Topic 1
1/105
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Solvent
Substances dissolve in it e.g. water+++
dipolar
Having a slightly positive charge and negative charge
Cohesive
They tend to stick together
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same type
Which side of the heart carries oxygenated blood?
left
Why is the left side of the heart thicker?
Because it carries oxygenated blood
Where does blood from the vena cava go to?
Right atrium
Where does blood from the pulmonary vein go to?
Left atrium
Why does the heart have coronary arteries on the surface?
It needs it's own supply of oxygen to pump the blood around the body
What is the valve between the atrium and ventricle?
Atrioventricular valves
What is the valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery?
Semi lunar valve
What is the valve between the left ventricle and aorta?
Semi lunar valve
What do valves do?
Stop the back flow of blood
What are the three blood vessels?
Arteries, veins and capillaries
What do the arteries do?
Carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body
What are features of the artery?
Thick muscle wall, lots elastic fibres, small lumen
What are the features for in an artery
To withstand the high pressure of the blood, to be able to stretch and recoil
What do veins do?
Take blood back to the heart
What are features of veins?
Large lumen, thin muscle wall, little elastic tissue
Why do veins have different features to arteries?
Veins are different because the blood that goes to them are under lower pressure.
what is atheroma?
it is a fatty deposit that makes the lumen get smaller.
How does atherosclerosis occur?
1)there is damage to the endothelial wall
2)this triggers an inflammatory response
3)white blood cells accumulate with chemicals in the blood
4)WBC enlarge with cholesterol and form a atheroma
5)this stretches the artery making it lose elasticity
6)calcium deposits and fibrous tissue build up forming plaque
7)lumen size reduces, higher chance of damage
what does atheroma do?
it produces postive feedback of the lumen getting smaller ad there being a higher chance of damage to the arteries.
Explain the process of blood clotting
Damaged blood cell releases thromboplastin
+ Ca ions coverts prothrombin to thrombin
Thrombin catalyses fibrinogen to fibrin (insoluble)
Fibrin mesh traps RBCs and platelets= clot
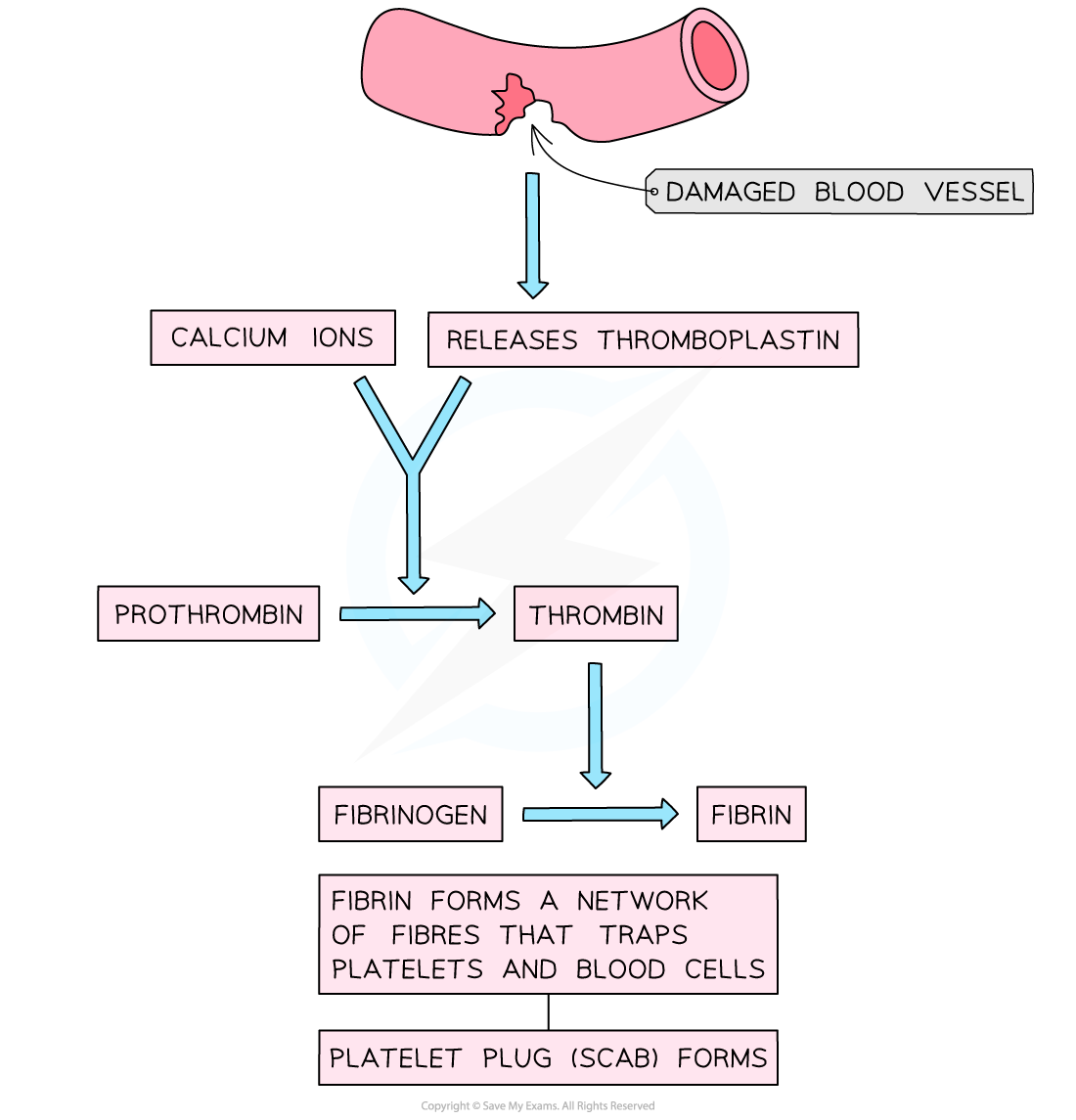
what is fibrin used for?
create the mesh that traps red blood cells.
explain the link between atherosclerosis and blood clotting
Atherosclerosis will make the lumen smaller so the chance of blood clotting is increased due to the fatty deposits.
what are the lifestyle factors that affect CVD?
Diet, high blood pressure, smoking and inactivity
explain diet in terms of affecting CVD
High saturated at diet increases blood cholesterol and atheroma formation.
