Biology Unit 2 Exam Fritz UT AUSTIN AHHHHHHHHHhh
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Miller-Vrey Experiment
Showed that early macromolecules needed for life could be created in presence of NH3, H2, CH4, but no O2.
Origin Of Plants
Mitochondria endosymbiosis first, THEN chloroplasts.
Origin of metabolic process.
Photosynthesis evolved first, THEN aerobic respiration. (Cant AR without O2.
Endosymbiosis
Infolding of outer membrane of eukaryote forms membrane bound counterparts. Free-living cells like (mitochondira/chloroplast ancestors) are engulfing by other living cells.
Nucleosome
DNA tightly wound around a histone protein, unable to be used transcription, replication, etc.
3 Classes of photosynthetic life
Multicellular Photosynthetic Plants
Single Cellular Photosynthetic Protists
Single Cellular Photosynthetic Bacteria
Endomembrane System
mRNA produced by nucleus is translated by bound ribosome in rough ER.
Membrane/Protein/Lipid produced by ER transported to Golgi apparatus by vesicles.
Golgi pinches off into vesicles that become lysosomes, or flower out into membrane bound proteins or secreted proteins.
Cell Membrane
Cell-Cell communication, Selective permeability, separates exterior from interior.
Made of 4 components;
Phospholipid Bilayer
Cholesterol
Glycoprotein (Transmembrane Protein)
Communication Carbs (EX; antibodies)
Fimbrae
Not an organelle Surface appendages that allow for attachment to other surfaces. Prokaryotic
Capsul
Not an organelle, Sticky gel coat outside cell. Prokaryotic
Nucleoid Region
Houses prokaryotic chromosomes, not membrane bound
Ribosome
Not an organelle. Synthesizes proteins, translates mRNA. Made of two subunits.
Cell Wall
Structure/Support. Made of proteins, cellulose, and plasmodesmata.`
Chloroplast
Double membrane, site of photosynthesis, has DNA/ribosomes.
Central Vacuole
Water storage, breakdown of waste, hydrolysis of macromolecules, homeostasis
Mitochondria
Double Membrane, site of celluar respiration, own DNA/ribosomes.Ro
Rough Er
Extensive network of membrane connected to nuclear envelope to translate mRNA with ribosomes.
Smooth ER
synthesis of oils, steroids, new membrane phospholipids and carbs.
Also drug detoxification, storage of calcium ions
Glogi appartus
Sorts, packages, and modifies proteins.
Nucleus
Transcription, assembles ribosomes, has loose euchromatin to transcribe, or tight hetrochromatin for when ready to divide.P
Peroxisome
Metabolic function, breakdown/detoxifcation, creates hydrogen peroxide and coverts it to H2O.
Lysosome
Hydrolyzes macromolecules. Fuses with food vacuoles to digest.
Microtubules
Seperate chromosomes during anaphase, construct flagella/cila.
Microfilaments
Allow for molecules transport in cell. Form cleavage furrow during telophase. Muscle Contraction
Intermediate Filaments
Cell-Cell Adhesion and anchoring organelle in cell.
Speed of Diffusion
Size of Molecules
Temperature of solution
Strength of gradient
Molecules that undergo simple diffusion
O2, CO2, Ethanol, Steroids and Fatty Acids, Nitrous Oxide
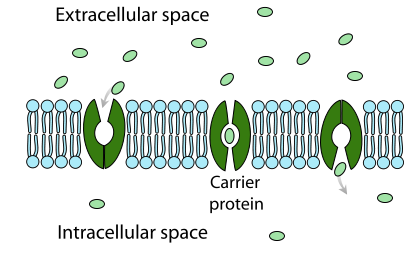
Carrier Protein
Binds to solute, changes, releases solute.
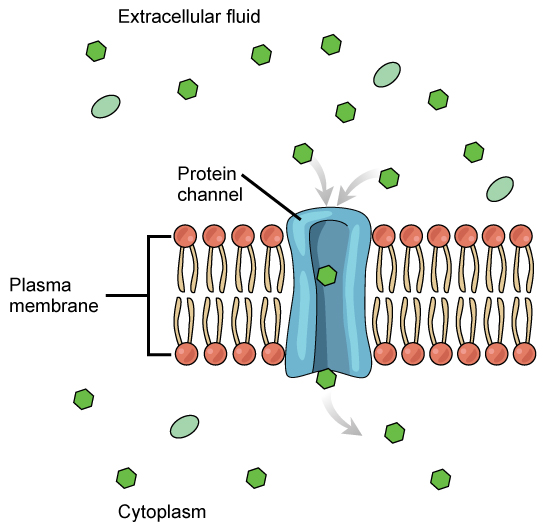
Channel Protein
Gate that opens allowing rapid diffusion of particles.
