Edexcel IGCSE Biology - Inheritance
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what is a genome?
the entire DNA of an organism
what is a gene?
a small section of DNA that codes for a specific protein
what is a chromosome?
a long length of DNA coiled up - consists of numerous genes
where are genes located in eukaryotic cells?
nucleus
how many chromosomes are there in a human cell?
46 → 23 pairs → one in each pair from mother/father
what does DNA stand for?
deoxyribonucleic acid
what is the structure of DNA?
two strands coiled to form a double helix
what are the building blocks of DNA?
nucleotides
what is a DNA nucleotide composed of?
a nitrogen containing base
a sugar (deoxyribose)
a phosphate group
what four bases are there in DNA?
adenine
thymine
cytosine
guanine
what is complementary base pairing?
DNA bases are always paired, and they only have one base which they pair to
Adenine + Thymine
Cytosine + Guanine
which bonds join DNA bases together?
hydrogen
what does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic acid
what is the structure of RNA?
single helix
what are the components of an RNA nucleotide?
a phosphate group
a sugar - ribose
a base
which bases make up RNA?
Adenine
Uracil
Cytosine
Guanine
which bases are complementary in RNA?
Adenine + Uracil
Guanine + Cytosine
what are the differences between RNA and DNA?
DNA - double helix; RNA - single helix
RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine
DNA - deoxyribose sugar; RNA - ribose sugar
RNA is shorter than DNA
what are the 2 stages of protein synthesis?
transcription
translation
what is a codon?
a group of 3 bases
what is an anticodon?
a group of 3 unpaired bases on a tRNA that is complementary to a codon on mRNA
why does transcription have to take place?
DNA is found in the nucleus and can’t be taken out due to its size, but protein synthesis takes place in the cytoplasm with ribosomes
describe the process of transcription
DNA helicase unwinds and separates the DNA strands in a gene
RNA polymerase binds to one of the strands on a non-coding region before the gene
free-floating mRNA nucleotides line up with their complementary base pairs and make an RNA copy of the gene
the mRNA molecule moves out of the nucleus and binds with a ribosome in the cytoplasm
what does the RNA polymerase do?
produces the complementary mRNA strand by attaching the nucleotides together
describe translation
a tRNA with the complementary anticodon to the first codon on the mRNA attaches to it, bringing the corresponding amino acid
this process continues until the mRNA strand ends
the ribosome attaches the amino acids together with peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide
the amino acid chain separates from the tRNAs and mRNA and coils up to form a protein
What is tRNA?
tRNA is an RNA molecule that contains an anti codon and a corresponding amino acid
what is an allele?
a different form of the same gene
what is a consequence of alleles?
people inherit different characteristics
how many alleles does a person have for each characteristic?
2 - one maternal, one paternal
what is polygenic inheritance?
a characteristic that is controlled by two or more genes working together - vast majority
what is monohybrid inheritance?
the inheritance of single gene that controls a single characteristic - rare
what is a dominant allele?
an allele that is always expressed in the phenotype (capital letter)
what is a recessive allele?
an allele that is only expressed in the phenotype if it is in the presence of another (same) recessive allele
what does homozygous mean?
2 identical copies of the same allele for a gene
what does heterozygous mean?
two different alleles for a gene
what does phenotype mean?
the expressed characteristics of an organism
what does genotype mean?
all the alleles that an organism has for a particular characteristic
what is codominance?
when you have two different dominant alleles that are both expressed
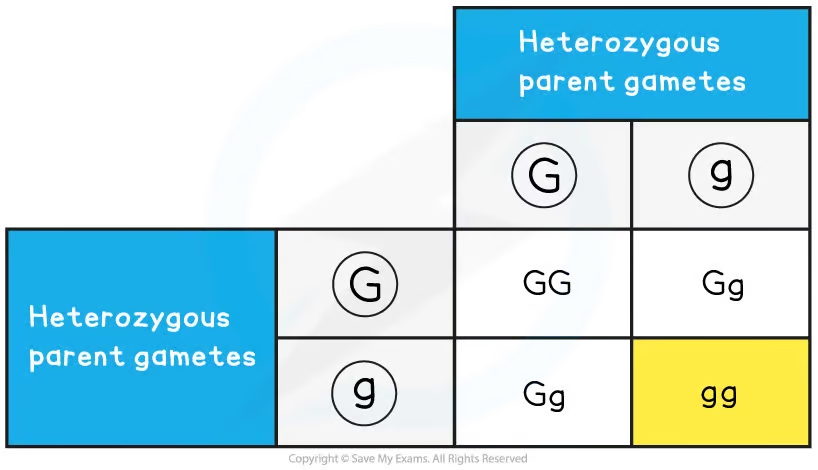
what genetic diagrams can you use to demonstrate/work out monohybrid inheritance? (mainly)
Punnett squares - also include alleles, gametes, genotypes, phenotypes
what is a family pedigree?