explain high blood pressure in terms of affecting CVD
This increases the risk to the damage of the arterial wall
how does smoking affect CVD?
- CO reduces amount of O2 in the blood so not enough o2 can get to tissue > stroke
- nicotin makes platelets sticky
how does inactivity affect CVD?
This increases blood pressure
what a factors that are beyond control in terms of CVD?
Genetics, age and gender
What are antihypertensives?
drugs that reduce blood pressure
what are benefits of antihypertensives?
- They can be given in combination to reduce blood pressure as they work in different ways
- Blood pressure can be monitored at the home so the patient can see if the drugs are working
what are risks of hypertensives?
Could cause fainting, headaches, drowsiness
What are statins?
They are drugs which lower the amount of 'bad' cholestrol in blood.
benefits of statins
Reduce the risk of developing CVD
Risks of statins
Could cause muscle and joint pain, nosebleeds, headaches and nausea
What are anticoagulants?
Drugs that reduce the ability of the blood to clot
Benefits of anticoagulants
prevent any existing blood clots from getting larger
Risks of anticoagulants
excessive bleeding, fainting, swelling
what are platelet inhibitory drugs?
drugs that reduce the formation of blood clots.
Benefits of platelet inhibitory drugs
can be used to treat someone already with CVD or blood clots.
Risks of platelet inhibitory drugs
Rashes, diarrhoea, excessive bleeding
What is a monosaccharide?
a single sugar unit
what are examples of monosaccharides?
glucose, fructose, galactose
What is a diasaccharide?
a two single sugar unit
what is the bond between a diasaccharide
glycosidic bond
what are examples of diasaccharides
maltose, lactose and sucrose
What is maltose made of?
glucose and glucose
What is lactose made of?
glucose and galactose
What is sucrose made of?
glucose and fructose
what reaction occurs in the formation of a diasaccharide
condensation reaction
how do you break two sugar units
using hydrolysis
What is hydrolysis?
breaking using water
What is a polysaccharide?
polymers of monosaccharides
what are examples of polysaccharides found in food
glycogen in animals and starch and cellulose in plants
what are examples of starch?
amylose and amylopectin
Does amylose or amylopectin have branches?
amylopectin
why is glycogen are source of energy
as it is branched, when it is broken down energy can be released from multiple places on it
What is a triglyceride?
fat
What is a triglyceride made of?
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what are the fatty acid tails made from?
hyrdocarbons
How is a triglyceride formed?
~ By a condensation reaction between fatty acids and a glycerol
~ Ester bond is formed and a molecule of water is removed
How is a triglyceride broken?
