Lines, Oxygen, Internal Devices
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
nasal cannula
flow:
%O2
liter per minute:
most frequently used
low flow through nostrils 21-60%
adult LPM: 0.25-8
infant LPM: <2
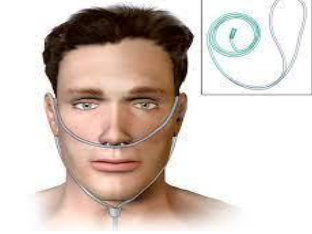
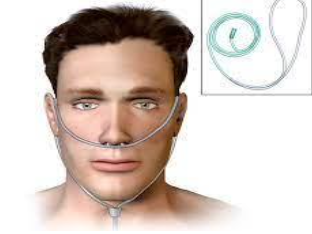
nasal cannula
simple mask
flow:
liters per minute:
if cannot tolerate cannula
low flow and short flow
LPM: 5-10
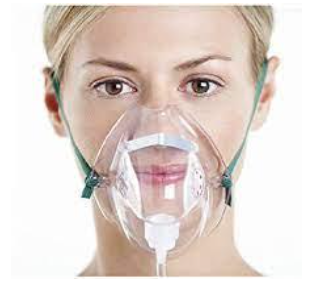
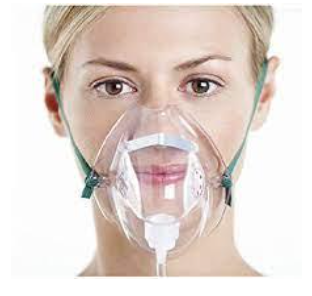
simple mask
partial rebreathing mask
flow:
liters per minute:
low flow
LPM: no less than 10
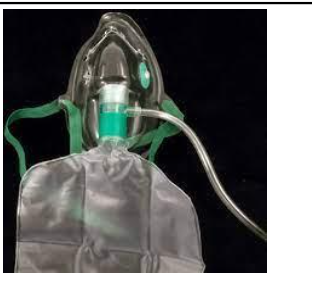
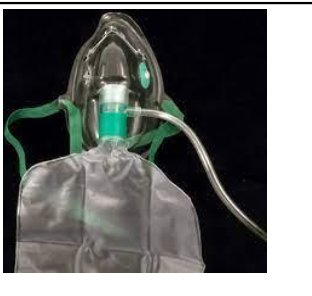
partial rebreathing mask
nonrebreathing mask
O2 percent
flow:
liters per minute:
low flow delivers 60-90% oxygen
LPM: no less than 10
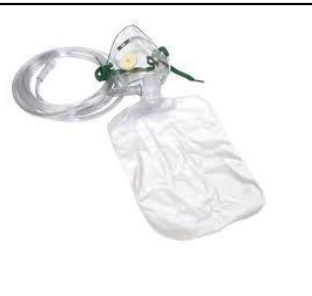

nonrebreathing mask
air entrainment/venturi mask
flow:
Liters per minute:
high flow mixes oxygen with room air
LPM: varies over 60
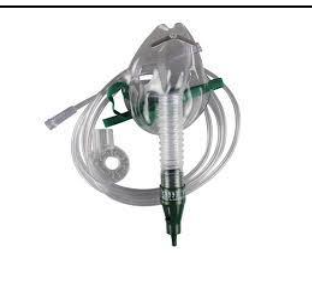
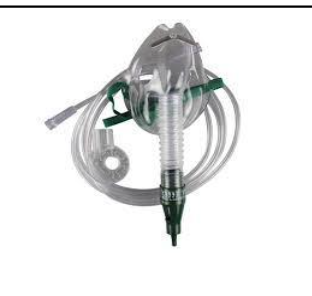
venturi mask/ air entrainment
oxyhood
flow:
liters per minute:
low flow
LPM: pediatric less than 7
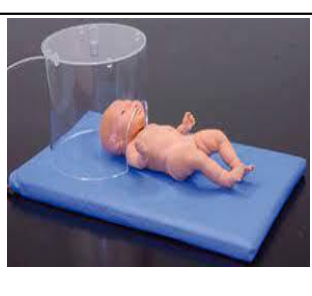
