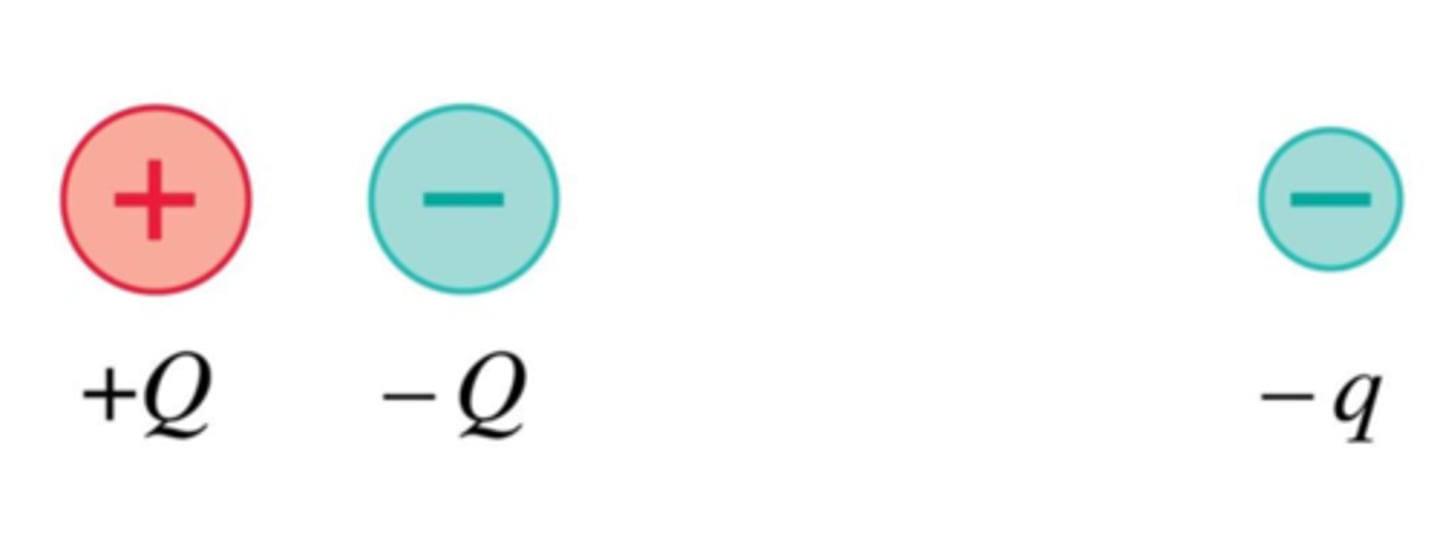Chapter 20: Electric Fields and Forces
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
A negatively charged rod is brought near a neutral metal sphere. Which of the following is true?
A. There is an attractive force between the rod and sphere.
B. There is a repulsive force between the rod and sphere.
C. There is no electric force between the rod and sphere.
A. There is an attractive force between the rod and sphere.
A neutral object:
A. Is identical to an insulator.
B. Has no charge of either sign.
C. Has no net charge.
D. Is not attracted to a charged rod.
C. Has no net charge.
Coulomb's law describes:
A. The electric field due to a point charge.
B. The force between two point charges.
C. The electric field due to a charged rod.
D. The electric potential of a point charge.
B. The force between two point charges.
The field inside a charged parallel-plate capacitor is:
A. Zero.
B. Uniform.
C. Parallel to the plates.
D. Directed from the negative to the positive plate.
B. Uniform
The electric field inside a metallic conductor is:
A. Positive.
B. Negative.
C. Zero.
C. Zero
Consider two objects A and B. Object A has a net charge while B is uncharged. Based on this information, it must be true that:
A. A is a conductor, B is an insulator.
B. A is an insulator, B is a conductor.
C. A and B are both insulators.
D. A and B are both conductor.
E. There's not enough information to tell.
E. There's not enough information to tell.
Charged glass and plastic rods hang by threads. An object attracts the glass rod. If this object is then held near the plastic rod, it will:
