards
a person who convey idea or information
Source/Sender
12
New cards
a person or group of persons at the other end of the communication process (Berlo, 1961)
Receiver
13
New cards
➢idea, purpose, or intention that has been translated into code or systematic set of symbols (Berlo, 1961)
Message
14
New cards
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION PROCESS 3 Factors:
* message code
* message content
* message treatment
* message content
* message treatment
15
New cards
any group of symbols that can be structured in a way that is meaningful to some person
message code
16
New cards
the material in the message selected by the source to express his/her purpose
message content –
17
New cards
decisions that the communication source makes in selecting and arranging both code and content
message treatment –
18
New cards
➢ The medium through which the message travels is called as channel
Channel/Medium
19
New cards
Channel/Medium is determined by:
* availability
* money
* source preferences
* money
* source preferences
20
New cards
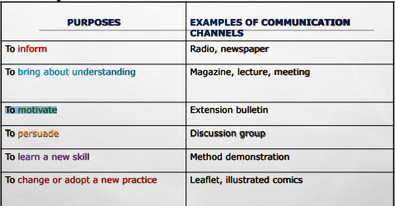
Purposes of Communication:
21
New cards
the outcome of a communication or the response of the receiver to the message of the source.
Effect
22
New cards
obvious or visible; responses include non-verbal cues (nodding of head, signing of a contract).
Overt Effect –
23
New cards
non-observable but sometimes they are the most important.
Covert Effect –
24
New cards
* communication response is feedback to both source and receiver.
* Feedback could take form of non-verbal or verbal cues.
* Feedback could take form of non-verbal or verbal cues.
Feedback
25
New cards
Types of Communication
1. Verbal communication
2. Non Verbal communication
26
New cards
communication takes place through face-to-face conversations, group discussions, counseling, interview, radio, television, calls, memos, letters, reports, notes, email etc.
Verbal communication
27
New cards
2 Major Forms of Verbal Communication:
* Written
* Oral
* Oral
28
New cards
includes traditional pen and paper, letters and documents, typed electronic documents, e-mails, text chats, SMS and anything else conveyed through written symbols such as language
Written Communication
29
New cards
either face-to-face or through phone, voice chat, video conferencing or any other medium
Oral/Spoken Word
30
New cards
messages or information is exchanged or communicated without using any spoken or written word
Non-Verbal communication ➢
31
New cards
Few Steps to Develop your Verbal Communication Skills
1. Use a strong, confident speaking voice
2. . Use Active listening
3. . Avoid filler words
32
New cards
Characteristics of Non-Verbal Communication

33
New cards
non-verbal communication is a communication without words or language.
No Use of Words
34
New cards
non-verbal communication is learnt in childhood, passed on to you by your parents and others with whom you associate
Culturally determined
35
New cards
non-verbal symbols can many meanings. cross-culture aspects give various meanings to same expression in respect of non-verbal communication.
Different Meaning
36
New cards
non-verbal communication is quite vague and imprecise.
Vague and imprecise
37
New cards
non-verbal communication is so deeply rooted, so unconscious, that you can express a verbal message and then directly contradict it with a nonverbal message.
May conflict with verbal messages
38
New cards
non-verbal communication is unconscious in the sense that it is usually not planned nor rehearsed. It comes almost instantaneously
Largely unconscious
39
New cards
facial expressions, gestures, body movements, the way you use your eyes – all communicate your feelings and emotions to others.
Shows feelings and attitudes
40
New cards
Non verbal communication does not follow any rules, formality or structure like other communication.
Informality
41
New cards
LEVELS OF COMMUNICATION
1. Intrapersonal–
2. . Interpersonal
3. . Mass Communication
42
New cards
communication with oneself
Intrapersonal
43
New cards
person-to-person communication
Interpersonal
44
New cards
communicating with large groups of people at one time through the use of mass media such as the press, radio, and film
Mass Communication–
45
New cards
Jamias used the following formula to explain the factors that contribute to effective communication:

