NAVIT, tour, strawberries MAR26
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What grape is a proposed descendent of Savagnin Blanc, comes from Burgundy Region of France, produced in cooler climates, somatic mutation lead to new grapes; Where is this grown
Pinot Noir ; West Coast
The grapes is from Bordeaux France, name means wild white, can taste tropical, grassy, floral, and fruity, direct descendent of Savagnin Blanc; where is this grown in the US
Sauvignon blanc; West Coast
What does TTB stand fpr
Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau
What does the TTB do
enforces laws related to the production, importation, and wholesaling of alcoholic beverages, tobacco manufacturing and importing, and alcohol labeling and advertising.
what does AVA stand for
American Viticultural Area
what regulates AVA
TTB
what is AVA and why was it created
it is a specific type of appellation of origin used on wine labels; wineries wanted this so they can denote the region of origin on their bottle
who cam up with qoute “wine is bottled poetry”
Louis stevenson
what are some issue that the Washington viticulture face
water, labor, smoke, heat and cold
What are some main pest and disease that Washington viticulture faces
Disease: powdery mildew
Pests: Nematodes (virus), Phylloxera, mealybugs (virus)
what are some issue that the Oregon viticulture face
Water, Labor, some heat and sold
What are some main pest and disease that Oregon viticulture faces
Disease: powdery mildew
Pests: Nematodes (virus), Phylloxera, mealybugs (virus)
What are some main pest and disease that coastal California viticulture faces
Disease: powdery mildew and Pierces disease
Pests: Nematodes (virus), Phylloxera, mealybugs (virus)
what are some issue that the Coastal California viticulture face
water and labor
what are some issue that the central valley California viticulture face
Water, salinity, labor, and heat
What are some main pest and disease that central valley California viticulture faces
Disease: powdery mildew and some Pierces disease
Pests: Nematodes (virus), Phylloxera, mealybugs (virus)
This Oregon grape researcher looks at Smoke taint, sensory fermentation, and aroma
Dr. Elizabeth Tomasino
This Oregon grape researcher looks at Red blotch and irrigation
Dr. Alexander Levin
This Oregon grape researcher looks at nutrition
Dr. Paul Schreiner
This Oregon grape researcher looks at crop load and canopy management
Dr. Patty Skinkis
What damage by this arthropods can look similar to nutrient deficiencies with tiny white/yellow spots that progress to bronze discoloration, burning, and webbing
Spider mites
what Washington researcher looks at physiology, water, and berry shrivel
dr. Bhaskar Bondada
what Washington researcher looks at aroma, chemistry, ripening, distillation, and aging
Tom Collins
what Washington researcher looks at Pest biology, plant physiology
Michelle Moyer
what Washington researcher looks at grape physiology, hardiness, and stress
Markus Keller
what California researcher looks at grape breeding, rootstock, neatodes, salinity, and drought
Dr. luis Diaz-Garcia
what California researcher looks at irrigation, maceration, process optimization for wine
Federico cassassa
what California researcher looks at bredding, powdery mildew, pierces disease
Dr. Summaria Riaz
what California researcher looks at looks at grapevines physiology, mechanization precision agriculture
Dr. Luca Brillante
what are the examples of macronutrients
nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
of the macronuntrients, which are primary? which are secondary?
Primary=nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium; secondary=calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
What are the examples of micronutrients
iron, manganese, copper, zinc, boron, molybdenum, chlorine
What nutrient is a components of chlorophyll, proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), some plant hormones
nitrogen
What nutrient is the component of energy compounds ATP, NADPH, NADP; nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and cell membrane
phosphorus
What nutrient is invovled in protein and enzyme synthesis and activation, maintaining proper water balance, and photosynthesis
potassium
What nutrient is needed for cell membrane stabilization, cell wall structure, and cell division and meristem growth
calcium
what nutrient is the componet of chlorophyll and involved in enzyme activation
magnesium
what nutrient is a componet of several primary amino acids
sulfur
what nutrient is a component of chlorophyll and many enzymes
iorn
what nutrient is needed for chlorophyll synthesis and enzyme activation
manganese
What nutrient is Needed for chlorophyll synthesis and is a component of many enzymes
copper
What nutrient is Required for fruit development involved in movement of carbohydrates and plant hormones
boron
what nutrient is Required for plant hormone synthesis and fruit development
zinc
what the role of molybdenum
component of enzymes
__ is higher concentration of H+ to OH- and __ is higher concentration of OH- to H+, __ is equal
acidity, basicity, neutral
What materials that raise soil pH
liming materials - calcium, magnesium, carbonates, oxidase, hydroxide
High pH soils may have a deficiency for what nutrients
iron, zinc, boron
sandy soils may have a defeicency for what nutrients
potassium, zinc, others
What type of induced deficiencies may occur
soil drainage, drought stress, heavy crops, nutrient antagonism (phosphorus and zinc)
the nutrient __ is mobile and __ is immobile
nitrogen; iron
precipitates of iron is unavailable in __ soils
calcareous
what nutrient deficiency symptoms appear as interceinal chlorosis in newer growth? why
iron, it is immobile
Should we always rely on visual symptoms?