A. Attract the plastic rod.
B. Repel the plastic rod.
C. Not affect the plastic rod.
D. Either A or B. There's not enough information to tell.
D. Either A or B. There's not enough information to tell.
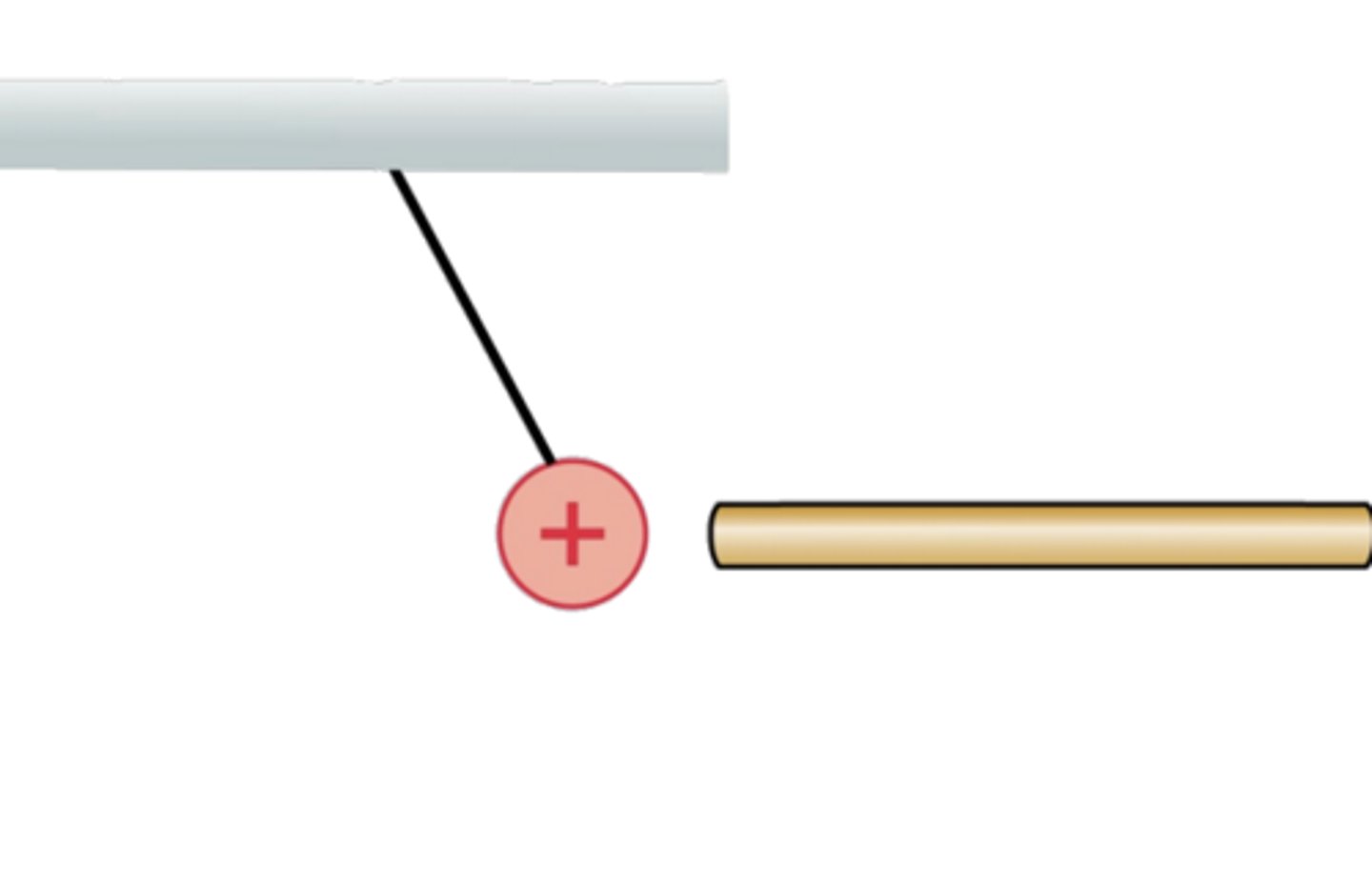
A rod attracts a positively charged hanging ball. The rod is:
A. Positive.
B. Negative.
C. Neutral.
D. Either A or C.
E. Either B or C.
E. Either B or C.
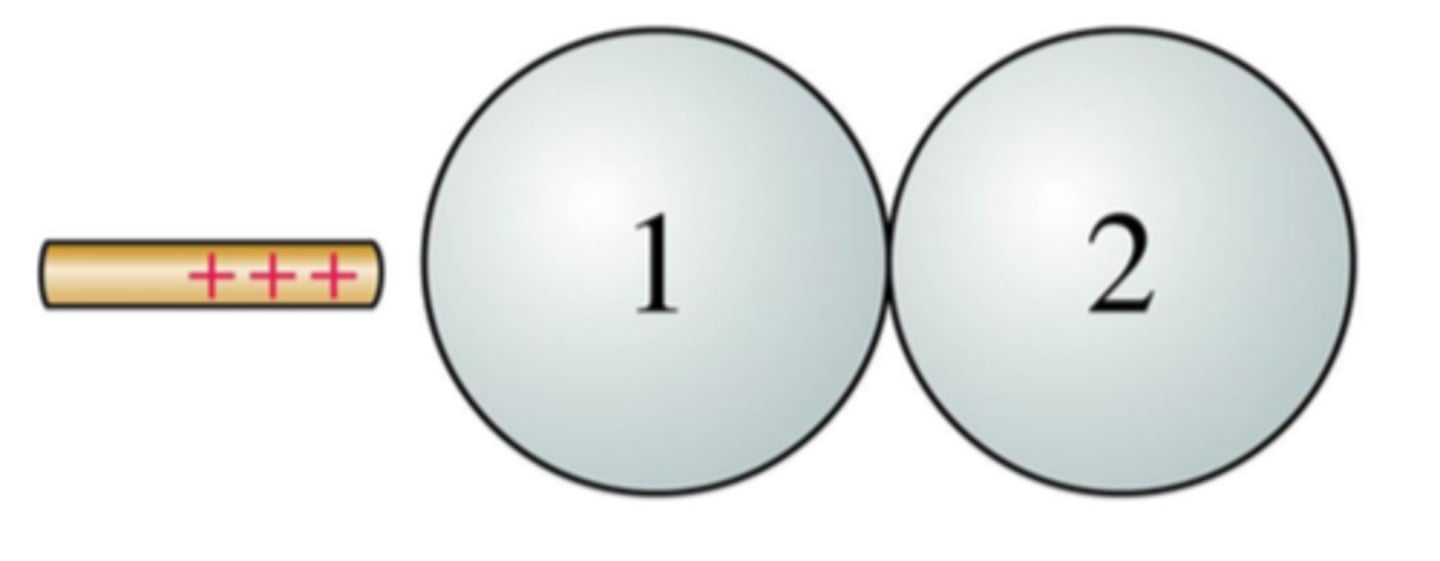
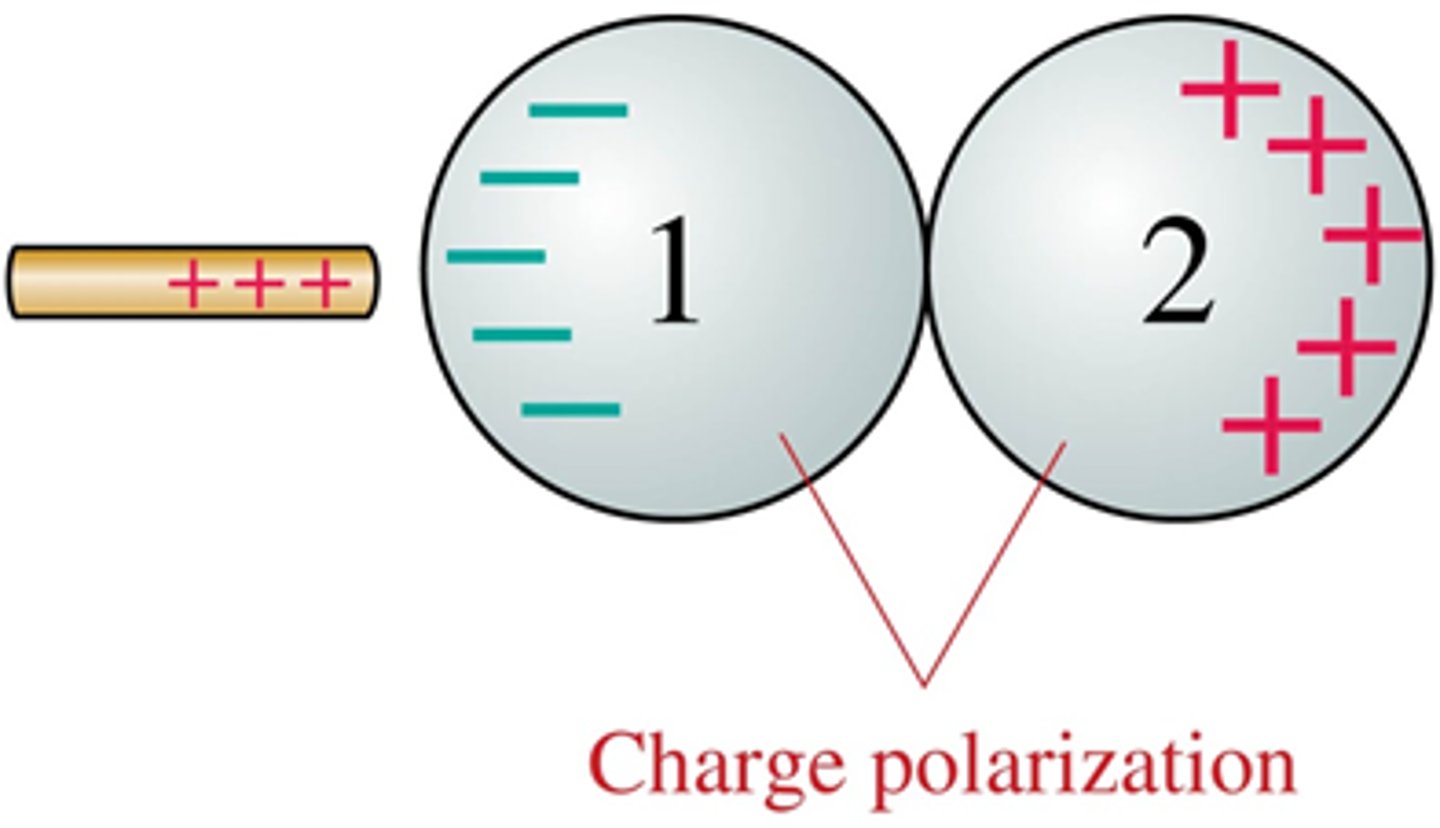
Metal spheres 1 and 2 are touching. Both are initially neutral.
a. The charged rod is brought near.
b. The charged rod is then removed.
c. The spheres are separated.
Afterward, the charges on the sphere are:
A. Q1 is + and Q2 is +
B. Q1 is + and Q2 is −
C. Q1 is − and Q2 is +
