Rods and Cones
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
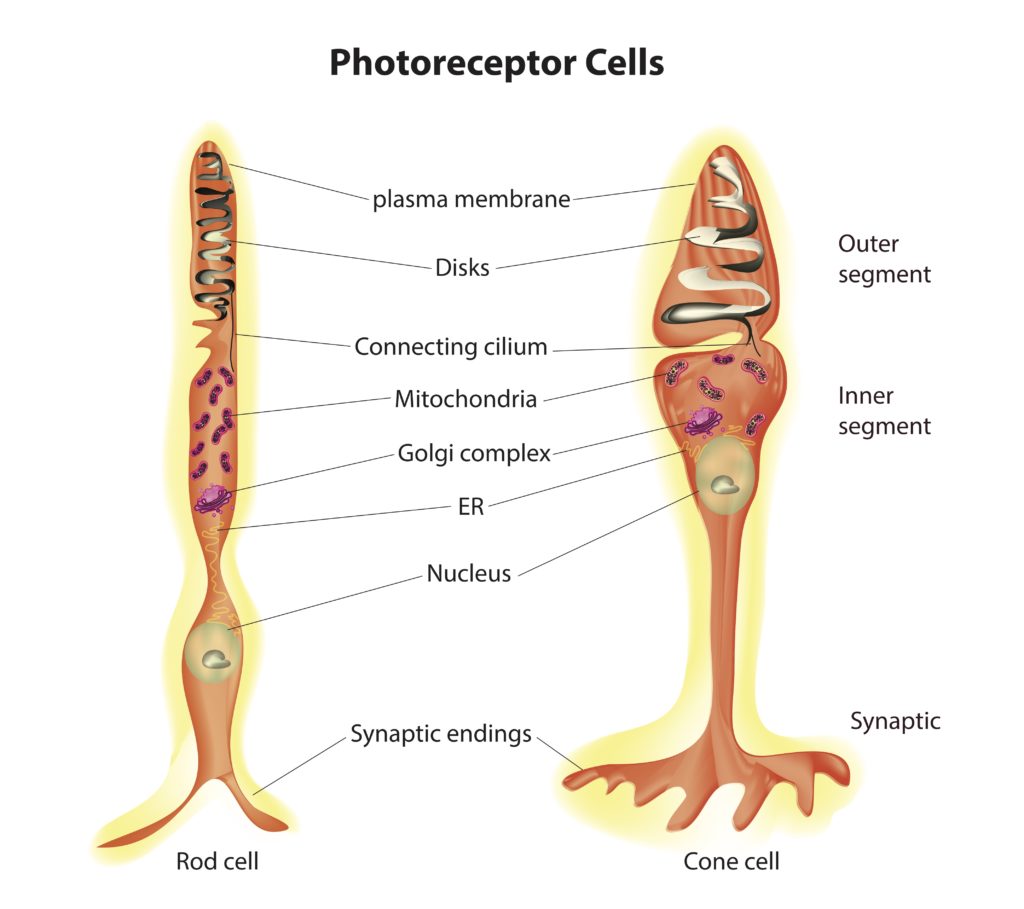
Cone Cells
Cone cells are photoreceptor cells located in the retina of the eye, primarily concentrated in the macula and fovea centralis. They are responsible for color vision, high visual acuity, and daylight vision. Cone cells contain photopigments that respond to different wavelengths of light, allowing for the perception of color. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different colors: red, green, and blue.
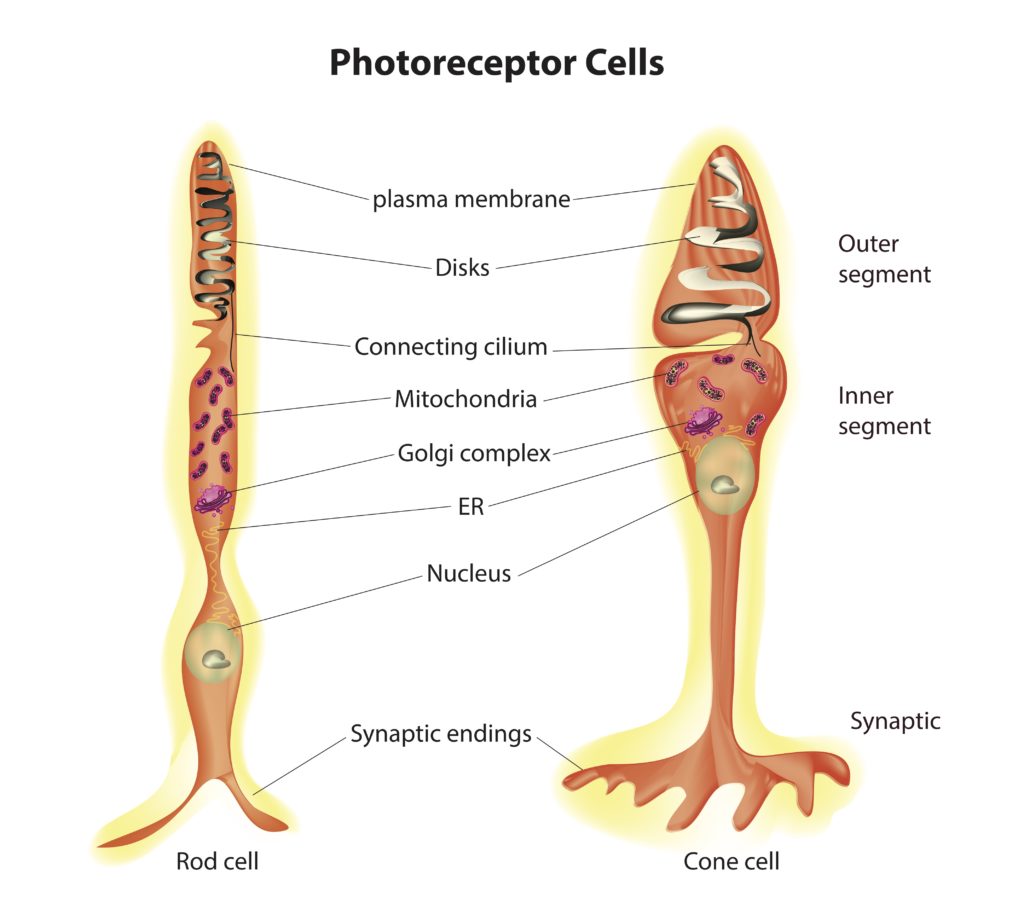
Rod Cells
Rods are photoreceptor cells located in the retina of the eye, distributed throughout the peripheral retina. They are highly sensitive to low levels of light and are primarily responsible for night vision and peripheral vision. Rods contain a single type of photopigment, allowing them to detect differences in light intensity but not color. Rods are crucial for vision in dimly lit environments and for detecting motion.
What happens if rod cells are impaired/malfunctioning?
Impaired rod cells lead to night blindness and decreased peripheral vision.
What happens if cone cells are impaired/malfunctioning?
Impaired cone cells result in colour vision deficiency, making it challenging to distinguish between different hues and shades.