Intro to competitive market, shifts in supply and demand curve, and elasticity
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is the central topic of Microeconomics?
the interaction of supply and demand in markets
What IS a market?
All the buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
What are the characteristics of highly organized markets?
All the buyers and sellers come together at a single location and an auctioneer sets the price.
What are the characteristics of a PERFECTLY COMPETITIVE market?
1. Goods are highly Standardized
2. Large numbers of buyers and sellers (therefore a single buyer/seller can't affect the price)
3. Buyers and sellers are all well informed about the price (of the good)
What is the Law of Demand?
When price increases, demand decreases
What is the demand schedule?
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
To find the market demand curve, you add the individual demand curves ________________
Horizontally
What is the difference between a shift of demand curve and shifts along the demand curve?
A shift of demand curve means that the demand curve (the entire line) SHIFTS left or right
Shifts along the demand curve mean points are moving along the demand curve (I.E. the demand curve DOES NOT SHIFT)
What are the factors that shift the demand curve?
TEN-IP
T astes
E xpectations
N o. of Buyers
I ncome
P rice of Related Goods
How does Tastes shift the demand curve?
If you start to hate Coca-Cola you will buy less of it
How does Expectations shift the demand curve?
If you expect something to be cheaper in the future you will try to not buy it now so that you can buy more later
How does No. of buyers shift the demand curve?
If there are more consumers, than the demand will increase (duh moment)
How does Income shift the demand curve
Two Types of Goods:
Normal Goods and inferior Goods
Normal Goods are normal, means that if you lose income you buy less of it.
Inferior Goods are weird, if you lose income you buy more of it (Good EG: Instant noodles, Bus rides)
How does the Price of Related Goods shift the demand curve?
Two types of "Related" Goods:
Substitutes: when price falls in a substitute, the substitute will be bought more and the original less. (for example, if Pepsi got cheaper, people would buy Pepsi more and less Cola, shifting Cola demand curve to the left)
Complements: when price falls in a complement, the original good will be bought more (for example, if price of CD players falls, more CD players will be bought( law of demand) and therefore more CDs will also be bought)
What is an easy way to understand what shifts the demand/supply curve?
Anything that increases/decreases the quantity supplied/demanded that is NOT the price of the good.
The price of the good does affect the quantity supplied/demanded but that does NOT shift the curve, it just shifts ALONG the curve.
DM me if you don't understand
What is the law of supply?
As prices rise, Supply also rises
What are factors that shifts a supply curve?
TEN-I
T echnology
E xpectations
N o. of sellers
I nput Prices
How does Technology shift the supply curve?
if there is a technological advancement, supply will increase
How does Expectations shift the supply curve?
If suppliers expect prices to rise in the future, they reduce quantity supplied today so that they can supply more later at a higher price.
How does No. of Sellers shift the supply curve?
More sellers mean more supply (no duh moment)
Where is market equilibrium?
where supply and demand intersect
What is cool about market equilibrium?
That the market has an automatic tendency to gravitate towards it.
What does the height of the market demand curve at each point reveal?
(simplified: what does the market demand curve represent)
It reveals the marginal buyer's willingness to pay. (marginal buyer is a buyer that would be indifferent between buying and not buying the good at that price. i.e. the value of the good to the marginal buyer is equal to the height of the demand curve)
Simplified: It represents the value of the good to consumers
What area is consumer surplus?
