Multiple Choice Questions for Modules 8 & 9
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Molecular & Ionic Compounds
A-Level Chemistry
AQA
Organic Chemistry
Module: 8
Module: 9
Cell division and Mitosis
Mitosis
Cell division
Cytokinesis
Cellular Reproduction
Cell division fundamentals
Module 9: Cell Division and Mitosis
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Cellular reproduction
Fermentation and Anaerobic Alternatives
Pyruvate Oxidation
Entry to Citric Acid
Citric Acid
Kerb Cycle
Foundational concept & Overview
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
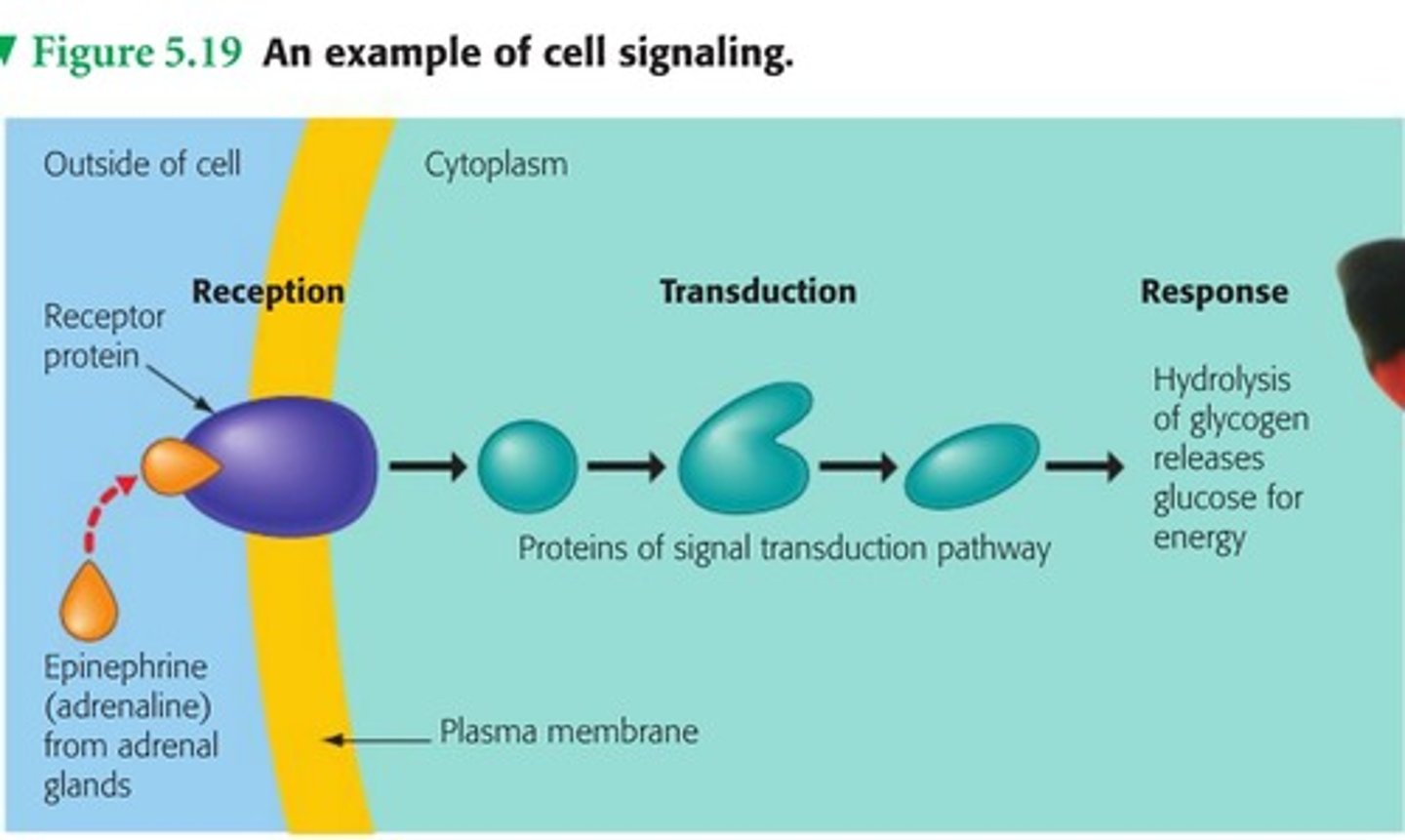
Signal transduction pathway
A series of molecular events and interactions that lead to a cellular response following the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor.
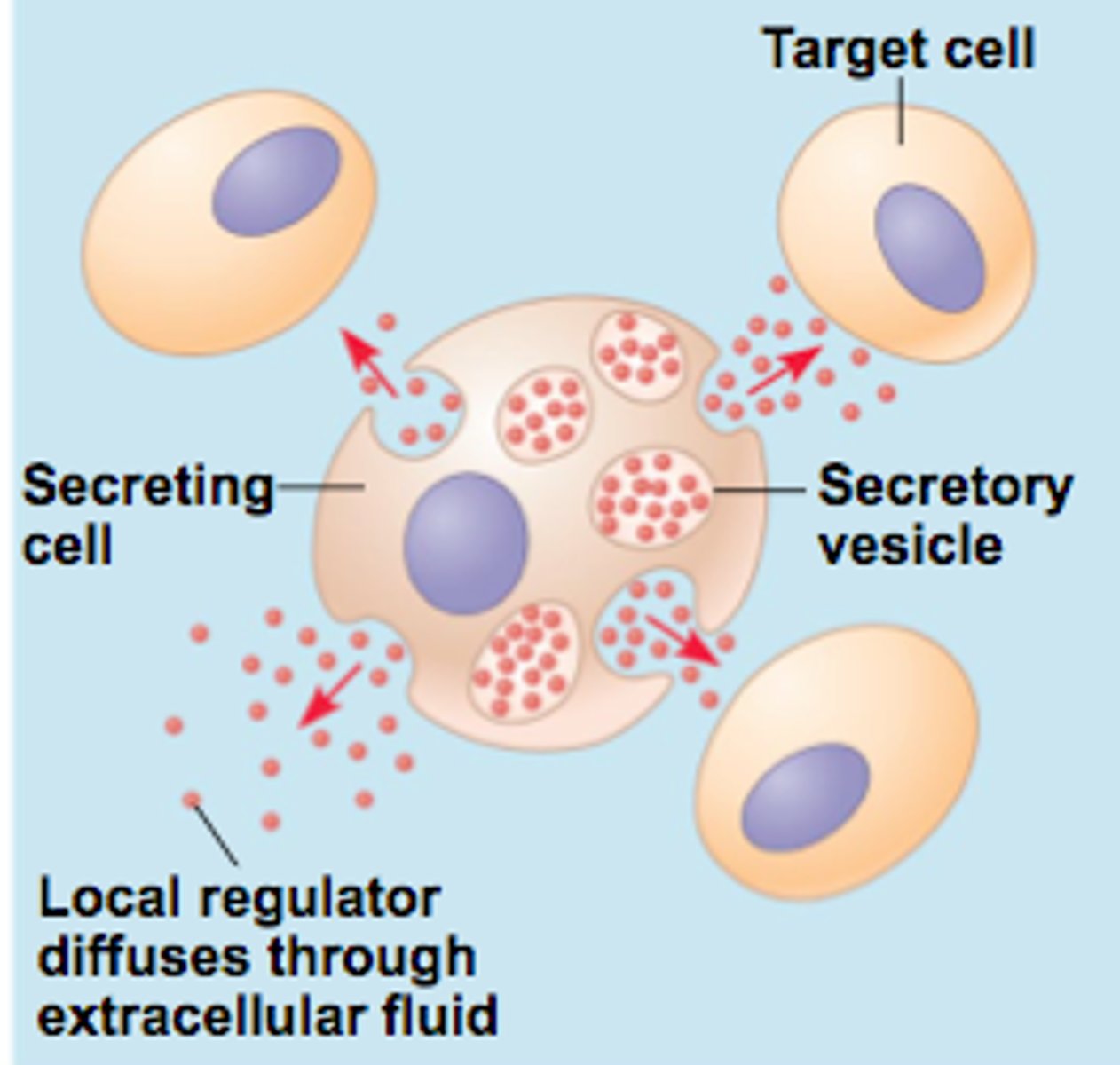
Local regulator
A signaling molecule that diffuses a short distance to stimulate nearby cells.
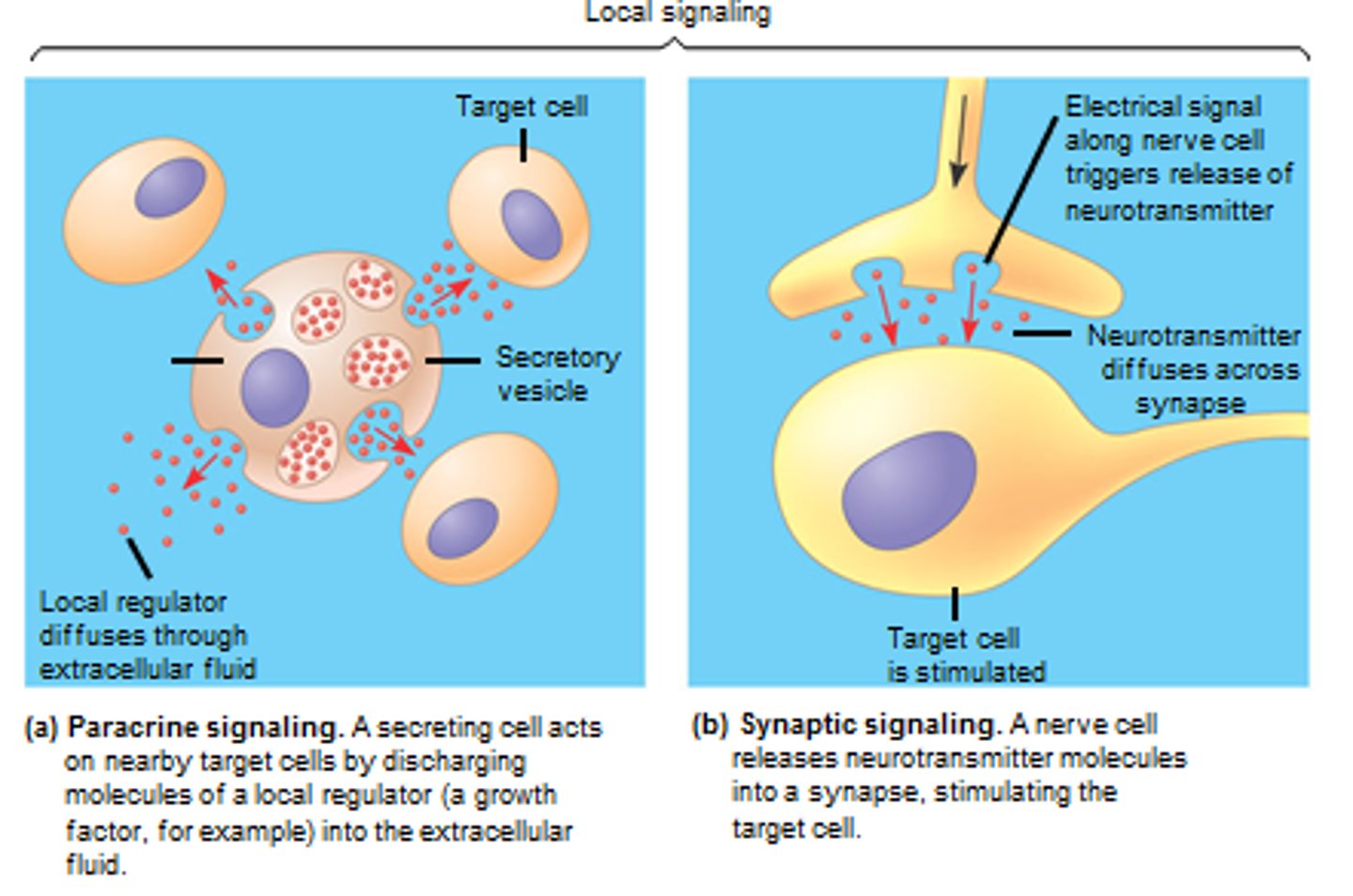
Paracrine signaling
A form of cell signaling in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells.
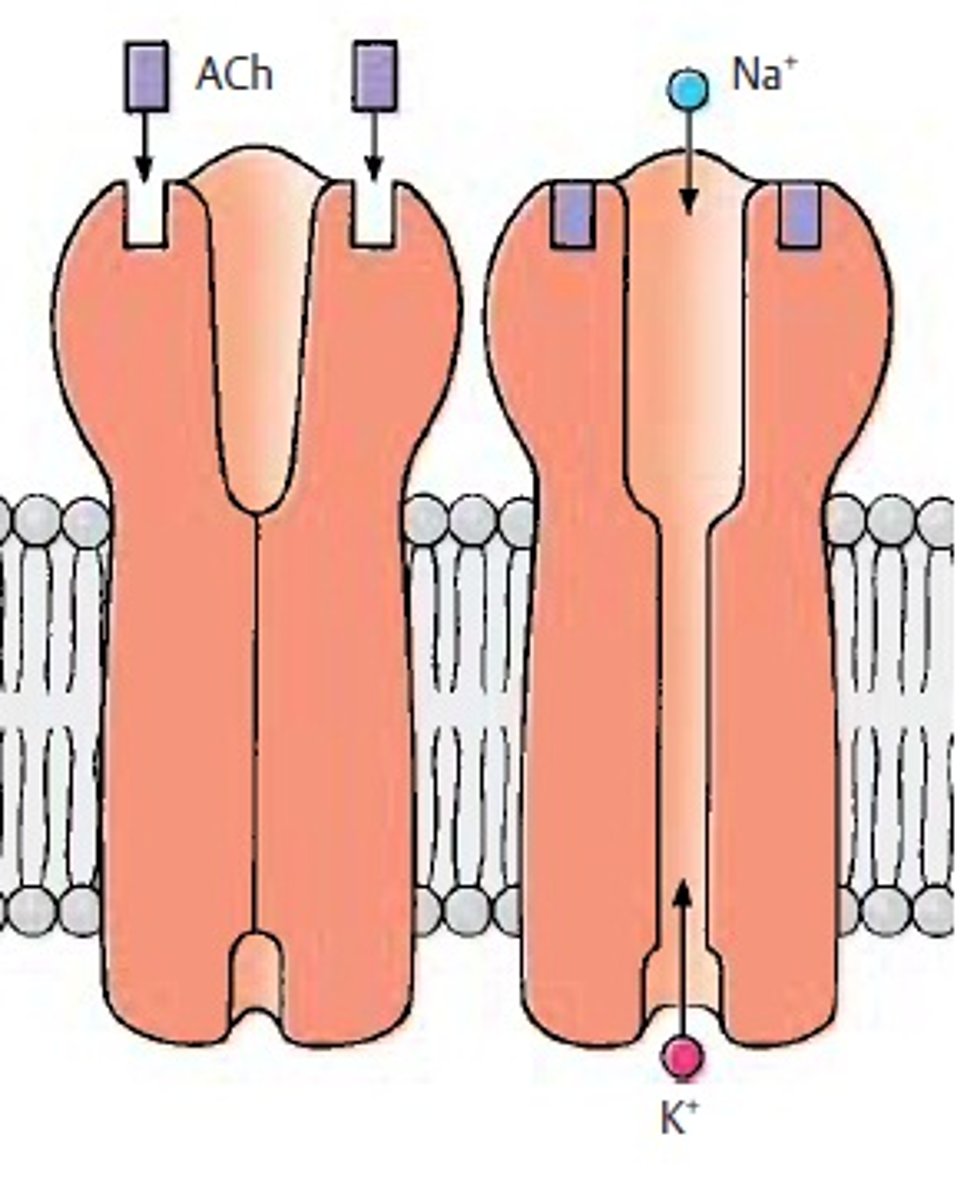
Ligand-gated ion channel
A type of receptor that opens an ion channel in response to the binding of a ligand.
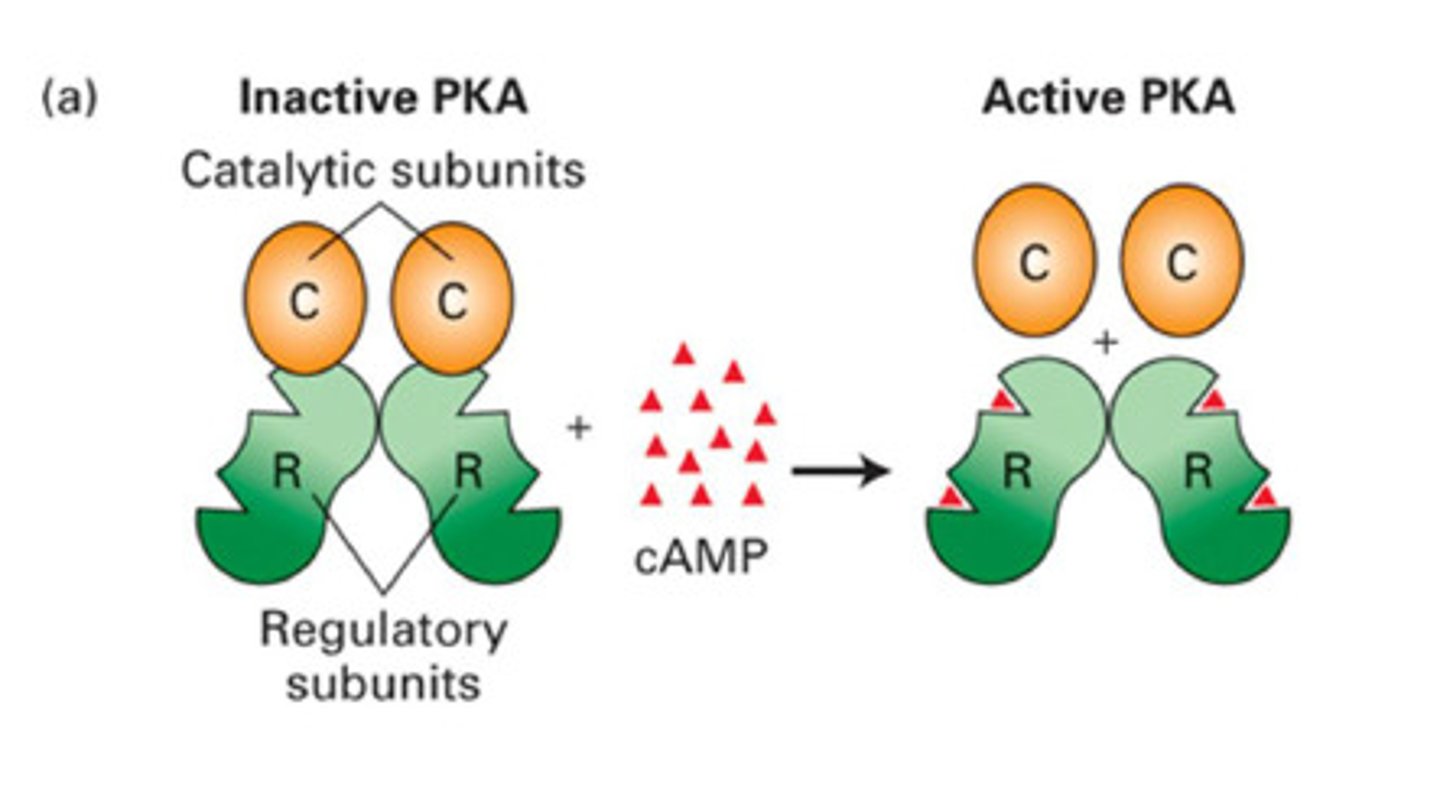
Protein kinase A (PKA)
An enzyme that is activated by cyclic AMP (cAMP) and phosphorylates target proteins.
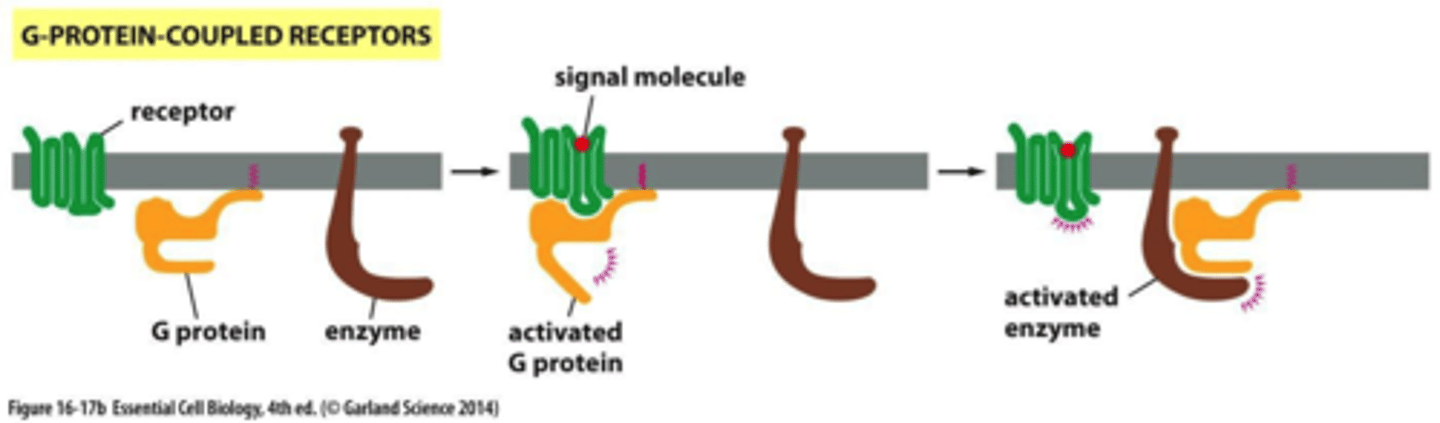
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
A large family of receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate internal signal transduction pathways.
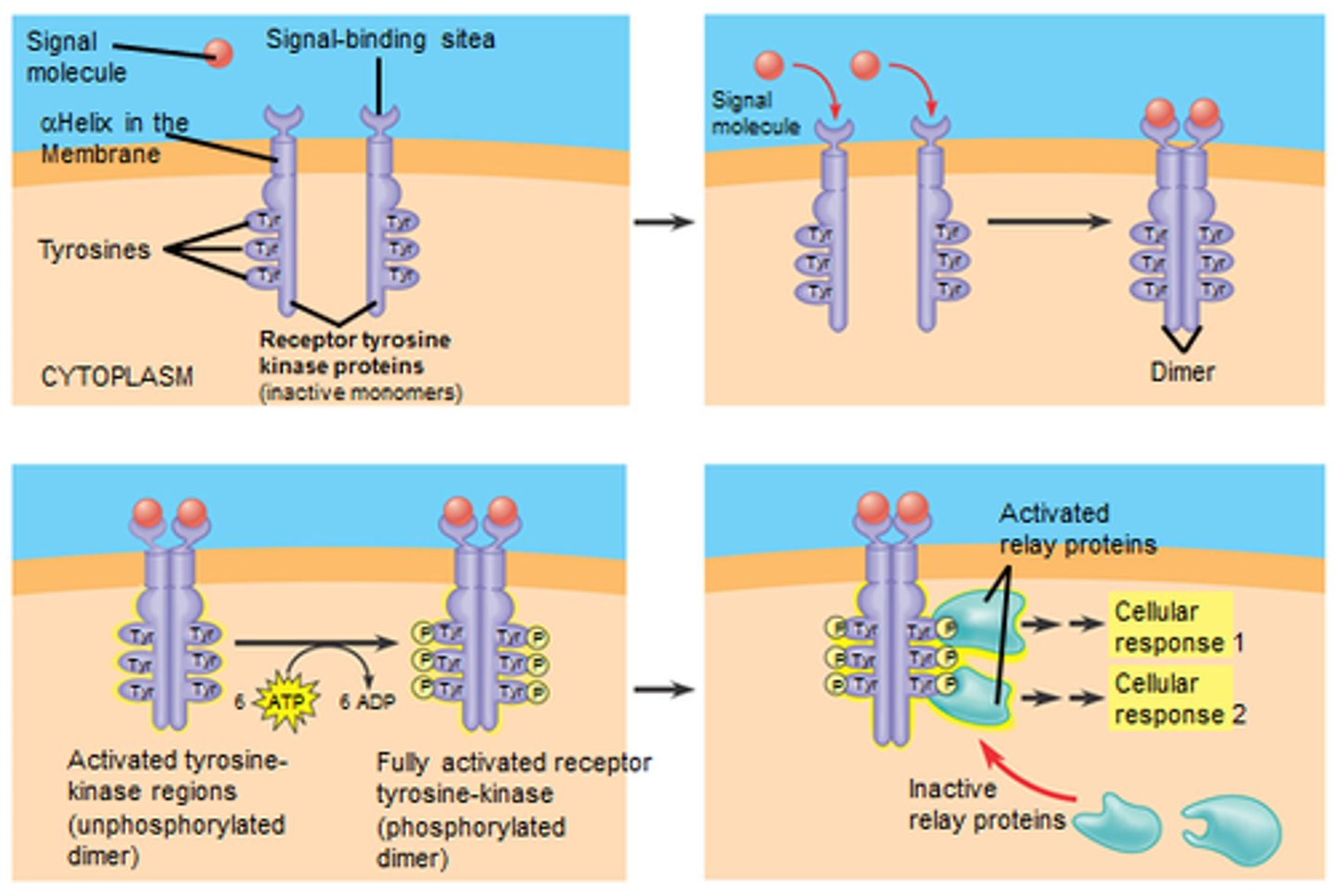
Receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK)
A type of receptor that, upon binding with a ligand, dimerizes and autophosphorylates to activate signaling pathways.
Phosphatases
Enzymes that remove phosphate groups from proteins.
