AP US Gov - Unit 3b - Elections
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
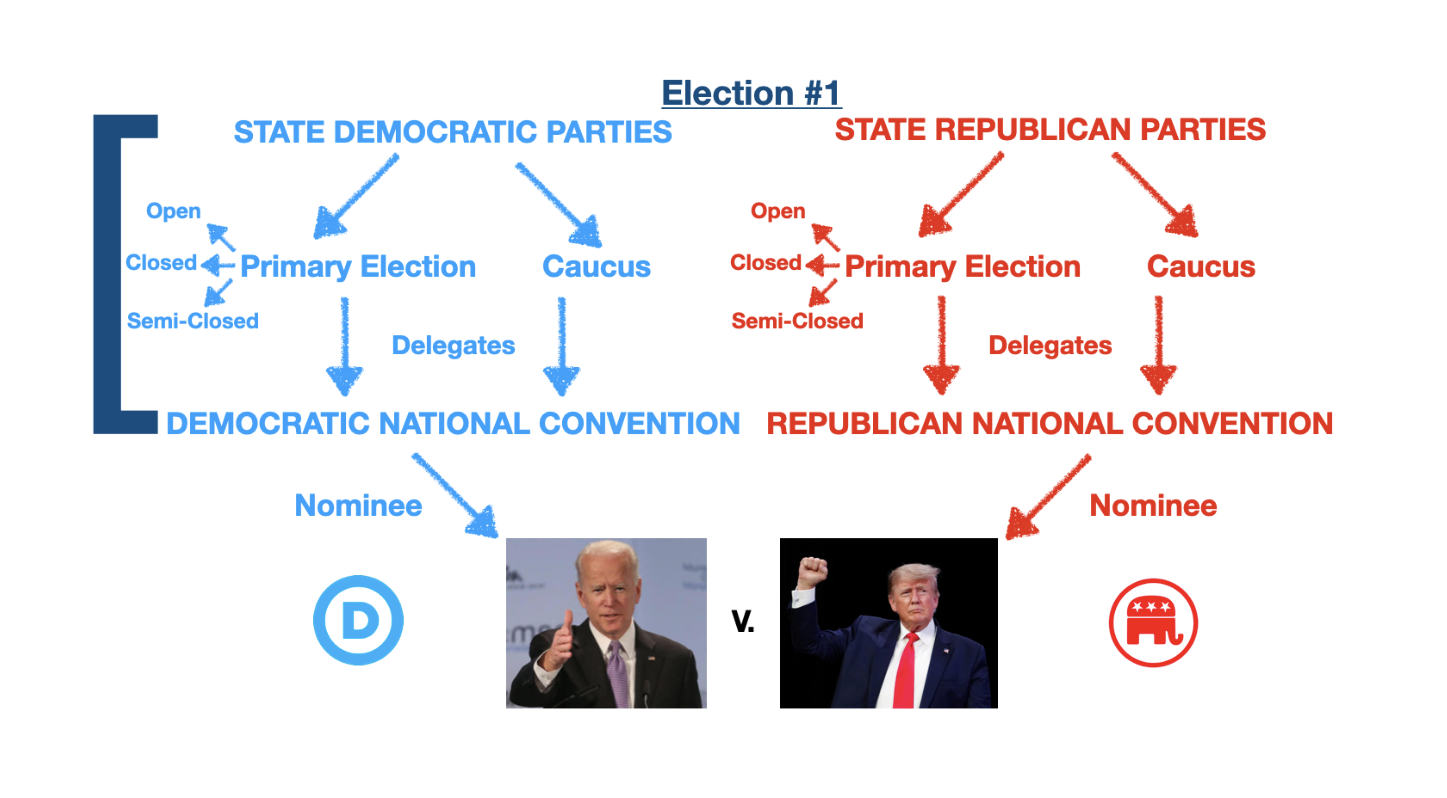
Open primary
all voters regardless of party affiliation may participate in any party's primary (you can only vote in one party's primary elections)
Closed primary
voters must affiliate/register with a given part to vote in that party's primary, you have to do it before going to the polling place
Semi-closed/modified primary
unaffiliated voters can choose which party's primary to vote in, though they have to affiliate with a party in order to vote, and is can be done on election day at the polling place
In order for a presidential candidate to win their party's nomination they must…
Compete in all 50 primaries and caucuses in each state
Win a majority of delegates sent to the party's national convention, if they win a majority, they win the nomination
Primary election
election between candidates of the SAME party, which decided who will be nominated by the party to run in the general election
Caucus
a meeting of party members (not all are from the same party) to select delegates supporting one or another primary candidate
can be very time consuming
Safe states
the plurality of citizens in a state that voted for the same party in the last 4 elections
Ex: missouri (republican), michigan (democrat)
Swing states
= the plurality of voters who sometimes voted for democratic or republican candidates
Ex: florida, arizona, wisconsin, ohio
→ Candidates don’t worry about safe states, they focus their attention onto swing states because they want to win those states
Also called “battleground” states
Compulsory voting
making voting a legal requirement for all eligible voters (people have a punishment if they don’t vote)
reapportionment
based on the population census it’s changed every ten years accurately represent the states and how many reps each state has in the house of representatives
Malapportionment
when representation isn’t proportional to the population (due to shifts in the population, ex: think before baker v. carr)
Redistricting
redrawing districts in a state (that states change the districts) districts have to be equal in population, contiguous, and cannot redistrict based on race (done at least every 10 years)
Gerrymandering
gives an advantage to one political party, and a disadvantage to another party, the drawing of district boundaries (can result in weird shaped districts) in order to create an advantage for one party
To create more “safe” districts for one political party, and less for another party (can lead to misrepresentation of voters in gov)
Winner-take-all system
whichever candidate gets a plurality of votes gets all of a states electoral votes (used by 48 states)
Compulsory voting
making voting a legal requirement for all eligible voters (people have a punishment if they don’t vote)
General election
Once a candidate has secured their parties nomination a candidate competes against other nominees
Voting rates depending on the election
Voting turnout rates differ between states that use caucus, and states that do primary elections
People are more likely to vote in a general election rather than a primary or caucus election
People are more likely to participate in primary elections
Most likely to participate in
General elections
Primary elections
Caucus elections
Least likely to participate in
requirements to become a presidential candidate
In order for a presidential candidate to win their party's nomination they must…
Compete in all 50 primaries and caucuses in each state
Win a majority of delegates sent to the party's national convention, if they win a majority, they win the nomination
Political elites in elections
- tend to be ideologically extreme
How labels such as “liberal” and “conservative” apply to political elites
They are more interest in politics, therefore they are more involved, and more informed
Activists spend more time with other activists, and there views can be more similar to each other
Candidates have to attempt to appeal to political elites in their party during primary elections
Super tuesday
a day (typically in march) when a lot of states have a primary or caucus on the same day
After the tuesday it gives people a better idea of who may win, and how many delegates that candidates are winning
Primaries and caucuses after super tuesday tend to not matter as much as primaries and caucasus on or before super tuesday
Consequences of elections
Contentious campaigning during the primary elections creates divisions within the party's coalition (kamala harris and joe biden in the 2020 democratic primaries)
Candidates are against each other as they fight to become president
Why National conventions are held
Parties typically pick swing states to hold their conventions in order to influence the states to support the candidates
Electoral College
- a process used in the US to select the president
The framers adopted this system because…
It was as compromise, some people in congress wanted to select the president (similar to parliamentary system) other wanted the president to be picked based on the popular vote
Minor/third Parties