D. Q1 is − and Q2 is −
E. Q1 is 0 and Q2 is 0
E. Q1 is 0 and Q2 is 0
Metal spheres 1 and 2 are touching. Both are initially neutral.
a. The charged rod is brought near.
b. The spheres are separated.
c. The charged rod is then removed.
Afterward, the charges on the sphere are:
A. Q1 is + and Q2 is +
B. Q1 is + and Q2 is −
C. Q1 is − and Q2 is +
D. Q1 is − and Q2 is −
E. Q1 is 0 and Q2 is 0
C. Q1 is − and Q2 is +
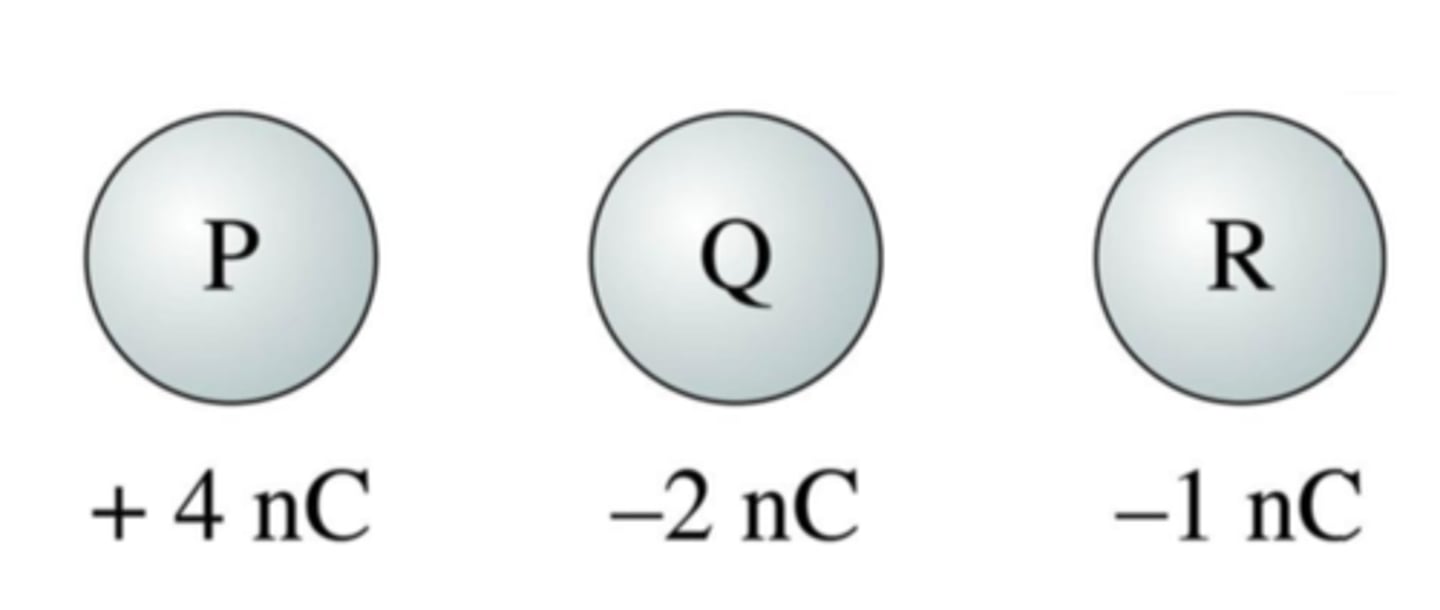
Identical metal spheres are initially charged as shown. Spheres P and Q are touched together and then separated. Then spheres Q and R are touched together and separated. Afterward the charge on sphere R is:
A. −1 nC or less
B. −0.5 nC
C. 0 nC
D. +0.5 nC
E. +1.0 nC or more
C. 0 nC
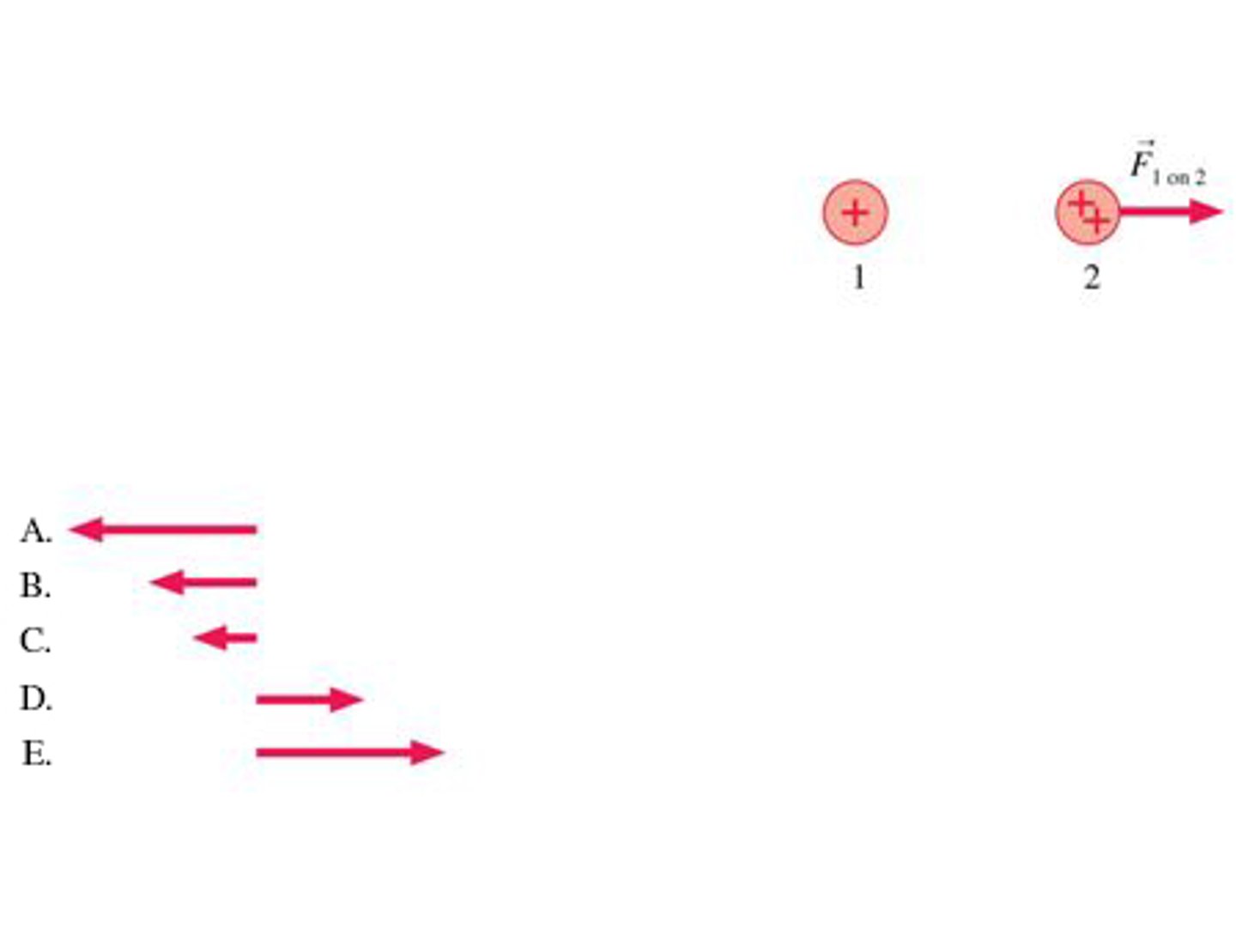
The charge of sphere 2 is twice that of sphere 1. Which vector below shows the force of 2 on 1?