Area beneath demand curve (so cost is less than the value) and above market price
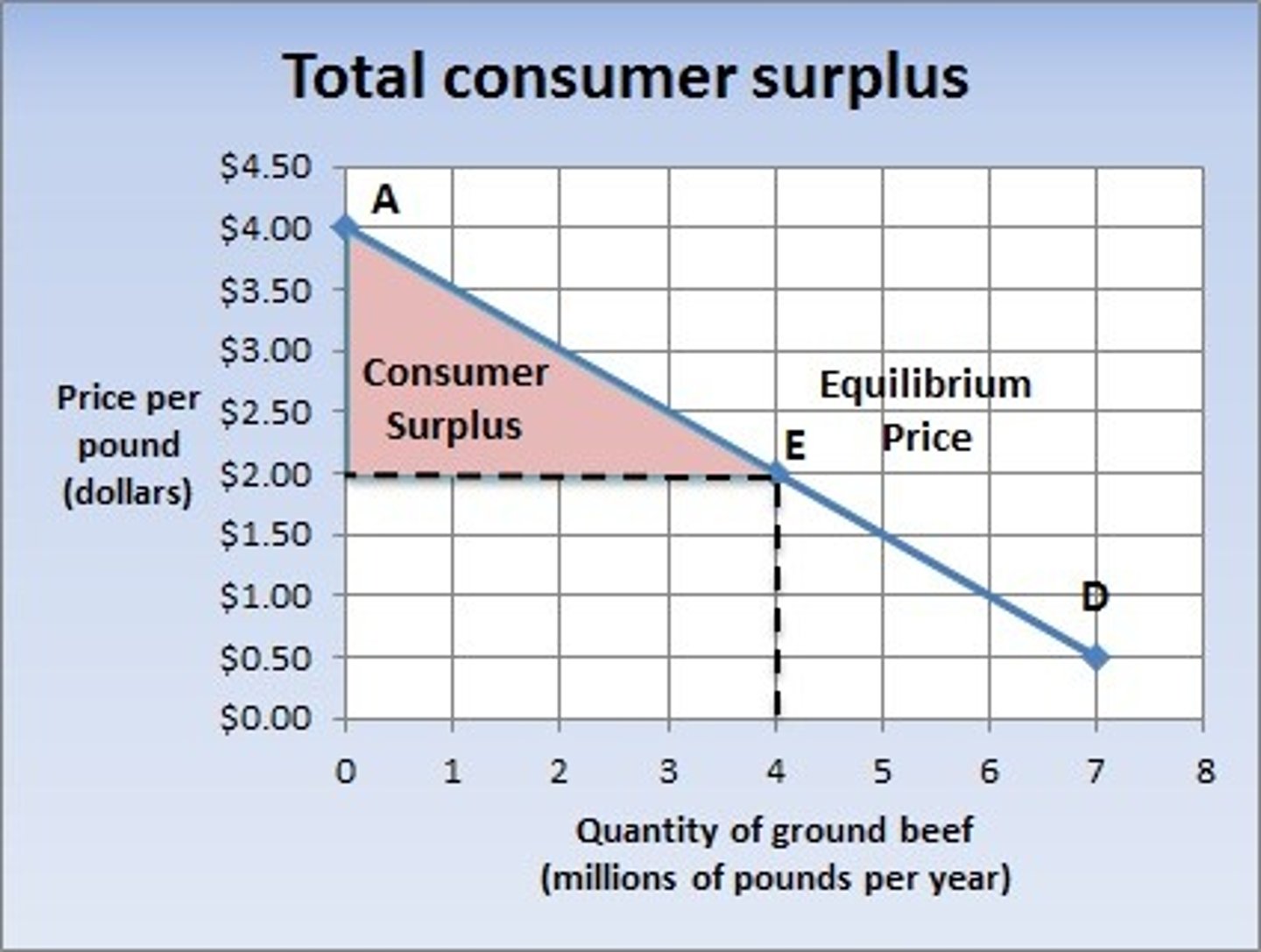
What does the height of the supply curve indicate?
The willingness to supply of the marginal seller
Simplified: the opportunity cost to the marginal seller
What area is producer surplus?
Area above supply curve (since price exceeds opportunity cost) and below the market price
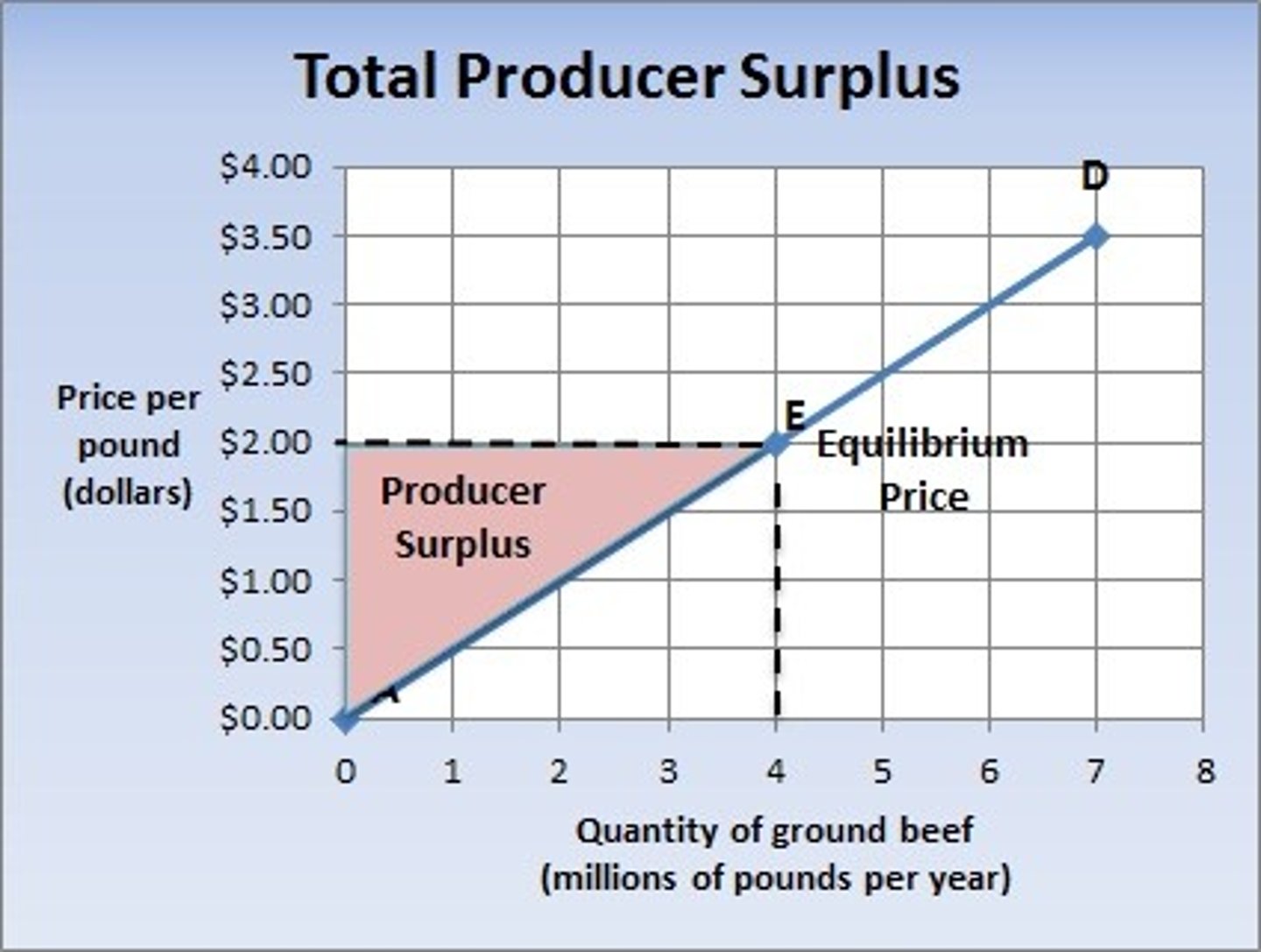
What should you do if they ask what happens when market equilibrium shifts or when a factor shifts supply/demand curve?
ALWAYS TRY TO VISUALIZE THE GRAPH AND HOW THE SUPPLY/DEMAND CURVES WOULD MOVE AND HOW THAT WOULD AFFECT THE AREA i.e. surplus of consumer and producer
What is price elasticity of demand?
The responsiveness of demand to a change in price
Formula of price elasticity of demand?
Percent change in quantity demanded/ Percent change in price
Eg.
Demand: 3 --> 2
Price: $5 --> $6
Percent change in quantity demanded: -1/3 = -33.33 %
Percent change in Price: 1/5 = 20%
-33.33/20 = -1.67
BUT it is conventional to take the absolute value (so no negative numbers!)
1.67
What are the factors that affect price elasticity of DEMAND?
4
Substitutes
Necessities
Market Definition
Time Horizon
How does Substitutes affect price elasticity of Demand?
It is easy for consumers to switch products if the price goes too high. (Eg. Cola)
How does Necessities affect price elasticity of Demand?
It is Not easy for consumers to switch products or to stop buying the product because it is a NECESSITY (Eg. houses, apartments, Gasoline)
How does Market Definition affect the price elasticity of Demand?
The broader the market definition, the fewer substitutes there will be, and the lower the elasticity of demand
How does Time Horizon affect the price elasticity of Demand?
Over time, people can adjust to changes in price i.e. higher price elasticity
For example, if gas prices were raised, at first, not much you can do. But over time, people will buy more electric cars, move closer to work, etc. that reduces their demand
The curve that is flatter will have a ______ elasticity?