Third party candidates often “split the vote” or have a “spoiler affect” where a strong third party candidate will “steal” votes from a major party candidate whose ideology is most similar to, hurting that majority party candidates chance of winning the election
To avoid the “spoiler effect” the 2 major parties often try to adapt parts of third party platforms in order to encourage potential party voters to join a major party instead
Our system doesn't allow for minor parties to have a relative change at gaining significant power (few exceptions)
Affects of Swing and Safe States
The votes of the citizens in lower population states their votes matter more than larger population states (voting weight)
Candidates favor swing states (larger population swing states)
Favors special interest groups in large swing states
→ winner take all has an affect on how candidates run their campaigns
Presidential elections v. Congressional elections
Size - presidential elections involve more voters, therefore they are more difficult to win and campaign for
Competitiveness - presidential races tend to closer and more competitive
Voter turnout - congressional elections have a lower voter turnout than elections that involve the president
Congress can serve their constituents - members of congress can help their constituents directly, and increase the incumbency
Ability to “duck” responsibilities - members of congress can denounce their own body (congress) and avoid accountability for things, where the president cannot denounce and is seen as responsible for their actions
Voter registration in the US
In the US there are low levels of voter registration
In the last election around 73% of the voting age population was registered to vote (if people aren’t registered they can’t vote)
Self registration is required for people in the US to be to vote
Tuesday elections with inconvenient voting hours
How to Solve the low percent of voter turnout
Make Election Day as a national holiday (Federal Law)
Move Election Day to a weekend (Federal Law)
Allow for Early Voting (State Law)
Allow No Excuse Mail-in Voting (State Law)
Allow Same-Day Registration (State Law)
Automatic Voter Registration (State Law
—> In other countries they use compulsory voting - Compulsory voting = making voting a legal requirement for all eligible voters (people have a punishment if they don’t vote)
How senators are distributed in the US
The # of senators is decided
2 per state (100 total, no matter the size or population of the state)
How Representatives are distributed in the US
The # of representatives
In total 435 people are representatives
Allocate the seats by using the data from the census to account for the shifts in population from the previous 10 year (reapportionment = assigning representatives to a specific district)
How to solve the misrepresentation of voters in the US
Determining the size (population) of the congressional districts
Answer: state governments → this changed because of baker v. carr so that all districts of a state must be the same size in population (to avoid malapportionment)
Solutions to gerrymandering
Changing state law so that parties do not have the power to redistrict
Creating a bipartisan committee to draw the district lines
Using computers to fairly redraw districts (people have not done this)
Getting rid of single members districts (republican or democratic districts), and replacing them with proportional representation (i.e. NO DISTRICTS)
Position issues
an issue in which the public is divided on which rival candidates or political parties adopt different positions
Valence issues
an issue in which most of the public agree, and candidates take similar positions on the issue that best represent people's widely-held view
Overall the candidates can believe the same thing but different candidates have different ideas on how to solve the issues
Ex: economy, inflation, education, crime, military, healthcare
Kitchen table issues
a group of issues that directly affect the average person (would be discussed at a kitchen table)
Ex: taxes, healthcare, economy (economic issues)
“Culture war” issues
disagreements between social or cultural issues between groups (liberals v. conservatives)
Ex: abortion, LGBTQ+ rights, critical race theory)
“Wedge issues”
issues that tend to divide a group such as a political party, one side wants one thing, the other wants the opposite (driving a wedge in the party)
Ex: israel or palestine
Parties will focus their campaigns on what issues public will have support for and issues that divide their opposition (the other party)
Candidate centered campaigns in the US
Campaigns in the US that focus more on candidates themselves than on the political party they represent, voters look at individual characteristics or candidates, and the less official policy stances
voters base their vote on if they get a “good” vibe from candidates
In states where the opposing party is dominant candidates distinguish themselves from other members of their party to try to appeal to voters
Factors that impact which candidate a voter votes for the presidency
Religious beliefs or affiliation, gender, race and ethnicity
Political issues
Political socialization