Oral Mucosa
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
vermillion border ; pharyngeal mucosa
The lining of the oral cavity is continuous with the _____ of the lips to _____ in the region of soft palate and anterior pillars of fauces
Ectoderm (except tongue)
Origin of the oral mucosa
Orban and Sicher
Classified the oral mucosa into 3 types
Masticatory mucosa
Areas of free and attached gingiva and hard palate
comes in primary contact with food during mastication
keratinized
Lining mucosa
Areas of the lips, cheeks, vestibule, floor of the mouth, inferior surface of the tongue, soft palate
little attrition
soft, pliable, nonkeratinized
adaptable, easily shaped
Specialized mucosa
Mucosa on the dorsum of the tongue
Protection
against mechanical forces
normal resident population in the oral cavity
Sensation
touch, pain, pressure, taste, gag and salivation reflexes
Secretion
Permeability and absorption
Thermal regulation (for lower mammals)
Functions of the oral mucosa
Xerostomia
Dryness of mouth; blockage of salivary glands
Orthokeratinized
Parakeratinized
Incomplete parakeratinized
Nonkeratinized
Types of surface epithelium according to keratinization
Orthokeratinized
Type of Keratinized Epithelium
Stratum corneum is homogenous and made up of flat, closely packed keratinized cells with no nuclei
Found in: hard palate, attached gingiva, lingual papillae
Parakeratinized
Type of Keratinized Epithelium
Presence of nuclei within the keratinized layer
Flat, keratinized cells with pyknotic nuclei and remnants of cytoplasmic organelles
Found in: dorsal surface of tongue (lingual papillae)
Incomplete parakeratinization
Type of Keratinized Epithelium
Least common; seen only in marginal gingiva
Outermost cells retain some nuclei and don't fully keratinize
Some are keratinized, some are not
Found in: marginal gingiva
Stratum superficiale
Stratified squamous epithelium with nucleus
Without keratin
Cells appear slightly more flattened
Stratum intermedium
Between stratum basale and stratum superficiale
Larger polyhedral-shaped cells which migrated away from basal layer and lost ability to divide
Forms the bulk of nonkeratinized epithelium
Stratum basale
Cuboidal or columnar cells resting on a basement membrane
Production of new epithelial cells
Papillary layer
CT that indents the epithelium; short or absent in some mucosa
epithelial ridges (rete pegs) interlock
richly vascularized
contains immune cells
Reticular layer
Consists of densely arranged connective tissue fibers, collagen fibers, some glands (reticular)
Marginal gingiva
Part of free gingiva that tapers to a knife-like edge extending along the cervical level of the tooth on labial or buccal and lingual surfaces
nagagalaw
Attached gingiva
Stippling/orange peel appearance
lighter color than alveolar mucosa
Inflammation / gingivitis
Loss of stippling may be caused by _____
Attached gingiva
Hard palate has the same color as _____
Alveolar mucosa
Soft palate has the same color as _____
Lingual
Which side is more painful when injected, lingual or buccal?
Marginal Periodontium (Gingiva)
Covers the coronal part of the alveolar process
Passes over the crest of the alveolar bone & interdental septa
Encircles the necks of the teeth
Inflammation
Marginal gingiva is rolled; interdental gingiva is rounded
Attachment of teeth and stabilization
Unites teeth into a continuous dental arch
Forms the epithelial cuff
Defense against infection
Functions of gingiva
Free gingiva
made up of a narrow band of tissue that follows the scalloped contour of the necks of the teeth and CEJ
can be moved mechanically along the tooth surface & away from the tooth
delicately attached to the tooth surface; can be torn and split clinically with negligible force
Free gingival groove
Separates the free gingiva from the attached gingiva
Gingival sulcus
A shallow groove between the tooth surface and free gingiva, extending around the circumference of the tooth
Col
The area of tissue in the interdental space that connects the facial and lingual free gingiva
Interdental folds
Slight depressions in between roots of teeth
Free gingival groove
Coronal boundary of attached gingiva
Mucogingival junction
Apical boundary of attached gingiva
Palatal side of maxilla
There is no attached gingiva in the _____
Deciduous dentition
Attached gingiva is narrower in _____
Maxillary lateral incisors
Attached gingiva is widest over the _____
Mandibular canine, 1st premolars (or deciduous 1st molars)
Attached gingiva is narrowest in _____
Anterior teeth
In the mandible, attached gingiva is narrower on the lingual surface of _____
Molars
In the mandible, attached gingiva is wide on the lingual surface of _____
Mucogingival junction
Separates attached gingiva from alveolar mucosa
Loss of contact area
Why is col not visible when teeth are extracted?