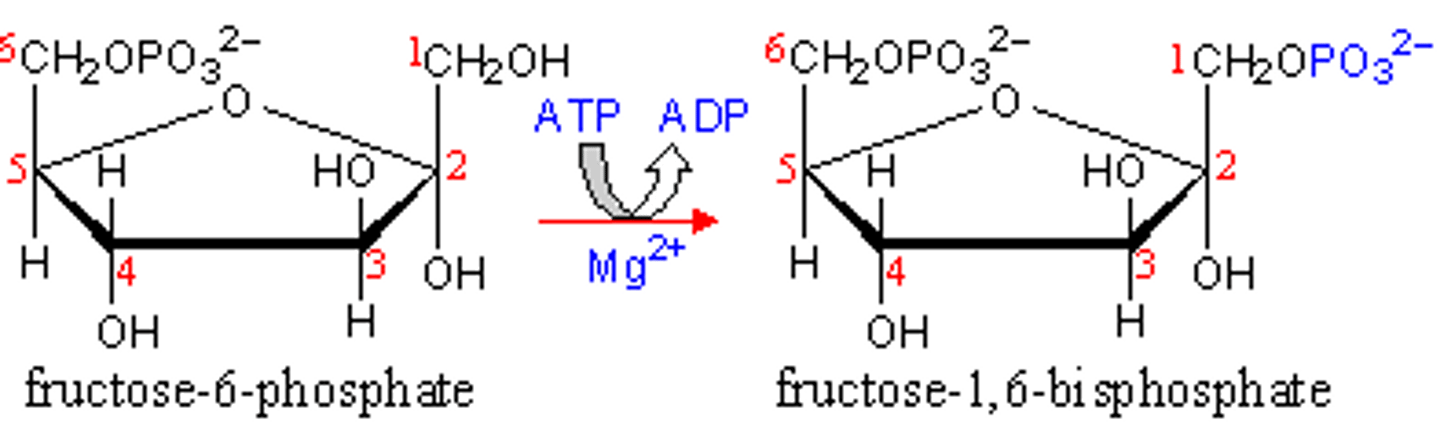
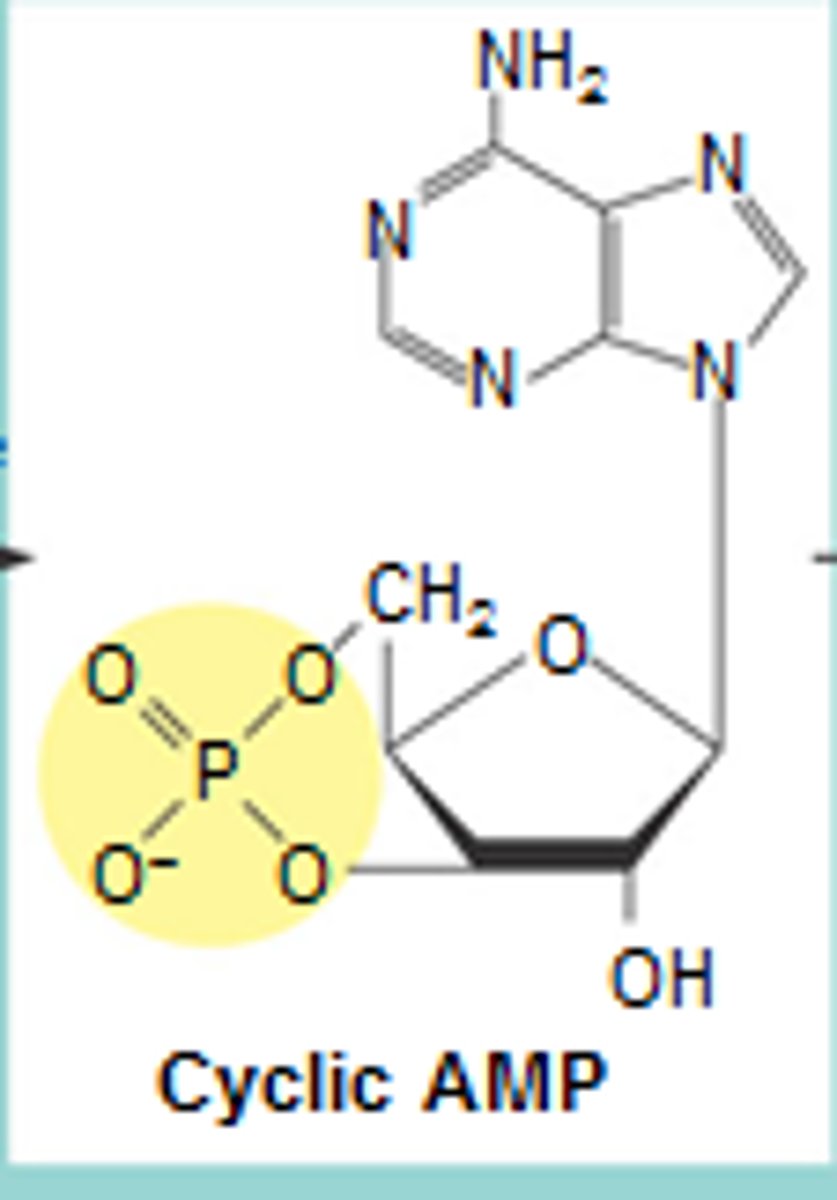
cAMP
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, a second messenger that is produced by adenylyl cyclase.
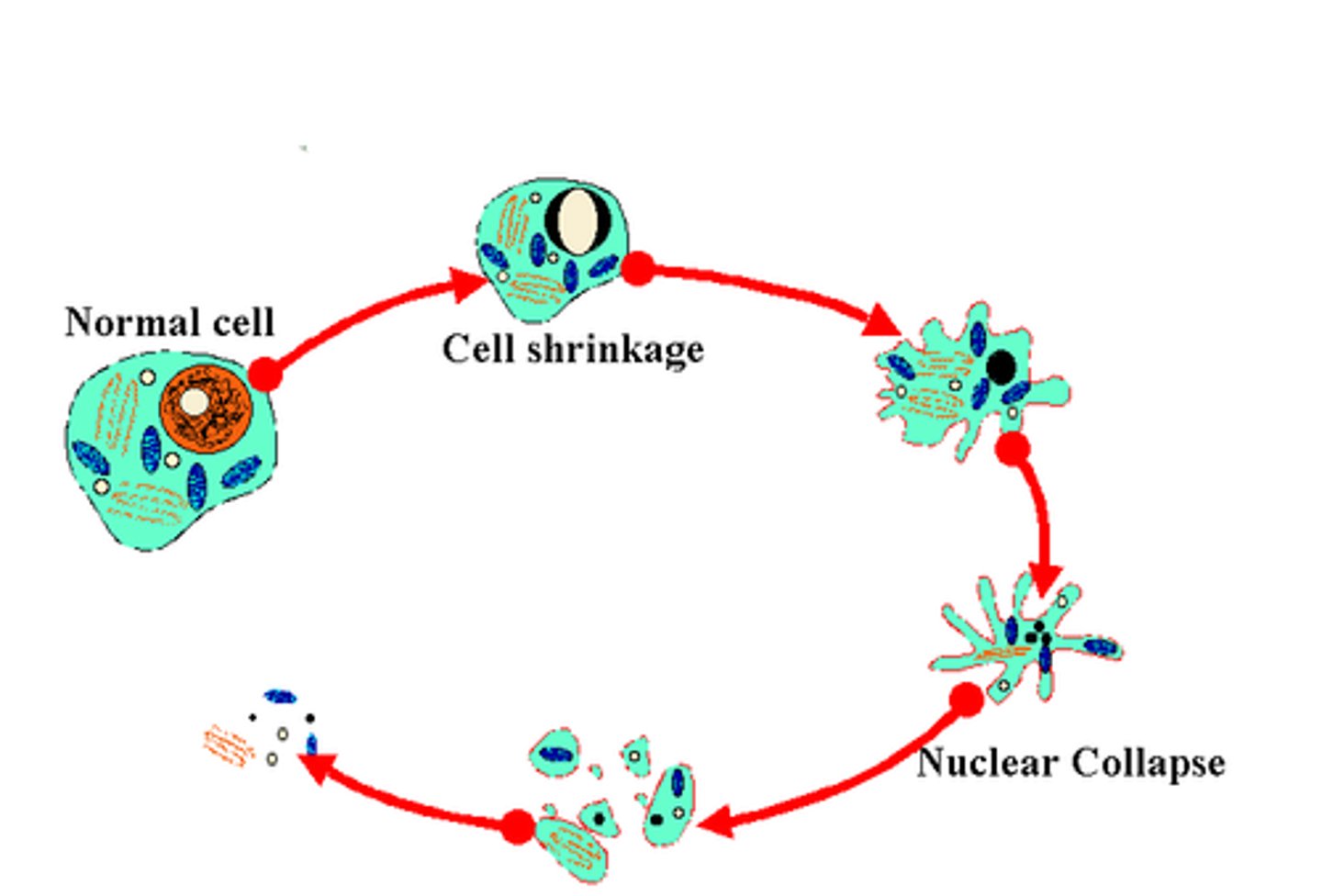
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms.
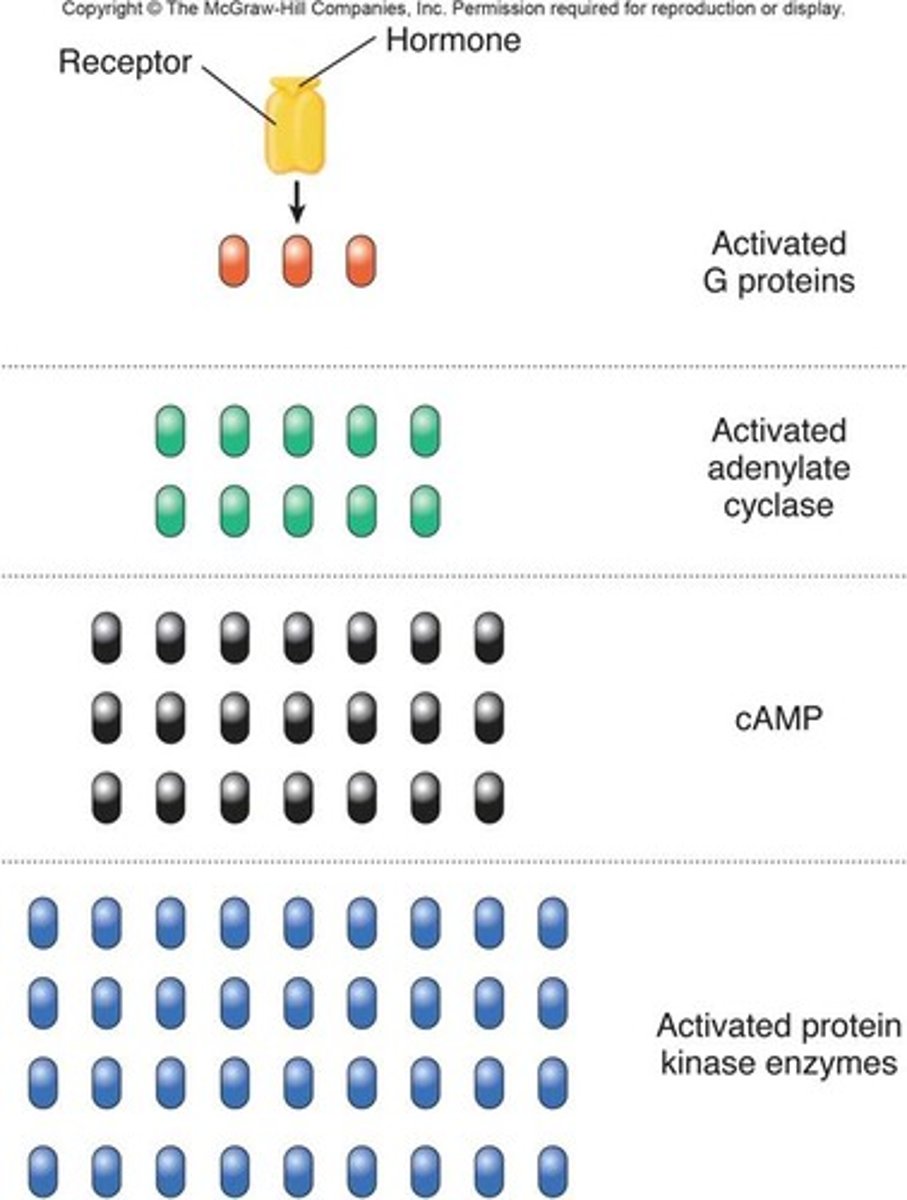
Amplification of the signal
The process in a signal transduction pathway where a single signal leads to the activation of multiple downstream proteins.
Cell division
The process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes.
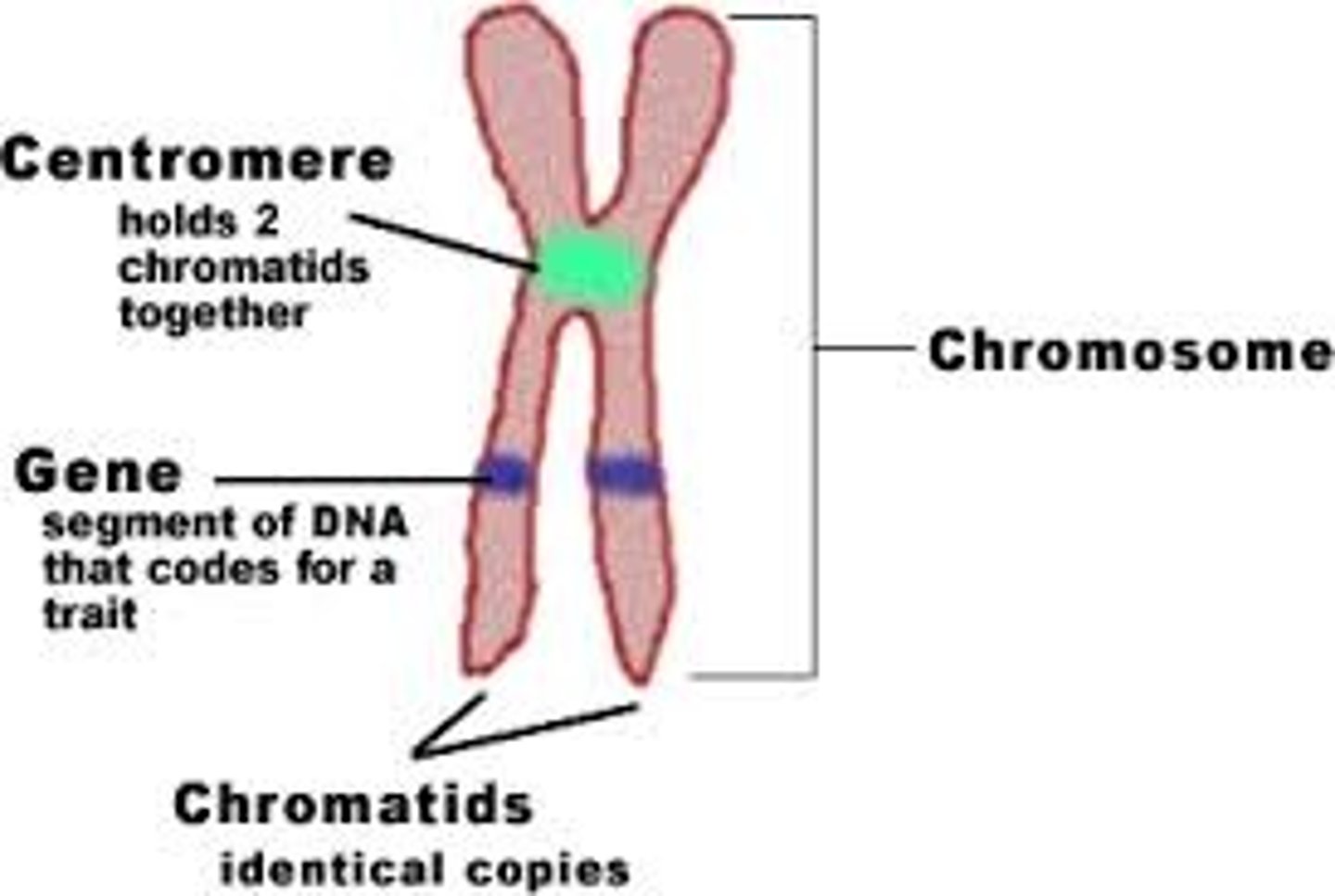
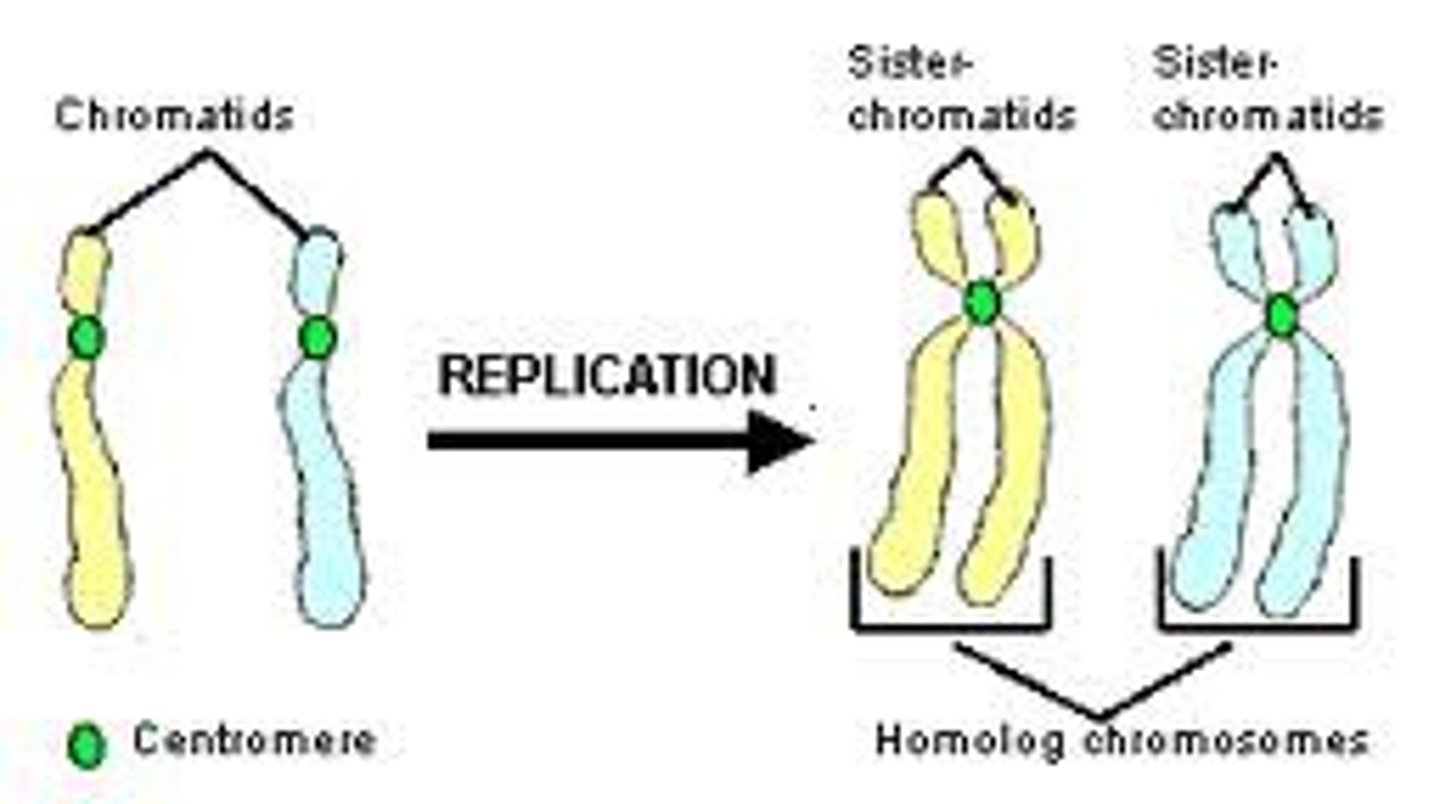
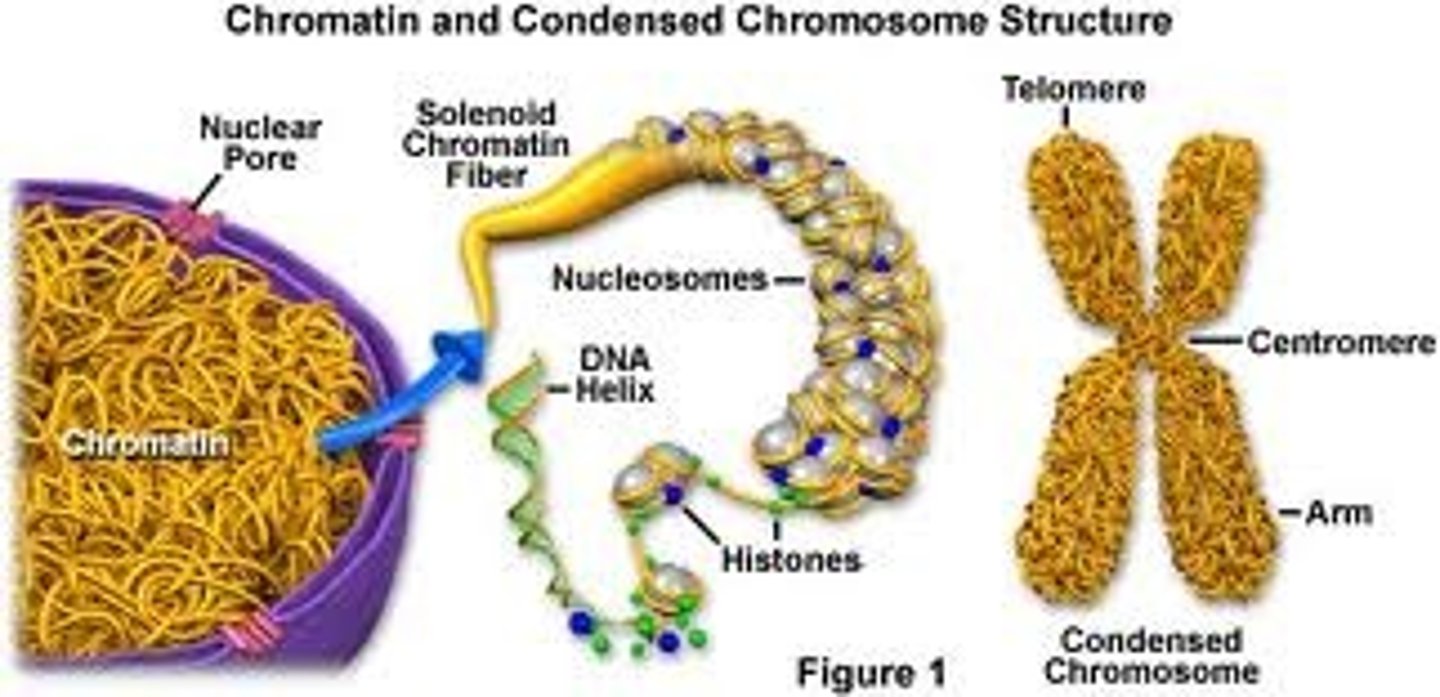
Chromosomes
Structures within cells that contain DNA and carry genetic information.
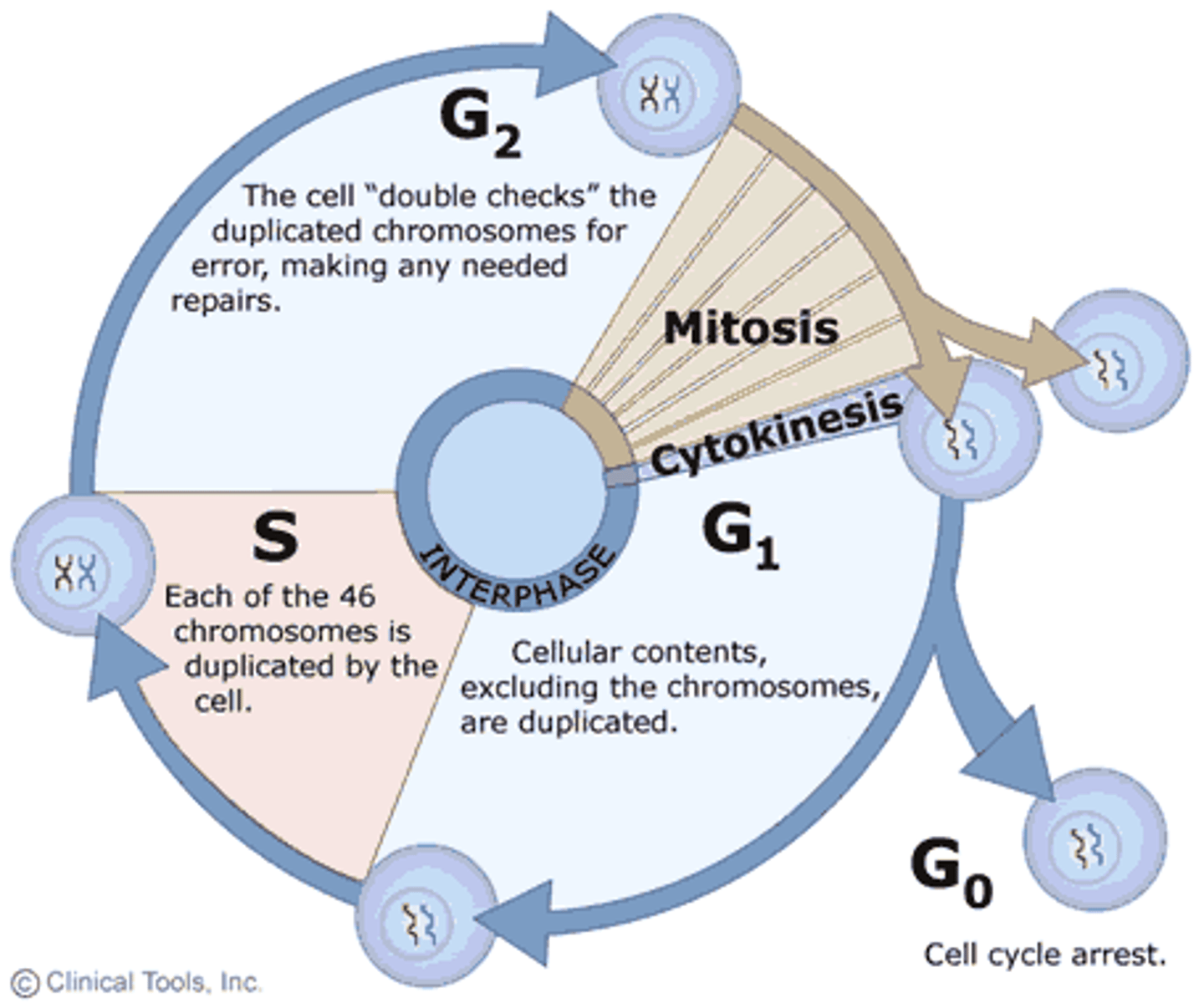
S phase
The phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated.