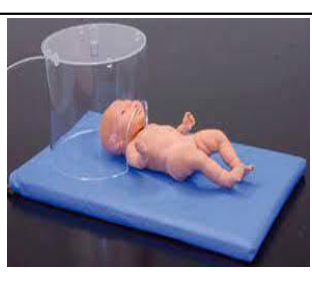
oxyhood
oxygen tent
flow:
liters per minute:
medium at higher concentration than room air (>21%)
LPM: 12-15
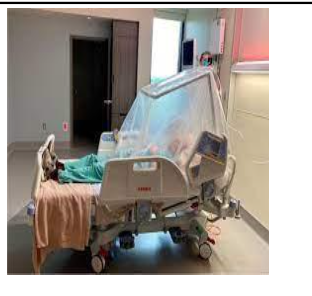
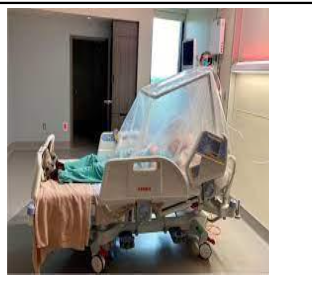
oxygen tent
thoracostomy tube
thin tube drains fluids from pleural cavity, pleural effusion or pneumothorax
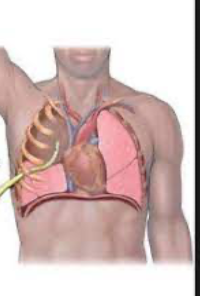
thoracostomy tube proper placement
placed through chest wall into plueral space
inserted through 4th or 5th intercostal space midaxillary
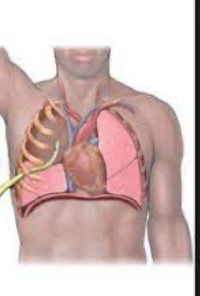
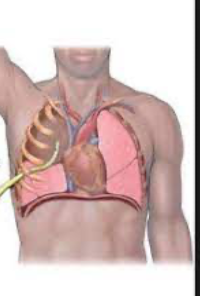
thoracostomy tube
central venous catheter proper placement
tip in superior vena cava
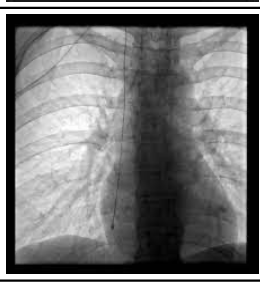
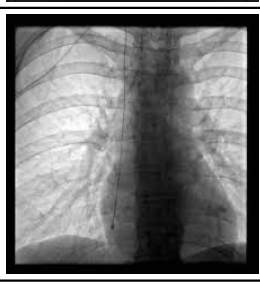
CVC
implanted access ports names/types
infusaport, port-a-cath, mediport
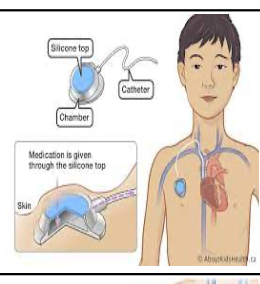
ports are used for
single, double, multilumen
chronic illnesses access for long periods od time
to draw blood, give meds, blood transfusions
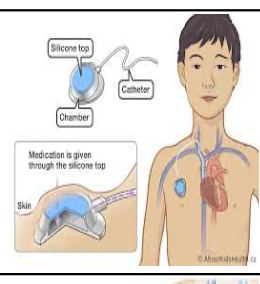
ports inserted where
subcutaneus in right chest
catheter into superior vena cava
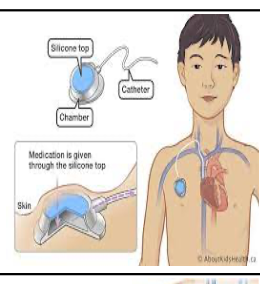
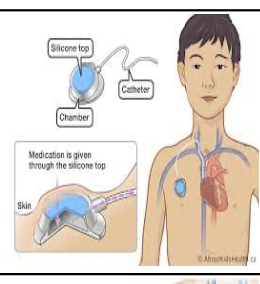