Dentinogingival junction
Interface between gingiva and the tooth surface
Reduced enamel epithelium (REE)
Embryonic origin of junctional epithelium
Epithelial attachment
Inner attachment epithelium
Epithelial cuff
Other previously known terms for junctional epithelium
Junctional epithelium
Binds gingiva to tooth surface
Epithelial part of the free gingiva NOT visible from outside
High turnover rate, contains a few leukocytes
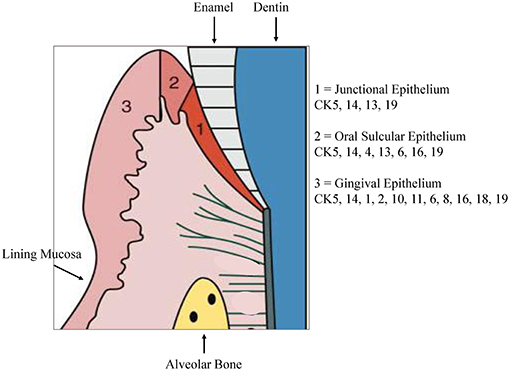
Junctional epithelium
Oral sulcular epithelium
Oral gingival epithelium
Dentinogingival junction consists of _____
Oral sulcular epithelium
Lines the lateral wall of the gingival sulcus
Continuous with occlusal end of junctional epithelium apically; with oral gingival epithelium occlusally
Histologically — dark cells due to basophilic staining
Stratified; frequently parakeratinized; no homogenous stratum corneum
Less permeable than junctional epithelium, not infiltrated with migrating leukocytes
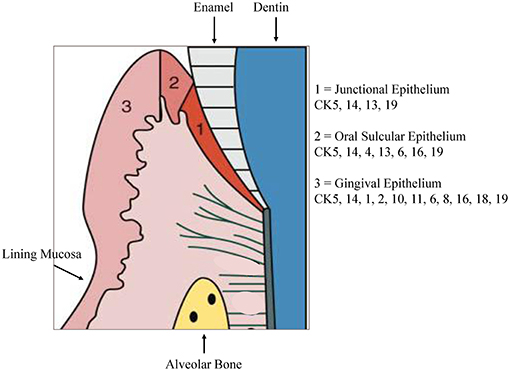
Oral gingival epithelium
Covers the vestibular and lingual/palatal surfaces of the marginal and alveolar gingiva and the interdental gingival papillae