46
New cards
CLASSIFYING COMMUNICATION BARRIERS
1. Technical Problems
2. Semantic Problems
3. Effectiveness Problems
47
New cards
how accurately the message can be transmitted. (e.g. radio static; bad cellular signal.
Technical Problems •
48
New cards
how precisely the meaning is conveyed. (e.g. translating a publication from one language to another.
Semantic Problems •
49
New cards
how effectively does the received message affect behavior. (e.g. editor makes comments for the purpose of making a piece of writing more concise or precise.
Effectiveness Problems •
50
New cards
COMMUNICATION BARRIERS
1. Channel Noise
2. Environmental Factors
3. Semantic Noise
4. Socio-Psychological Barriers
5. Other Barriers
51
New cards
* e.g. static, wrong spelling, letters too small to read, dead air on the radio.
* • these affect the channel, medium, or instrument used in transmitting a message. in turn, they affect the fidelity of the message.
* • fidelity means that the message received is faithful to the one sent.
* • these affect the channel, medium, or instrument used in transmitting a message. in turn, they affect the fidelity of the message.
* • fidelity means that the message received is faithful to the one sent.
Channel Noise
52
New cards
* e.g. uncomfortable sitting arrangements, rooms that are too hot, wall paper is too bright, meeting right after lunch.
* • barriers that are present in the environment in which a communication takes place.
* • they are external to the communication process but may create conditions under which communication effectiveness is hampered.
* • barriers that are present in the environment in which a communication takes place.
* • they are external to the communication process but may create conditions under which communication effectiveness is hampered.
Environmental Factors
53
New cards
* it happens when the message received as sent but the meaning received was different from the meaning sent.
* • occurs when we use, hear, or read words with double meanings.
* • e.g. gay meant happy or joyful
* • language serves as a bridge between peoples and culture, however, it can also serve as a barrier
* • occurs when we use, hear, or read words with double meanings.
* • e.g. gay meant happy or joyful
* • language serves as a bridge between peoples and culture, however, it can also serve as a barrier
Semantic Noise
54
New cards
* e.g. emotional blocks, charisma, stereotyping, first impressions, and absent-mindedness
* • Stereotyping – means judging people before you know all the facts about them; believing that they have common characteristics common among members of each group.
* • Stereotyping – means judging people before you know all the facts about them; believing that they have common characteristics common among members of each group.
Socio-Psychological Barriers
55
New cards
* @@**Ethnocentrism**@@ – *in viewing a group or culture as superior to all others.*
* • e.g. we interpret messages from the context of our experiences. Most of the time it help us respond appropriately to stimuli, however at times, negative experiences makes us dysfunctional (disbelief, rejection, distortion, or misinterpretation).
* • e.g. we interpret messages from the context of our experiences. Most of the time it help us respond appropriately to stimuli, however at times, negative experiences makes us dysfunctional (disbelief, rejection, distortion, or misinterpretation).
. Other Barriers
56
New cards
Common Barriers to Effective Communication
* Stress and out-of-control emotion
* Lack of focus
* Inconsistent body language
* Negative body language
* Lack of focus
* Inconsistent body language
* Negative body language
57
New cards
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION
1. Know your audience
2. Know your purpose
3. . Know your topic
4. Anticipate objections and be prepared to accept them
5. Follow through on what you say
6. Communicate a little at a time
7. Present information in several ways
8. Develop a practical, useful way to get feedback
9. Use multiple communication techniques
58
New cards
The imparting or exchange of thoughts, opinions, or information by speech, writing, or signs
Communication
59
New cards
* A system of moral principles
* Deals with values relating to human conduct, with respect to the rightness and wrongness of certain actions and to the goodness and badness of the motives and ends of such actions
* Deals with values relating to human conduct, with respect to the rightness and wrongness of certain actions and to the goodness and badness of the motives and ends of such actions
Ethics
60
New cards
The principle governing communication, the right and wrong aspects of it, the moral-immoral dimensions relevant to interpersonal communication are called the ethics of interpersonal communication
Communication Ethics
61
New cards
The principle of honesty on both sides should be completely applied because any amount of insincerity from either the listener or the speaker would not be prudent
Communication Ethics
62
New cards
Fundamentals of Ethical Communication
\

63
New cards
Threatens the quality of all communication and consequently the well-being of individuals and the society
Unethical Communication
64
New cards
Principles of Ethical Communication

