B1.1: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Macromolecules
Large biological molecules neccessary for life (Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleic Acids)
Macromolecules bonding
Condensation reaction
Macromolecules breaking down
Hydrolysis
Smallest form of carbohydrate
Monosaccharide
Monosaccharide formula
CnH2nOn, where n = number of carbons
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides bonded together
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides bonded together
Monomers of triglycerides
Glycerol and fatty acids
Lipid type depends on
Fatty acids
Per g of substance:
Lipids store about 2x the amount of energy compared to carbohydrates
Why is life on Earth carbon-based?
The four main macromolecules that build up living organisms contain carbon
3 main monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
OH functional group
Hydroxyl (alcohol)
NH2 functional group
Amino/Amine
COOH functional group
Carboxyl
P functional group
Phosphate
Peptide bond
New covalent bond is created between two amino acids, breaking covalent bonds within each individual molecule and producing a water molecule. Catalysed by enzyme.
What indicates the shape of a monosaccharide?
The number following c in the formula. Ie. Ribose = C5H10O5 , thus ribose is pentose.
Properties of glucose
Molecular stability (covalent bonds)
Highly soluble in water (polarity)
Therefore easily transportable
High energy yield from oxidation
What does (1-4) and (1-6) refer to in glycosidic linkages?
Carbon numbers of the two carbons joined together by the bond.
A starch with only (1-4) linkages will have what shape?
Linear helix
What does the addition of (1-6) linkages create?
Branches
Which polysaccharide consists of only 1-4 linkages?
Amylose
Which polysaccharide is known for having 1-6 linkages?
Amylopectin and glycogen
Starch
Polymer of glucose containing amylose and amylopectin
Excess glucose is stored as
Glycogen
What does alpha and beta refer to in a monosaccharide?
Orientation of the hydrogen and hydroxyl group
Alpha orientation
Hydrogen on top
Beta orientation
Hydroxyl on top
Difference between bonds in cellulose and amylose
Cellulose uses beta 1-4 linkages whereas amylose uses alpha 1-4 linkages
Glycoproteins and blood transfusion
Glycoproteins facilitate cell-to-cell recognition, on red blood cells they form the antigens that decide blood type (A, B, AB, O)
Type O can give blood to
Any blood type, as neither A or B glycoproteins (antigens) are present
Types of lipids
Fat, oil, wax, steroid (changes form depending on temperature)
How are triglycerides formed?
1 glyceride + 3 fatty acids
How are phospolipids formed?
1 glyceride + 2 fatty acids + 1 inorganic phosphate
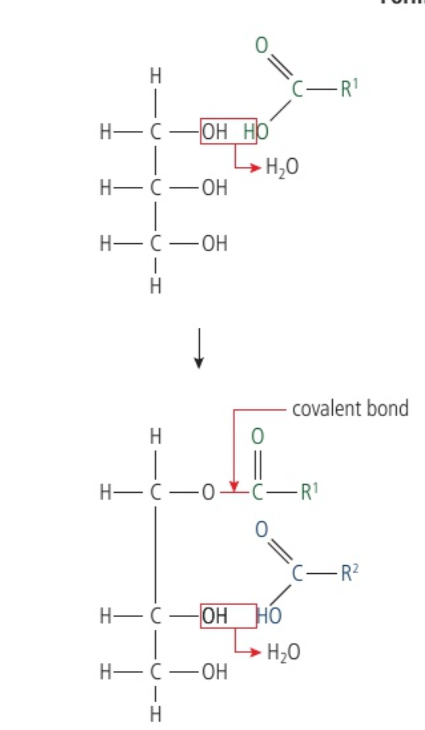
How do phosphates/fatty acids bind to glycerol?
Glycerol is a 3-carbon molecule with each carbon bonded to a hydroxyl group. Every fatty acid has a terminal carboxyl group. This facilitates a condesation reaction, removing the hydroxyl group entirely and allowing the remaining oxygen molecule in the fatty acid to bond to the carbon in the glycerol.
Saturated fatty acids
Higher melting point, more rigid and linear structure, fats at room temp, all carbons have single bonds meaning that all available carbons are bonded to hydrogen
Monounsaturated fatty acids
Lower melting point, oil form at room temperature, one double bond between two carbons.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Also oil at room temp, low melting point, multiple double bonds between carbons.
Adipose tissue
Cells that store fat (triglycerides) for long-term energy storage - e.g blubber in whales and seals. Typically found next to skin, used for thermal insulation
Steroid hormones
Chemical messengers. Lipid-based and therefore insoluble, pass through membrane easily to direct transcription.
Why are starch and glycogen good energy stores?
Their coiled, branched structure makes them compact
They are relatively insoluble so they don’t draw extra water by osmosis
Glucose can be easily added or removed according to neccessity
Triglycerides
Fats and oils