hematology exam 2 🩸
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Describe the red blood cell indices related to the anemic process
MCV (less than femtoliter), MCH (blank), MCHC (less than 32%)
List the microcytic anemias considered in a differential diagnosis of microcytic processes.
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA), Thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, anemia of chronic disease (ACD/AOI)
Describe iron transport from ingestion to incorporation in hemoglobin.
Iron3+ converted to iron2+ by stomach acid then iron 2+ converted to transferrin (iron absorbed), Heme returned to bone marrow and globin returned to amino pool (recycled iron), ferritin, hemosiderin (iron stores), blood loss (iron loss).
List the 3 stages of iron deficiency
Stage 1 (continuum of iron depletion from marrow, Prussian blue stain will show absence of iron), stage 2 (iron deficient erythopoiesis, slight macrocytic hypochromic picture), stage 3 (a fully developed case of IDA in peripheral circulation, microcytes and hypochromia)
Describe the physical symptoms of a patient with iron deficiency anemia.
Fatigue, pallor, vertigo, dysphea, cold intolerance, lethargy, pica
Identify the laboratory test used in the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia.
CBC test
Describe the iron overload conditions.
Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH), when the body absorbs and stores too much iron.
Define the pathophysiology of hereditary hemochromatosis.
Autosomal recessive disorder on chromosome 6, abnormal HFE gene, iron accumulation in tissue, present in 8-95% of the patients.
Outline symptoms of patients with hereditary hemochromatosis
Chronic fatigue and weakness, cirrhosis of the liver, hyperpigmentation, hair loss, diabetes, impotence, tender swollen joints, abdominal symptoms, sterility, cardiac arryth.
Describe the diagnosis and clinical management of patients with hereditary hemochromatosis.
Transferrin saturation, serum ferritin, HFE gene analysis, therapeutic phlebotomy, reduce ferritin levels to less than 10 micrograms and hemoglobin= 32%, iron chelating agent (deferral through transfusion pump or oral)
Describe the basic pathophysiologic defect in thalassemia syndromes.
Alpha gene deletions and defective beta gene
List the three types of beta thalassemia
Beta thalassemia minor, beta thalassemia intermedia, beta thalassemia major.
Describe the major hemoglobin in each of the thalassemic states.
Hemoglobin A, hemoglobin F (2 alpha globin and 2 gamma globin), hemoglobin A2 (2 alpha globin and 2 delta globin)
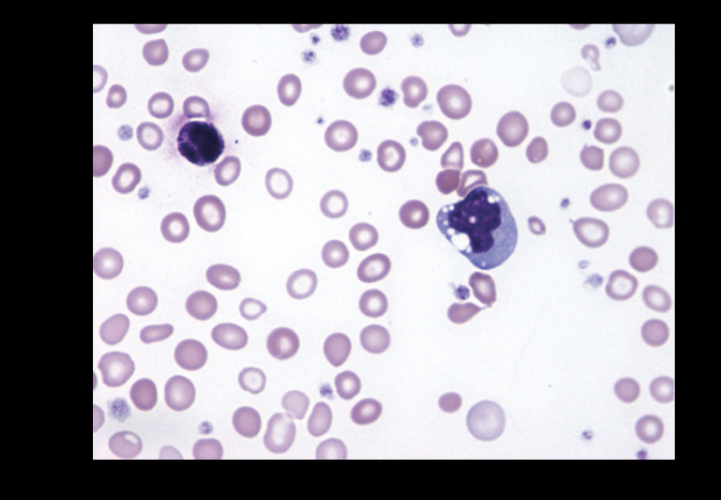
Iron deficiency anemia
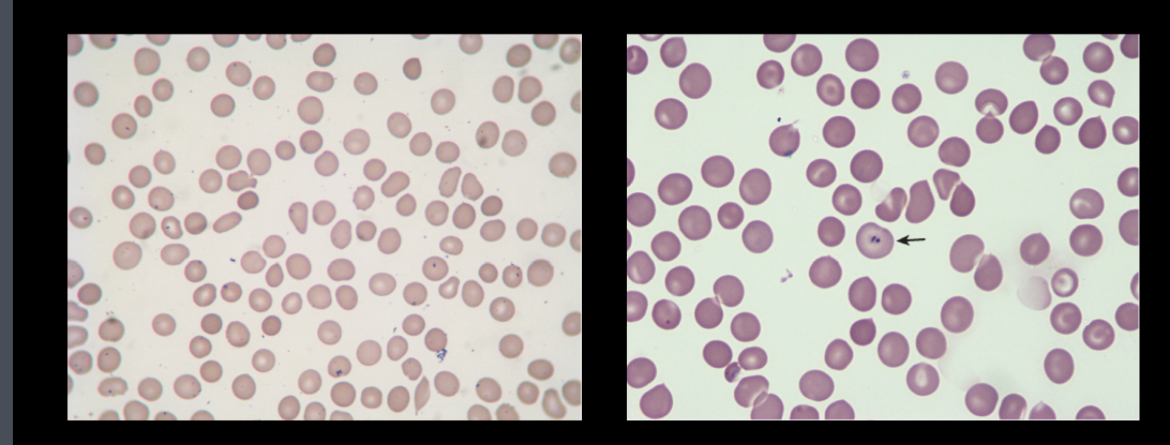
Sideroblastic anemia
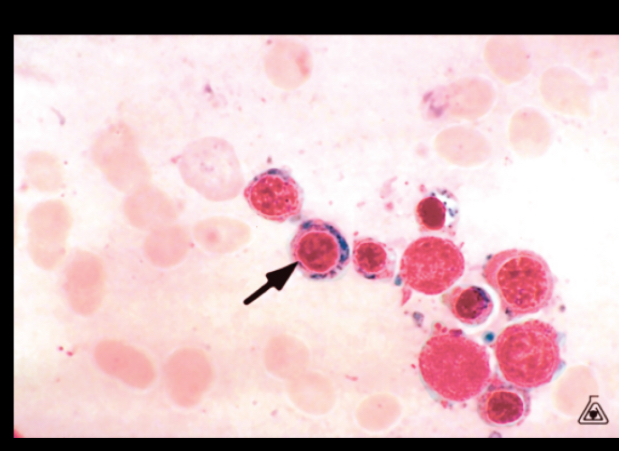
Ringed sideroblasts
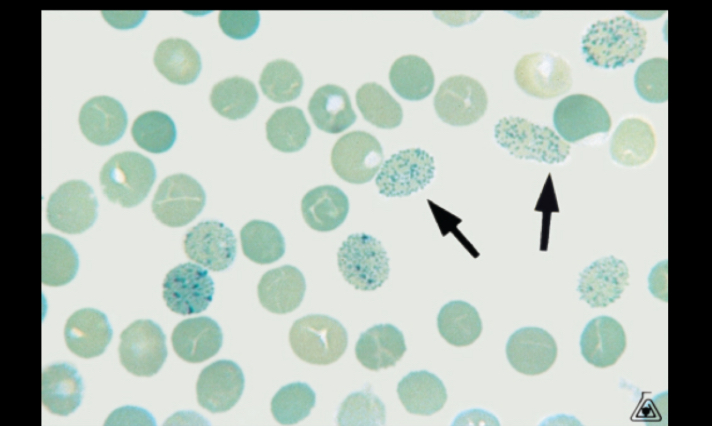
Hemoglobin H inclusion