65
New cards
refers to communication with another person
Interpersonal Communication
66
New cards
Interpersonal communication is divided into
* ➢ Dyadic communication
* ➢ Public communication
* ➢ Small-group communication
* ➢ Public communication
* ➢ Small-group communication
67
New cards
– is communication between two people or creatures
Dyadic communication
68
New cards
– is a method to share programs, ideas or propaganda to public. To give people new information or knowledge. Message can come from personal, company and government
Public communication –
69
New cards
– when more than 2 persons exchange their information face to face. A group consists of at least 3 members and at a maximum of around 12 to 15 members. - 2 and more than 15 members not considered as small grou
Small Group Communicaton
70
New cards
➢The most frequent basis of our decision making processes, expressing a commitment to the most basic principles.
Deontological Ethics
71
New cards
➢Focuses on the results and whether or not it would benefit the majority
Utilitarian Ethics
72
New cards
➢Concerned with moral character and places more weight or value on the dignity of an individual and a humanity’s task of caring for one another.
Virtue Ethics
73
New cards
There is no absolute approach to situations, each situation should be addressed as different from each other.
Situational or Contextual Ethics
74
New cards
Seven C’s of Effective Communication
1. Completeness
2. Conciseness
3. Consideration
4. Clarity
5. Concreteness
6. Courtesy
7. Correctnes
75
New cards
Three Different Types of Communication
1. Verbal
2. Non Verbal
3. Visual
76
New cards
* entails the use of words in delivering the intended message
\
2 Major Forms of ___Communication:
1. Written
2. Oral
\
2 Major Forms of ___Communication:
1. Written
2. Oral
Verbal
77
New cards
entails communicating by sending and receiving a wordless message
\
2 Major Forms of ___
* Physical non-verbal communication or body language
* Paralanguage - the way something is said, rather than what is actually said , is an important component of nonverbal communication
\
\
2 Major Forms of ___
* Physical non-verbal communication or body language
* Paralanguage - the way something is said, rather than what is actually said , is an important component of nonverbal communication
\
Non Verbal
78
New cards
Other forms of nonverbal communication
* @@**Aesthetic communication**@@ or creative expressions such as dancing, painting, and the like. ▪
* @@**Appearance**@@ or the style of dressing and grooming, which communicates one’s personality. ▪
* @@**Space languages**@@ such as paintings and landscapes communicate social status and taste. ▪
* @@**Symbols**@@ such as religious, status, or ego-building symbols
* @@**Appearance**@@ or the style of dressing and grooming, which communicates one’s personality. ▪
* @@**Space languages**@@ such as paintings and landscapes communicate social status and taste. ▪
* @@**Symbols**@@ such as religious, status, or ego-building symbols
79
New cards
____ communication through visual aids such as signs, typography, drawing, graphic design, illustration, color and other electronic resources
Visual
80
New cards
A __ is widely used to depict any idea, thought or a concept in a more simpler way through diagrams, pictorial representations etc.
model
81
New cards
According to this model, the speaker plays a key role in communication. He is the one who takes complete charge of the communication
Aristotle’s Model of Communication
82
New cards
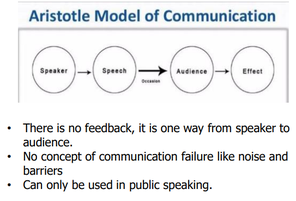
Aristotle’s Model of Communication
83
New cards
Aristotle model of communication is the__ to excel in public speaking, seminars, lectures where the sender makes his point clear by designing an impressive content, passing on the message to the second part and they simply respond accordingly
golden rule
84
New cards
* this model of communication takes into account the emotional aspect of the message.
* it operates on the SMCR model.
* it operates on the SMCR model.
Berlo’s Model of Communication
85
New cards
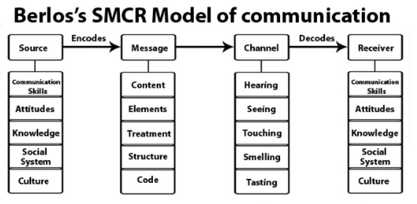
Berlo’s Model of Communication
\
86
New cards
SMCR stand for?
* Source
* message
* channel
* receiver
* message
* channel
* receiver
87
New cards
The __ in other words also called the sender is the one from whom the thought originates.
source
88
New cards

enumerate all the elements under “Source”
* Communication Skills
* Attitude
* Knowledge
* Social System
* Culture
* Attitude
* Knowledge
* Social System
* Culture
89
New cards
When an individual converts his thoughts into words, a __ is created.
message
90
New cards
The process is also called as __
Encoding.
91
New cards

enumerate all the elements under “Message”
* Content
* Element
* Treatment
* Structure
* Code
* Element
* Treatment
* Structure
* Code
92
New cards
All the five senses are the __which help human beings to communicate with each other.
channels
93
New cards
When the message reaches the__, he tries to understand what the listener actually wants to convey and then responds accordingly.
receiver

94
New cards
Criticism of Berlo’s SMCR model of communication:
\

95
New cards
most popular model of communication and is widely accepted all over the world.
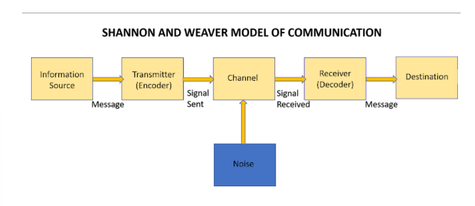
Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication
96
New cards
Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication

97
New cards
Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication
98
New cards
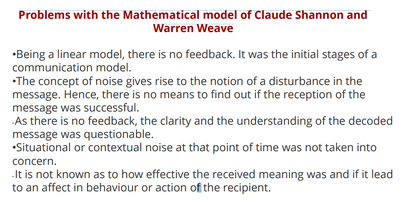
Problems with the Mathematical model of Claude Shannon and Warren Weave
99
New cards
proposed the model of communication in 1954
Wilber Schramm
100
New cards
It can be used to determine how communication between two people works when they’re exchanging information, ideas, or attitudes.
Schramm’s Model of Communication