B (because newton's third law)
The charge of sphere 2 is twice that of sphere 1. Which vector below shows the force of 1 on 2 if the distance between the spheres is reduced to r/2?
D - none of the above
At half the distance, the force is four times as large:

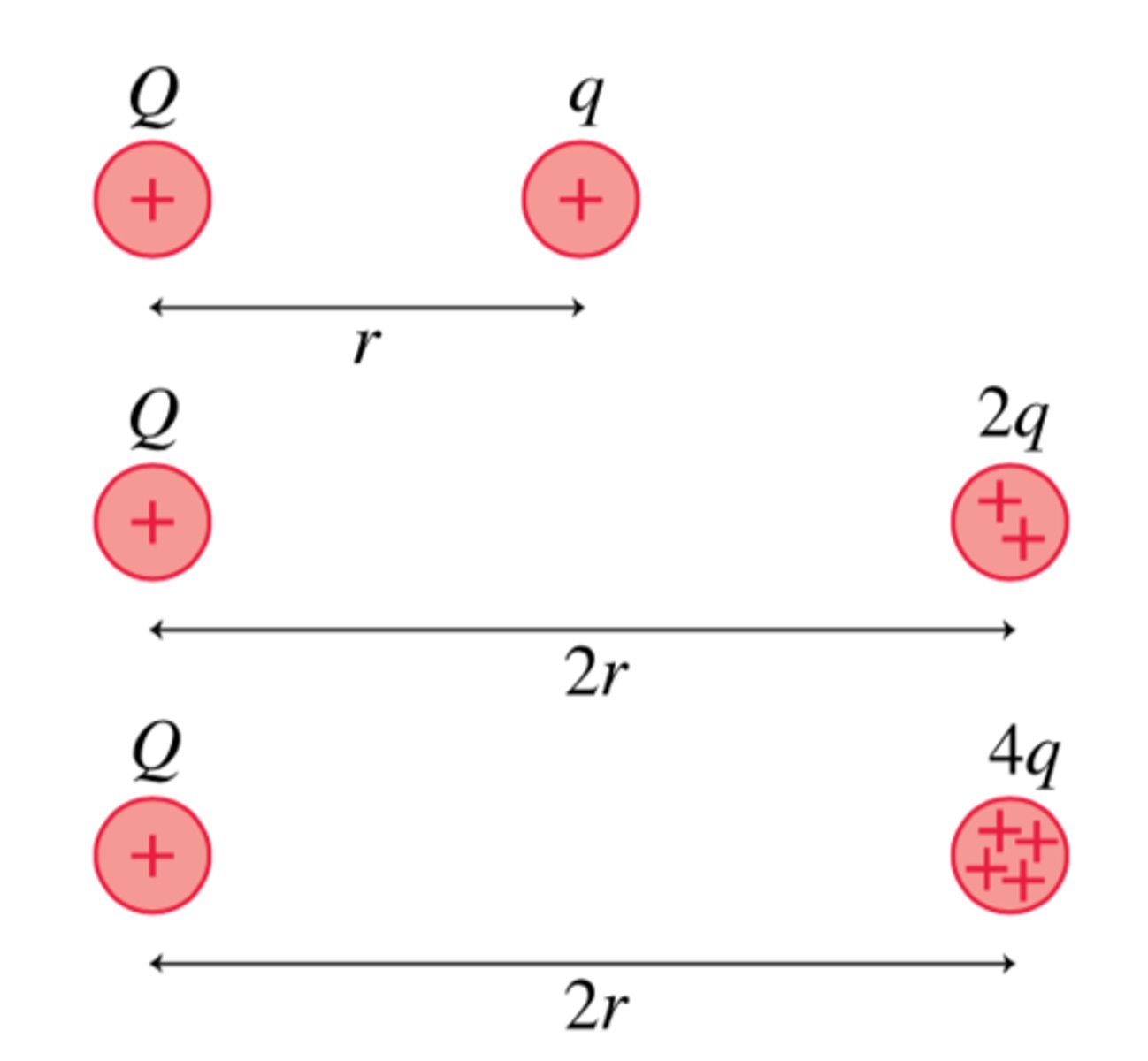
Which of the three right-hand charges experiences the largest force?