By hydrolysis reactions
what are the two types of lipids?
saturated and unsaturated
saturated lipids
DONT have a double bond between the carbons atoms in their hydrocarbon tail
unsaturated lipids
DO have a double bond between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon tail
what lipid increases the risk of CVD?
saturated
what is a type of lipid made in the body?
cholesterol
What are lipoproteins?
any kind of fat transporter e.g. LDL, HDL
What is HDL cholesterol?
good cholesterol that is made of mainly protein
what is the function of HDL?
to reduce total blood cholesterol when the level is too high
What is LDL cholesterol?
bad cholesterol that is made from mainly lipid
what is the function of LDL?
to increase the total blood cholesterol when the level is too low
what are twp types of obesity indicators?
waist-to-hip ratio and BMI
What is the BMI formula?
weight (kg) / height (m^2)
What is the waist to hip ratio?
waist circumference / hip circumference
what can stopping smoking do?
reduce the risk of CVD based on scientific research
what can frequent exercise do?
reduce the risk of CVD based on scientific research
what are the consequences of energy imbalance?
weight loss, weight gain and development of obesity
what happens when their is weight gain?
the energy intake is higher than the energy output which could lead to a person becoming obese
what happens when their is weight loss?
the energy intake is lower than the energy output which could lead to a person being underweight
why is a supply of energy needed?
so that organisms can grow. move, reproduce etc
what is energy budget
the amount of energy taken in and used up by an organism
what are the different circulatory systems?
open, single closed and double closed
What do open circulatory systems allow?
substances to diffuse between blood and cells, mass flow of nutrients to cells
what do closed circulatory systems allow?
the blood system to be more efficient at delivering substances around the body.
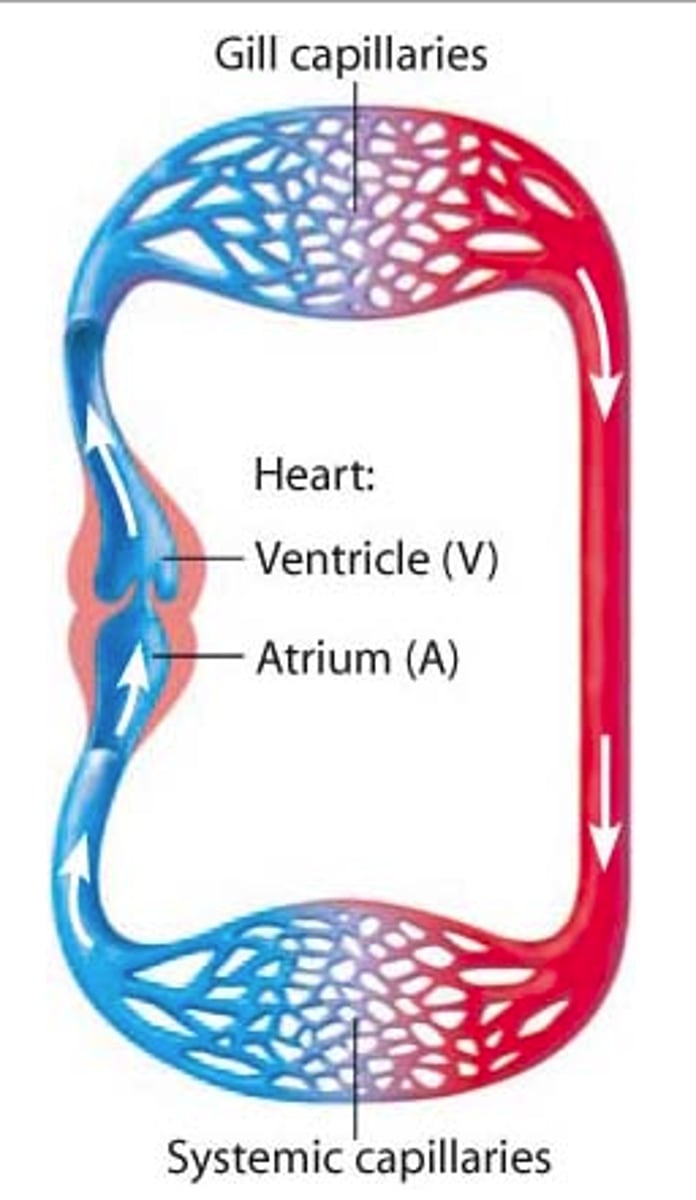
Single closed circulatory system
Arteries, capillaries and veins surrounding organs and all cell have an equal chance for food.