port
peripherally inserted central catheter
small soft tube, short term treatment up to a few weeks
for meds and liquid nutrition
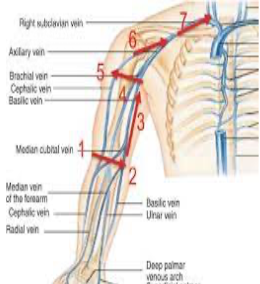
PICC line placement
right basilic vein! or cephalic, brachial or medial cubital
advanced to lower third of superior vena cava
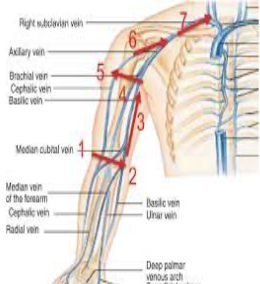
PICC line
externally tunneled catheter types
Broviac, Hickman, Groshong, RAAF
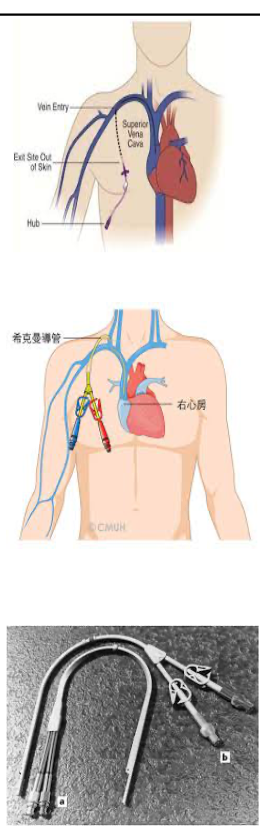
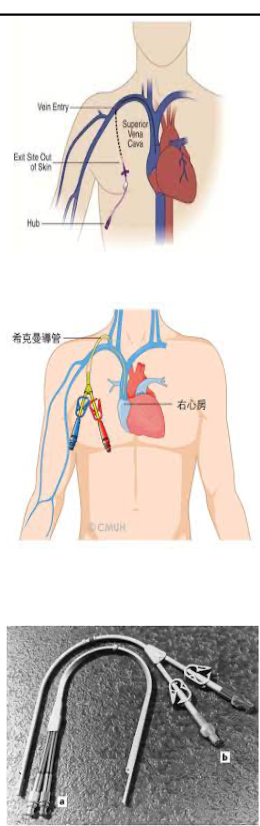
externally tunneled catheter use
long thin hollow tube
for fluids, meds, hemodialysis, draw blood
long-term use
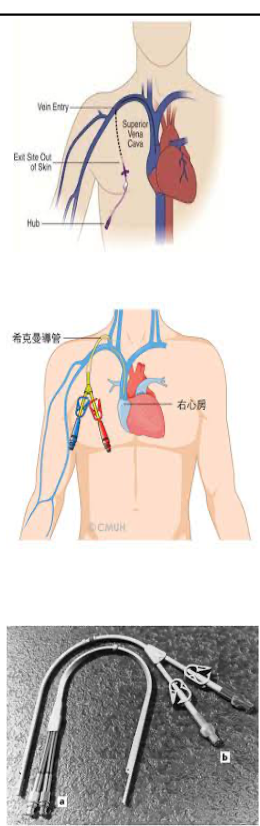
externally tunneled catheter placement
placed on right side of chest wall into a large vein
jugular or subclavian
advanced to superior vena cava
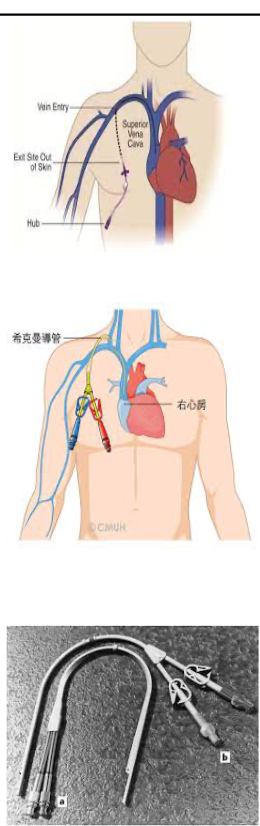
externally tunneled catheter
Swanz-Ganz use
pulmonary cathether
to diagnose right and left ventricular failure and pulmonary disorders
monitor effects of meds
monitor blood pressure
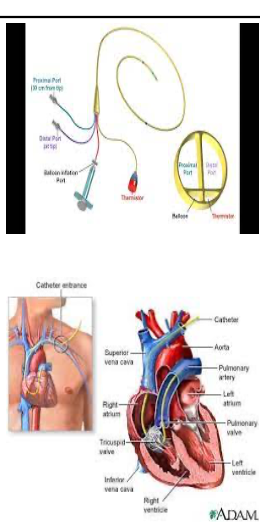
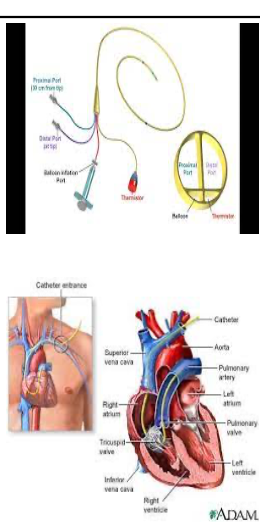
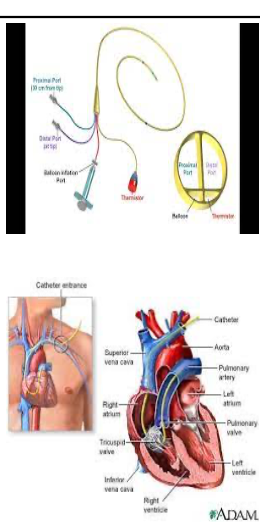
Swanz-Ganz placement
through large vein
femoral or jugular