a genetic diagram that shows the history of a trait in a family
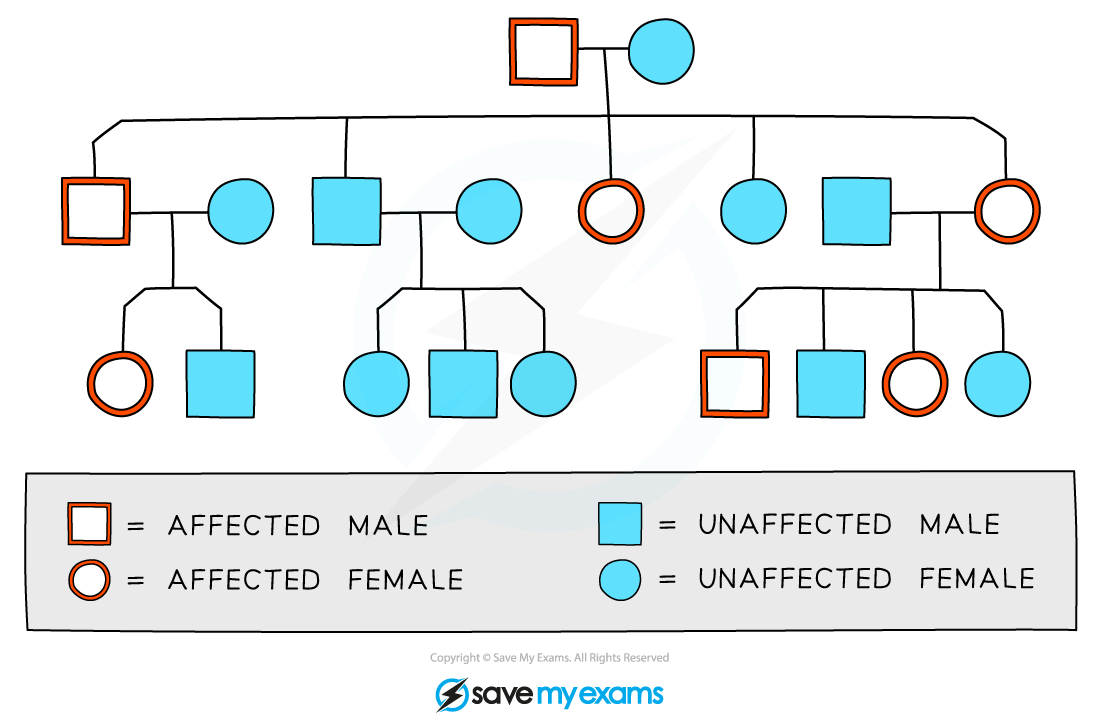
how can you determine if a trait is recessive from looking at the phenotypes present in a family pedigree?
if the trait skips generations - is present in children but not parents - it suggests that parents must be carriers and so the gene is recessive
how can you determine if a trait is dominant from looking at the phenotypes present in a family pedigree?
if the characteristic does not skip generations
which pair of chromosomes controls the sex of a person?
23rd pair - XY
which pair of chromosomes makes the sex of a person female?
XX
which pair of chromosomes makes the sex of a person male?
XY
what is a diploid cell?
a cell with two copies of each chromosome - in humans, 46 chromosomes/23 pairs
what is a haploid cell?
a cell with one copy of each chromosome - in humans, 23 chromosomes
what are the two process of cell division?
mitosis
meiosis
when does mitosis occur?
growth
repair
cloning
asexual reproduction
where does mitosis occur?
all body cells
what does mitosis produce?
2 genetically identical diploid cells
how many divisions are there in mitosis?
1
when does meiosis take place?
production of gametes
where does meiosis take place?
ovaries/testes/anther
what does meiosis produce?
4 genetically different haploid cells
how many divisions occur in meiosis?
2
describe the process of mitosis
the DNA in a cell duplicates and then forms x-shaped chromosomes - each arm is a duplicate of the other (chromatid) - there are 46 sets of duplicates
the chromosomes line up at the centre of the cell and cell fibres pull them apart
the two arms of each chromosome go to opposite sides of the cell and membranes form around each set
the cytoplasm divides
describe the process of meiosis
the DNA in a cell duplicates and then forms x-shaped chromosomes - each arm is a duplicate of the other (chromatid) - there are 46 sets of duplicates
these chromosomes each line up in the middle of the cell - the mother’s and father’s are next to each other
crossing over occurs - some bits of mothers and fathers swap over
these pairs are split in half, producing two genetically different diploid cells
each of the 23 chromosomes now line up in the middle of the new cell
the arms are pulled apart
you end up with 4 genetically different haploid cells
what does random fertilisation produce?
genetic variation of offspring
what are the two causes of variation within a species?
genetic - e.g. eye colour, blood group
environmental - e.g. health, intelligence
usually a mixture of both
what is a mutation?
a random, rare change in the genetic material - DNA base sequence of a gene - that can be inherited
what do mutations do?
change the DNA base sequence of an organism
produces a genetic variant (altered version of gene)
can lead to a change in the protein that the gene codes for - this could stop the production of an enzyme or change the shape of it’s active site
why might a mutation have no effect?
most common
occurs in an unimportant region of DNA
a mutated codon may code for the same amino acid - not alter shape or function of protein
may occur in a recessive allele
why might a mutation have a slight effect?
may cause a change of amino acid
however this may only have a slight effect on the protein’s structure and function
why might a mutation have a significant effect?
may cause an entirely different protein to be formed which can no longer carry out its function
can be harmful or beneficial
what can the incidence of mutations be increased by?
exposure to ionising radiation - gamma and x-rays
exposure to chemical mutagens - like tobacco
what is continuous variation?
variation in a population that is influenced by genetics and the environment
what is discontinuous variation?
variation in a population that is controlled by a single gene and has no environmental influence
describe Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection
variation arises in a population due to mutation, random inheritance of alleles and environmental factors
some organisms may possess characteristics which make it easier for them to survive/survive for longer
these organisms are more likely to reproduce and pass on these advantageous alleles to their offspring
this process repeats over many generations and the prevalence of the allele increases
give an example of natural selection and briefly summarise it
antibiotic resistance - some bacteria may have mutated to be resistant to antibiotics; they are more likely to survive and reproduce; over time the prevalence of the allele increases in the population
what is a negative effect of antibiotic resistance?
make infections difficult to control