Maintains electrochemical gradient across membrane
Open in response to stimulus to allow ion flow
Close to allow electrochemical gradient to reform.
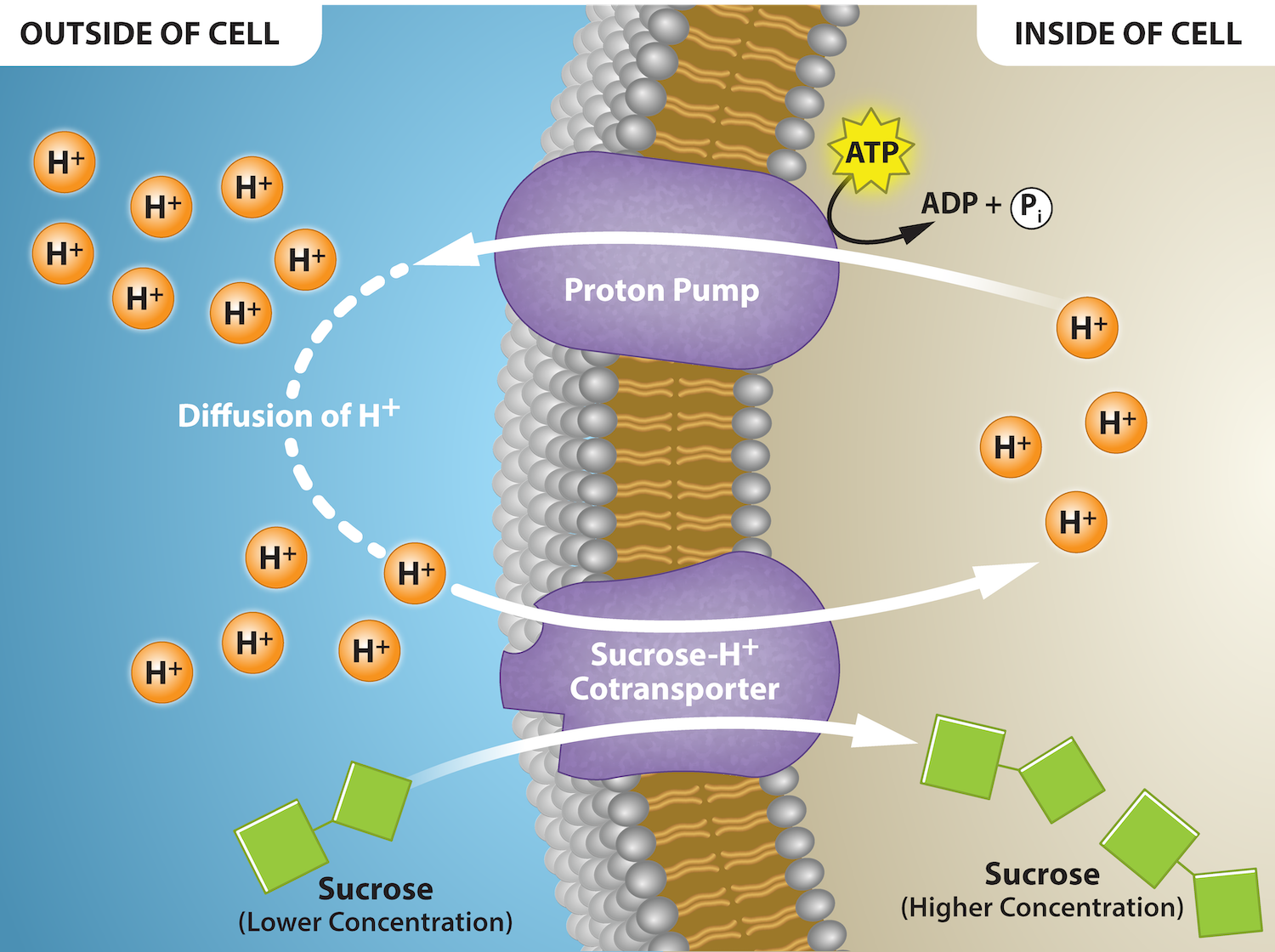
Active Transport
Specific solute binds to protein pump
hydrolysis of atp causes shape change in protein pump.
solute molecule moves across membrane to area of high concentration.
Hypotonic Solution
More solution inside cell, causes cells to lyse
Hypertonic solution
More solute outside cell, causes cell to shrivel.