Higher
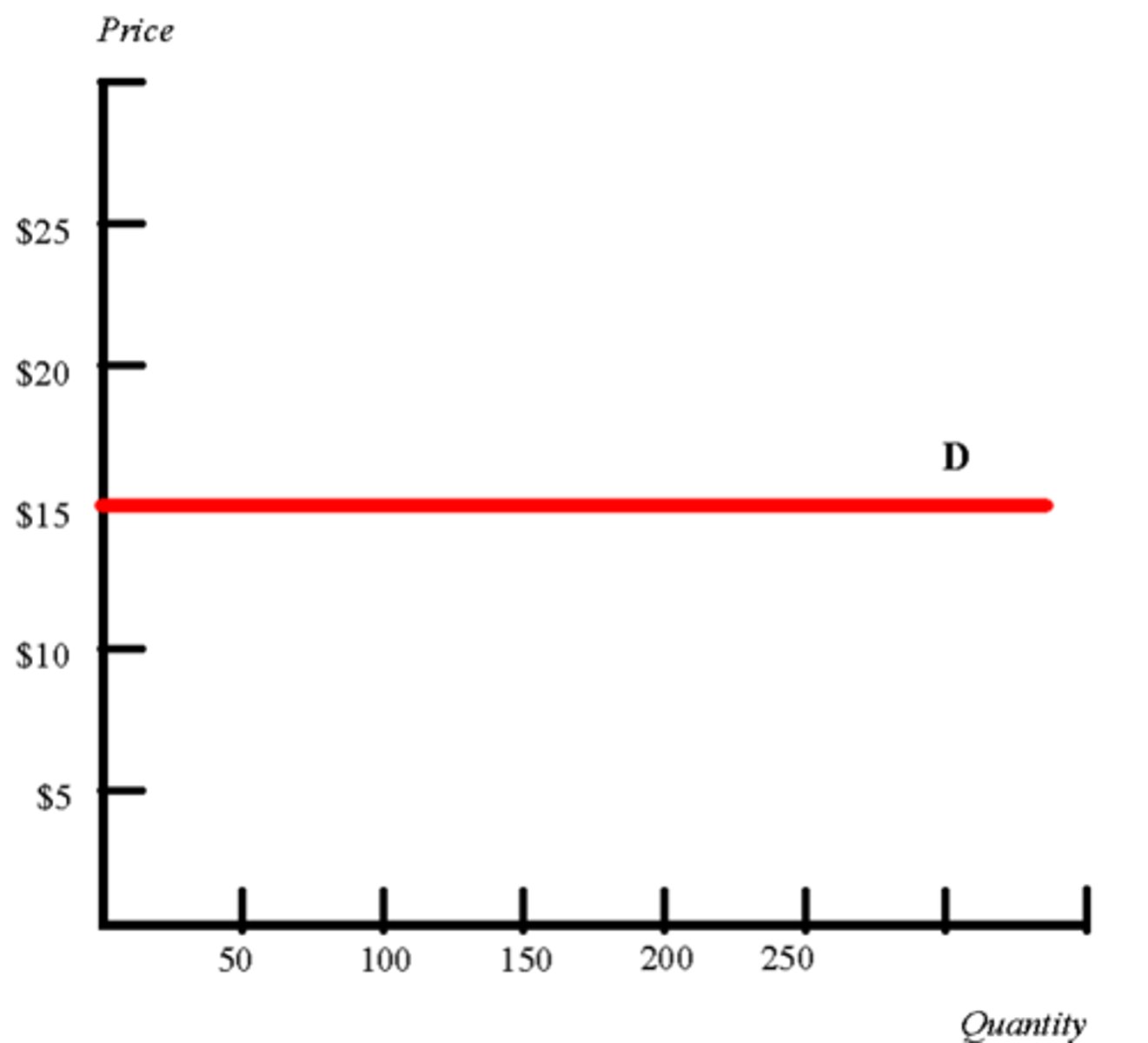
What does perfectly elastic mean?
When elasticity is infinity. (the demand/supply curve is a horizontal line)
For demand elasticity
If price goes any higher (even a cent) people will not buy at all.
If price goes any lower, people will buy an infinite quantity
For supply elasticity
If price goes any higher, suppliers will supply an infinite quantity
If price goes any lower, suppliers will supply none.
What does it mean when a curve is elastic?
When the elasticity value is over 1 and under infinity
What does it mean when a curve is UNIT elastic?
When the elasticity value is equal to 1
What does it mean when a curve is inelastic?
