Exam 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the three levels of priority problems in EB Assessment?
First-level priority problems (ABC) are life-threatening conditions that require immediate attention, including airway, breathing, and circulation issues. Second-level priority problems include those that are urgent but less critical, such as severe pain, mental status changes, medical problem, urinary elevation problem or risk of infection. Third-level priority problems are those that are important but not urgent, such as chronic pain management or health education needs.
What is the difference between subjective and objective data?
Subjective data is what the patient reports, whereas objective data is what the clinician observes.
What is the focus of health promotion and disease prevention?
To enhance well-being and prevent disease.
What is diagnostic reasoning?
A process of analyzing patient data to derive insights and guide clinical decisions.
What is an appropriate verbal response for an examiner during an interview?
Active listening and reflecting the patient's feelings.
What are the Ten Traps of Interviewing?
The Ten Traps of Interviewing are common pitfalls that can hinder effective communication with patients. These traps include: 1) Providing false assurance - reassuring the patient without basis can diminish trust; 2) Using authority - relying on power rather than collaboration can alienate patients; 3) Avoiding difficult questions - shying away from sensitive topics can prevent full understanding; 4) Giving advice prematurely - providing solutions without fully exploring the patient's concerns can be counterproductive; 5) Talking too much - dominating the conversation can prevent patients from sharing their experiences; 6) Interrupting - cutting off patients can discourage them from opening up; 7) Using jargon - complex terminology can confuse patients and hinder comprehension; 8) Expressing disapproval - showing judgment can create defense mechanisms and hinder honest communication; 9) Overreacting - exaggerated responses can intimidate patients; 10) Focusing on the nurse rather than the patient - allowing personal thoughts or feelings to dominate can prevent patient-centered care.
Give an example of an open-ended question.
Can you describe your symptoms?
Give an example of a closed-ended question.
Do you have pain?
What is the primary purpose of a health history?
To gather comprehensive data about the patient’s health.
What should be documented as the Reason for Seeking Care?
The patient’s main complaint or concern during the visit.
When is a general survey conducted?
At the beginning of a patient assessment.
What are the components of a general survey?
Physical appearance, body structure, mobility, and behavior.
What are normal healthy adult vital sign ranges?
Temperature 98.6°F, Pulse 60-100 bpm, Respiratory rate 12-20 breaths/min, Blood pressure 120/80 mmHg.
When should apical pulse be obtained?
When assessing heart rate or when there are irregularities in the radial pulse (when giving bp med as well)
What are common errors in blood pressure management?
Common errors include using the incorrect cuff size which can lead to inaccurate readings (too small gives falsely high readings, too large gives falsely low readings). Incorrect placement of the cuff can also affect accuracy. Additionally, failure to palpate the radial pulse prior to auscultation can lead to missing the true systolic pressure due to its requirement for establishing baseline readings.
What do vital signs measure?
Physiological status, including cardiopulmonary function.
What are orthostatic vital signs?
Measurements taken when a patient is supine, then sitting, then standing, to assess for hypotension. (-20 is systolic and -10 in diastole)
What is OLDCART used for in pain assessment?
It's a mnemonic for assessing pain: Onset, Location, Duration, Characteristics, Aggravating/Alleviating factors, Related symptoms, Treatment.
What does PQRST stand for in pain assessment?
Provocation, Quality, Radiation, Severity, Timing.
What are the types of pain described in Table 11.3?
Nociceptive pain, neuropathic pain, and psychogenic pain.
What are the differences between acute and chronic pain?
Acute pain is sudden, while chronic pain persists over time.
How does aging affect the head, face, neck, and regional lymphatics?
Loss of connective tissue resilience and changes in lymph node characteristics.
What are signs of abnormal lymph nodes?
Nodes that are hard, non-tender, fixed, and larger than 3 cm.
Describe the expected findings from objective eye assessment.
Normal visual acuity, appropriate eye movements, and no abnormalities in fundoscopic examination.
What is the proper insertion technique for an otoscope?
Position the otoscope gently in the ear canal and visualize the tympanic membrane.
What should be included in subjective data questions for the aging adult?
Changes in vision, hearing, and general health perception.
What are some indications of hearing loss during an interview?
Misunderstanding questions, lip-reading, and asking for repetitions.
What changes occur in the aging ear?
Dryer cerumen, increased ear size, and potential presbycusis.
What findings are expected when examining the mouth and throat?
Moist mucous membranes and intact structures.
How are vital signs recorded?
In the patient's chart noting the method of measurement used.
What is the significance of the CRIES neonatal scale?
A tool for assessing pain in neonates.
When is it appropriate to educate a patient about code status?
During admission or initial health assessments.
What is the role of hand hygiene in patient care?
To prevent the transmission of infections.
What is the behavior of a client experiencing acute pain?
Facial grimacing, restlessness, and verbal expressions of distress.
How should a clinician confirm a patient's identity?
By asking for name and date of birth and verifying with a wristband.
What does a nurse assess during a physical examination?
General appearance, vital signs, and relevant body systems.
What does documentation of expected findings involve?
Detailed descriptions of a patient’s normal assessment outcomes.
What is the importance of pain tools such as OLDCART and PQRST?
They help clinicians systematically evaluate and manage patients' pain.
What is the meaning of 'lymphadenopathy'?
Swelling or enlargement of lymph nodes beyond 1 cm.