A. q
B. 2q
C. 4q
D. q and 2q are tied
E. q and 4q are tied
E. q and 4q are tied
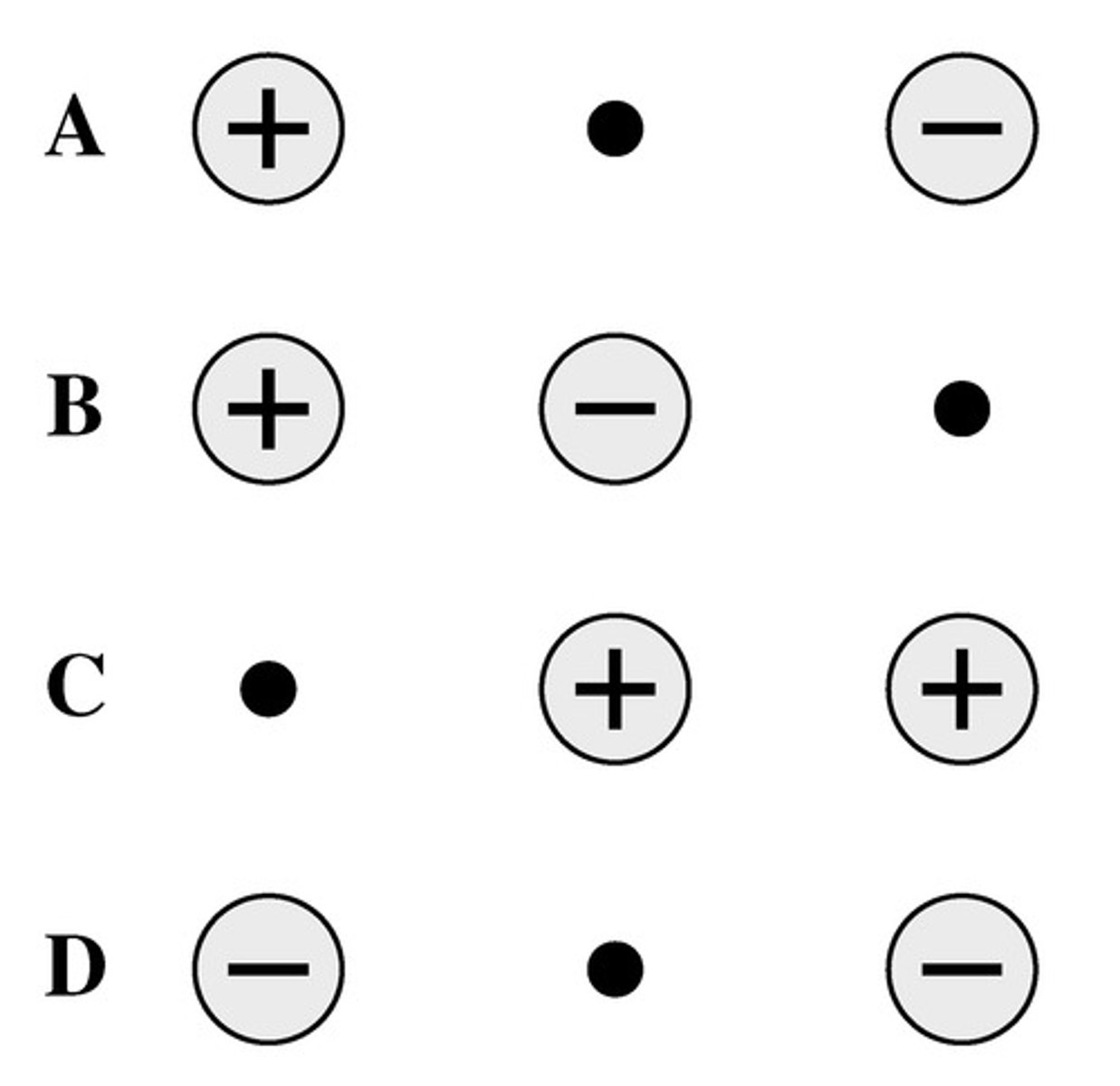
In each of the following cases, an identical small, positive charge is placed at the black dot. In which case is the force on the small charge the largest?