When the elasticity value is between 0 and 1
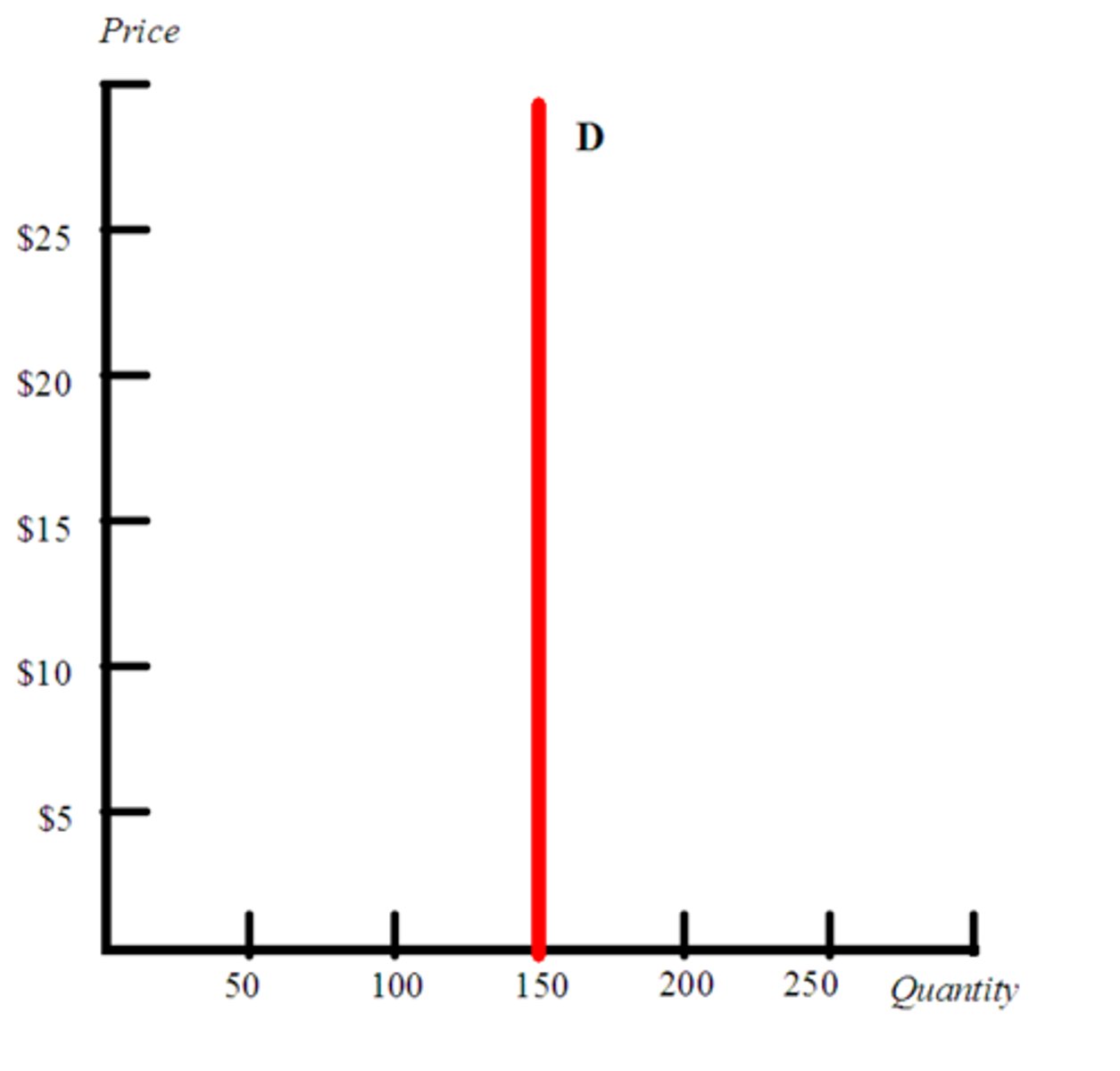
What does it mean when a curve is perfectly inelastic?
When the elasticity value is 0.
Changes in price does NOT affect the quantity supplied or demanded.
What are the factors of the price elasticity of SUPPLY?
3
Ease of entry and exit
Scarce resources
Time Horizon
How does Ease of entry and exit affect elasticity of Supply?
If it is easy for businesses to enter or leave a business, then supply is more elastic (because increase/decrease in suppliers means increase/decrease in supply)
How does Scarce Resources affect elasticity of Supply?
Elasticity of supply for scarce resources is low.
For example, the supply of beachfront vacation homes is inelastic because the amount of beachfront property is limited.
How does Time Horizon affect elasticity of supply?
The longer the time horizon, the greater the elasticity of supply.
Over longer time horizons, firms will be able to hire and train additional workers and buy equipment in response to the price changes