no!
what is the species of strawberries
Fragaria x ananassa
strawberries ploidy is __ meaning how many chromosome total and how many sets
octoploid; 56 total; 8 sets (7 in each set)
What species were crossed to create strawberries
Fragaria virginiana x fragaria chiloensis
what helps turn value for strawberry farms? (sales wise)
U-pick and direct sales
__ is a planting style that allows farmers to buy less plants per acre, fill in plants with growth from own plants
matted row
what are the disadvantages of matted rows
less productive due to decline overtime, higher disease control demands
what are the advantages of plasticulture raised beds
increase inputs and decrease chemicals, less rot due to no contact with soil, more drainage
Growth of strawberries emerges from where
crown
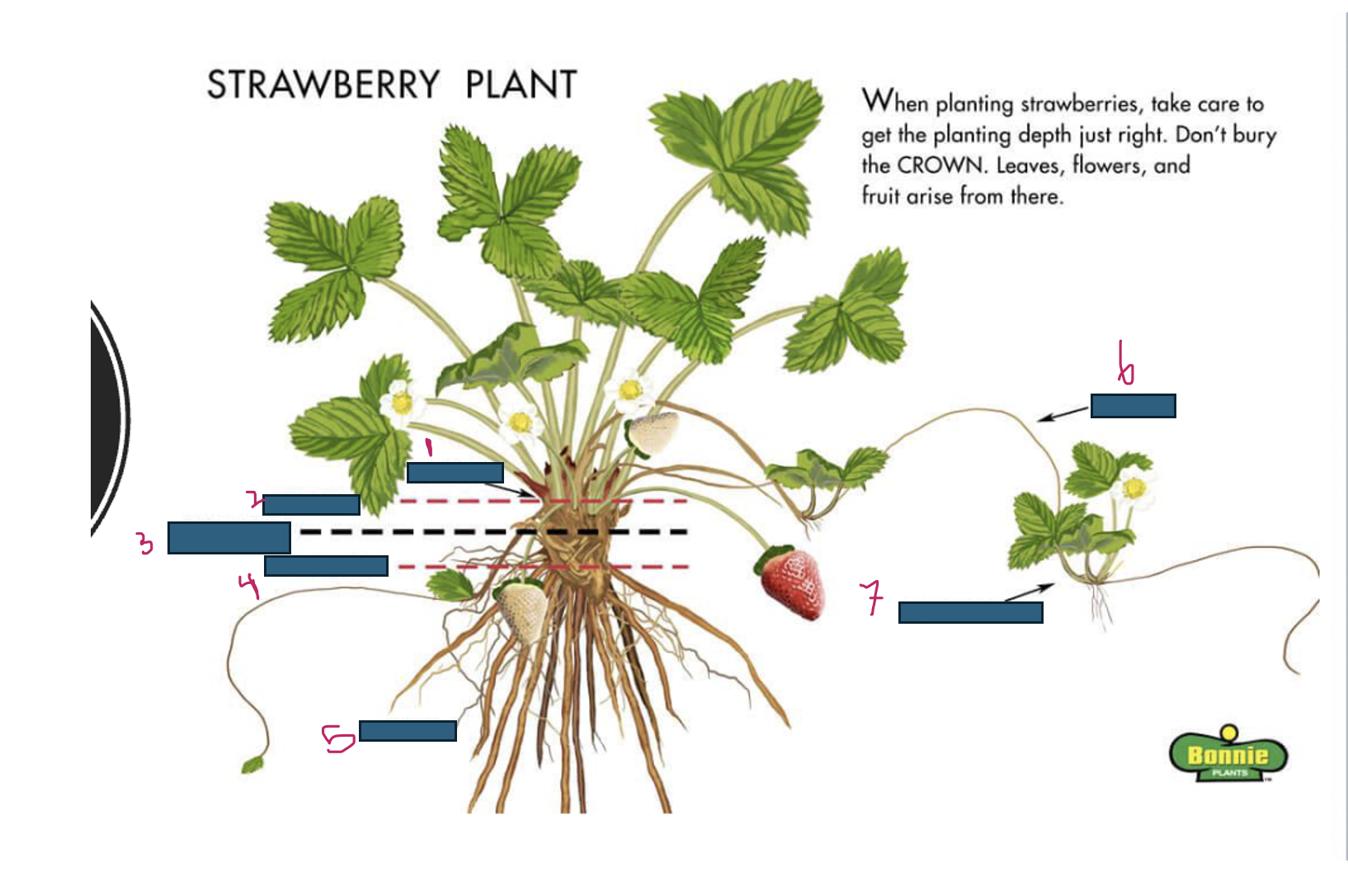
What is 1
Crown