Resembles epithelium of hard palate
Lamina propria
Greatest portion of the free and attached gingiva
50-60% collagen fibrils
fibroblasts
type I, II, V collagen
collagenase
ground substance
Biologic width
Attachment of gingiva to tooth from base of sulcus down to crest of the alveolar bone
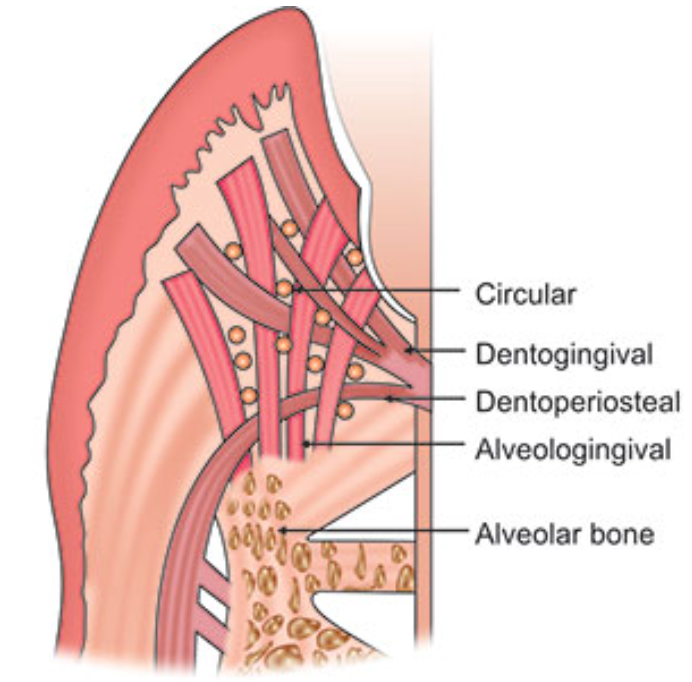
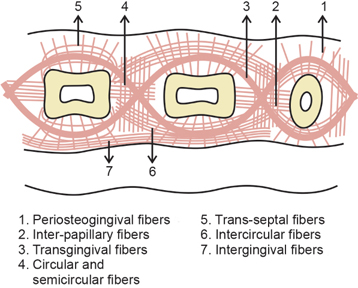
Dentogingival fibers
Most numerous fiber
Consists of 3 groups:
Extends from cementum in an obliquely coronal direction
Streams horizontally from the cementum into free marginal gingiva
Run parallel with dentoperiosteal fibers
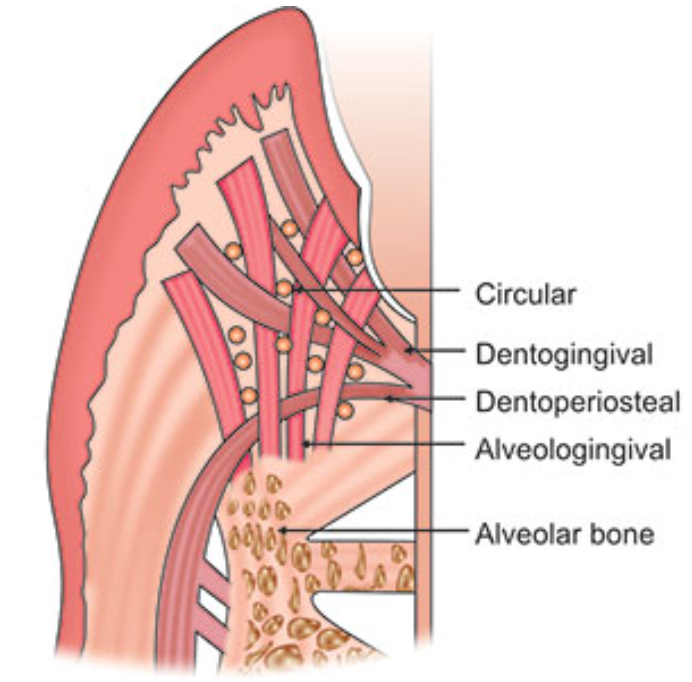
Dentoperiosteal fibers
Insert into the supra-alveolar cementum at the same level as the transseptal fibers
Pass apically over the crest of alveolar bone through vestibular and oral gingiva and into the periosteum of the cortical plates of alveolar process
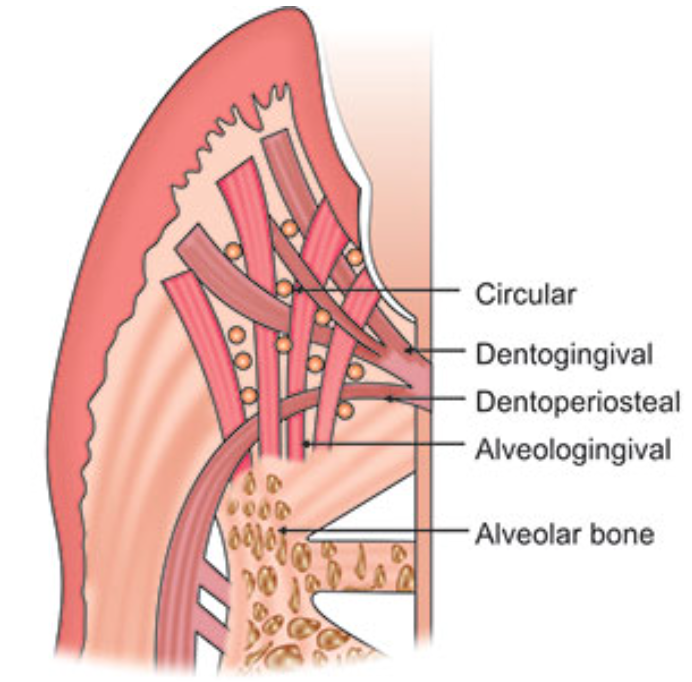
Alveologingival fibers
Insert into the crest of the alveolar bone