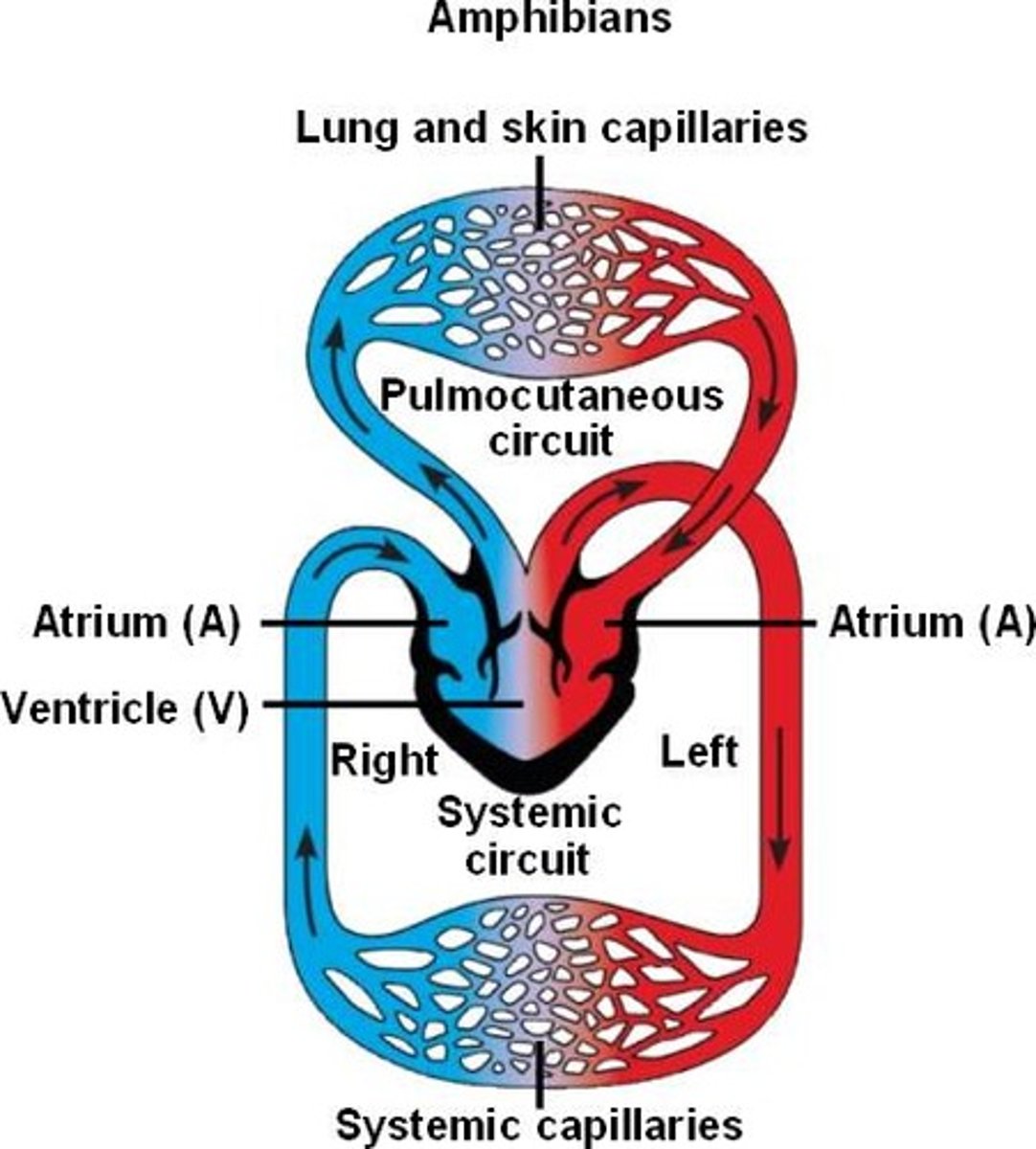
Double closed circulatory system
mass transport of either oxygenated blood of deoxygenated blood depending on what side.
Limitations of open CS
- struggle to control the velocity of blood
- struggle to vary amount of oxygen they take in
limitations of closed single
-Blood flow is rare
-blood pressure is lower so there is a slower rate of flow
limitations of closed double
-high blood pressure
-more complex so their is a higher chance of errors occuring
What is a cardiac cycle
a sequence of contraction and relaxation of the atrium and ventricle
What is systole?
Contraction
What is diastole?
relaxation
What is atrial systole?
contraction of the atria
what valves are open in artial systole
atrioventricular valves
what is ventricular systole?
ventricular contraction
what happens in atrial systole?
the pressure increase whilst the volume decrease