L8 Cornea Anatomy, Physiology, and Imaging
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
____ with the tear film makes up 2/3 of total refractive power of the eye
cornea
t/f the cornea is a key barrier against infection and damage to deeper ocular structures
true
the cornea is ___-____ mm horizontally ~__mm smaller vertically
11.5-12mm, 1mm
the cornea's anterior refractive power is ___ to ___
43 to 43.50
cornea is ___ shape
prolate
cornea is _____ centrally and _____ peripherally
steeper, flatter
corneal epithelium has ___ junctions between superficial cells
tight
apical projections increase ___ ___ contact
surface area
basal cells are the most
posterior
basal cells have ___ junctions and ____ making it slighly more permeable
gap and zonulae adherens
basal cells are the only epithelial cell capable of ____
mitosis
basal cells are adherent to basement membrane via _____
hemidesmosomes
corneal epithelium complete turnover every ___ -___ days
7-10
basement membranes require _ weeks to reconstruct and heal. during this time overlying epithelium has ___ __ during healing
6, unstable bonds
t/f epithelial stem cells localized to limbal basal epithelium
true
limbal stem cells in the epithelium migrate ___ and ____ to differentiate
apically and centrally
the corneal stroma have fibers aligned in parallel fashion within each ____
lamella
the corneal crystallins within the corneal stroma serve the purpose
reduces forward light scatter
the corneal stroma gives _____ strength
mechanical
t/f peripheral stroma is thicker than central stroma
true
keratocytes in the stroma make up ___% of the volume
10
is the corneal stroma rigid? yes or no
yes
_____ is more rigid compared to the posterior
anterior
the corneal stroma is innervated via
nasociliary branch of V1
cornea is steeper ____ and flatter ____
centrally, peripherally
cornea is thinner ____ and thicker ____
centrally, peripherally
____is a monolayer of cell that flatten to 4mm in thickness in adulthood
endothelium
endothelium contains ___ and ___ junctions
gap and tight
endothelium layer functions to
maintain stromal deturgscence or regulate fluid so there it little to none within the stroma
________cells/mm2 = risk for corneal edema
<500
the physiology of endothelium consists of ___ and ___ pump sites, intracellular ____ anhydrase pathway
Na and K, carbonic
metabolic disorders, hypoxia, toxins, injury, alteration in pH and glaucoma are stressors that causes changed to
endothelium and cell density loss
from __ to ___ hours the cells at edge of defect migrate and spread to cover the defect. fibronectin and laminin protein play a role
minute and 5-6 hours
___ to ___ hours mitosis begins so with basal cells, transient amplifying cells and limbal stem cells
24-30
persistent epithelial defects during wound healing can occur such as damage to ___ nerves which reduces growth factor and substance P AND damage to ___ cells. matrix metalloprotease 9 is thought to play a role... loss of sensation?.
corneal, epithelial
what is matrix metalloprotease 9?
enzyme that helps with wound healing and response to wound heal
what happens if there is an over expression of matrix metalloprotease 9?
it will degrade extracellular matrix leading to tissue destruction
stroma's ___ repair to maintain clarity
avascular
in the stroma, keratocytes are activated which enlarge and _____ to injured area
migrate
keratocytes are triggered by functional ____ basement membrane
epithelial
t/f when the stroma is wound healing it results in opacity of the injured area
true (bc keratocytes ?)