Course coronally and enter the free and attached sections of the marginal and interdental gingiva
Circular fibers
Small group of fibers that form a band around the neck of the tooth, interlacing with other groups of fibers in the free gingiva
Helps bind free gingiva into the tooth
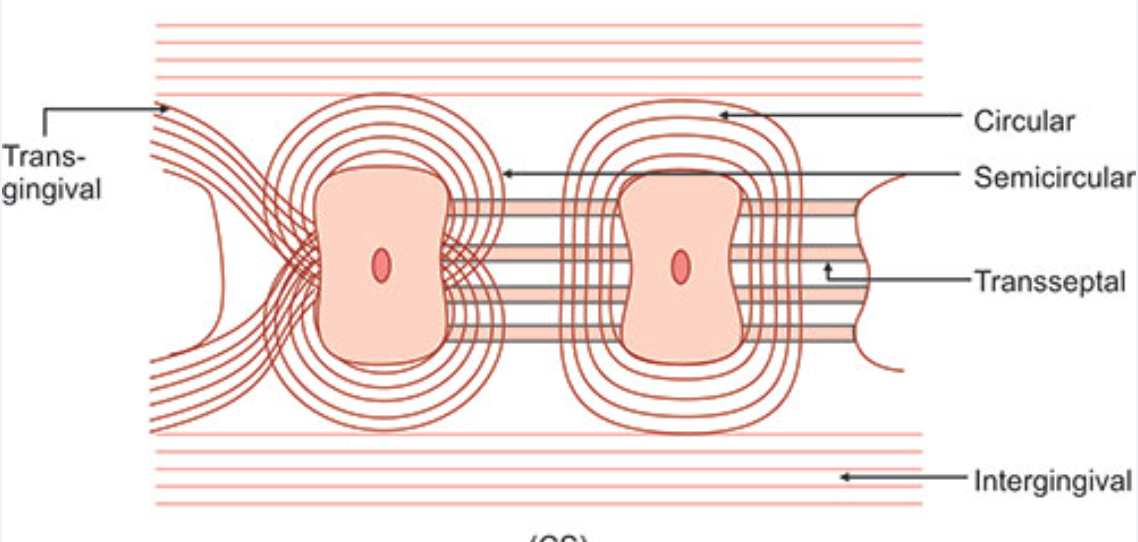
Semicircular fibers
Insert in the interdental cementum and encircle only the vestibular or oral half of the root
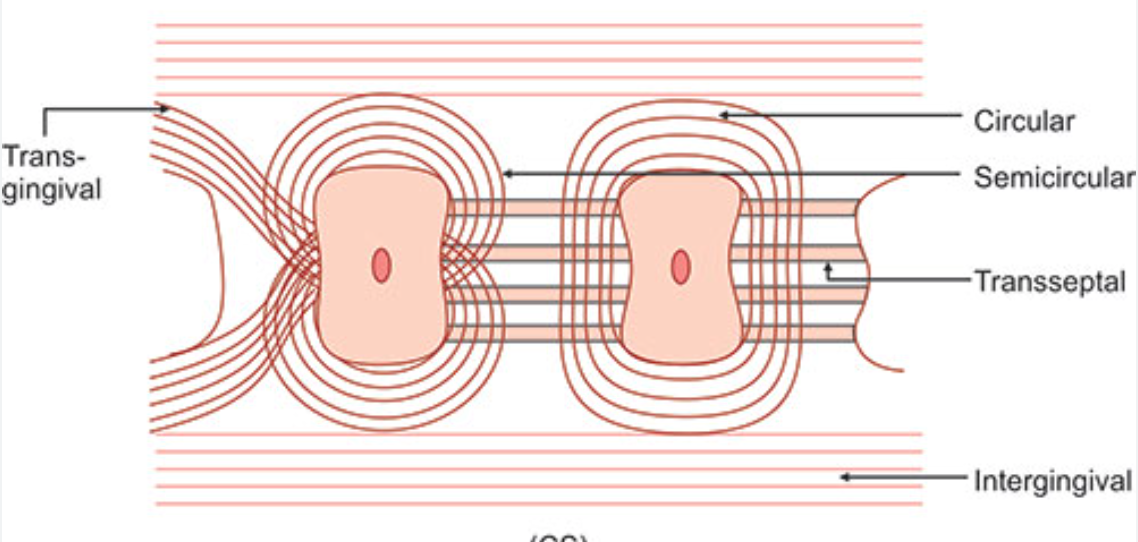
Transseptal fibers
Cross the CT of the interdental gingiva (mesiodistally)
Traverse the interdental septum as a strong membrane
Bind the supra-alveolar cementum of one tooth to that of the adjacent tooth
aka Interdental ligament
Major cause of post retention relapse of orthodontically positioned teeth
Capable of protein turnover and/or remodelling under normal physiologic conditions
Transgingival and intergingival fibers
Reinforce the circular and semicircular fiber bundles
Parts of it are identical with semicircular fibers
Insert interdentally into supra-alveolar cementum
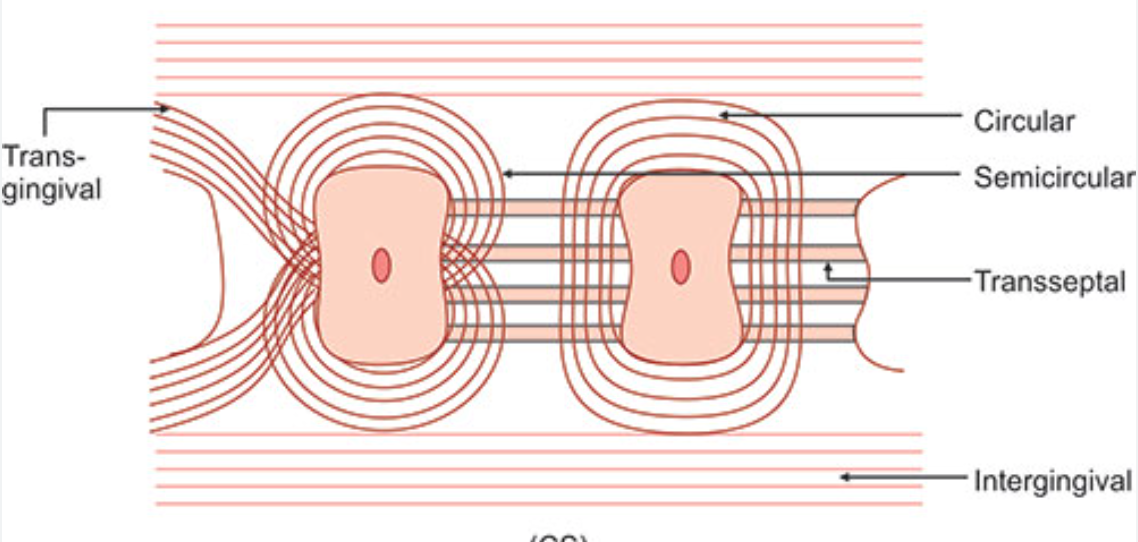
Interpapillary fibers