C
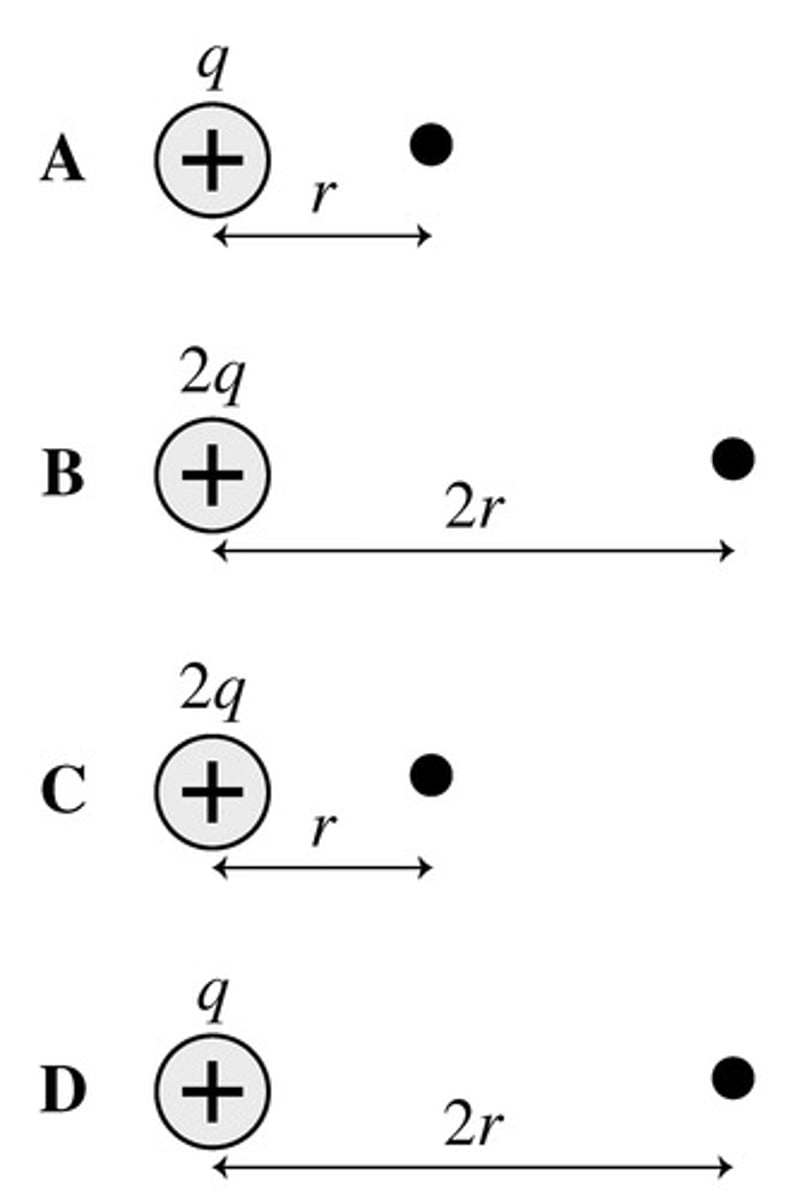
In each of the following cases, an identical small, positive charge is placed at the black dot. In which case is the force on the small charge the largest? (All charges shown are of equal magnitude.)
A
The direction of the force on charge −q is:
A. Up
B. Down
C. Left
D. Right
E. The force on −q is zero
D. Right ; −Q is slightly closer than +Q.