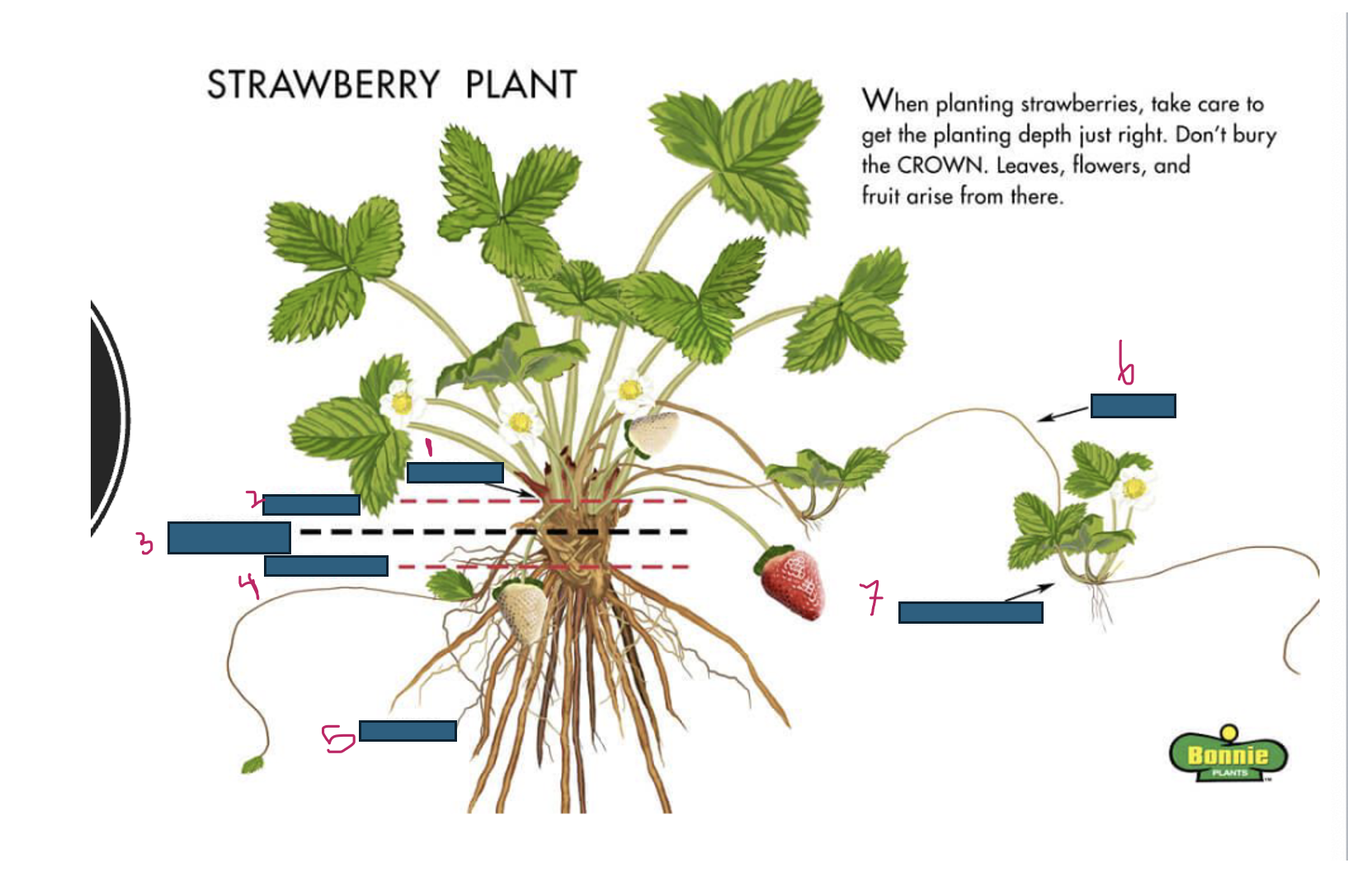
What is 2
too deep
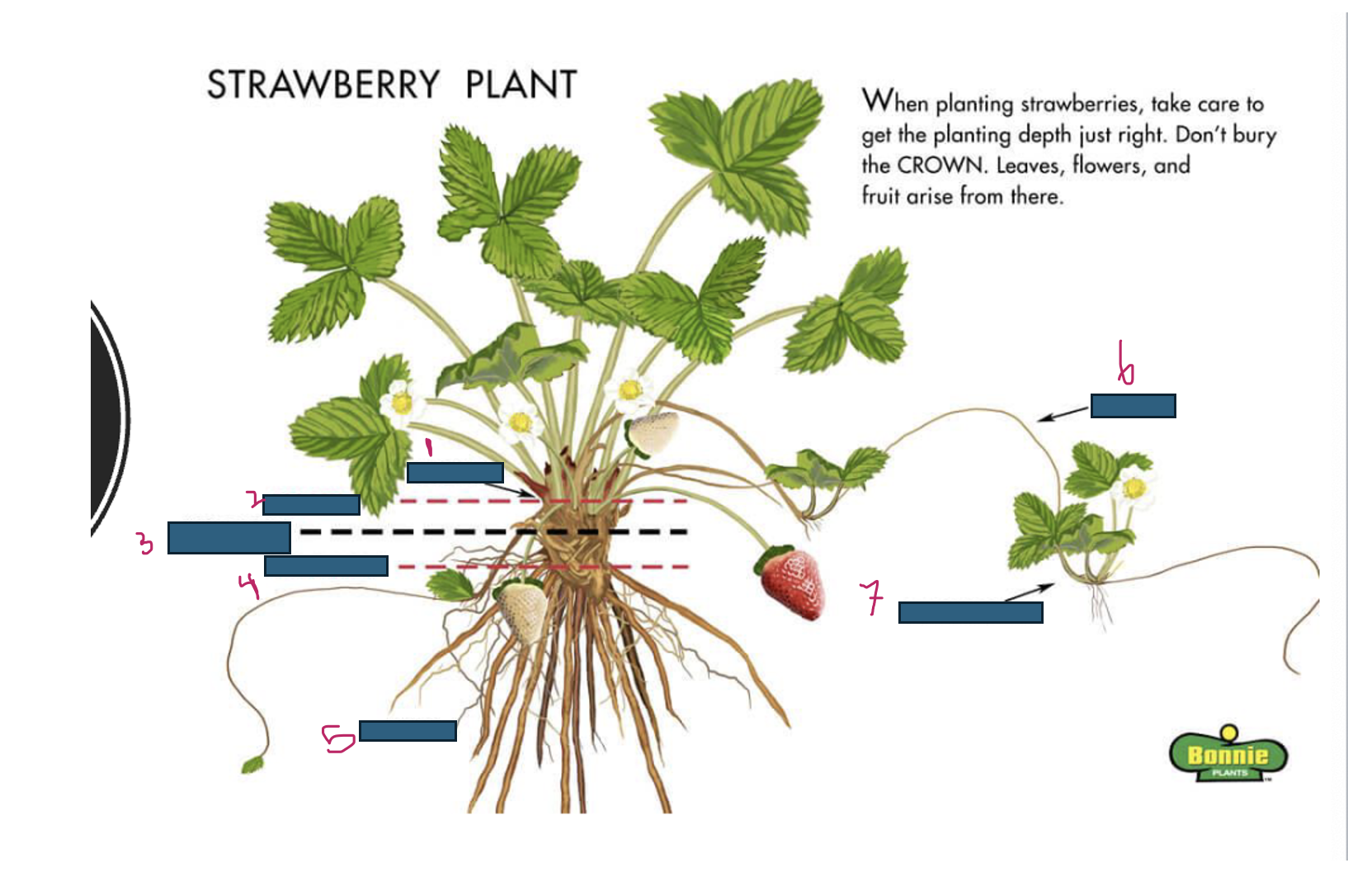
What is 3
just right
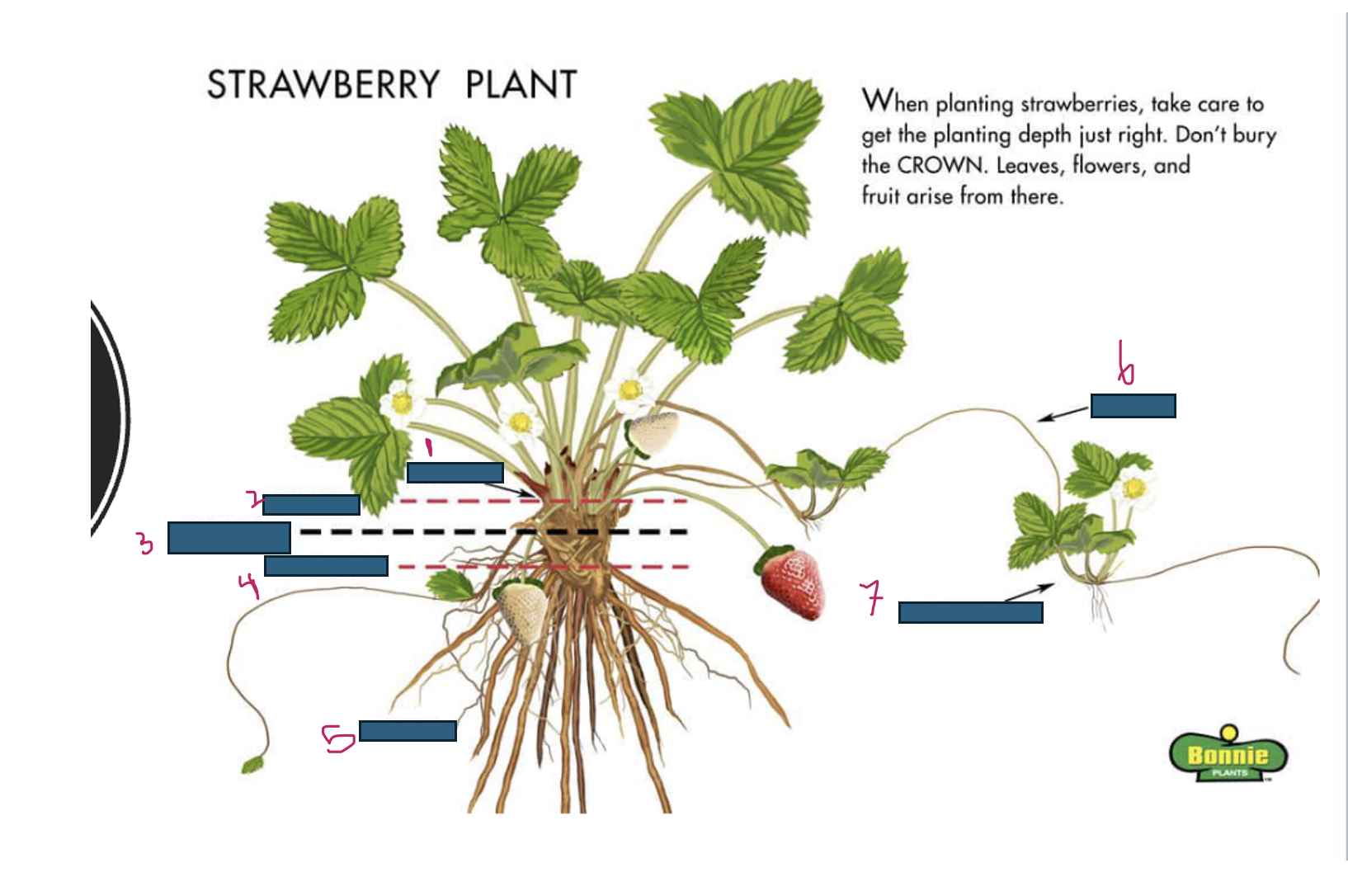
What is 4
too shallow