tip of catheter placed in pulmonary artery
Swanz Ganz
Nasogastric tubes
Levin, Salem-sump, Dobhoff
Levin
nasogastric tube (nose to stomach)
single-lumen
feeding or gastric suction
long-term drainage


Levin
Salem-Sump
nasogastric tube (nose to stomach)
double lumen- one large and small for air vent
suction
nutrition and meds


Salem-Sump
Dobhoff
nasogastric or nasoenteric tube (nose to stomach/duodenum)
single lumen specialized NG small bore and flexible, more comfortable


Dobhoff
Miller-Abbott
nasoenteric (nose to duodenum)
treat obstructions in small intestines
double-lumen
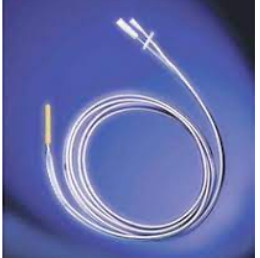
Miller-Abbott
Cantor
nasoenteric (nose to duodenum)
single-lumen
mercury-weighted tab attached to tip to help tube go through stomach to intestines
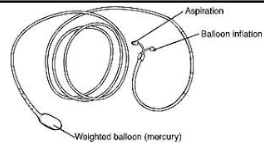
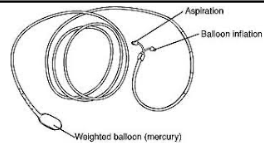
Cantor
Adult heart rate
70-80
children heart rate
70-100
infant heart rate
100-160
adult bp
110-140, 60-90
children bp
70-112, 26-70
infant bp
60-105, 22-60
breathing adult
12-20
breathing children
30-60
normal temp adult oral
96.8-99.8
normal temp adult rectal
0.5-1 degree above 96.8-99.8
normal temp adult axillary
0.5-1 degree below 96.8-99.8