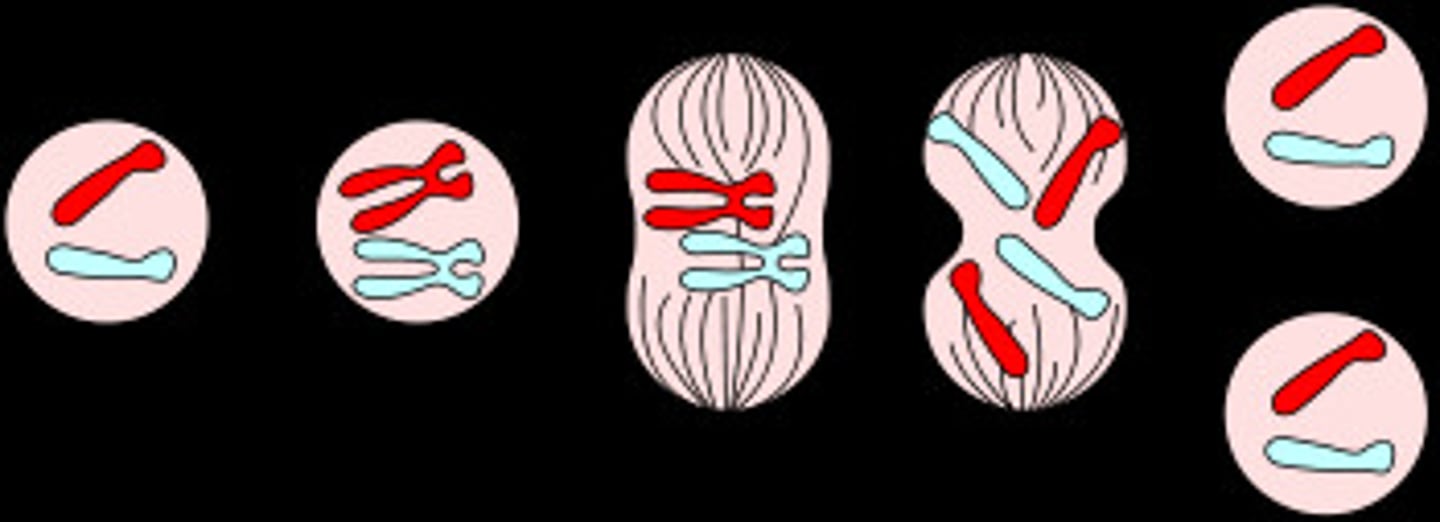
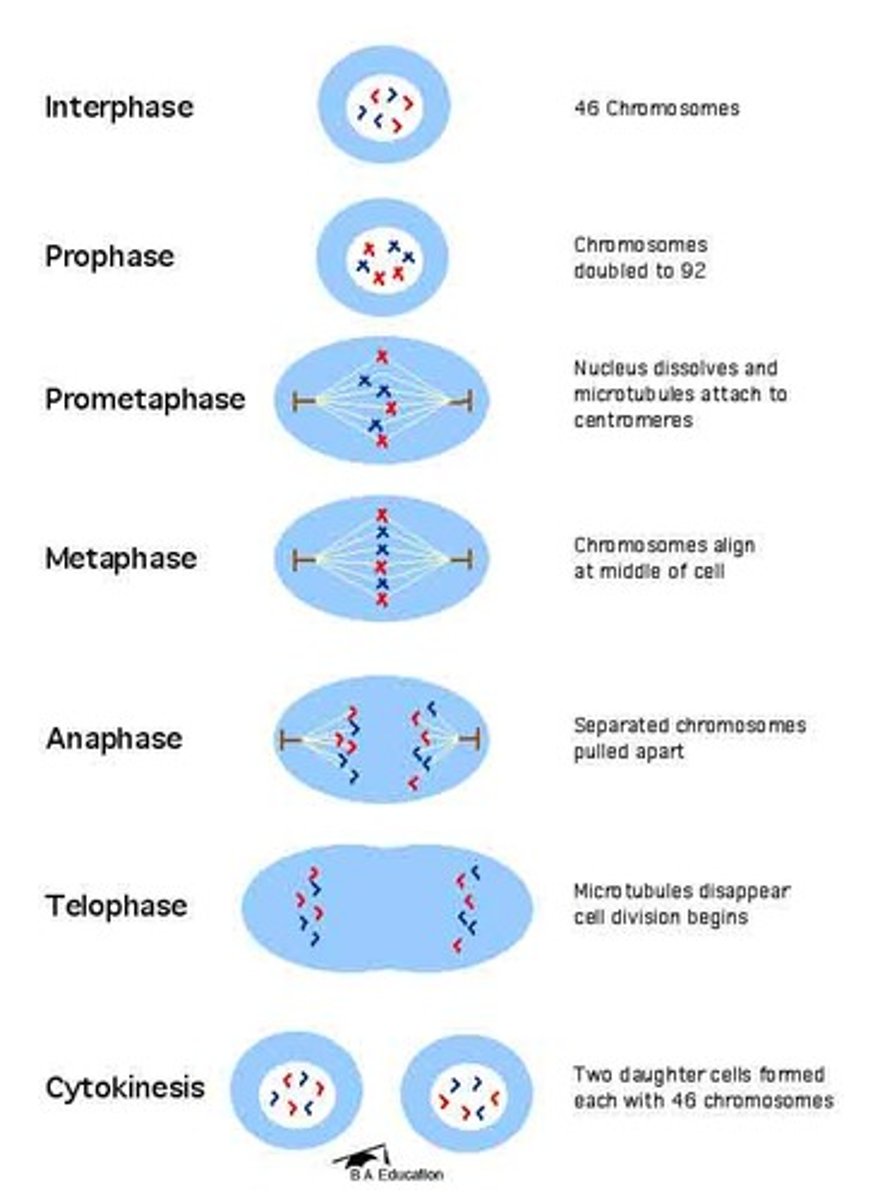
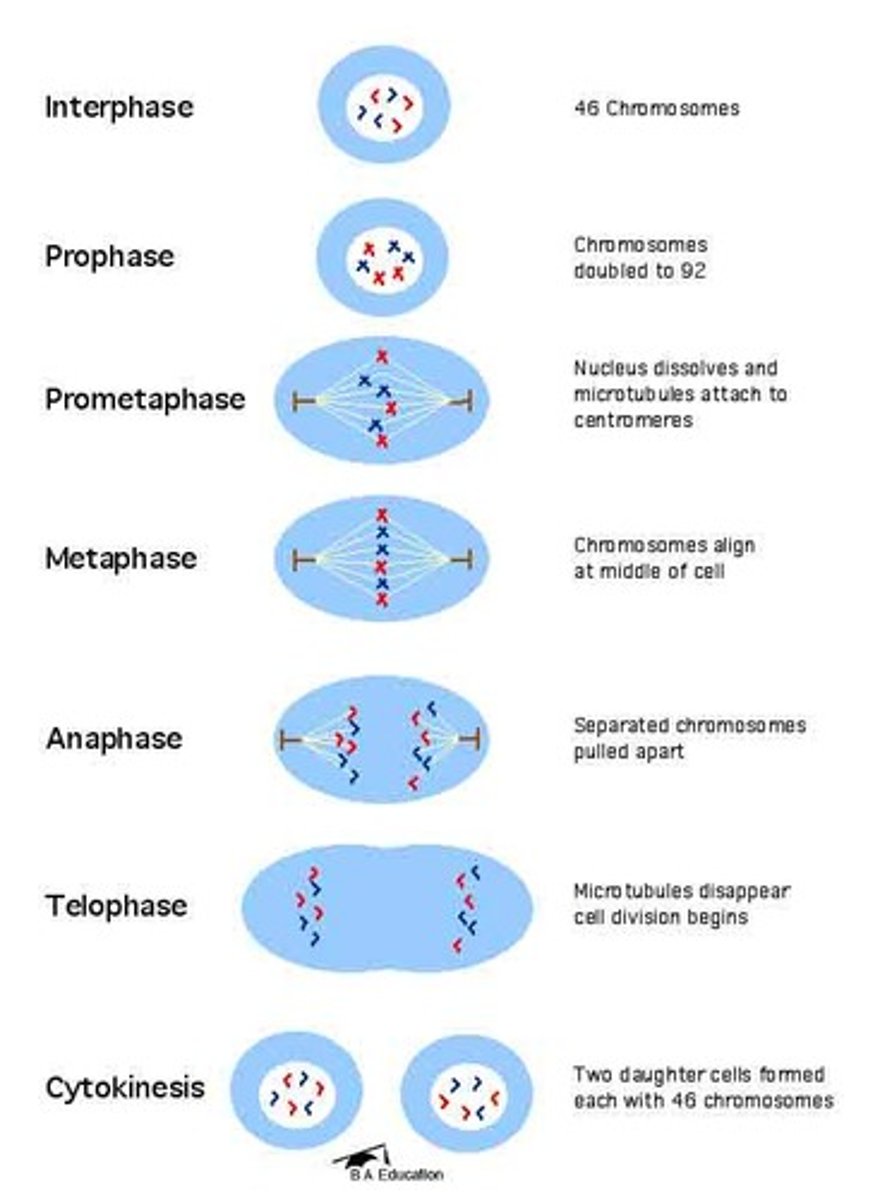
Mitosis
A process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells.
Genetically identical cells
Cells that have the same genetic material as the parent cell.
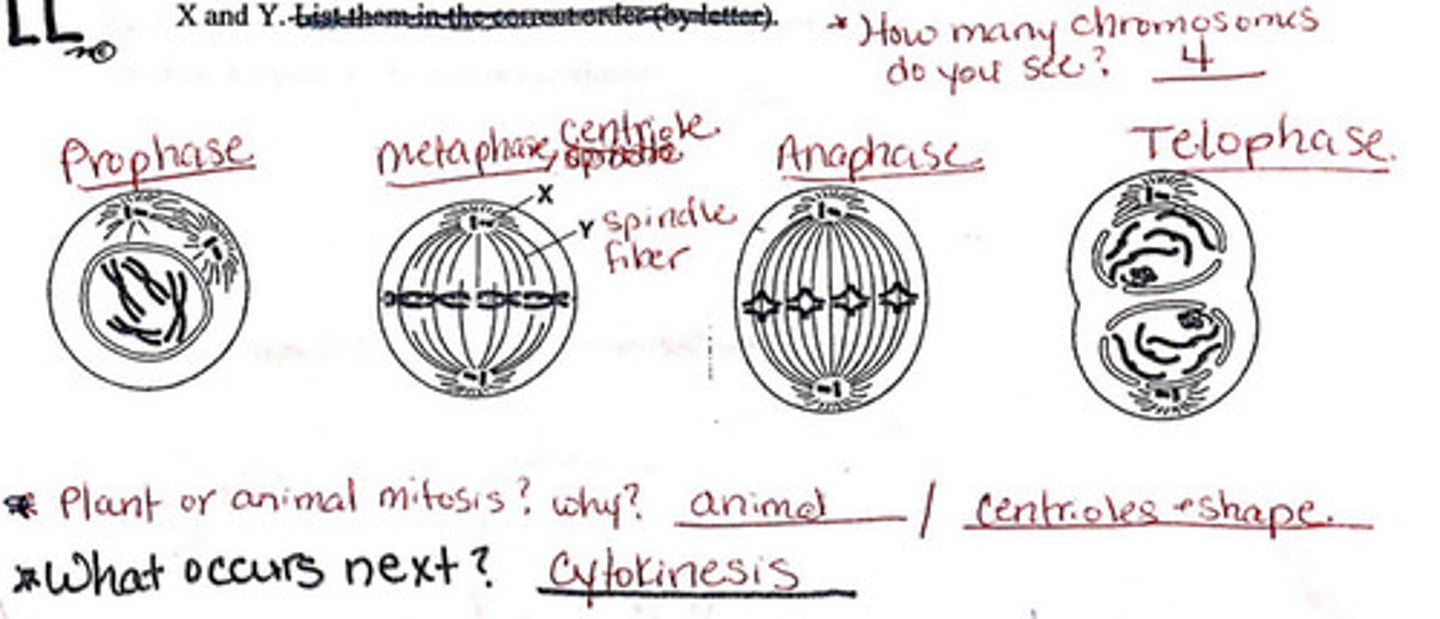
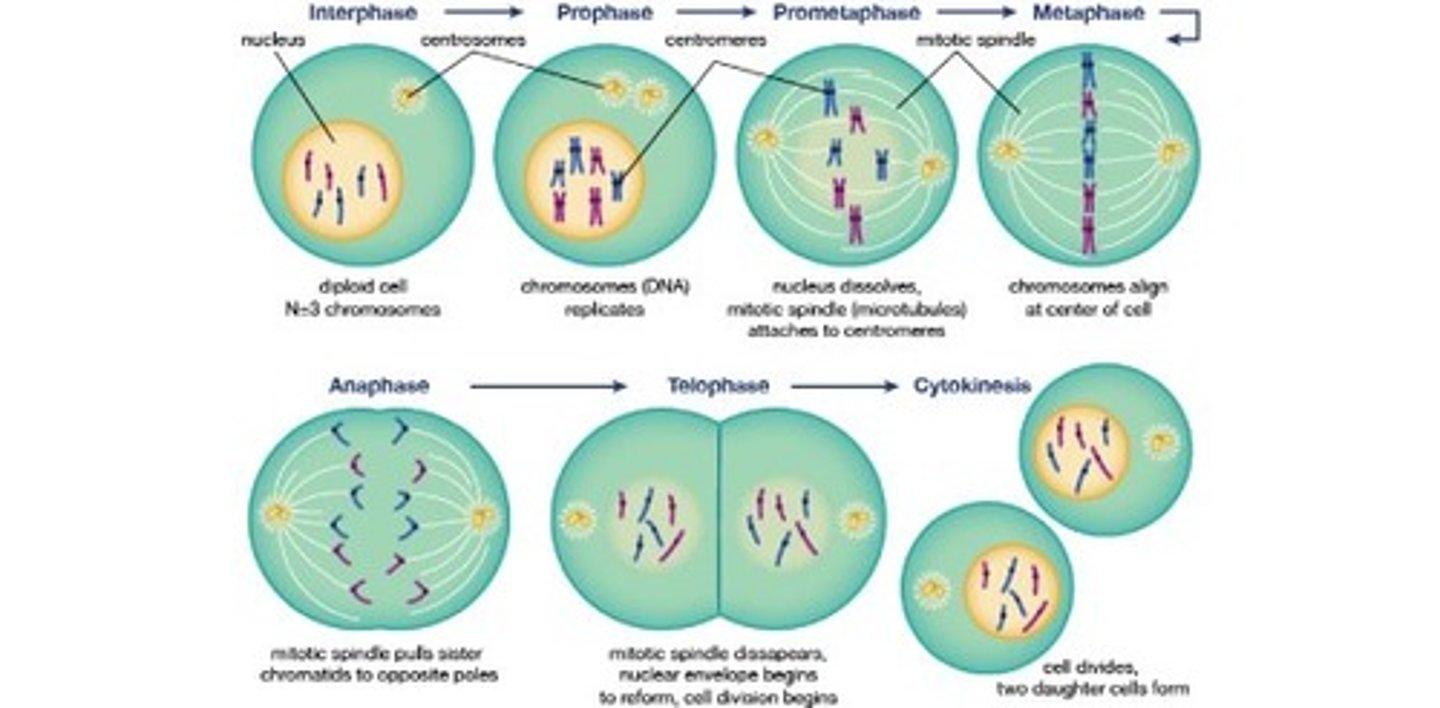
Phases of mitosis
The stages of mitosis include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
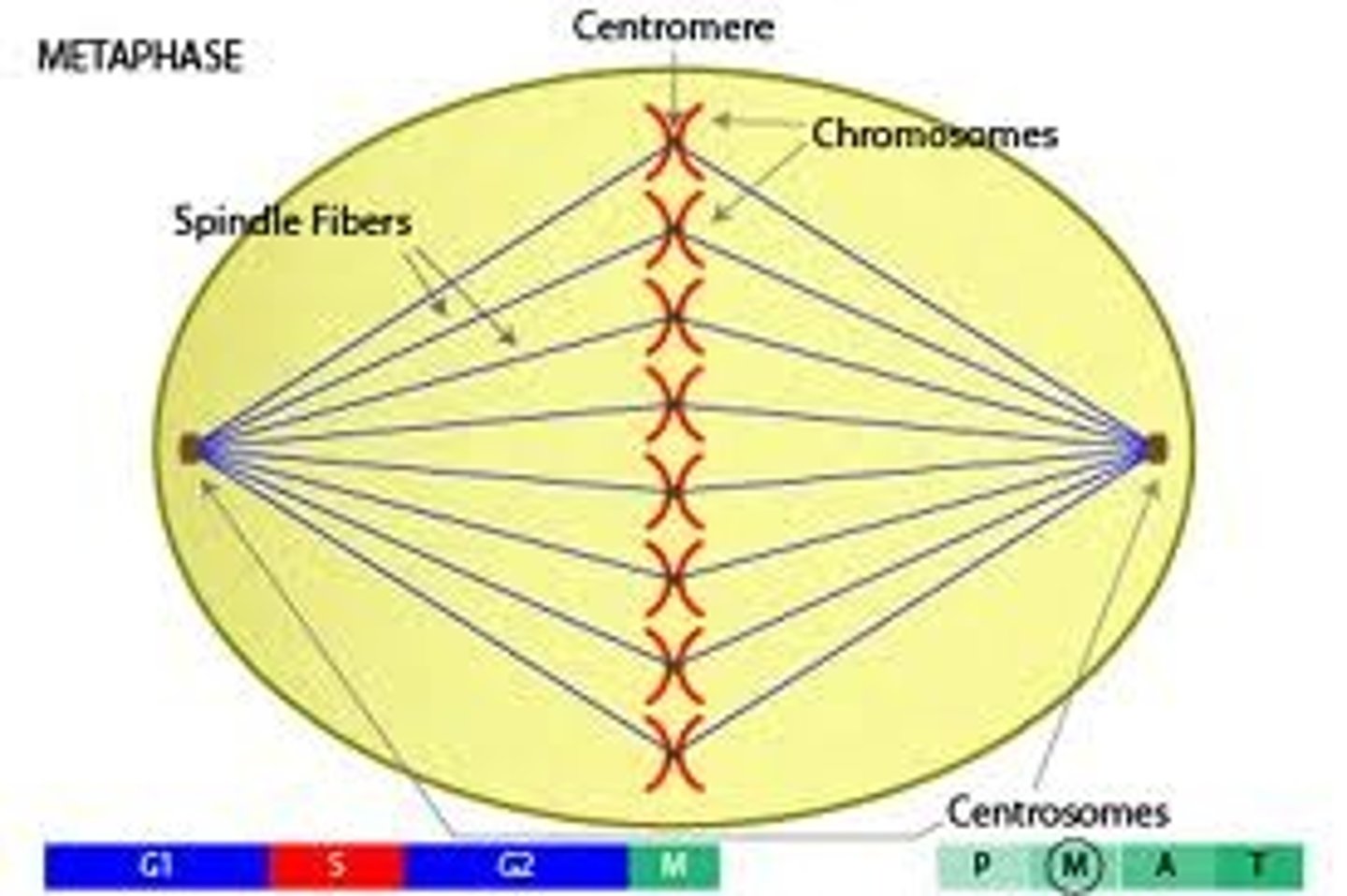
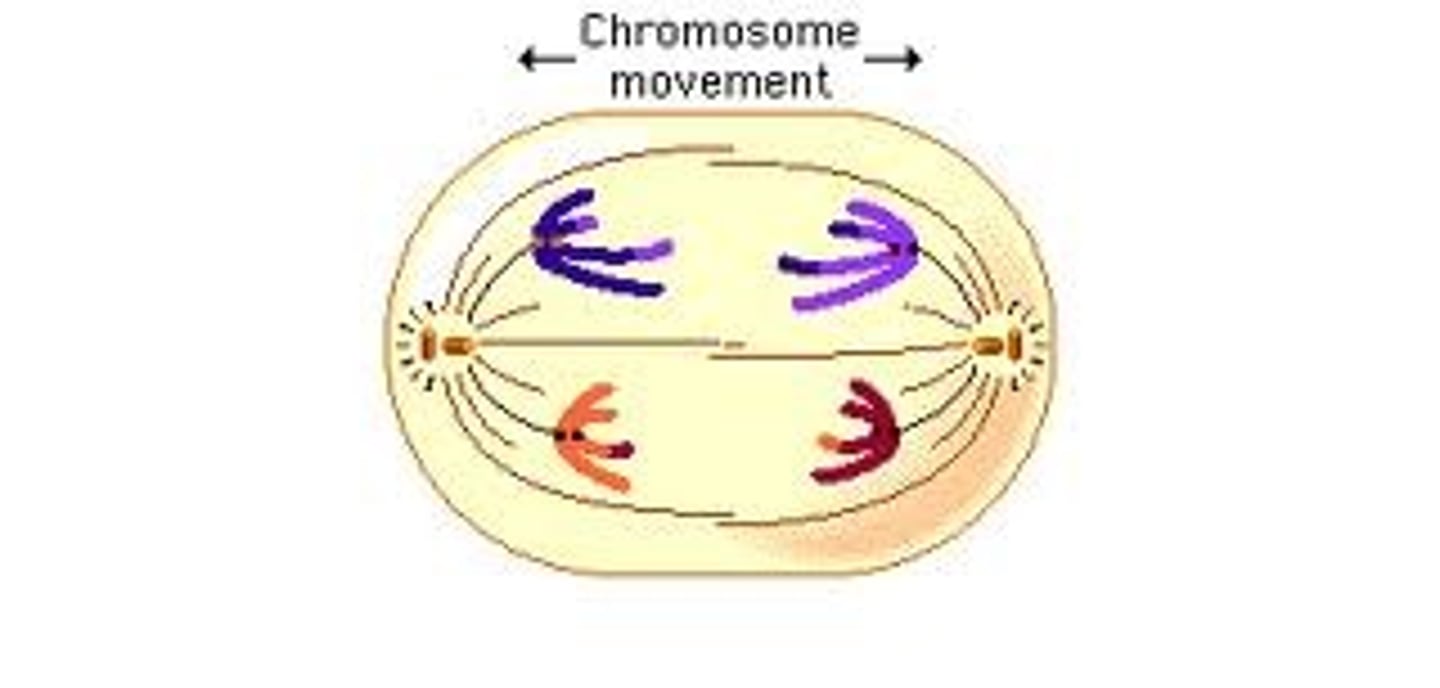
Centromere
The region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids are joined.
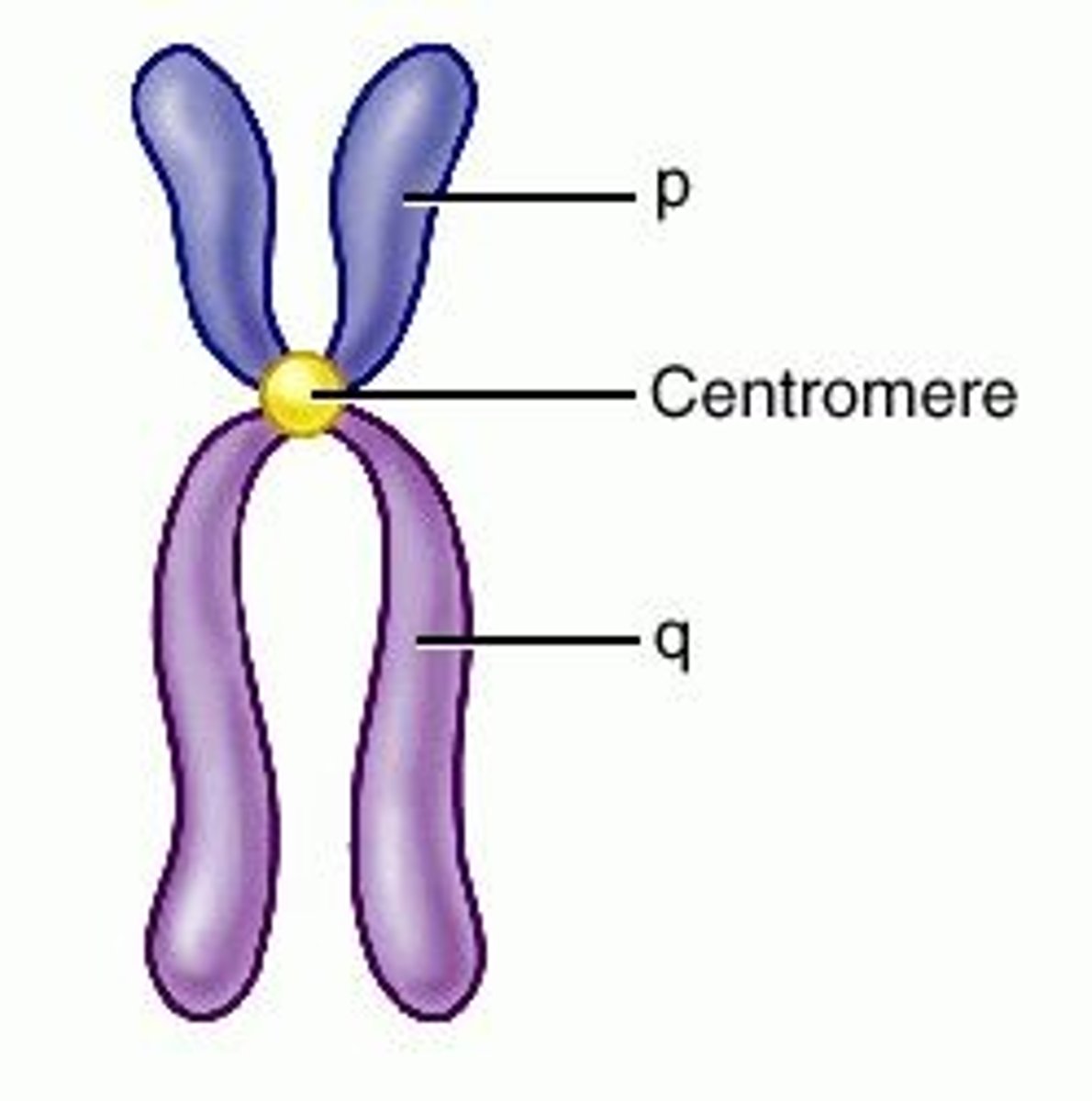
Kinetochore
A protein structure on the chromosome that attaches to the spindle fibers during cell division.
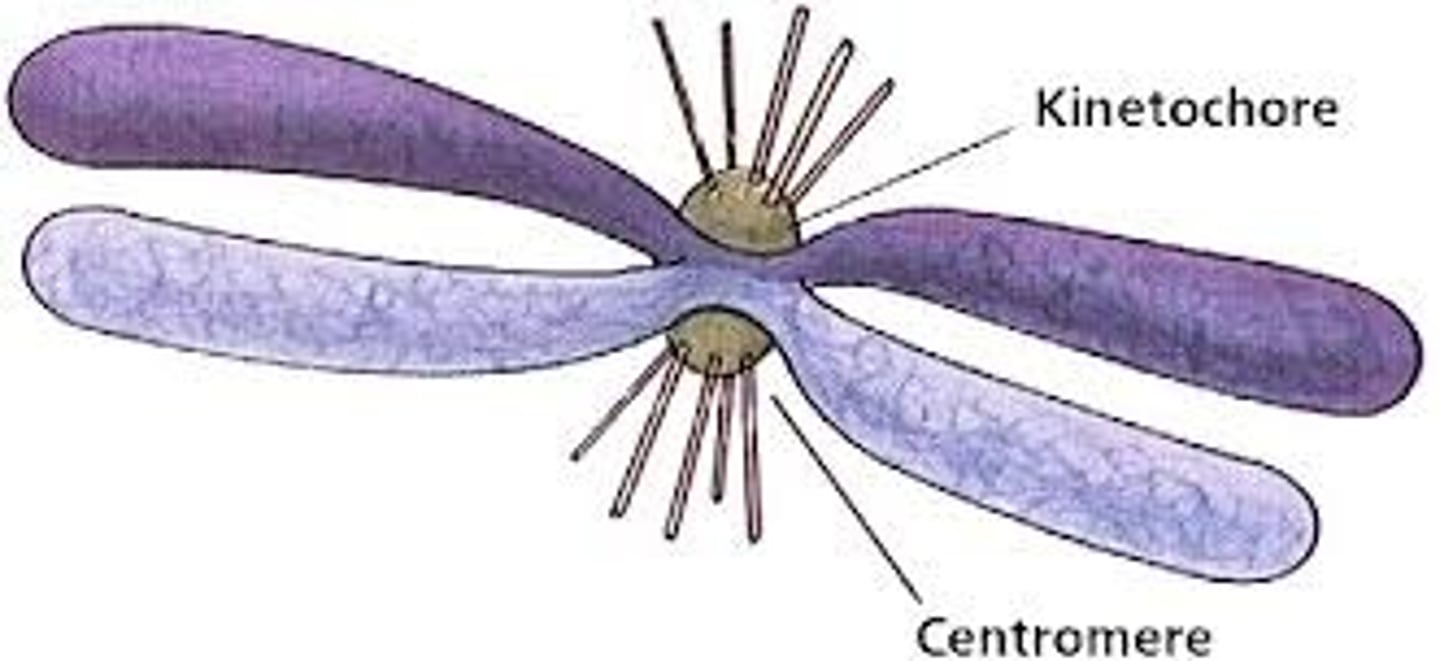
Sister chromatid
One of the two identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.