within 1-2 of stromal healing, ____ become involved and increases the expression of MMPs
myofibroblasts
during wound healing the endothelium becomes distorted from injuries anteriorly? yes or no
yes
in the endothelium wound healing, surrounding cells ___ and migrates _-_ days after injury
enlarge, 1-3
____ is the method of measuring the radii of curvature of the two principal corneal meridians by measuring the size of the mire reflections
keratometry
corneal power can be calculated from radius of curvature by
D= 0.3375/r OR r=337.5/D
keratometry is designed to measuere the curvature at a _-_mm diameter within pupil
3-4
list two clinical applications of keratometry
fitting CL
IOL calculations (IOLmaster and lenstar) except refractive sx
___ ____ Is a method of visualizing the power of the corneal surface by videoing anterior corneal images + computer processing giving u a map of corneal surface power distribution
corneal topography
examples of corneal topography (3)
medmont, oculus keratograph, and ziess atlas
corneal topography clincial applications (3)
dx/ manage pathology
evaluating vision (RK/PRK)
screening for refractive sx
keratometry

corneal topography
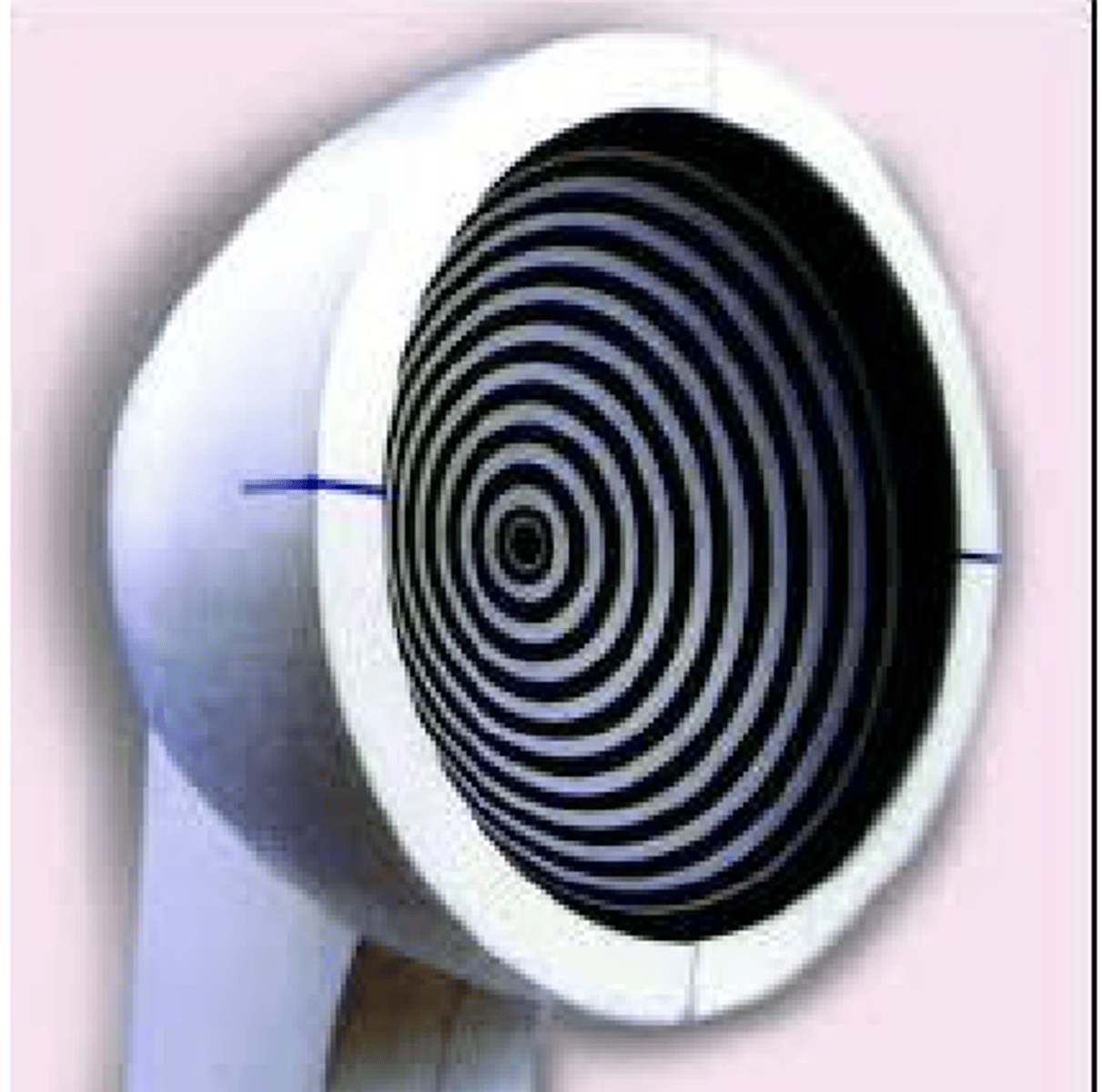

placido disk based topography works by
reflection based: measuring rings reflected from anterior corneal surface
for the placido disk topography the close spacing of the mires mean ___ areas of the cornea whereas broad spacing of the mires indicate ___ areas of the cornea
steeper, flatter
what is a limitation of placido disk based topography?
