Indirect Tax
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What are indirect taxes
Expenditure tax that is an extra charge when goods/services are sold that increase costs of production for firms and this can be transferred to consumers via higher prices
What are direct taxes
Tax on income that can’t be transferred to anyone else, unlike an indirect tax which can be passed on to consumers, such as VAT, through higher prices.
Examples of Indirect Tax
VAT, Cigarettes tax, Alcohol tax, sugar tax
Direct taxes examples
Income Tax, National Insurance, Corporation Tax
Indirect taxes are used for two core reasons
To raise government revenue e.g: VAT
Solve market failure for goods/service e.g: Cigarettes, Alcohol, sugar that cause harm to society
What are the two types of taxes that government use
Indirect Tax
Direct Tax
Indirect taxes can be
Specific in nature or Ad valorem
A specific indirect tax is
A tax per unit e.g: alcohol duty attacks per unit so every bottle of wine has a tax
the way in which specific indirect taxes shift the supply curve is unique
because they shift the s curve parallel, because the vertical distance between the two supply curves represents the value of the tax e.g: if tax was 2.23/bottle the parallel distance would show 2.23
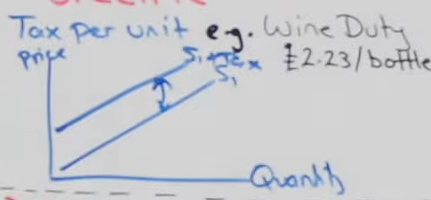
e.g of specific indirect taxes: It doesn’t matter whether it’s the 100th or 1000th bottle being sold
each bottle will be taxed the same £2.23
What is an Ad valorem indirect tax
Tax a % of a price e.g: VAT is 20%
What does an Ad valorem indirect tax mean for the shift of the supply curve
The supply curve will shift pivoted from S1 → S1 + tax

The vertical distance between the two supply curves of Ad valorem tax
will represent the value of the tax and any distance from the two curves will = the same tax shown on the diagram

The vertical distance is always 20%
but 20% of a high price is a high amount of revenue for the government. vice versa.
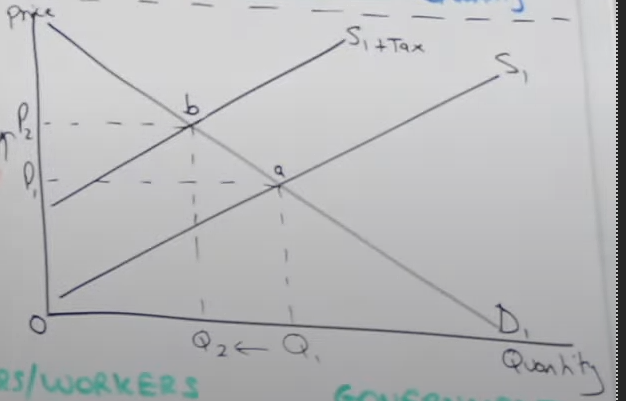
How is the S curve impacted from Indirect Tax
S curve shifts upwards from S1 → S1 + Tax, because it increases firms COP
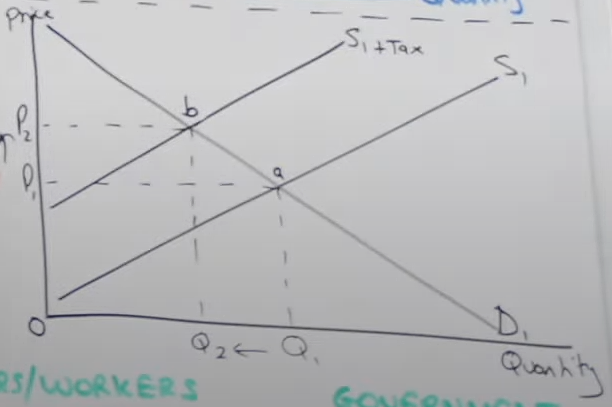
How is price and quantity impact from indirect tax
price has increased from p1 to p2 and q1 to q2
How do you work out the amount of government revenue collected
Go to the new equilibrium (p2,q2) at point b, then work out the vertical distance between the two supply curves, which represents the tax per unit. Then multiply the distance between all the units being prod/sold, which is everything up to Q2. p2,b,c,e is the area that represents the total government revenue