Chromatin
The material of which the chromosomes of organisms are composed, consisting of protein, RNA, and DNA.
Genetic variation
Differences in DNA sequences among individuals.

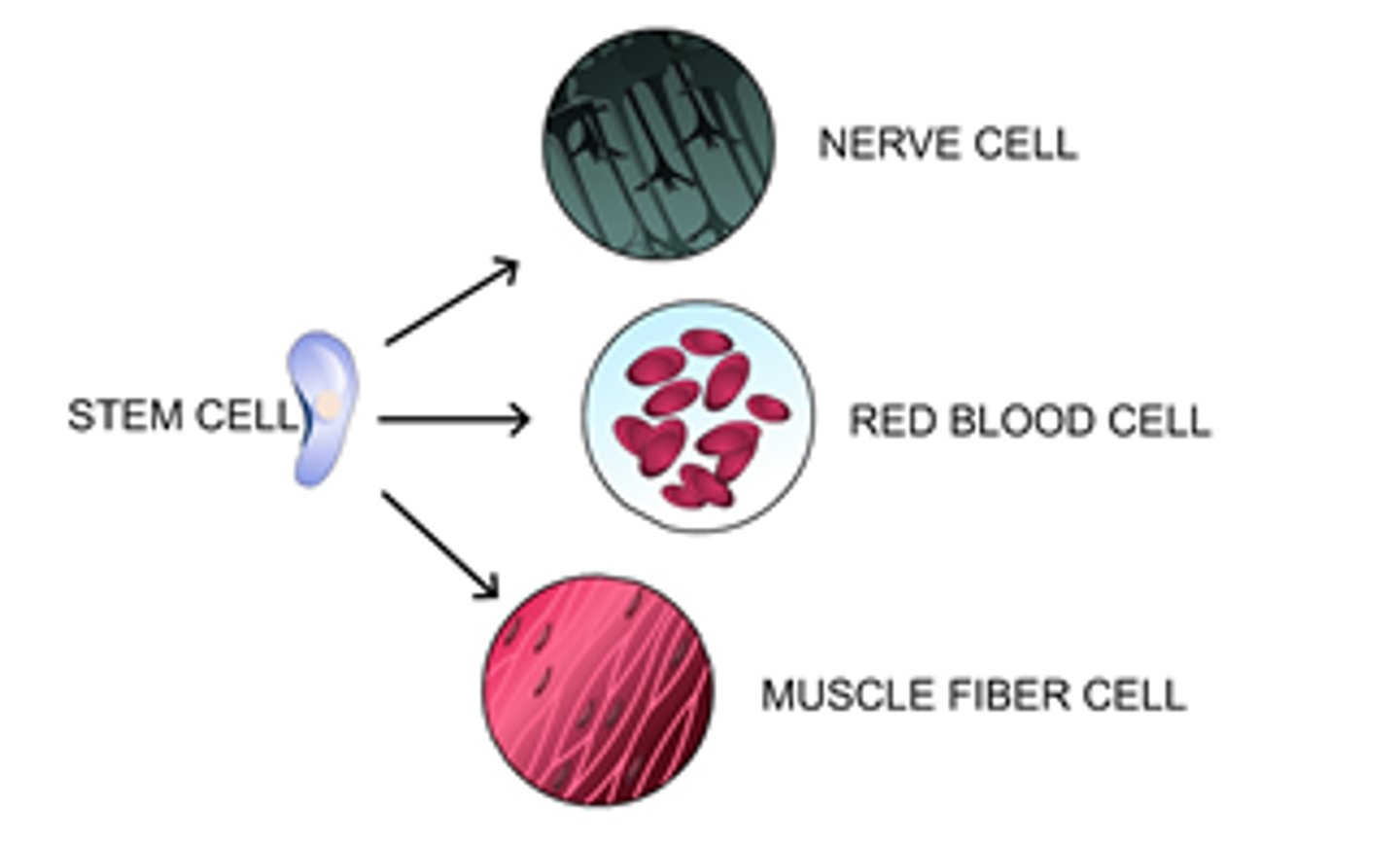
Cell specialization
The process by which generic cells change into specific cells meant to do certain tasks.
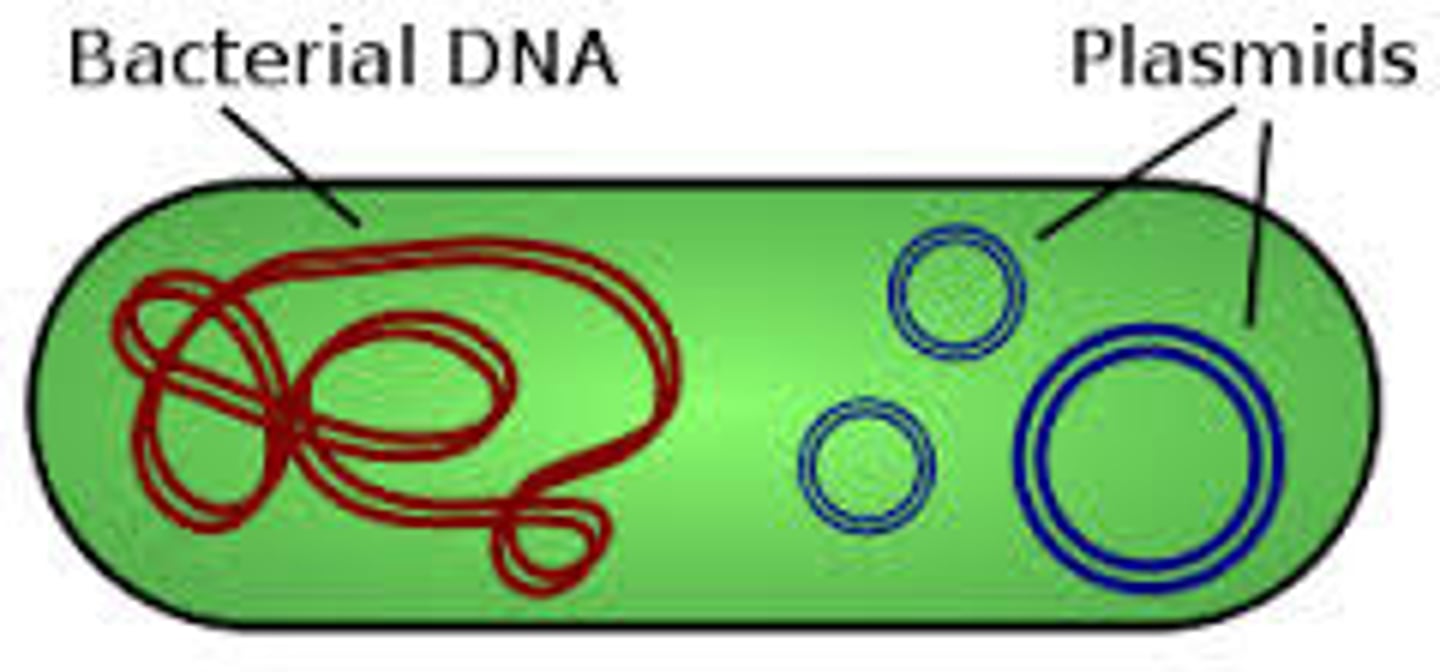
Plasmids
Small, circular DNA molecules found in bacteria that are separate from chromosomal DNA.
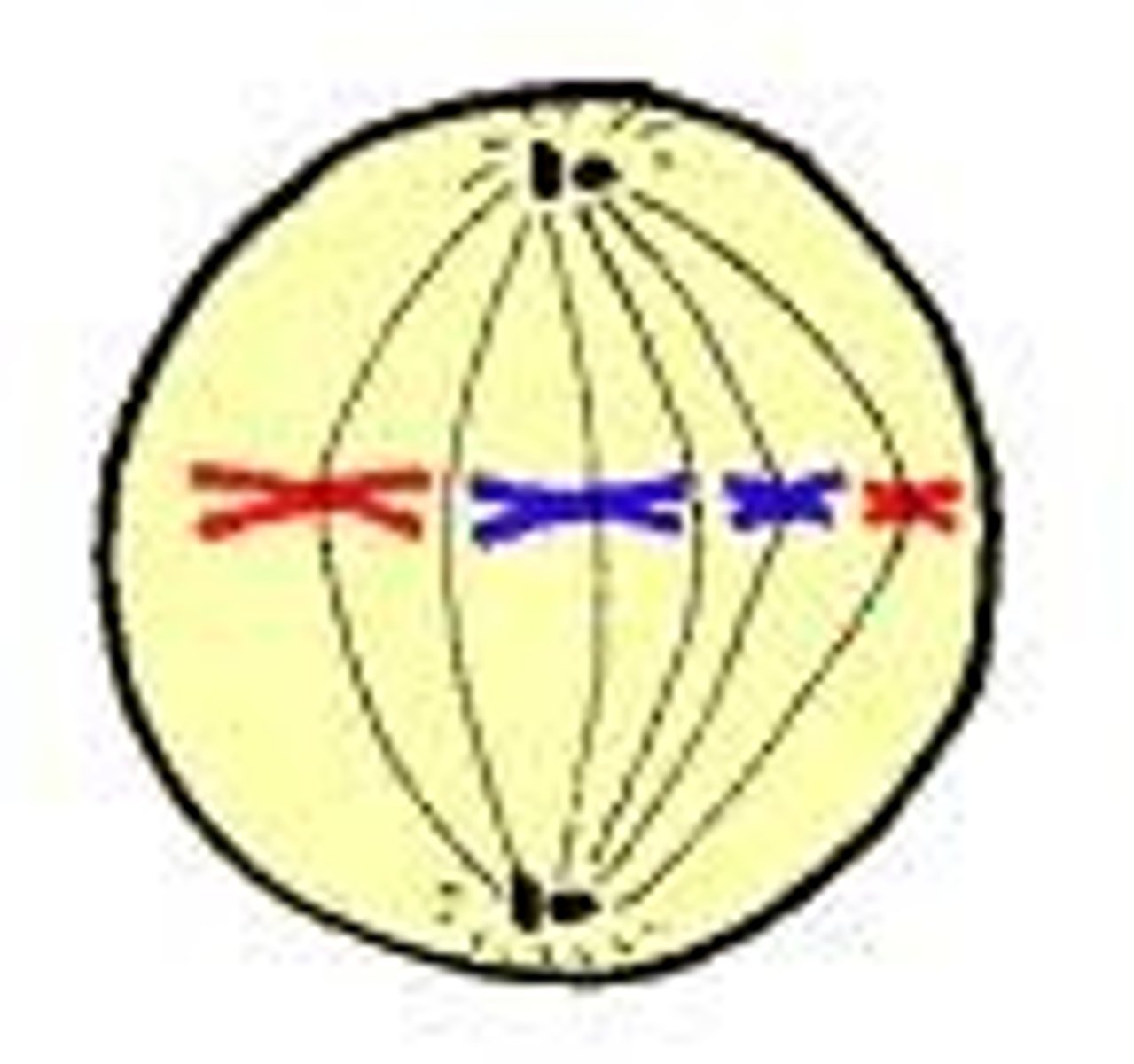
Metaphase
During metaphase, chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate.
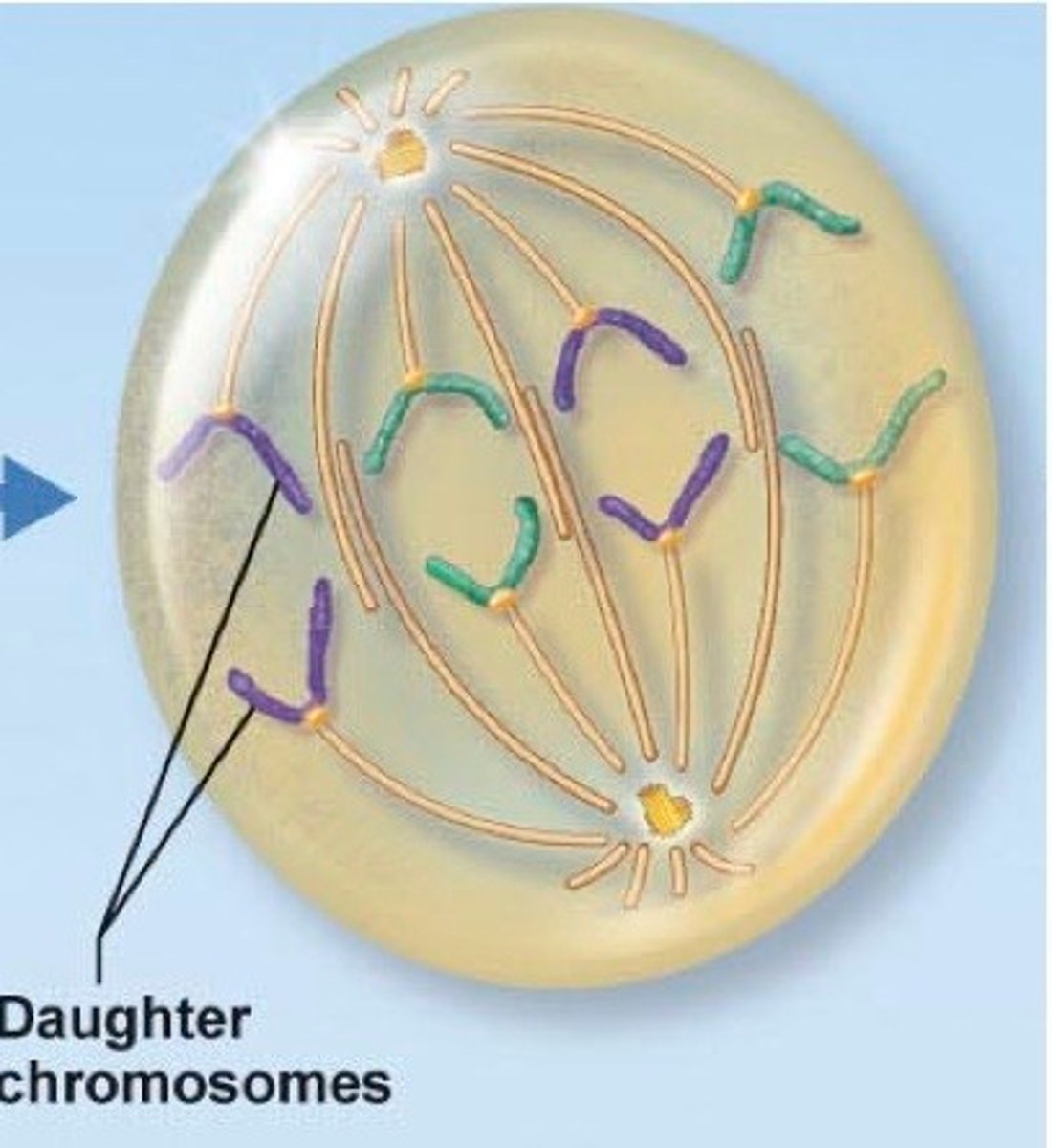
Separation of sister chromatids
The separation of sister chromatids occurs during anaphase.
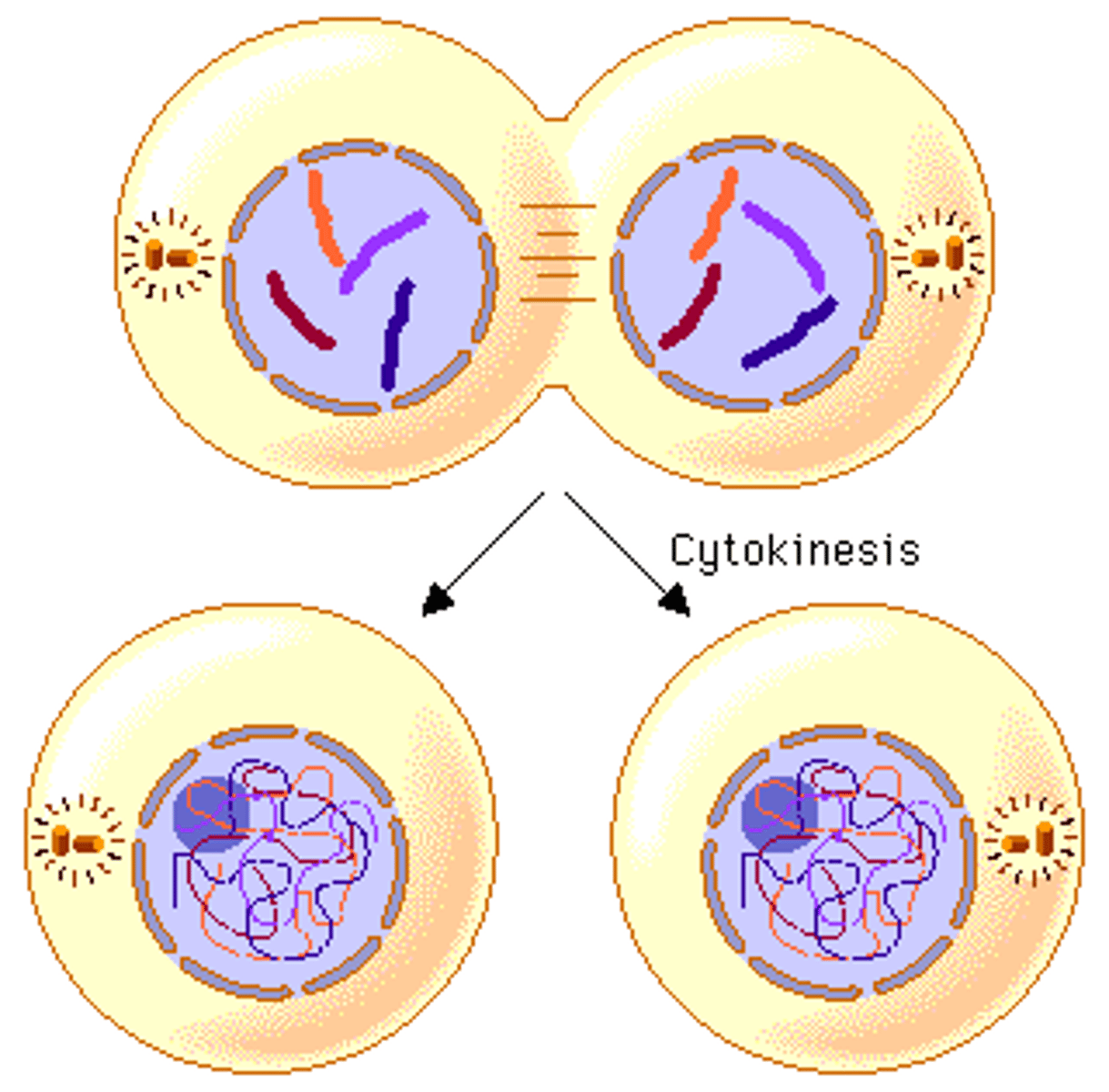
Cytokinesis in animal cells
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves the formation of a cleavage furrow.
Mitotic spindle
The mitotic spindle is composed of microtubules.
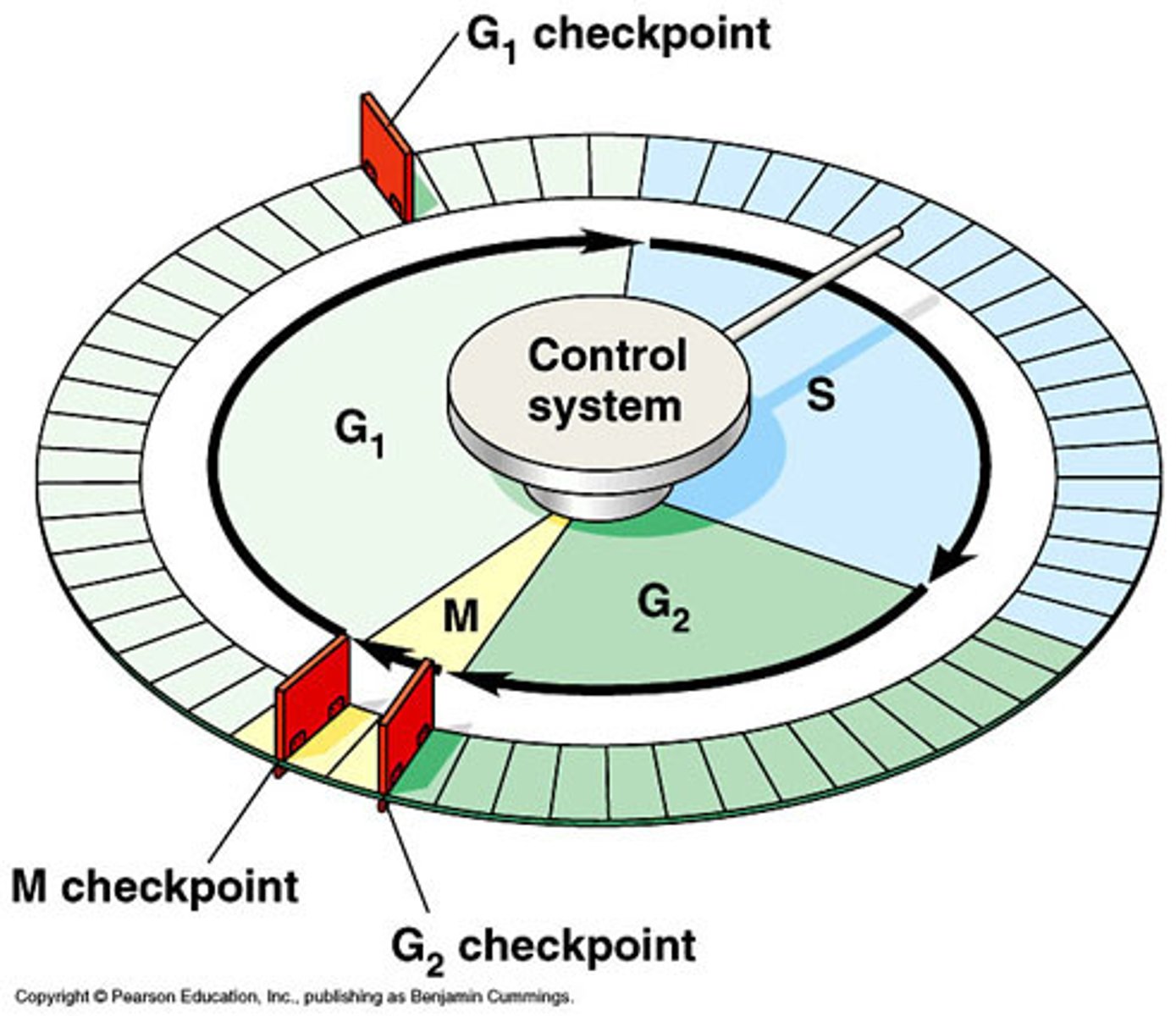
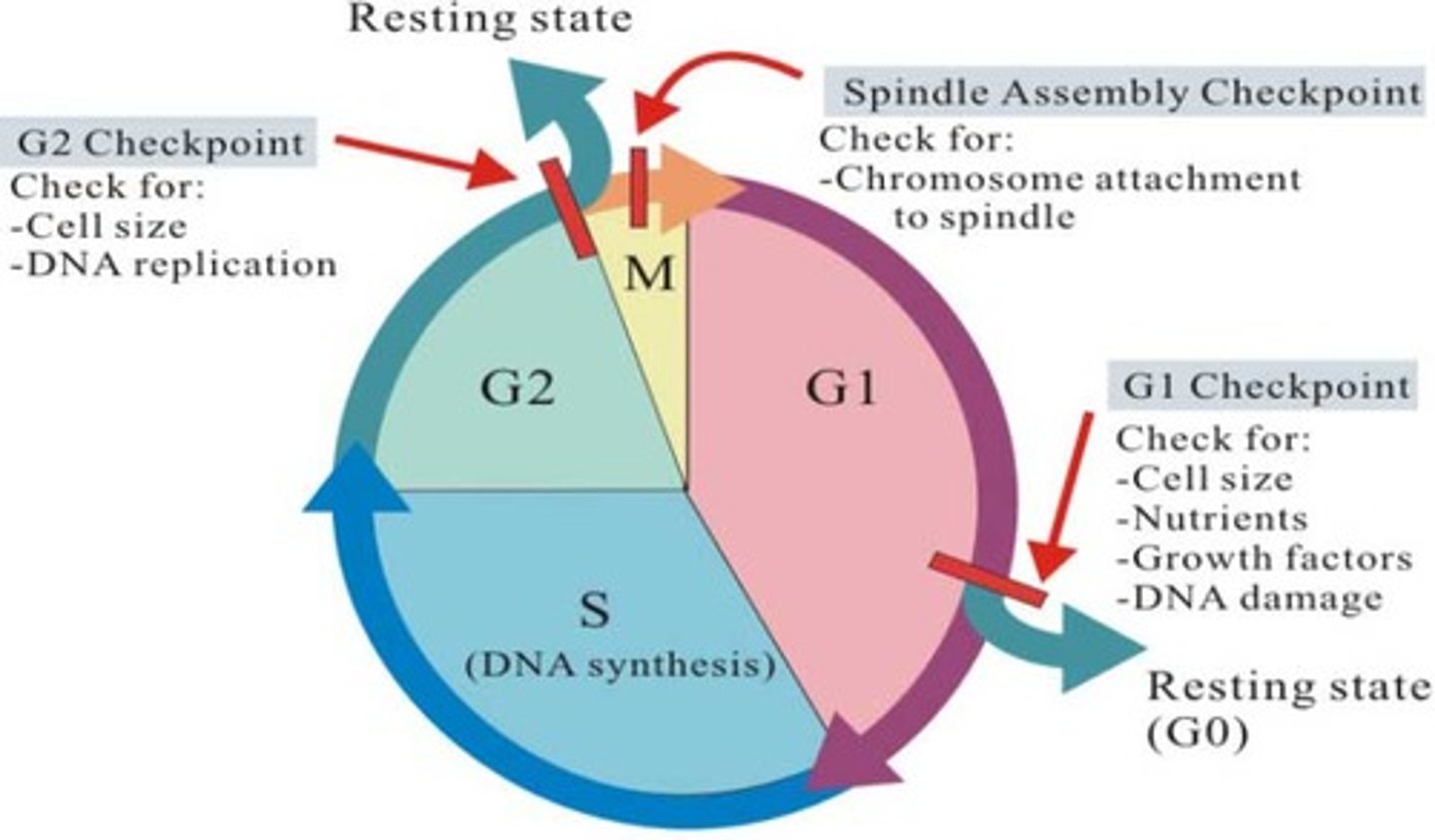
Cell cycle checkpoints
Cell cycle checkpoints are important because they ensure the accuracy of DNA replication and chromosome segregation.