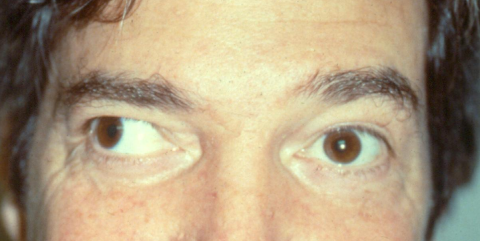
Hypertropia
superior rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique muscles
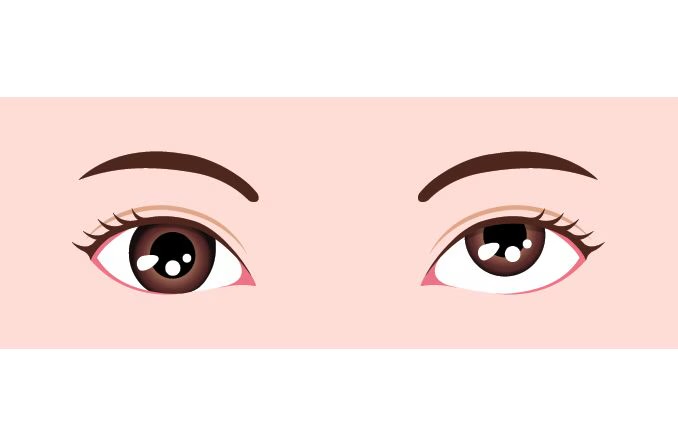
Esotropia
lateral rectus muscles
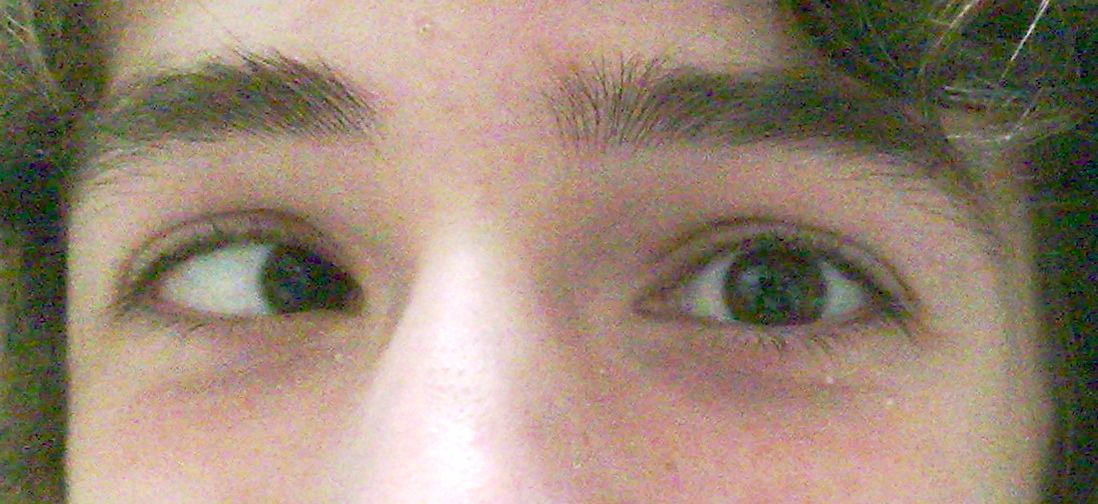
Exotropia
lateral rectus, medial rectus, and oblique muscles.
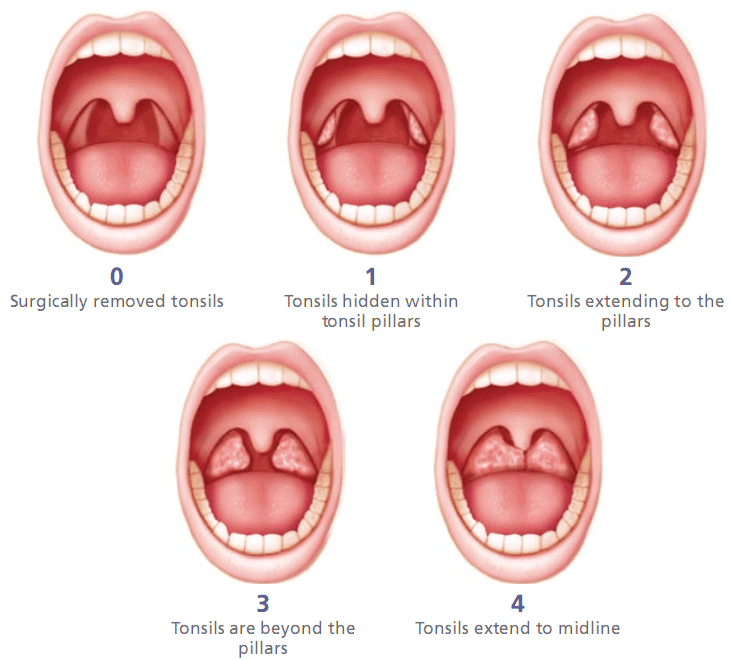
Grading tonsils
Whisper test
The examiner stands 1–2 feet behind the patient
The patient blocks one ear canal with their finger
The examiner whispers a word or numbers
The patient repeats the word or numbers
The test is repeated for the other ear
PERRLA
P: Pupils
E: Equal
R: Round
L: Light
A: Accommodation