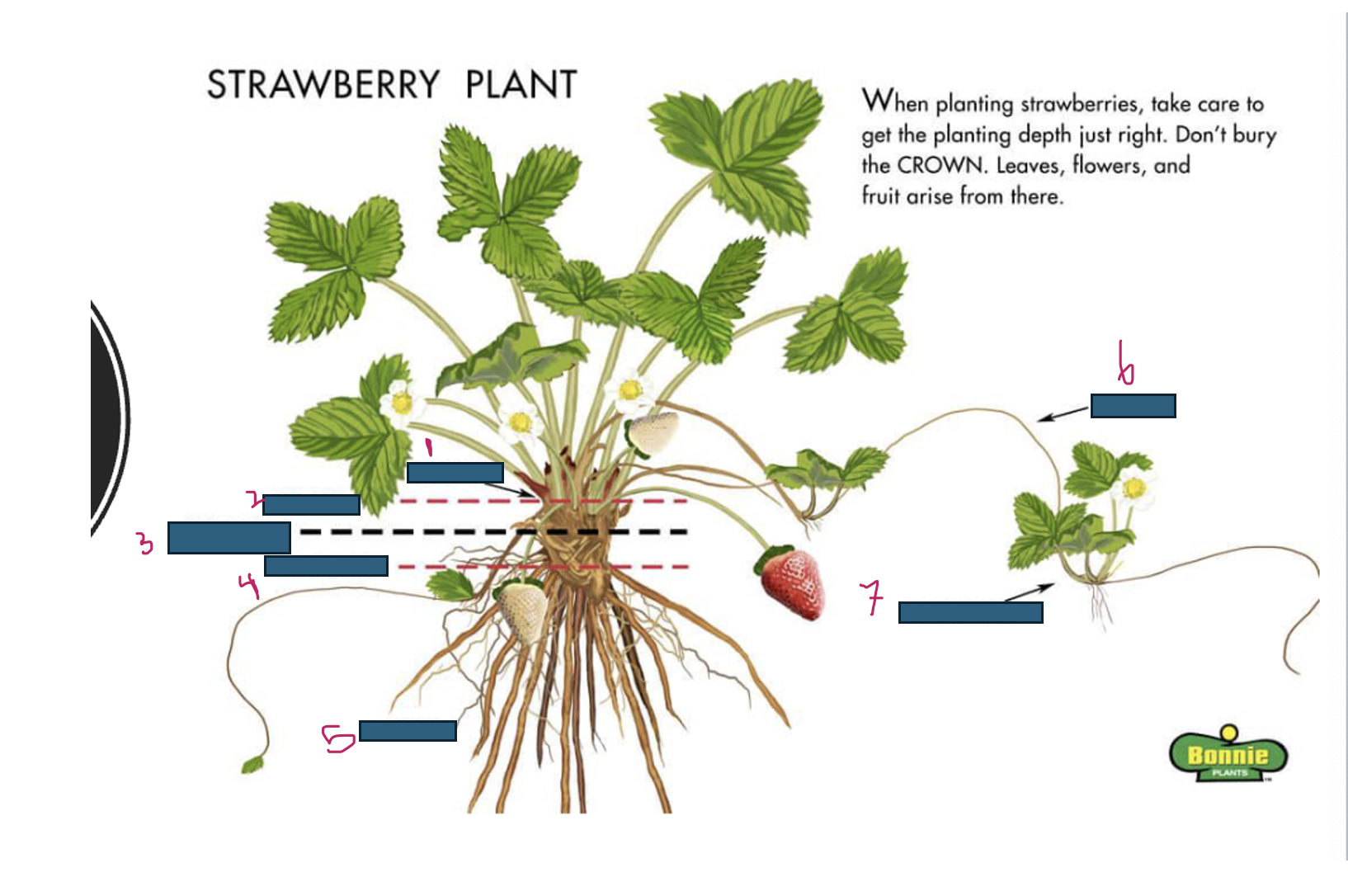
What is 5
roots
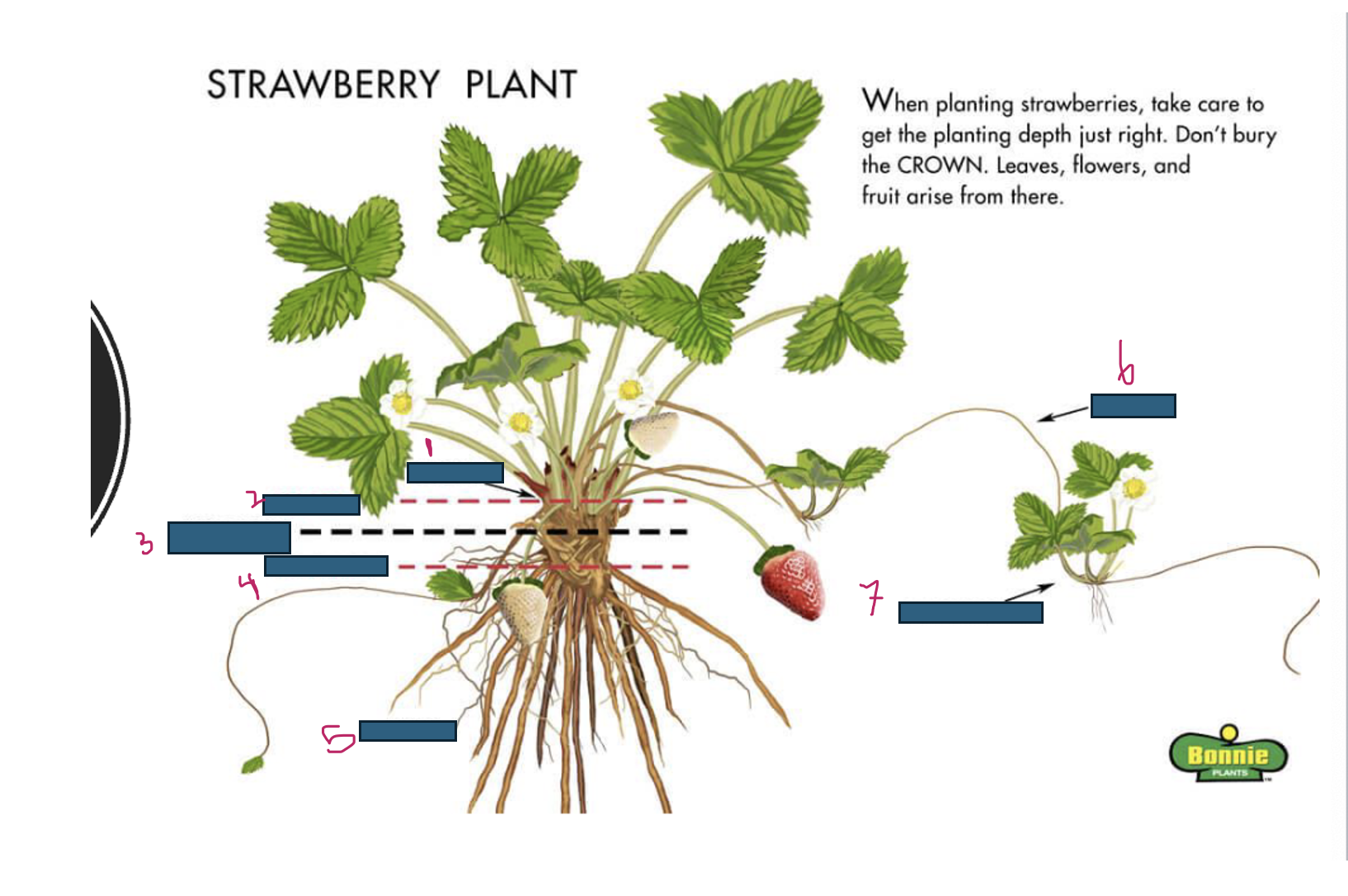
What is 6
runner
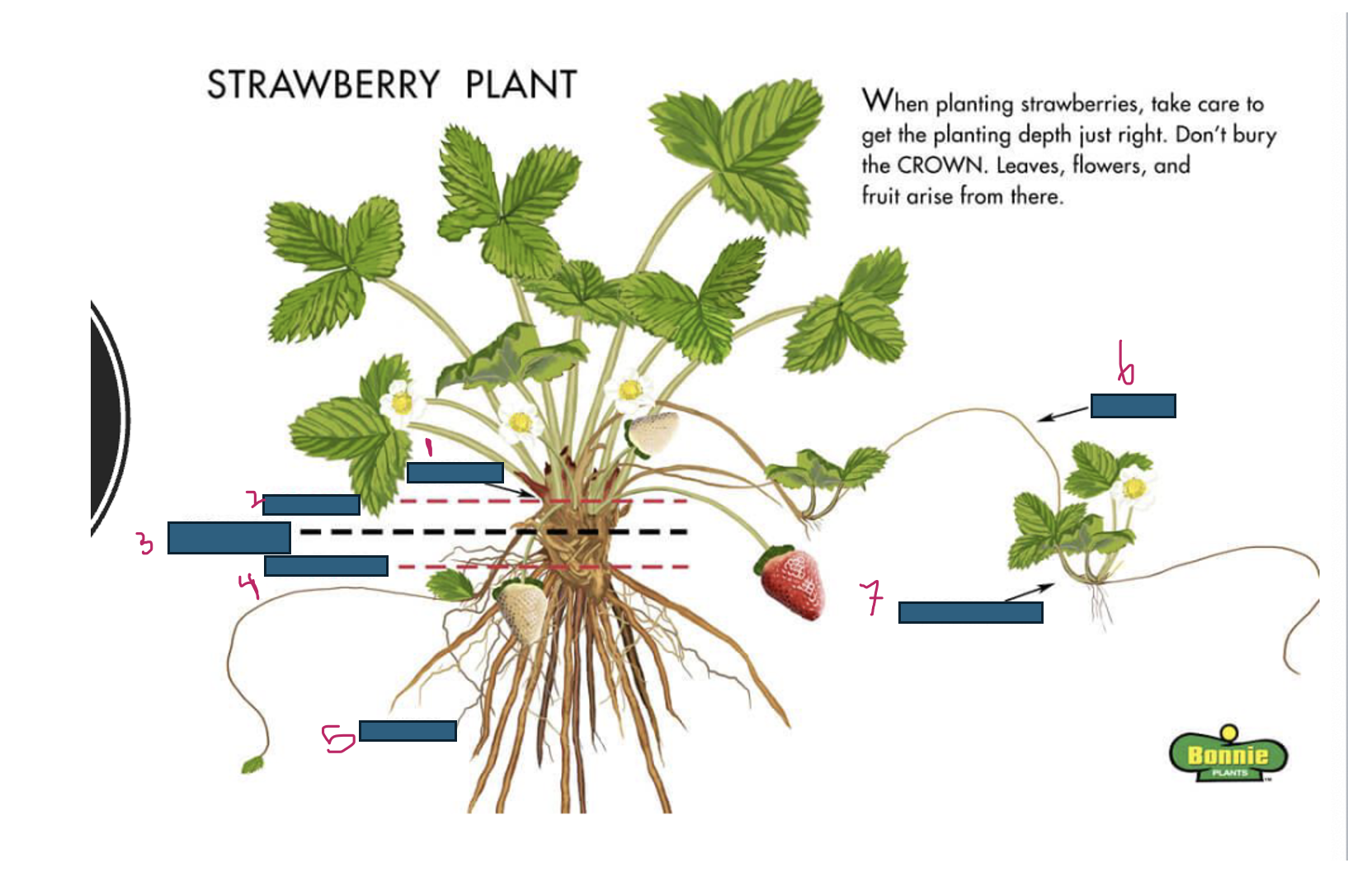
What is 7
daughter plant