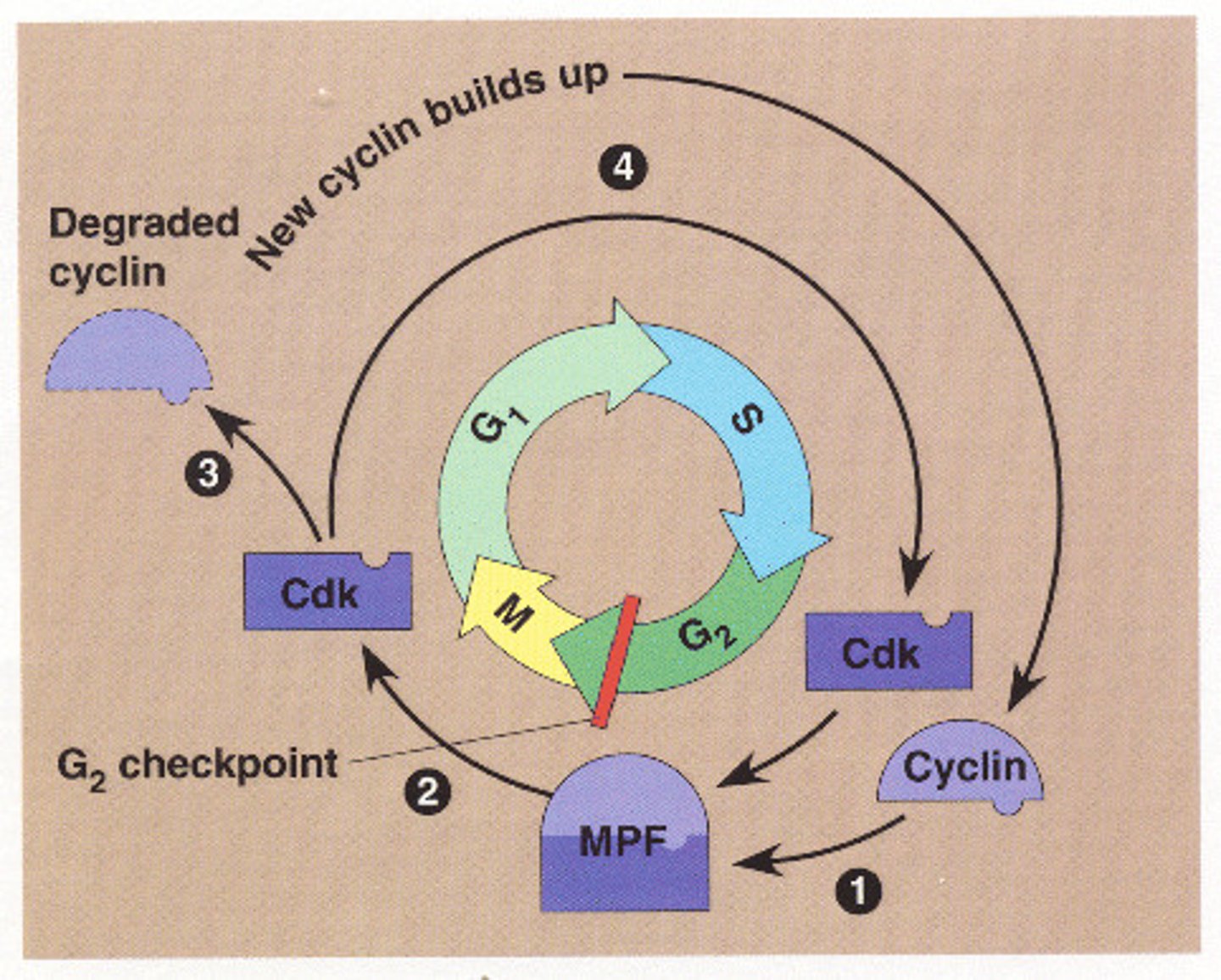
MPF
MPF, a key regulator of the cell cycle, is composed of cyclin and a protein kinase.
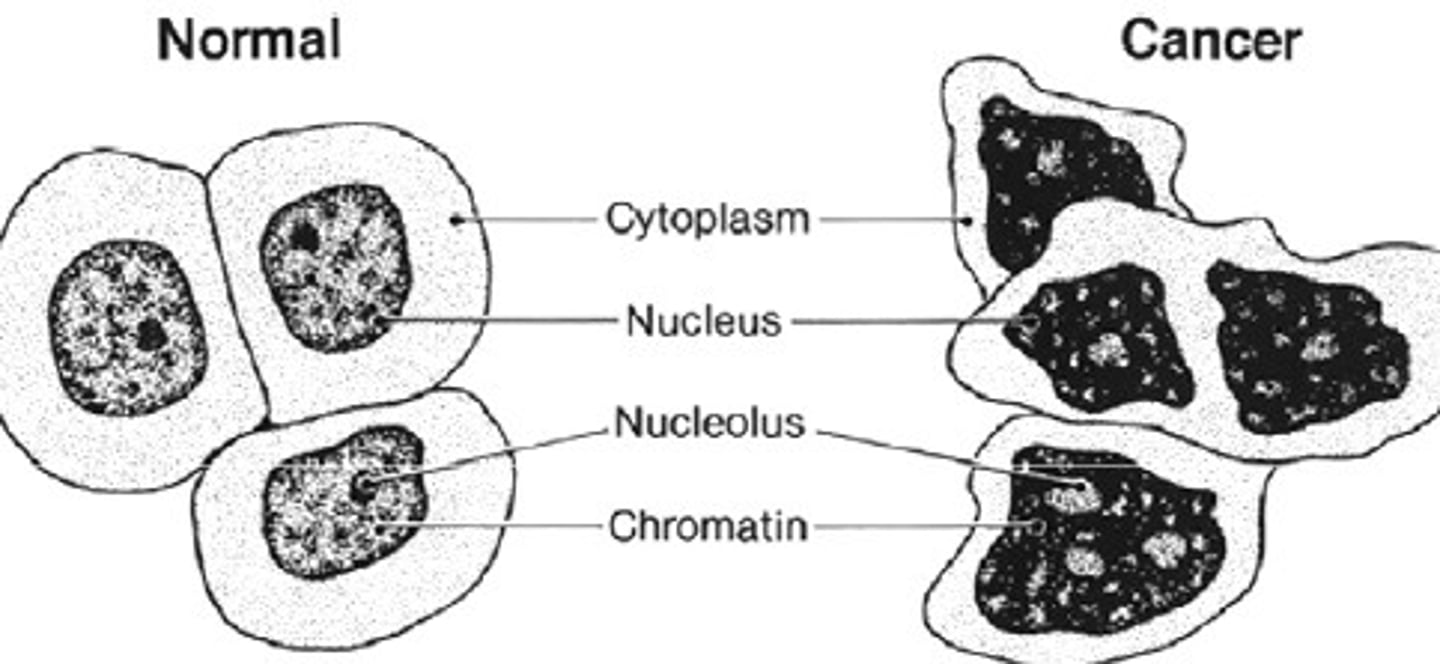
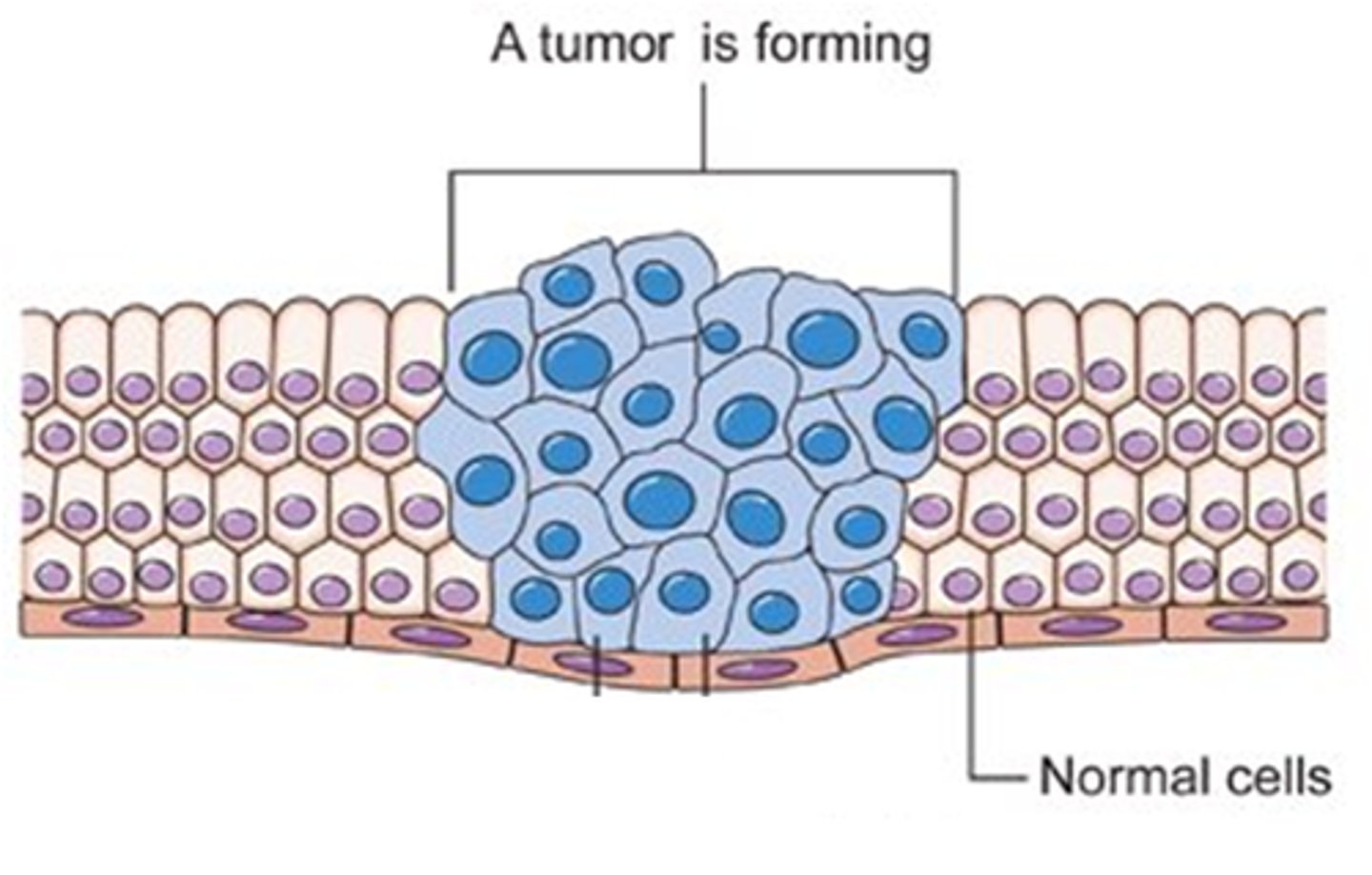
Cancer cells
Cancer cells differ from normal cells in that cancer cells may continue to divide even when tightly packed.
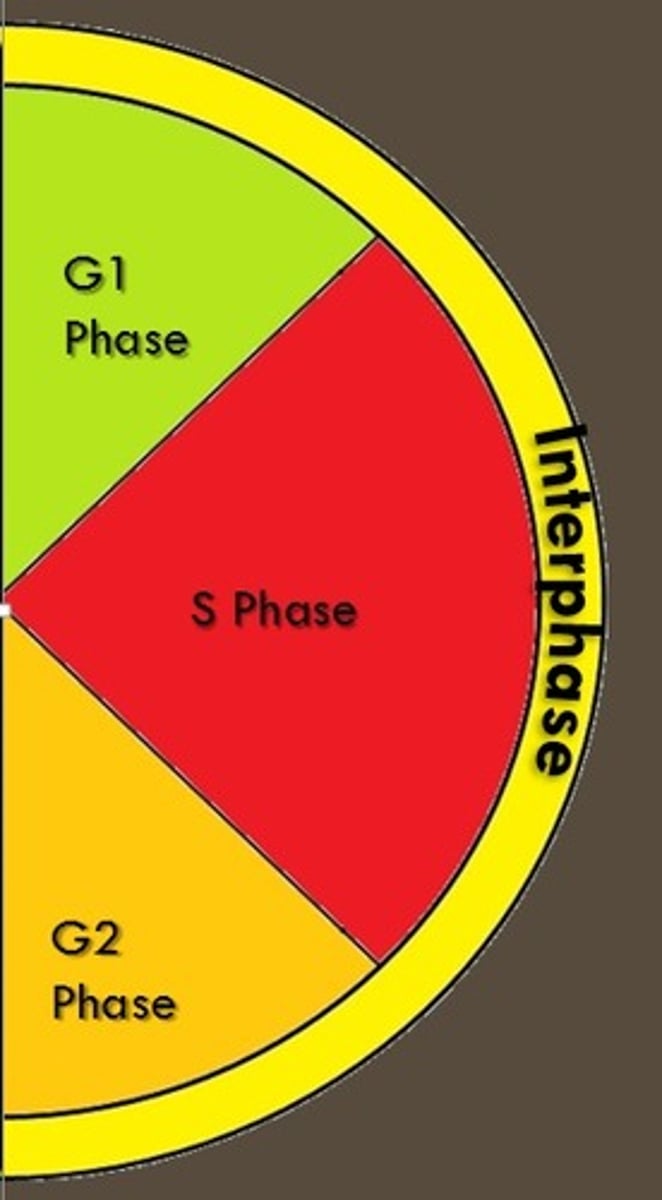
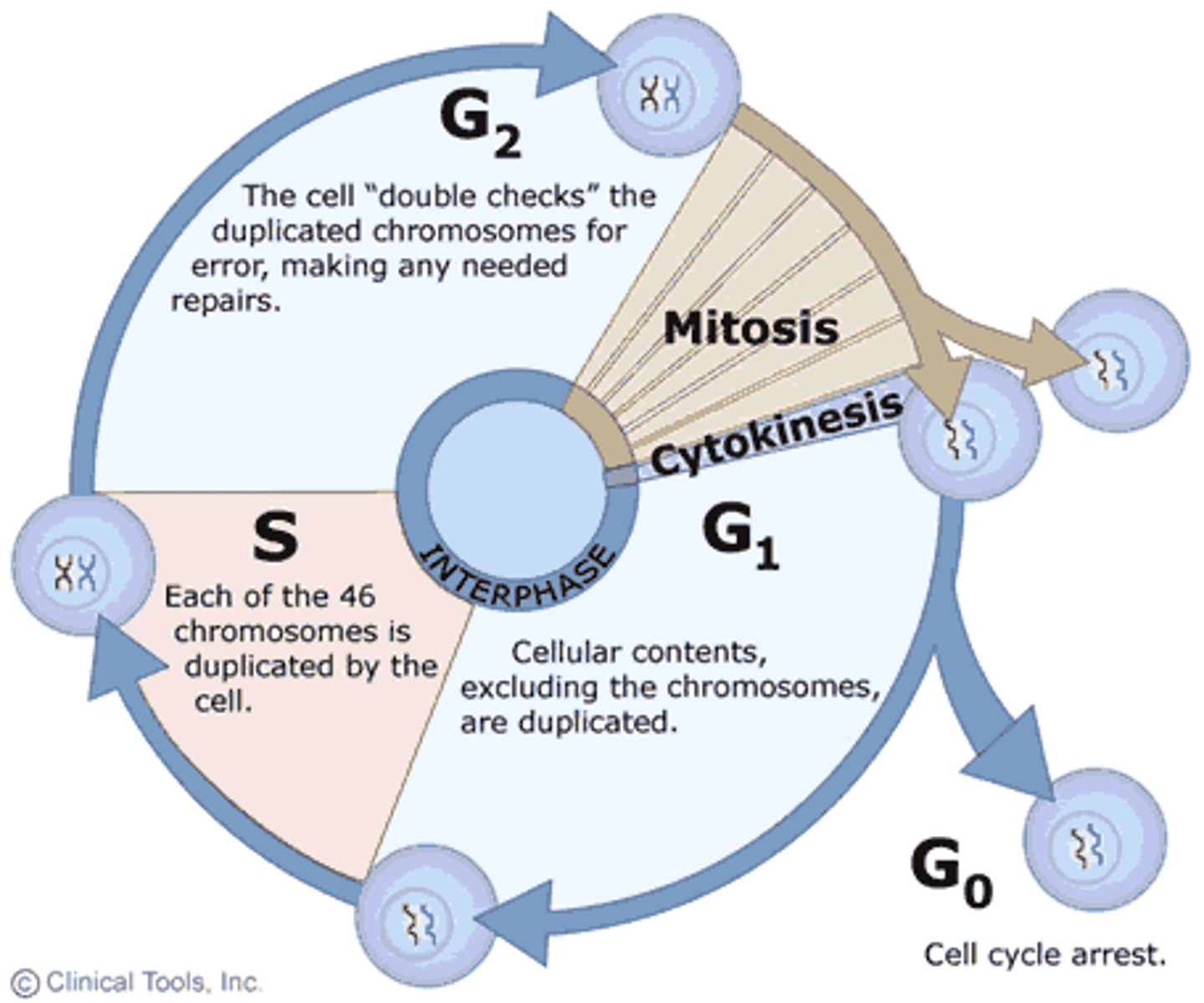
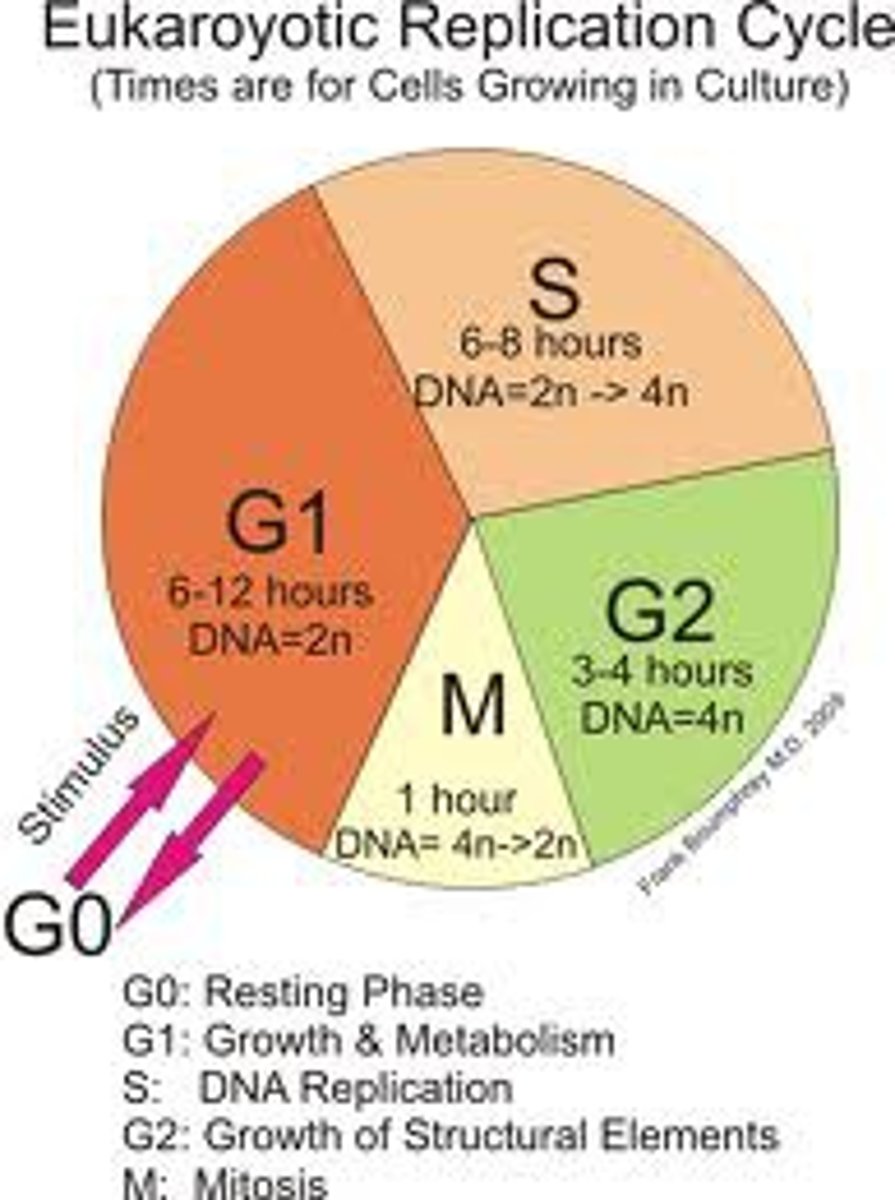
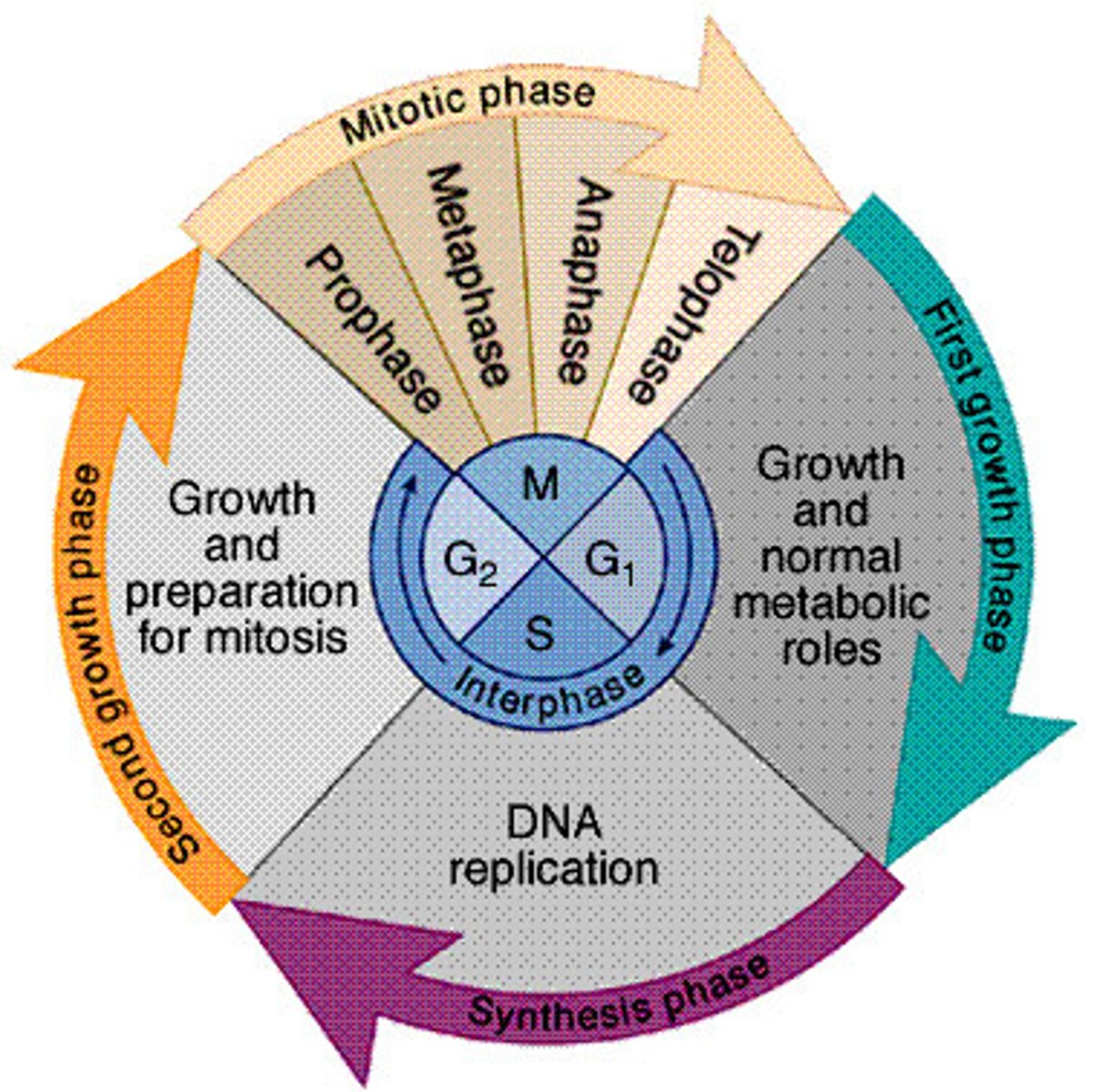
G1 phase
A cell that is metabolically active but not preparing to divide is in G1 phase.
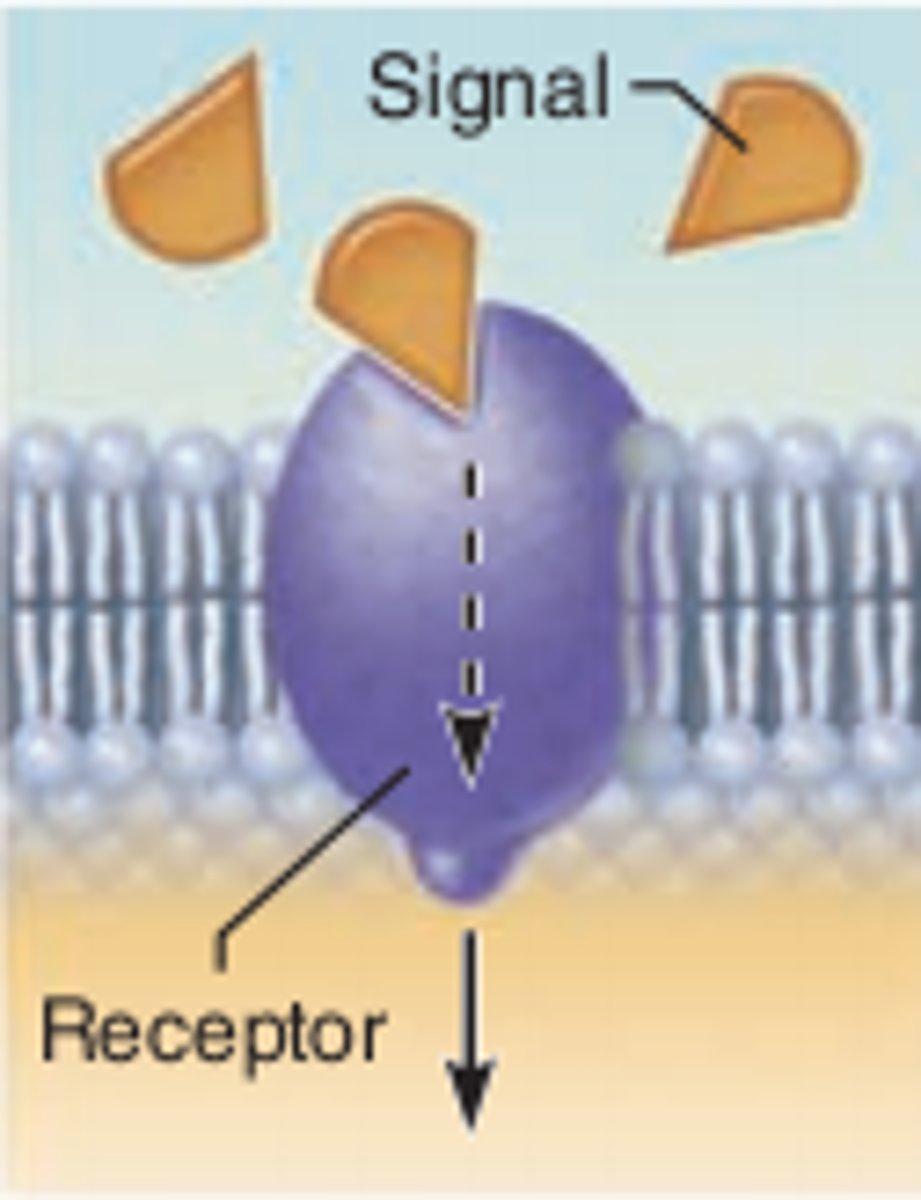
Signal transduction
The process of signal transduction usually begins when a cell receives a signal.