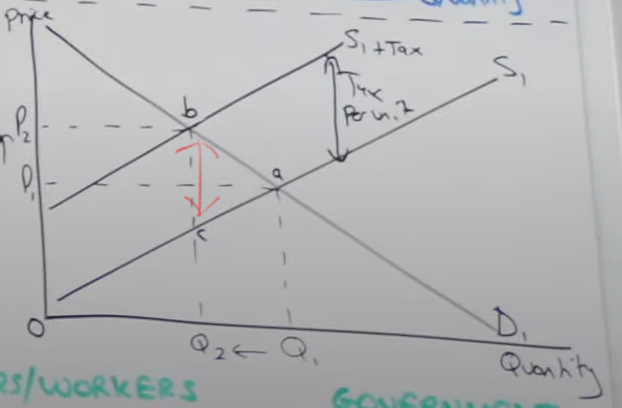
How do you calculate how much the government revenue consumer is paying
You look the gov revenue box and of that box the difference in price portion is the consumer burden p1,p2,b,d
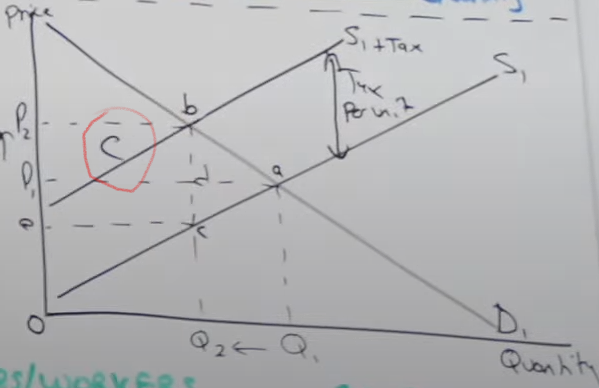
What do you call the amount producers/consumers are paying to the government
Consumer and Producer Burden
How do you calculate how much the producer is paying for government revenue
What ever is left from working out the consumer burden (p1 → p2) is the producer burden, p1, e, c, d
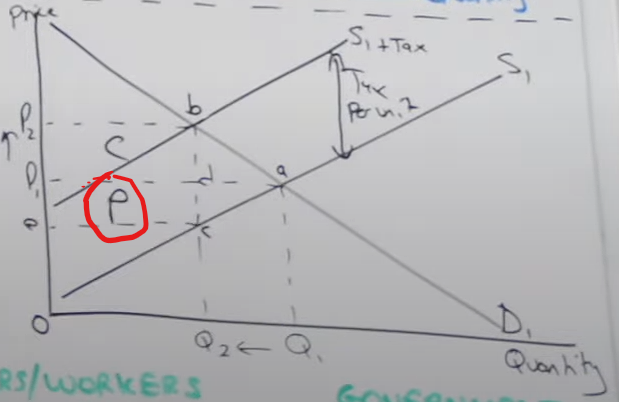
the only reason consumers are paying higher prices
is because of the indirect tax which is passed onto them in higher prices on goods/services
How do you workout the producer revenue
Price x Quantity (p1 x q1 giving us the area P1,A,Q1,0)
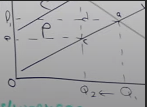
How would you work out the producer revenue given an indirect tax implemented
You may think it’s going to P2xQ2 giving the area p2,b,q2,0
However some of that revenue is going to the government so you have to minus the gov revenue, so producer revenue is only e,c,Q2,0, there PR has fallen
By the government intervening reducing QQ, there is
DWL (Dead weight welfare loss)
What is DWL (Dead Weight Welfare Loss)
the loss of economic efficiency when market equilibrium is distorted, like a tax leading to a reduced total surplus
What does indirect tax impact key stake holders like consumers
Consumer don’t like IT, because it
raises prices
lowers consumer surplus, quantity
IT are regressive taking a larger proportion of income of low-income households than high income
How does indirect tax impact key stake holders like producer/workers
They don’t like IT,
Producers see lower producer revenue, producer surplus
Workers could loose their job as labour is a derived demand and with Q falling there’s less need for workers to produce
What does indirect tax impact key stake holders like Government
In theory gov likes IT, because they achieve their two goals (raise gov revenue, solve market failure), but they don’t like the unintended consequences of IT
Indirect tax inelastic diagram
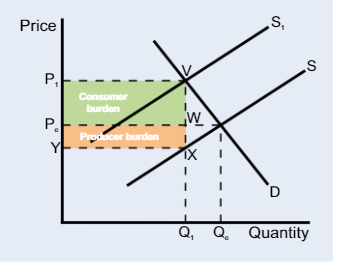
Indirect tax elastic diagram
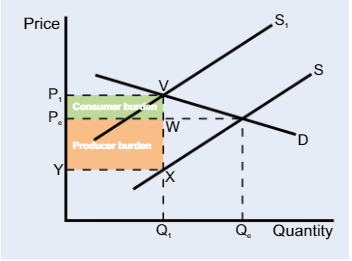
The revenue for the government generated by the tax
is the entire shaded box and can be split into two parts: consumer/producer burden
The more price inelastic the demand curve
the greater the tax burden for the consumer
The more price elastic the demand curve,
the greater the tax burden for the producer