Cross through the free portion of interdental gingiva tissue in an orovestibular direction to tie the oral and vestibular gingival papillae together
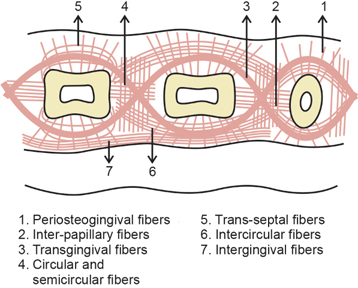
Periosteogingival fibers
Insert into the periosteum of the cortical plates of the alveolar process
Pass facially and orally into the section of all attached gingiva lying over it
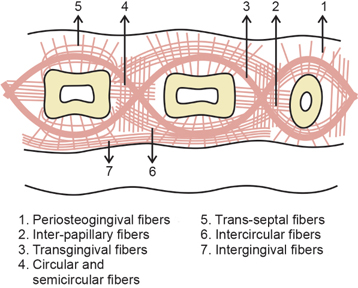
Intercircular fibers
Located on the vestibular and oral sides of the interdental gingiva
Connect the circular bundles of neighboring teeth
Form part of the intergingival fiber bundles
Rete pegs / epithelial ridges
Projections of the epithelium to the CT
Interact with the dermal papillae
Interdental papilla
Gingival tissue in the interdental spaces, if proximal contact exists
Epithelial attachment
Between junctional epithelium and tooth surface
Product of junctional epithelium
Maintains the bond between gingiva and tooth surface
Connective tissue attachment
Between the crest of the alveolar bone on interdental bony septum and the CEJ, fiber bundles of the gingival connective tissue insert into the supra-alveolar cementum