Characteristic feature of cancer cells
A characteristic feature of cancer cells is metastasis.
Cell cycle phase labeled 'X'
In the figure, the phase labeled 'X' represents G1 phase.
Molecules involved in cell signaling
The molecules commonly involved in both cell signaling and the regulation of the cell cycle are protein kinases.
Relation of cell cycle and cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled cell cycle.
Primary role of mitosis
The primary role of mitosis is to produce diploid cells.
Chromosome duplication
Chromosomes duplicate during S phase.
Proteins attached to centromeres
The proteins attached to centromeres are kinetochores.
Division of cytoplasm
The division of cytoplasm is called cytokinesis.
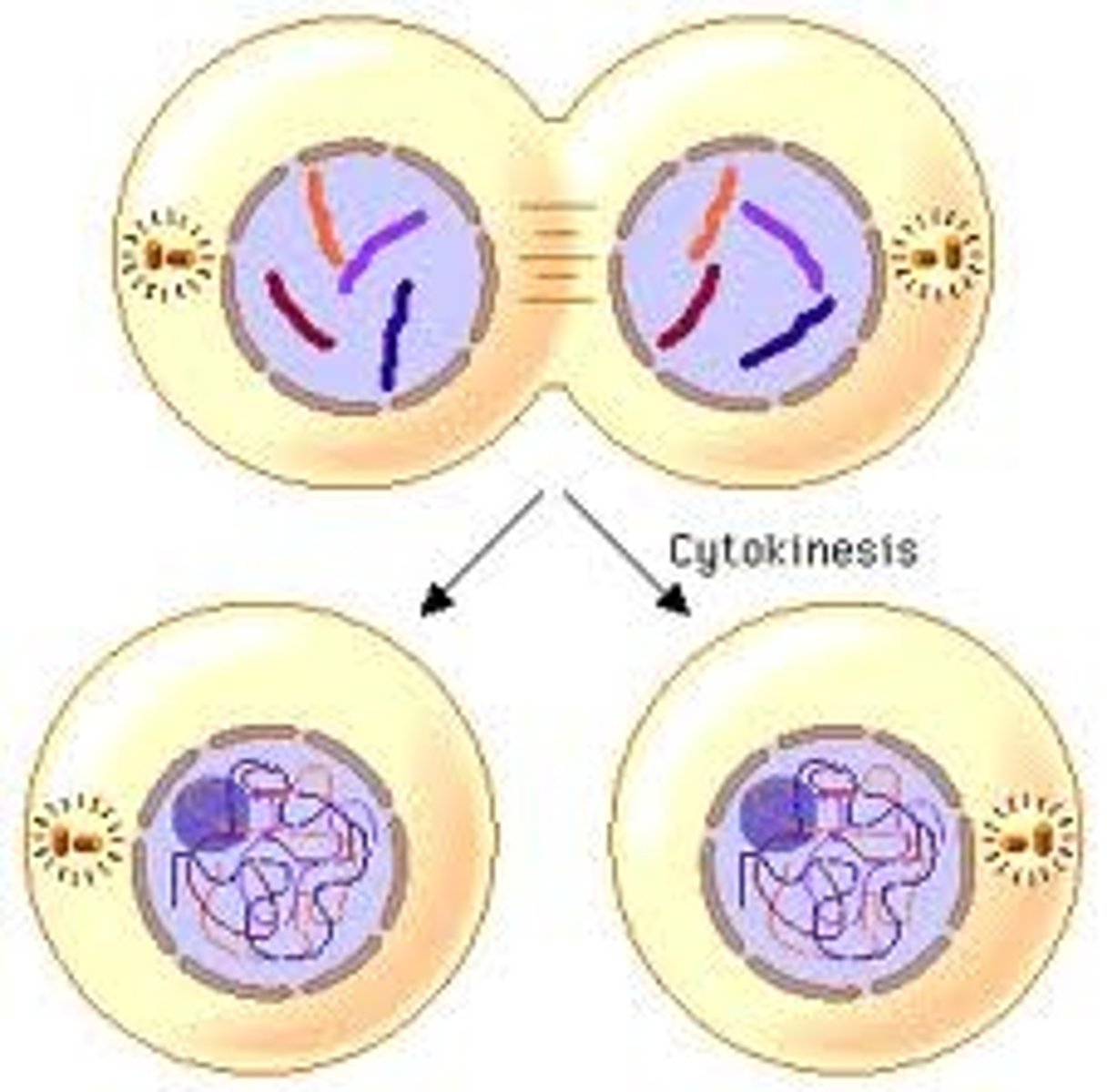
Structure that divides plant cells
The structure that divides the cell in plant cells is called the cell plate.
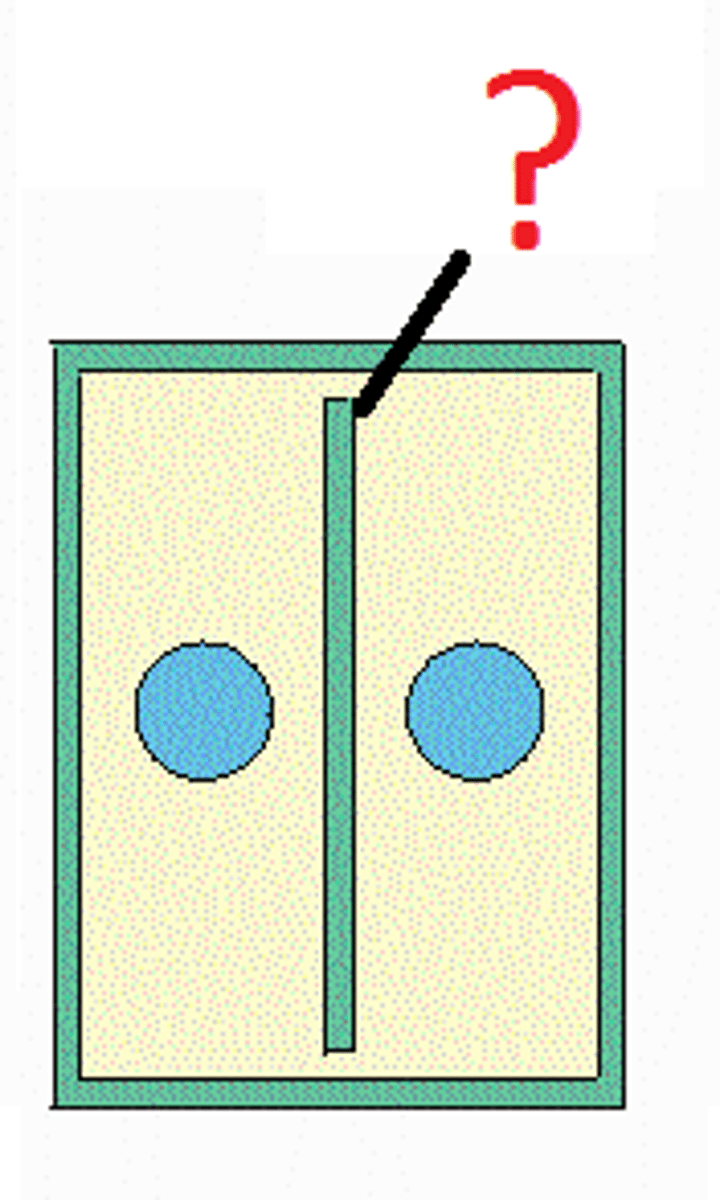
Main steps of cell division
The two main steps of cell division are mitosis and cytokinesis.
Longest phase of the cell cycle
The longest phase of the cell cycle is interphase.
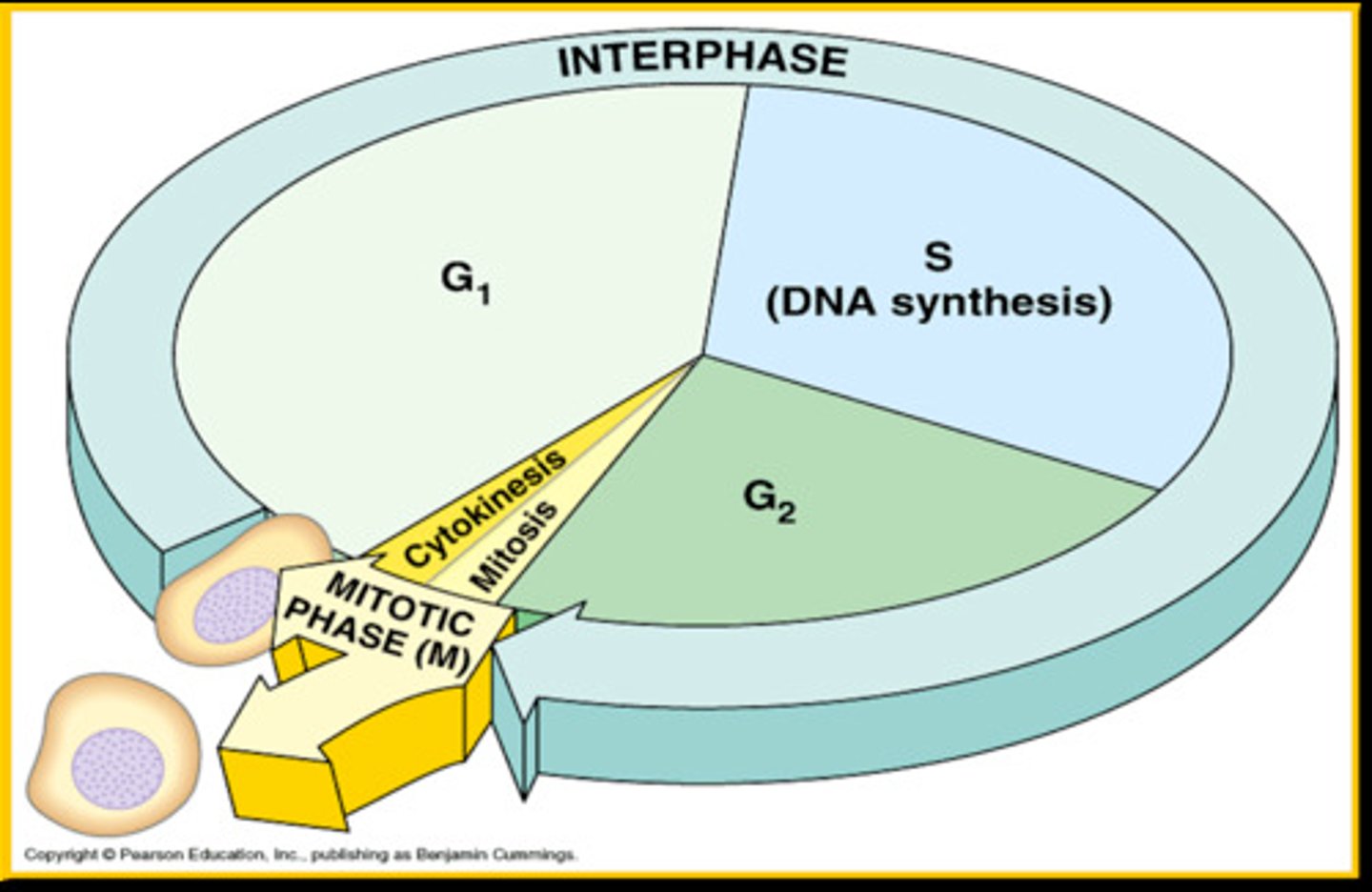
Non-dividing phase of the cell cycle
The non-dividing phase of the cell cycle is called G0 phase.
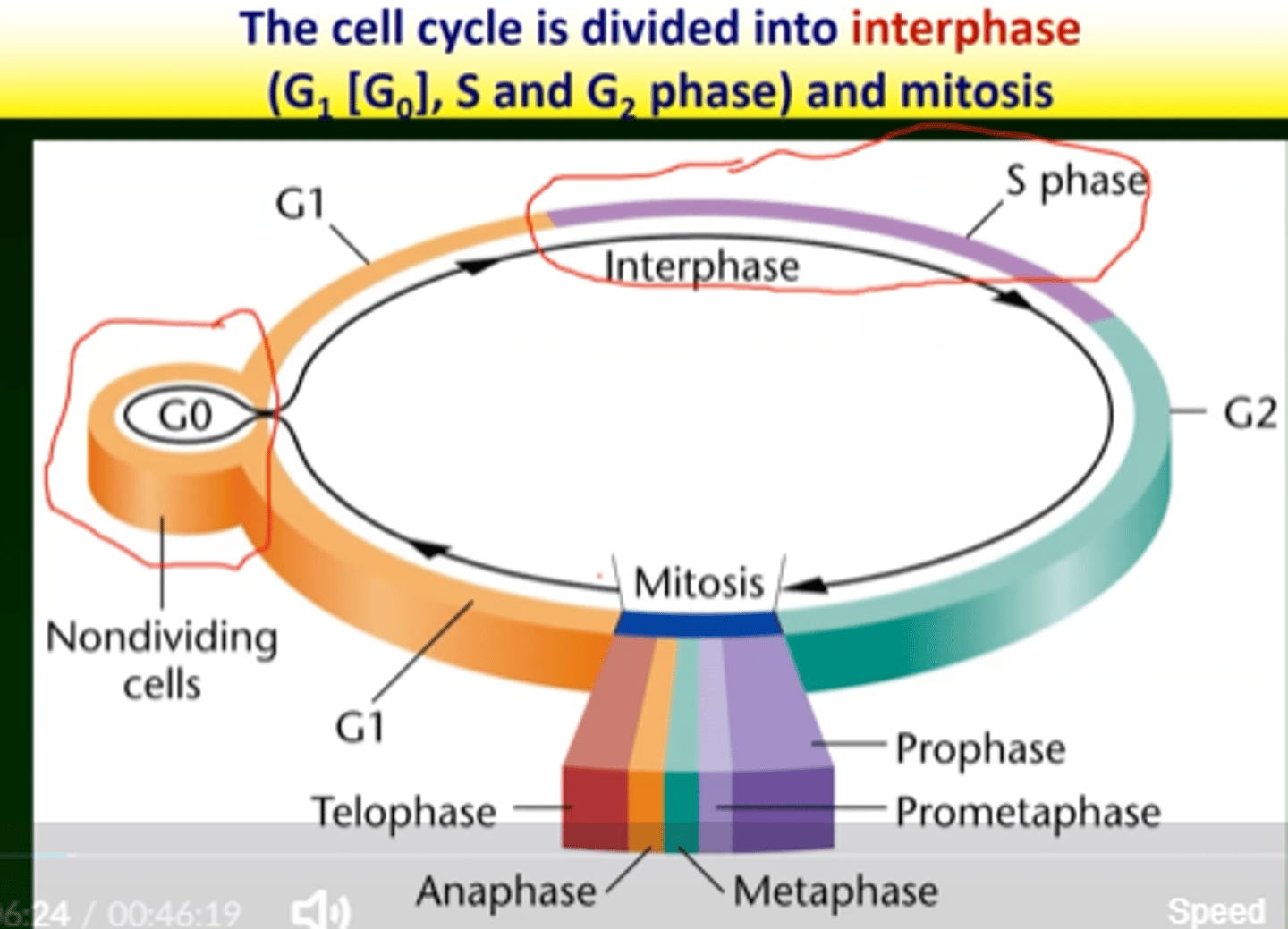
S phase
A phase of the cell cycle where DNA is replicated.
G0 phase
A resting phase where the cell is not actively preparing to divide.
M phase
The phase of the cell cycle where mitosis occurs.
G2 phase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell prepares for mitosis.
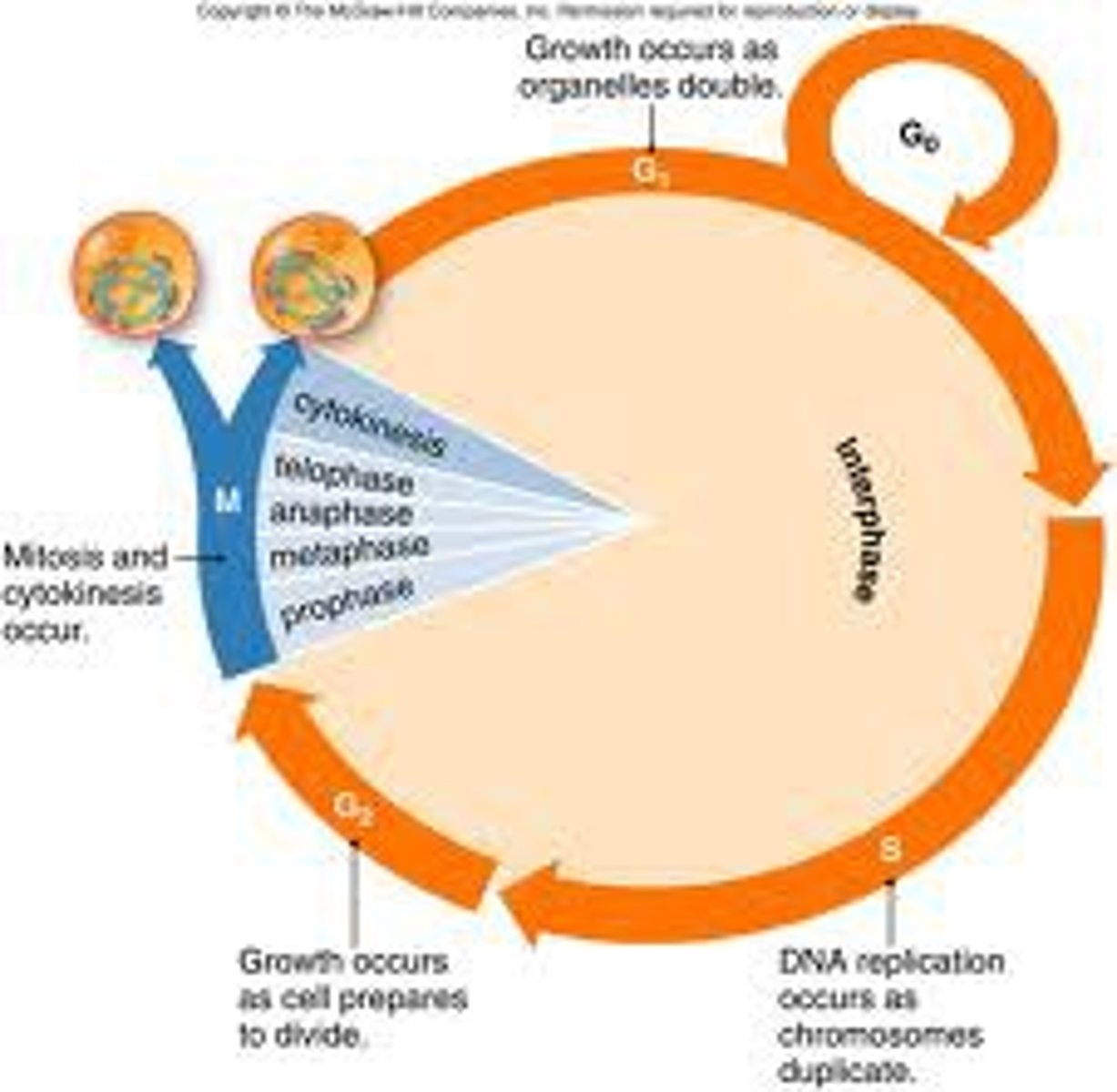
Cell cycle checkpoints
To ensure the accuracy of cell division.
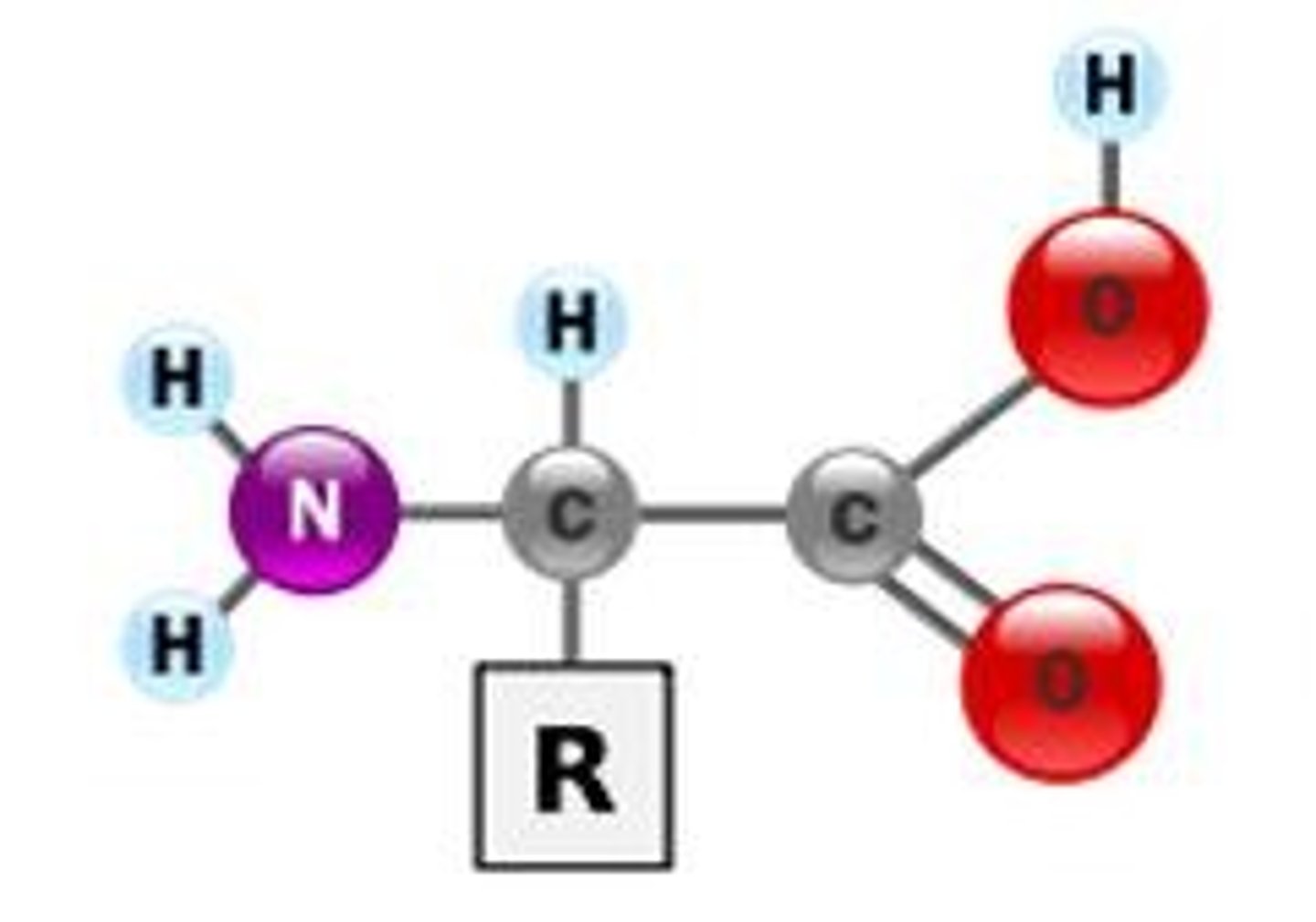
Major component of organic molecules
Carbon (C).
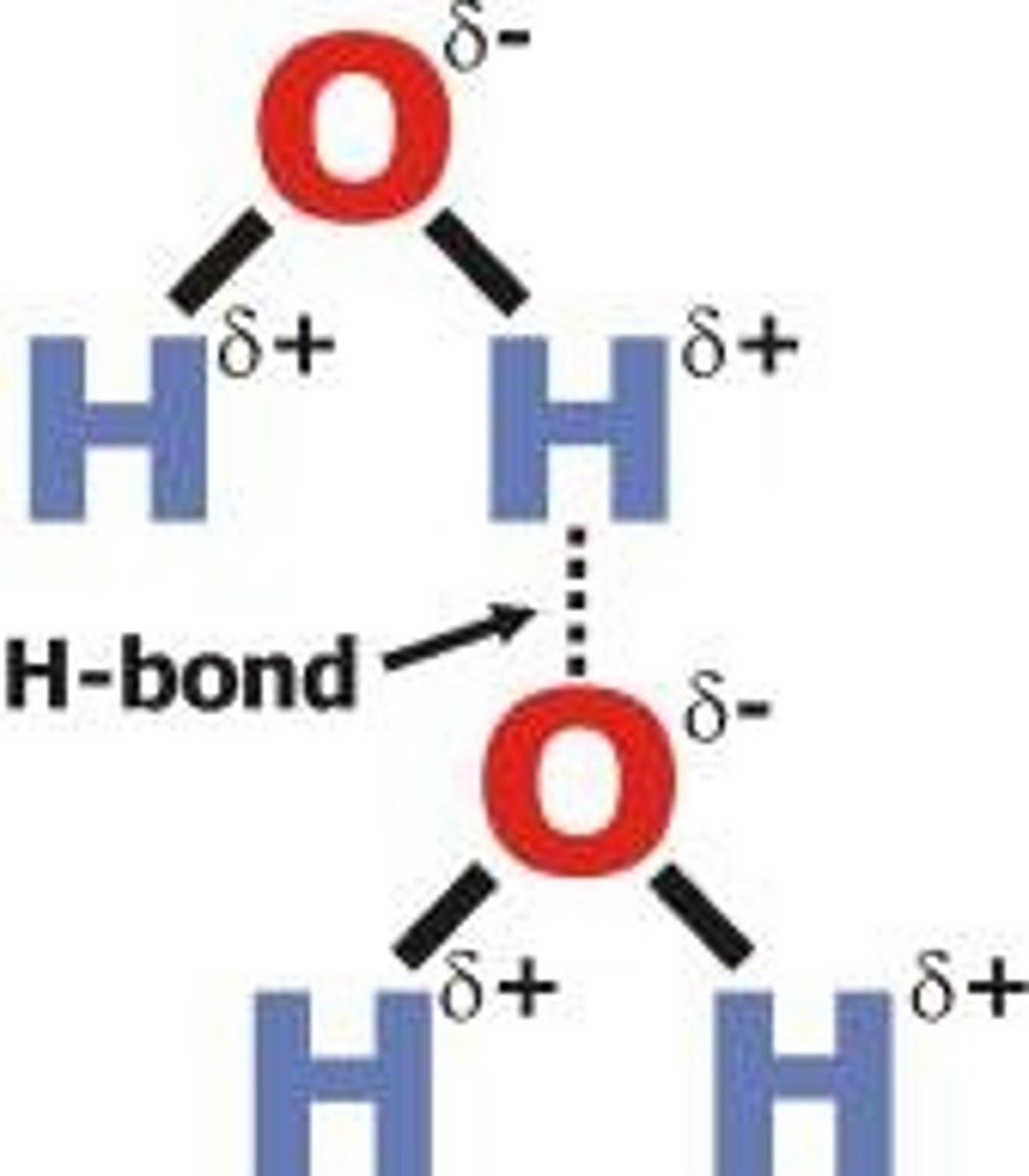
Type of chemical bond in water
Covalent bond.