Cell Stimulus
Reception; cells receive signal from other membrane or intracellular receptor.
Transduction; chemical reactions, often phosphorylation, activate target molecule.
Response; change in metabolism, change across membrane, change in gene expression.
Direct Signaling
gap junctions touch on cells, allow quick communication with cells while remaining independent.
Paracrine signaling
Ligands move by diffusion through extracellular matrix, elicit quick short responses, ligands removed by enzymes/neighboring cells quickly.
Endocrine signaling
Hormones travel through bloodstream and reach target cell in low concentrations
Autocrine signaling
Most important during development, regulates pain, inflammation, programmed cell death, and celluar differentiation during development.
G protein coupled receptor
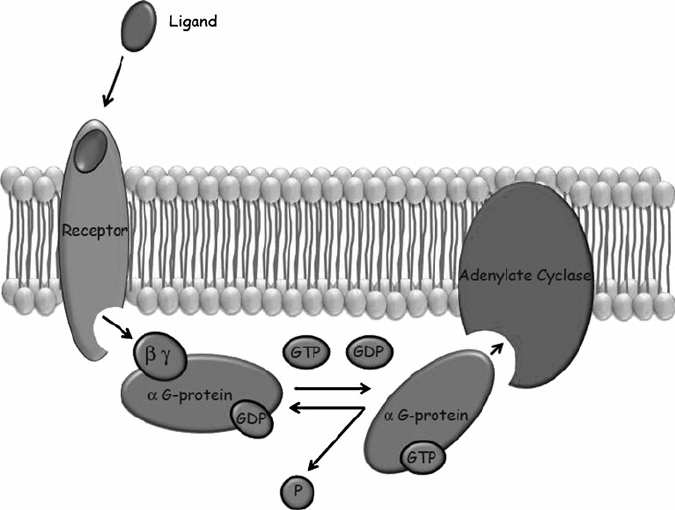
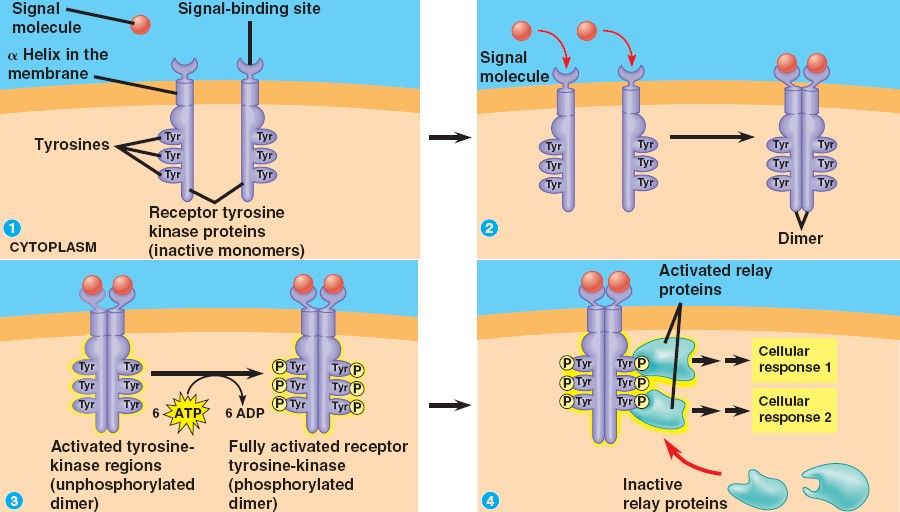
Receptor Tyrosine-Kinase Protein
Two structures requiring ligands, using 6 ATP to produce celluar reactions.
Catabolic/Excergonic
Releases Energy,
Spontaneous
DeltaG is negative
Anabolic/Endogonic
Consumes energy
Nonspontaneous
DeltaG is positive
Ezynmes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy, provide active sites for substrates to intermolecularly bind.
Transition state molecule
Stressed by enzyme, ready to reaction.
Requirements For Enzyme affected reaction
Must collide w/ enzyme
Sufficient activation energy
Molecules have proper orientations.
Cofactor
enzyme “helper molecule”, inorganic ion, initiate transition state in substrate
Coenzyme
Organic nonproteins, carry chemical groups between enzyme. Chemical inhibitors of enzyme.
Prosthetic Group
covalently bound non-amino acid components of an enzyme
Competitive Inhibitor
Similar shape to substrate, effect is reduced in high concentration of substrate, acts as a plug.
Non-competitive inhibitor
doesnt bind to active site, but changes shape of active site.
Kinases
enzyme that add phosphate groups
Phosphatases
Enzymes that remove phosphate groups.