sensitive to disruptions of tear film so perform before drop and IOP testing
grid style reflection corneal topography
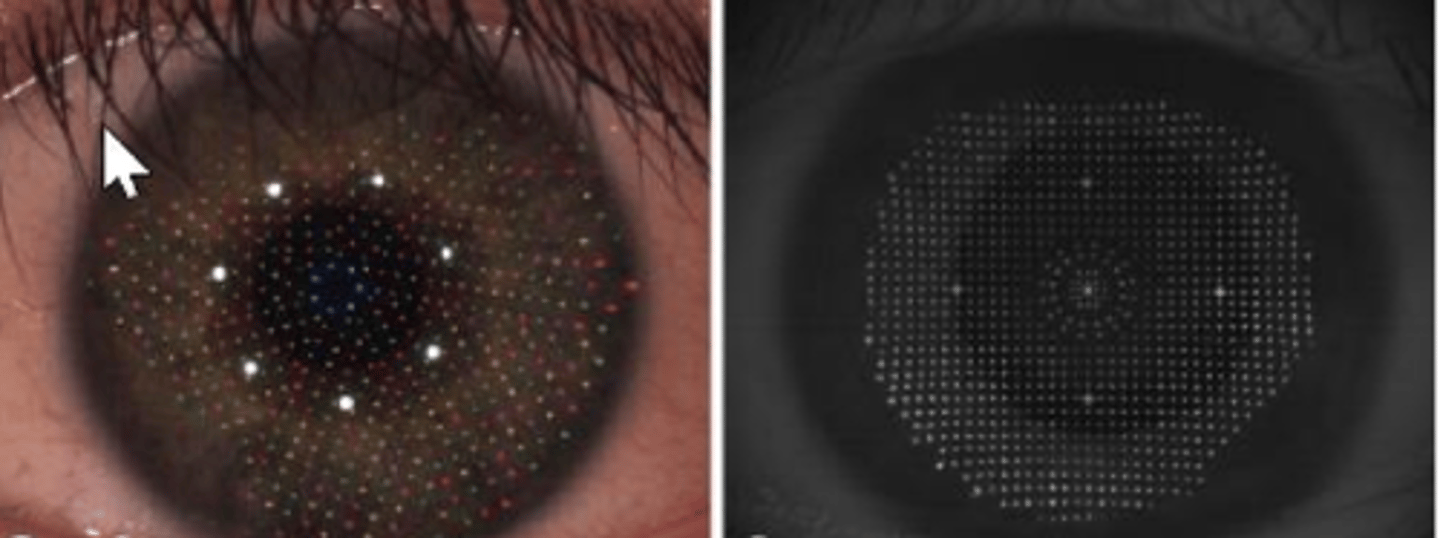
____ ____ is point to point reconstruction of specular reflection of color LEDs. it offers increased accuracy and precision
grid style target
___ ___ directly measures both anterior and posterior corneal surfaces to calculate the corneal power
corneal tomography
what are the 3 types of corneal tomography
slit scanning, scheimpflug, and OCT
1. uses series of slit beams at regular intervals to capture light scatter from both surfaces. its able to measure corneal shape and thickness, but less accurate on posterior curvature/power
this describes
slit scanning tomography
oculus pentacam is an example of
slit scanning tomography
___ ____ takes saggittal sections of anterior segment imaged using sheimpflug optics. It increases depth of focus, simulataneous images of the cornea, anterior chamber and lens
sheimpflug tomography
Pentacam HR, sirius, galilei G4 are all examples of
sheimpflug tomography
similar to topography, OCT clinical applications are (4)
dx pathology like keratoconus
evaluating vision (RK/PRK)
screening for refractive sx
cataract sx
in topographic maps, _____ indicate steeper curvature or higher dioptric power whereas _____ are flatter curvature or lower dioptric power
warm, cool
t/f the normal cornea is prolate
true
Topographic maps have a scale where smaller intervals equal more ____ and larger intervals ___ irregularities
noise, mask
1. best overview of the corneal power
2. commonly used for routine screening or diagnostic
3. averages to make smooth map
all describes what kind of map
axial curvature topographic map
this map is the most sensitive meaning it the most accurate for individual points
tangential topographic map
this map shows areas of relative elevation or depression based on best-fit-sphere
elevation display topographic map
pachymetry map shows
corneal thickness
____ is a noninvasive, noncontact imaging using interference pattern of reflected light and relies on reconstructed images from cross sectional (A scans)
anterior segment OCT aka AS-OCT
what are the two types of AS-OCT
time domain and fourier domain
___ ____ is a deeper penetration due to longer wavelength. from a light beam
time domain
___ ___ is higher resolution and faster scans than TD OCT
fourier domain