Characteristic of a buffer solution
It resists changes in pH.
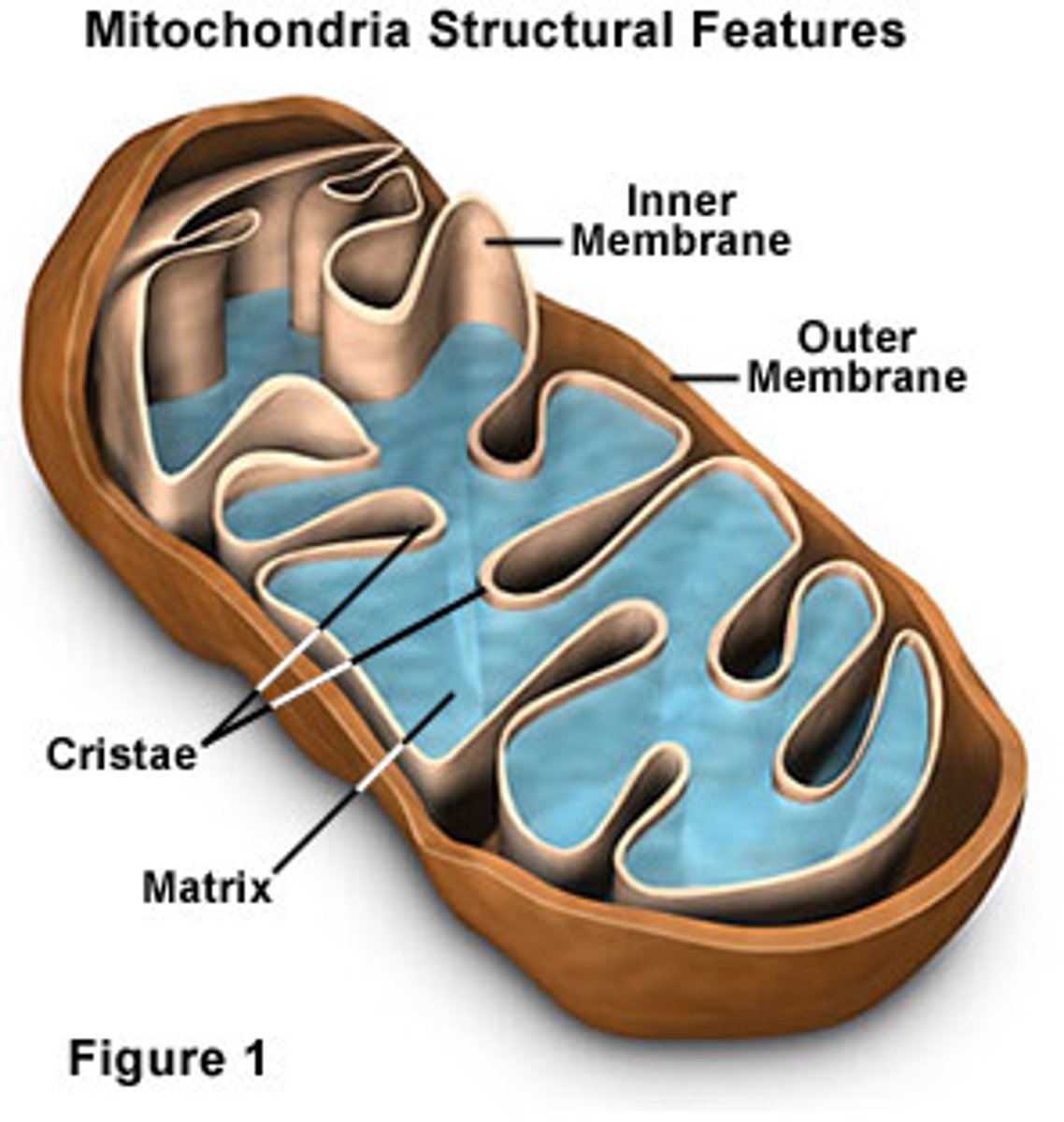
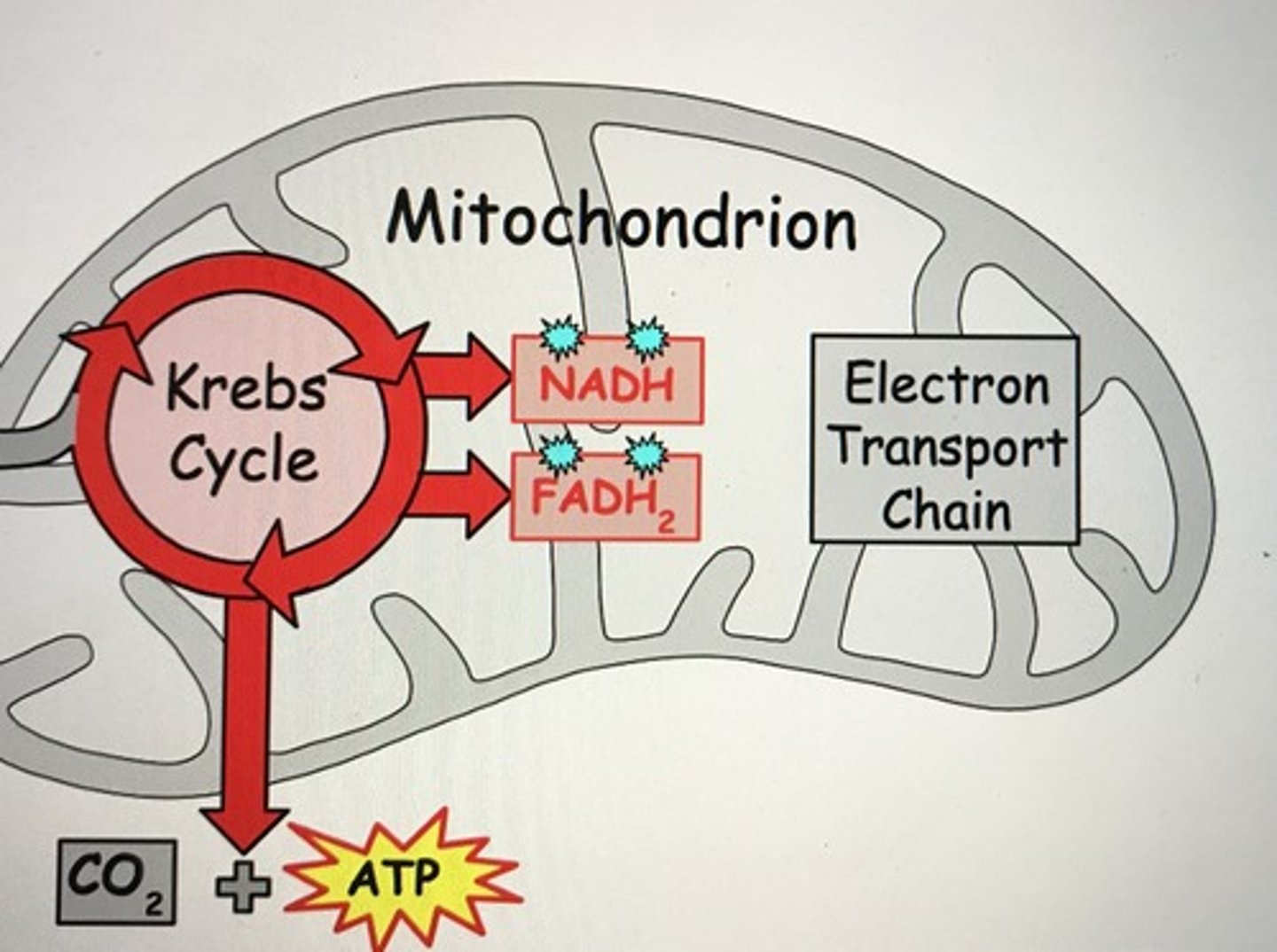
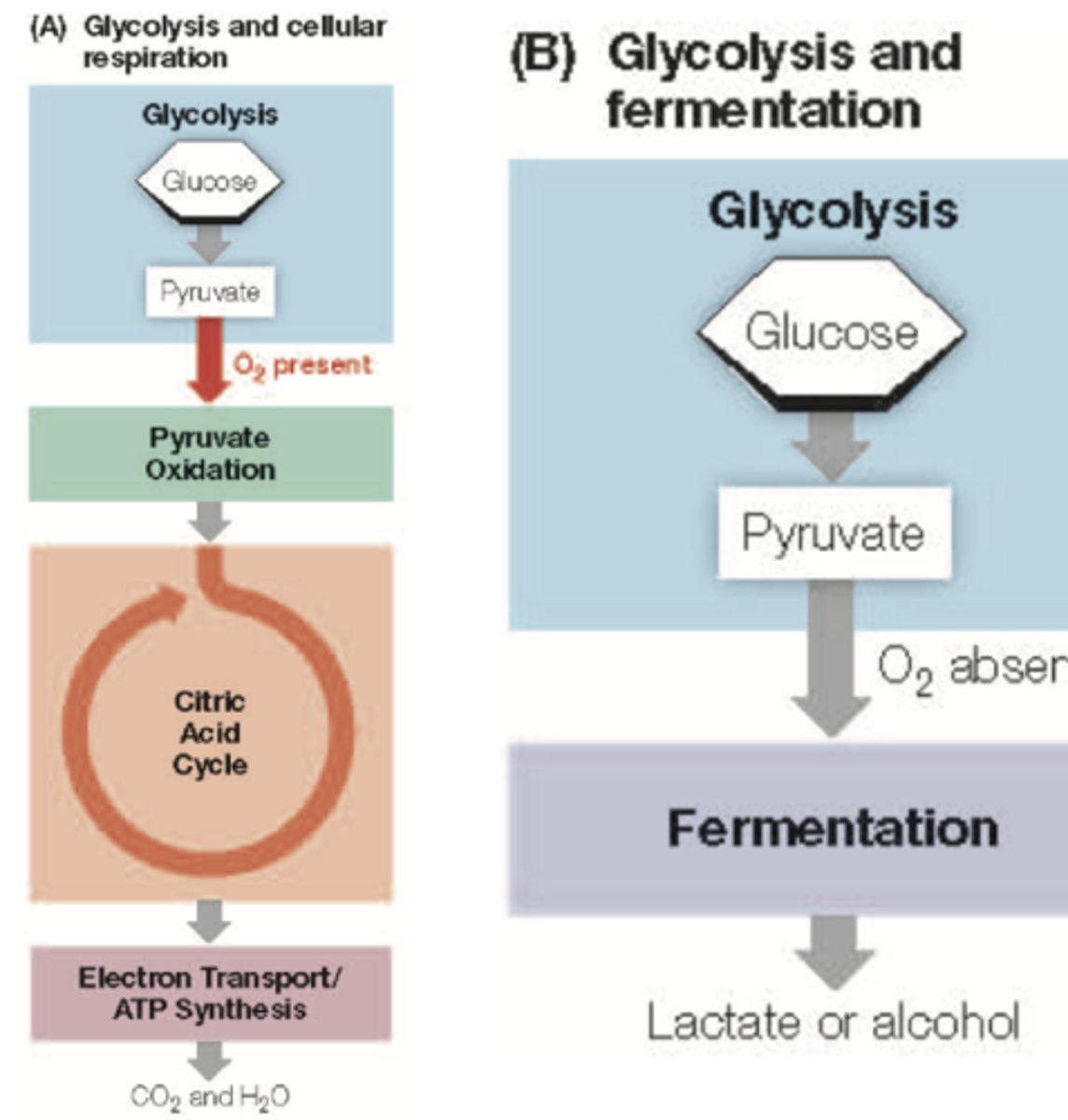
Krebs cycle location
mitochondrial matrix in eukaryotes
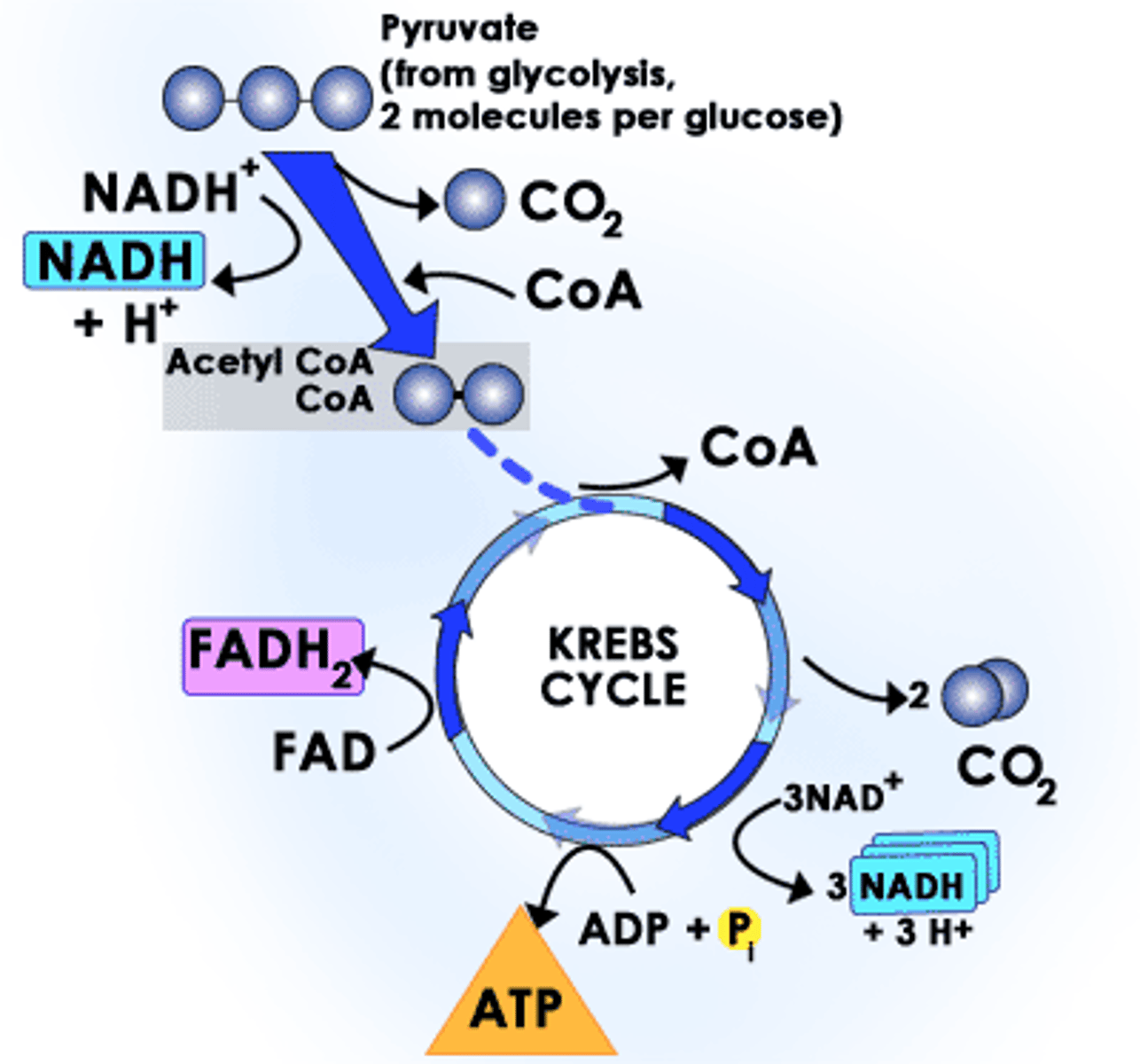
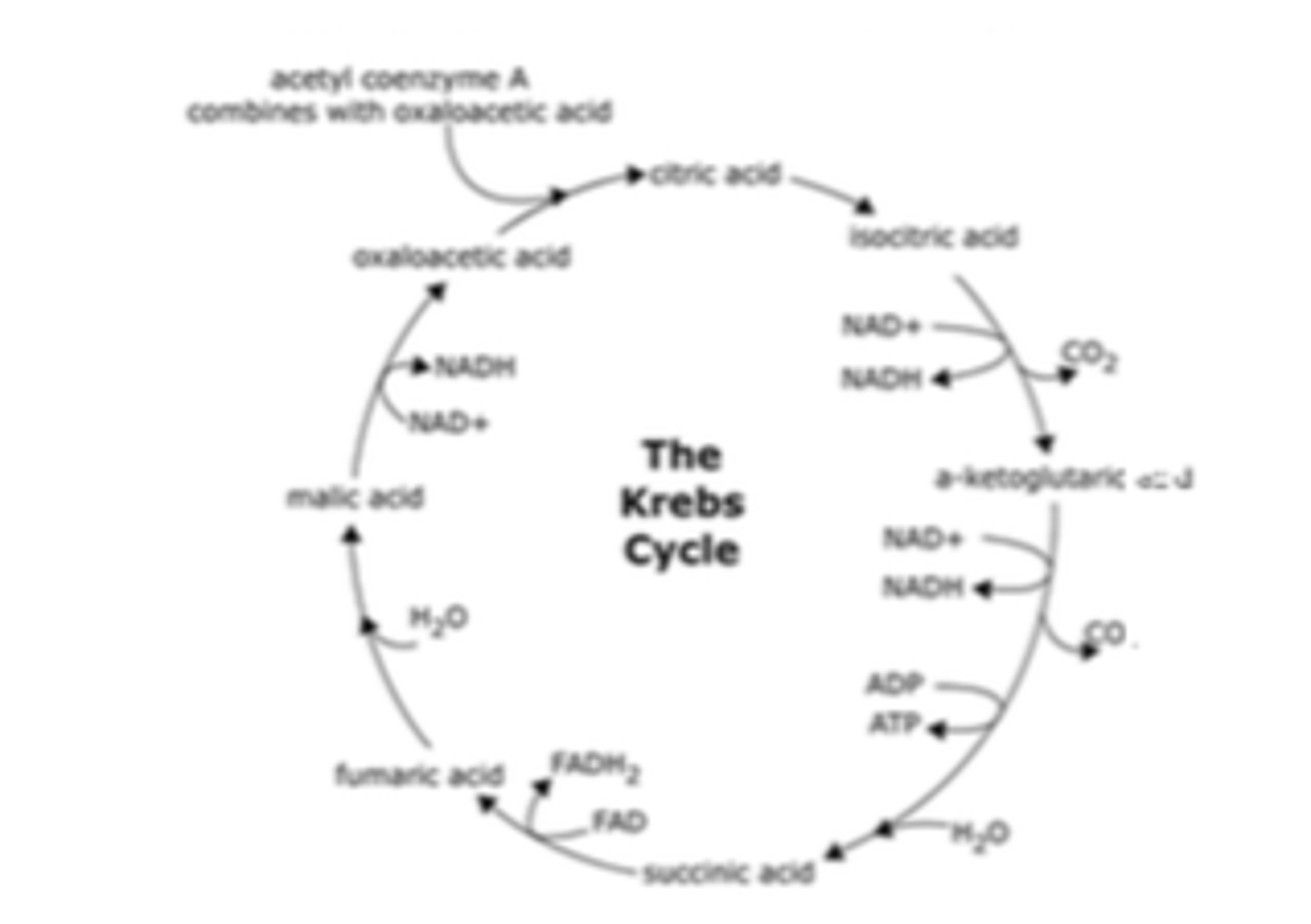
Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate
Combine to form citrate.

Produced during the Krebs cycle
ATP.
Main purpose of the Krebs cycle
Oxidize glucose to CO2.
NOT directly involved in the Krebs cycle
DNA.
ATP produced by one glucose in Krebs cycle
2 ATP.
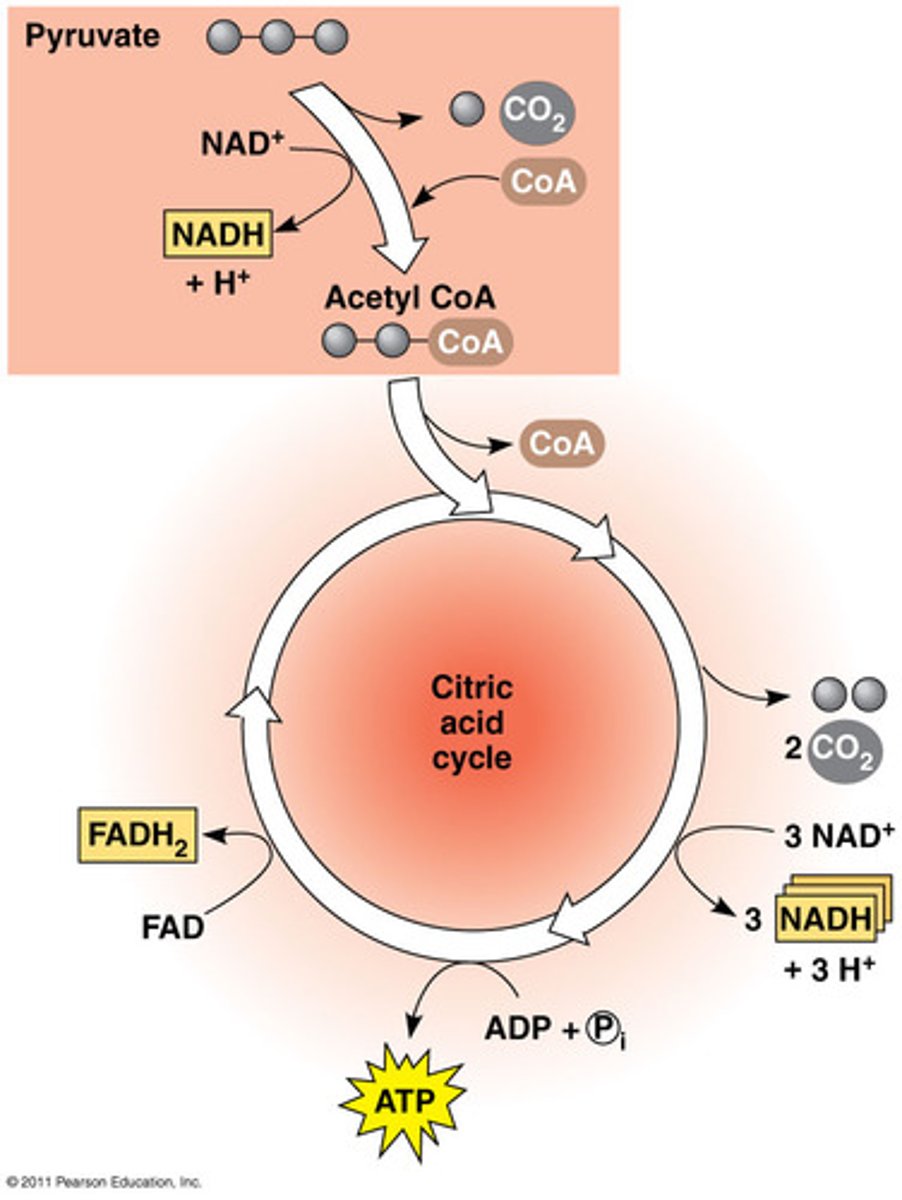
Ultimate fate of carbons in glucose
Released as CO2.
