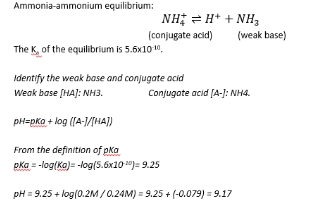Cell biology lecture 22
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Acids, bases and buffers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
LOs
Biological importance of acidity.
Water dissociation.
pH as a measure of H+ concentration.
Weak acids, acid dissociation constant,
pKa.
Buffers.
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
Why should we care about pH?
pH measures the acidity/ basicity of a solution.
Living organisms are very sensitive to small pH changes
Water dissociation
H3O+, OH- ions are highly reactive
Note:
H3O+ is commonly just called H+.
Free H+ does not exist in water, it’s just a convenient shorthand.
Water acts as an equilibrium with H+ and OH-
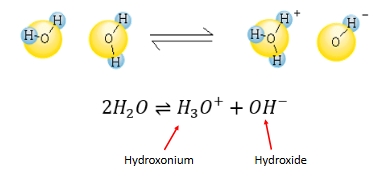
How much does water dissociate - Kw?

Kw equation

Acid
produces H+ ions by dissociation
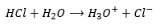
Base
releases OH- ions
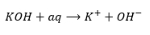
What do acids and bases do?
change the amount of h+ available to react with other species
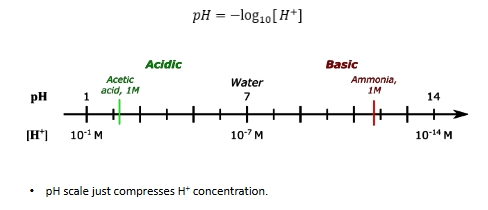
pH scale
measures conc of H+

pH scale vs H+ concentration
what do buffers do?
stabilize the pH of a solution
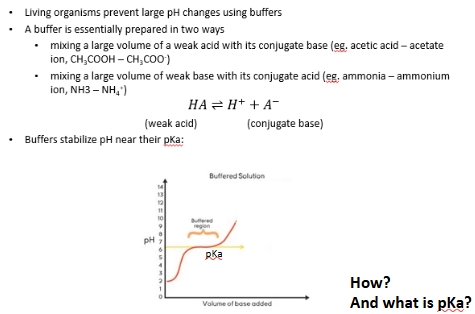
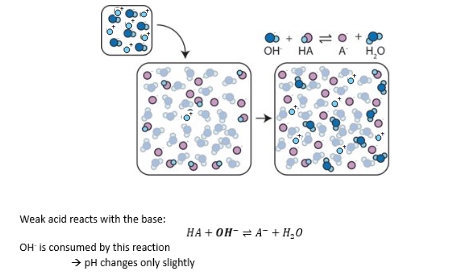
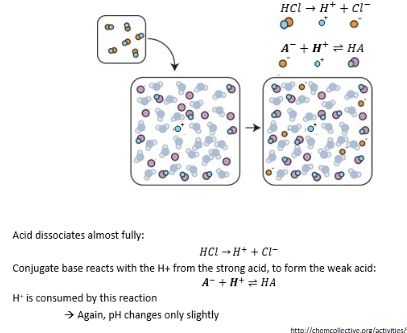
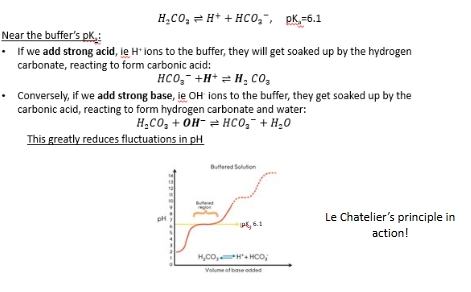
Visual explanation of pH buffering
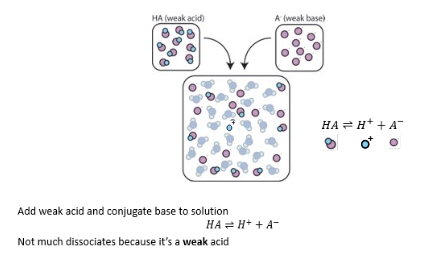
Buffer + strong base
Buffer and strong acid
Ka
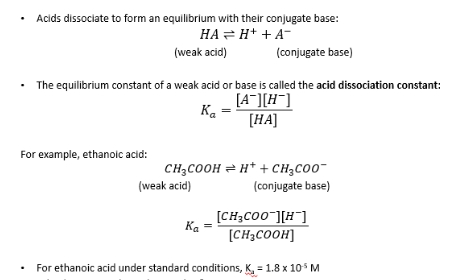
pKa
expresses acidity of weak acids

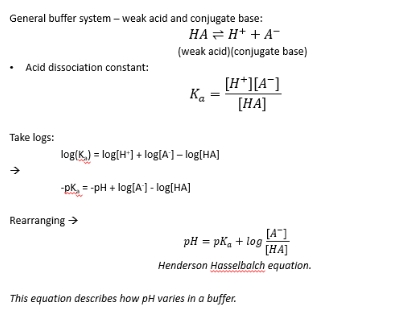
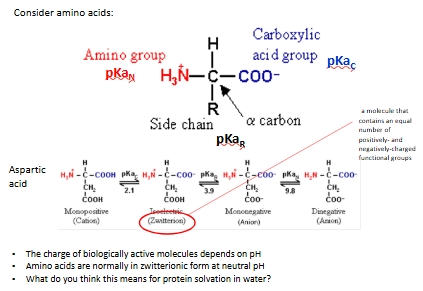
Henderson-Hasselbalch: Calculating buffer pH
Biological buffers
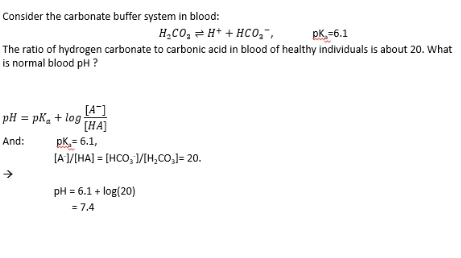
Buffer pH example
Buffer practice 2
Answer = 40
pH = pKa + log A/HA
7.7=6.1 + logA-/HA
1.6 = logA-/HA
10 to the 1.6 = a-/HA
39.8 = ratio
So answer is 40
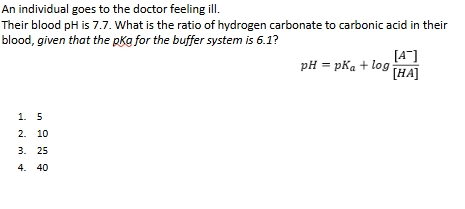
pKa of amino acids if pH equals pKa

pKa of amino acids if pH is larger than pKa

pKa of amino acids if pH is less than pKa
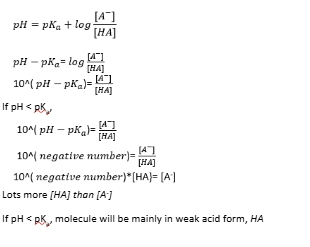
State of molecules at a given pH
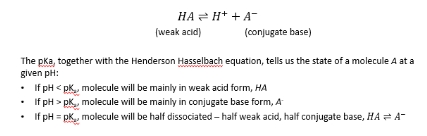
Why is pH important for AAs and enzymes ?
Consider an enzyme with a carboxyl group. The structure of that group will depend on the pH, If the enzyme needs to be protonated in order to be active, then the enzyme will only work in the pH range in which the majority of the enzyme molecules have their carboxyl group protonated.

Henderson Hasselbach practice