fourier domain has two types which are
spectral domain and swept source
____ _____ has higher resolution and faster scans than FD OCT, improved signal to noise ratio and more structural detail. it also uses a broadband light source. whereas ___ ___ is similar but with a longer wavelength allowing imaging of anterior chamber to posterior lens and used a swept source laser
spectral domain, swept source
refractive surgery, ectasia disorders, s/p corneal grafts, tear film eval, ocular surface tumors, cataract sx and keratitis are applications of _____ ____
anterior segment OCT
what is one limitation of anterior segment OCT
limited visualization of structures posterior to the iris
___ _____ uses high frequency ultrasound waves and direct contact
high resolution ultrasound biomicroscopy
___ ____ works by echoing from tissues at varying depths are recorded at different time intervals to construct the image
high resolution ultrasound biomicroscopy
ultrasound biomicroscopy is useful for evaluatoin of ocular structures posterior to ___ iris and in areas of _____ corneas
posterior, opaque
ultrasound biomicroscopy clinical applications include (3)
deep ocular masses of iris or CB, gluacoma (acute angle closure) and ocular trauma
___ ____ uses light reflection to allow imaging and analysis of the corneal endothelium
specular microscopy
___ ___ provides pachymetry measurement, endothelial cell density, mean cell area, % of hexagonality or pleomorphism and coefficient of variation
specular microscopy
specular microscopy clinical applications include (3)
corneal dystrophies, corneal transplant sx with eval and cataract extraction w IOL
corneal biomechanical assessment include (2)
ocular response analyzer (ORA)
and
Corvis ST
corneal biomechanical assessment clinical application
associated with glaucoma progression
ocular response analyzer is made up of _____ ___ which is viscoelastic damping of the cornea and ______ ___ which is overall resistance of the cornea
corneal hysteresis, corneal resistance factor
___ ___ is noncontact tonometer that uses air pulse to monitor for corneal deformation response
corvis ST
___ ___ ___ is real time high resolution cellular imaging in 4d layer by layer
in vivo confocal microscopy
in vivo confocal microscopy clinical apps include (5)
DED, neuropathic corneal pain, infectious keratitis, demodex, and corneal deposits and dystrophies