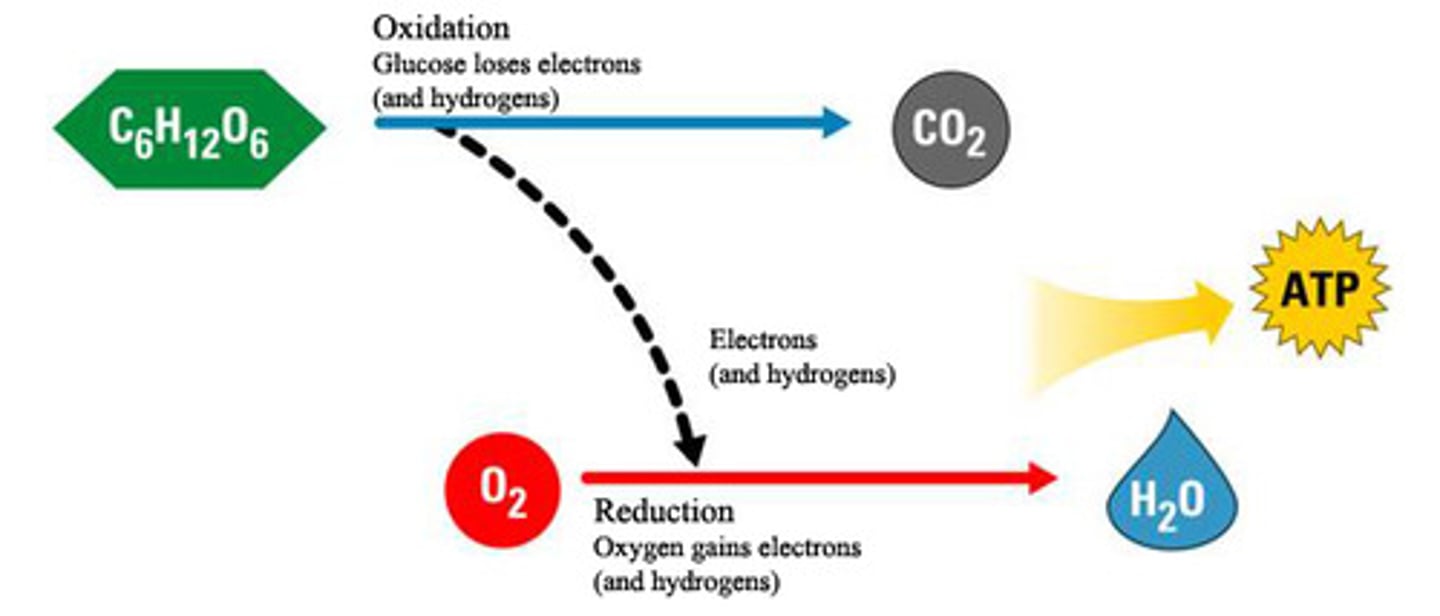
Role of oxygen in cellular respiration
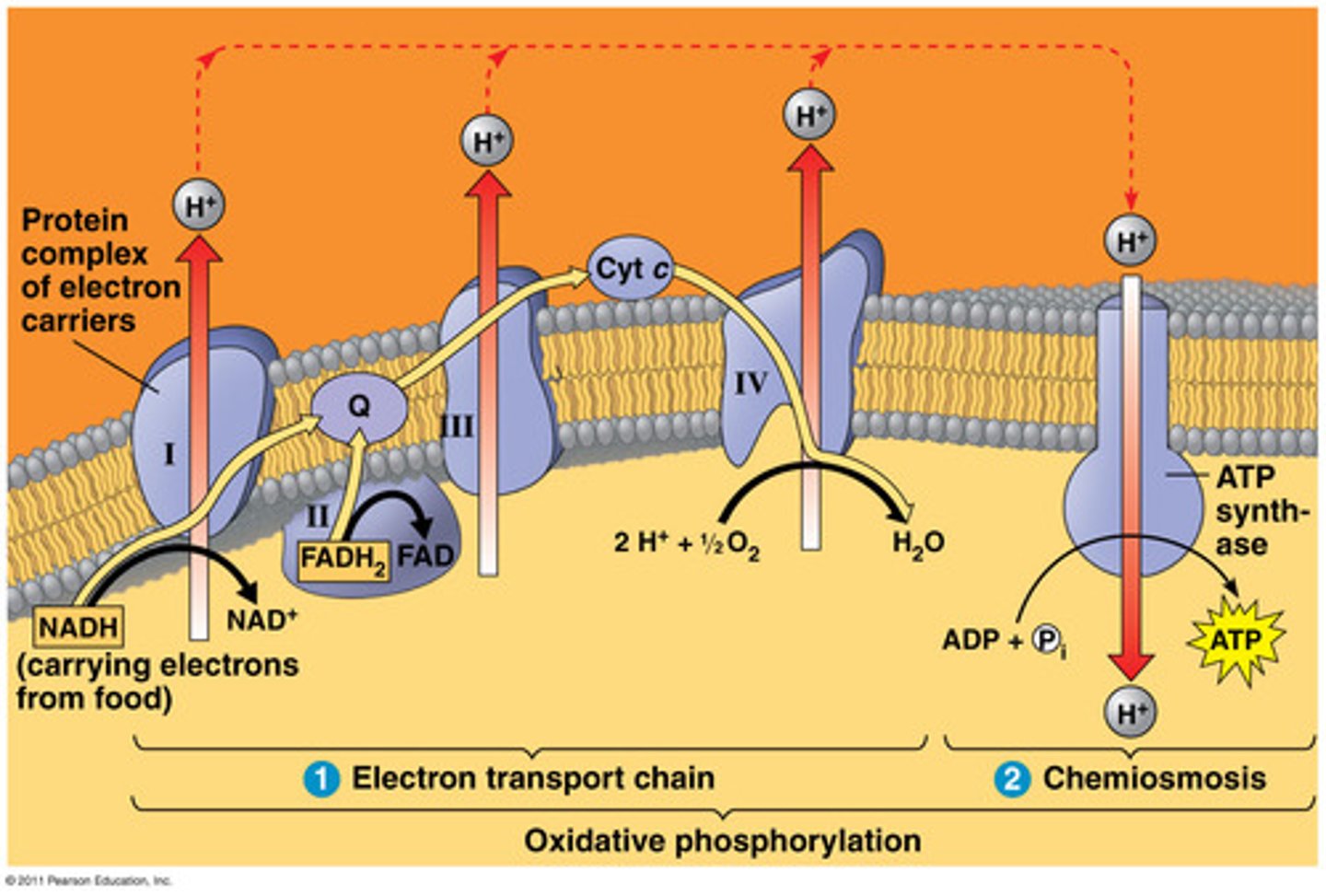
To accept electrons at the end of the electron transport chain.
Most ATP produced in cellular respiration
Oxidative phosphorylation.
Processes occurring in the cytoplasm
Glycolysis.
Energy released during Krebs cycle
Carried by NADH and FADH2.
Lack of cellular respiration
ATP.
Example of potential energy
A molecule of glucose.
Enzymes function as
Catalysts.
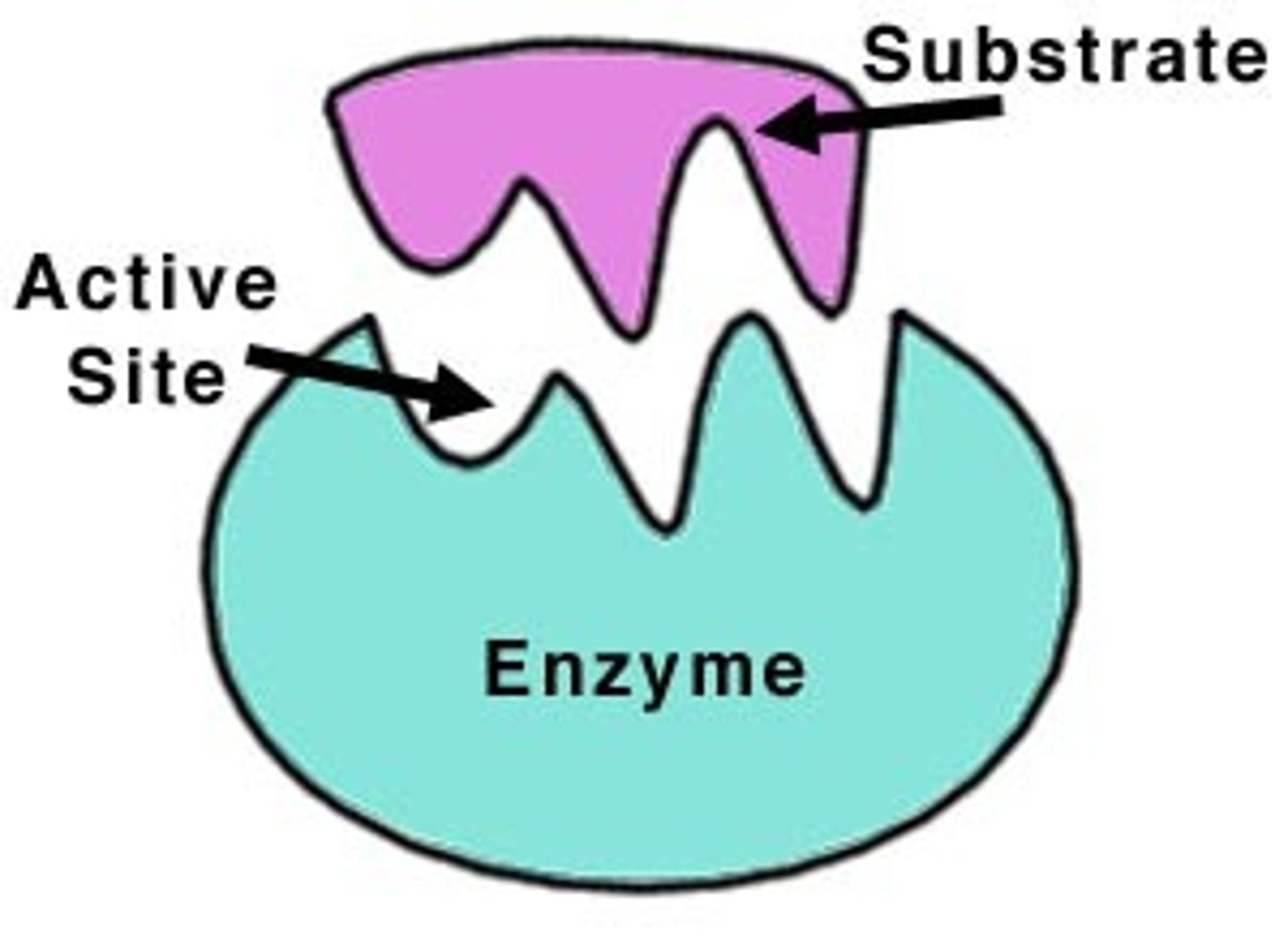
NOT a characteristic of enzymes
They are consumed in the reaction.
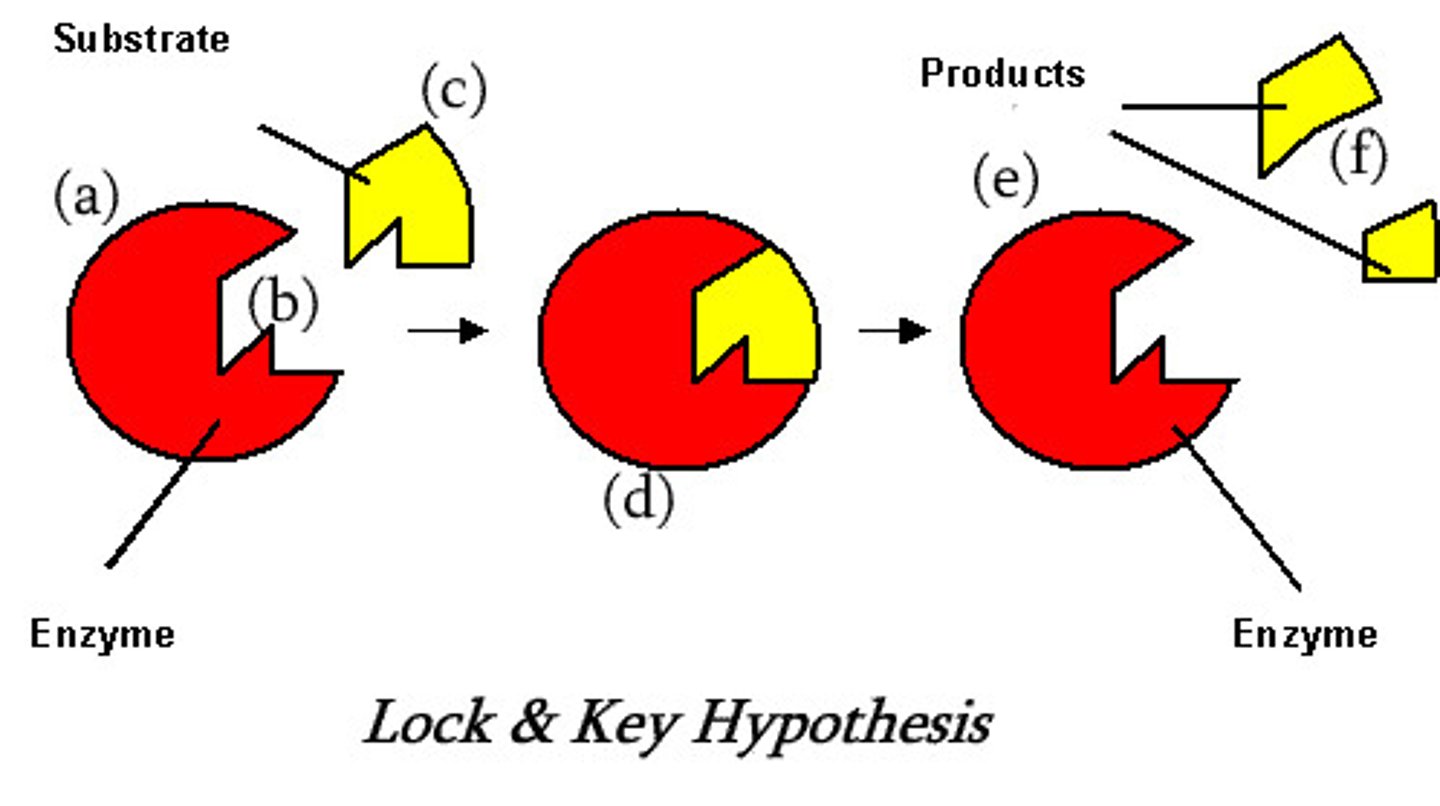
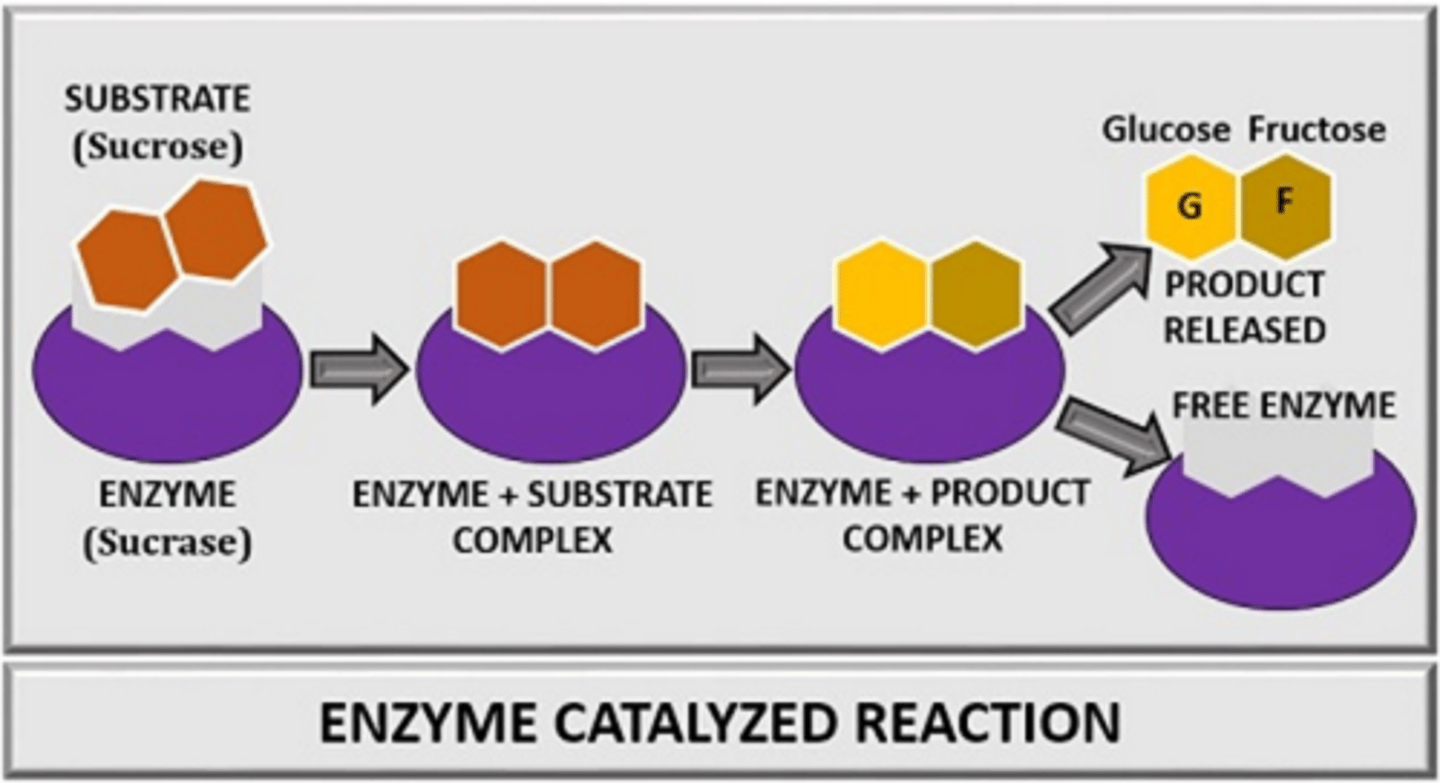
Location where substrate binds to enzyme
Active site.
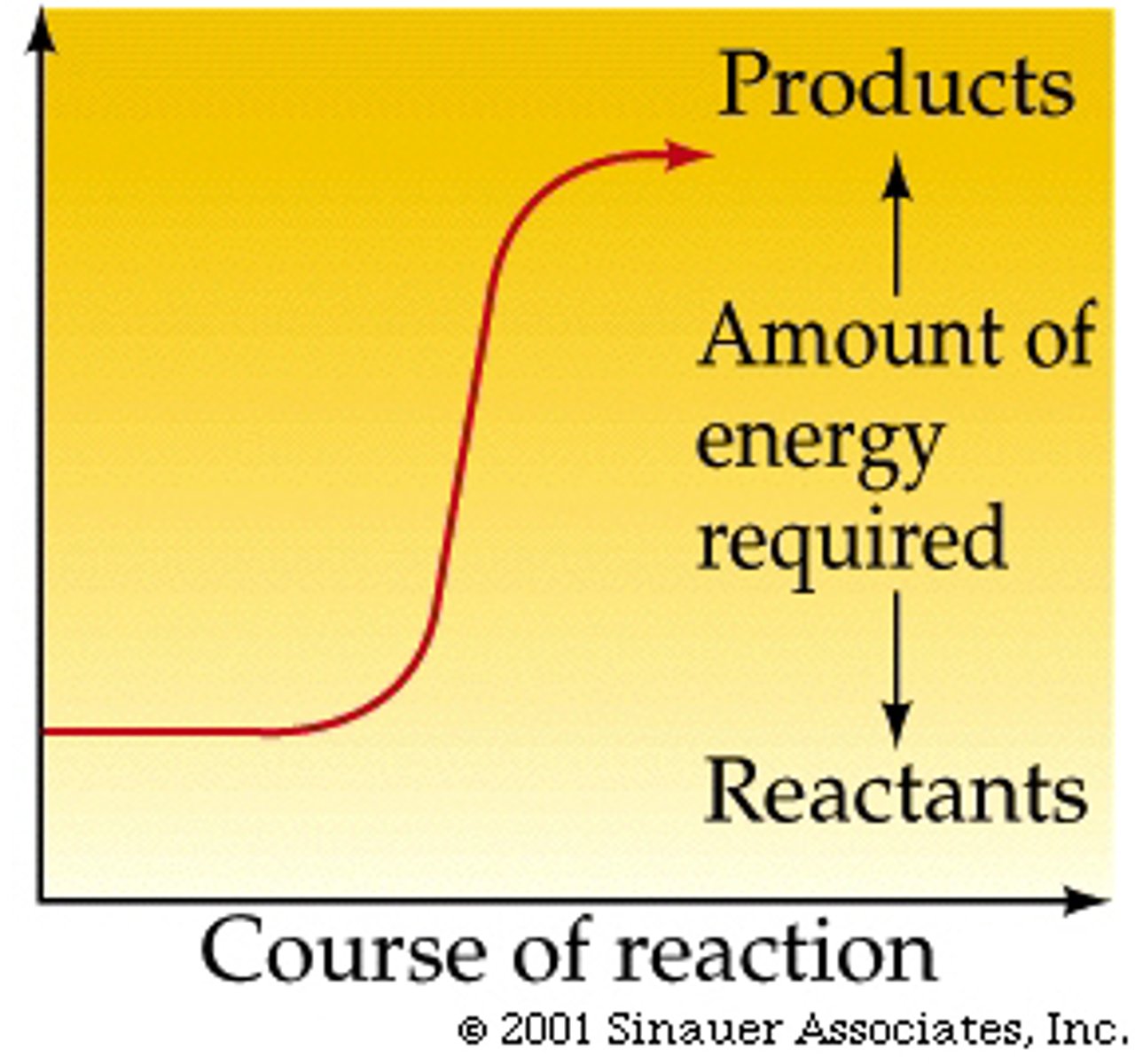
Energy required to start a chemical reaction
Activation energy.
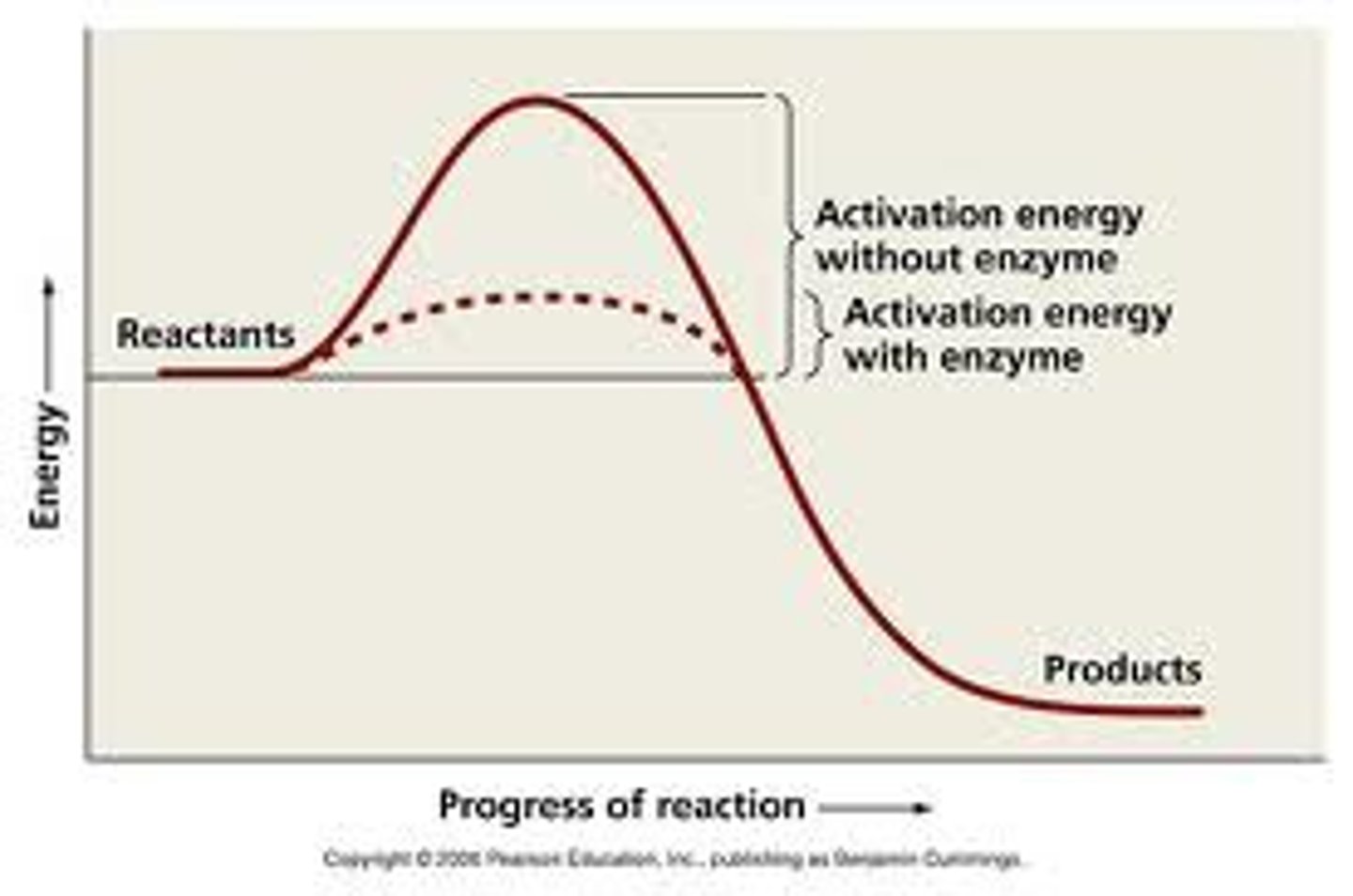
Reaction that releases energy
Exergonic.
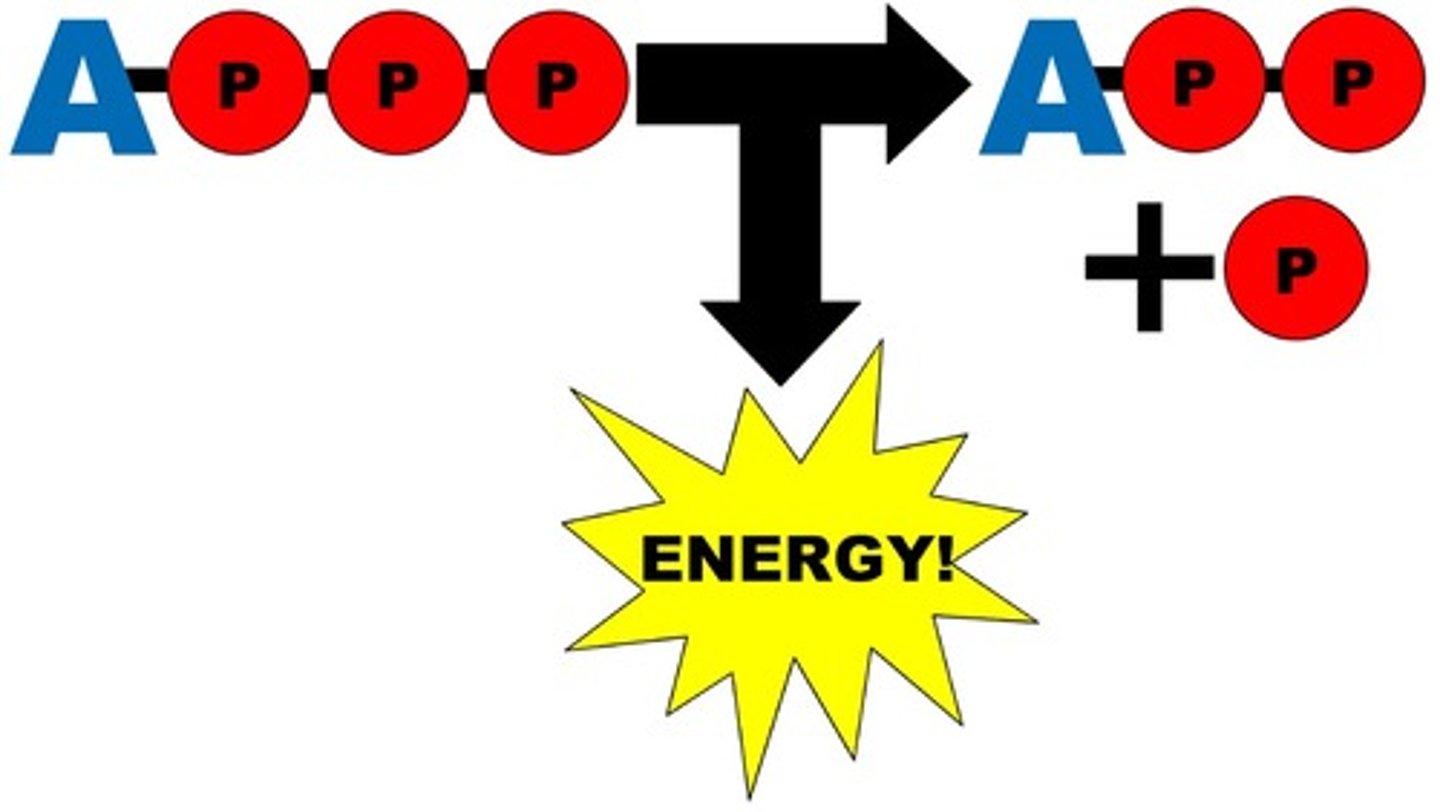
Represents an exergonic reaction
Cellular respiration.