Meiosis I
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
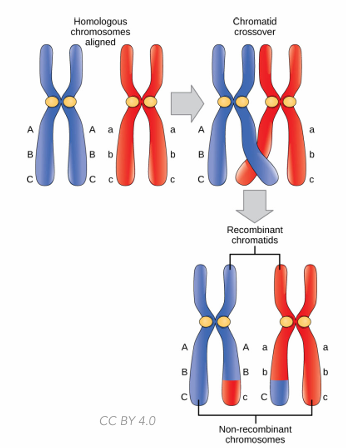
What happens during prophase I of meiosis?
the nucleus disassembles, the nucleolus disappears, the nuclear envelope breaks down, chromatin condenses, and the mitotic spindle develops.
Homologous chromosomes pair up (synapsis), forming tetrads, and crossing over occurs, leading to genetic recombination.
What is synapsis in prophase I?
is the process in which homologous chromosomes pair up to form tetrads (groups of 4 chromatids), allowing for genetic recombination through crossing over.
What is the significance of crossing over in prophase I?
is the exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids at the chiasmata, increasing genetic diversity.
What are the five stages of prophase I?
Leptotene - Chromosomes begin condensing.
Zygotene - Synapsis begins, and the synaptonemal complex forms.
Pachytene - Synapsis is complete, and crossing over occurs.
Diplotene - Synaptonemal complex disappears, but chiasmata remain.
Diakinesis - Nuclear envelope fragments, chromosomes condense, and tetrads are ready for metaphase.
What occurs during metaphase I of meiosis?
homologous chromosome pairs align along the metaphase plate, and microtubules attach to the kinetochores of one member of each homologous pair.
What happens during anaphase I of meiosis?
homologous chromosomes within tetrads uncouple and are pulled to opposite sides of the cell, a process known as disjunction.
What happens during telophase I of meiosis?
the nuclear membrane reforms, and each pole forms a new nucleus with half the number of chromosomes. After cytokinesis, the daughter cells are haploid.
How is the chromosome number affected after meiosis I?
After meiosis I, the chromosome number is halved, and each daughter cell becomes haploid.