externalities
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
definition of externalities?
spill overs the impact on third parties of a transaction between others
definition of external benefits?
are benefits that individuals or firms confer on others without receiving compensation.
Benefits we receive without incurring costs
examples of external benefits?
beehives next to almond orchards
Education
Preserved farmland
definition of external costs?
an uncompensated cost that an individual or firm imposes on others
examples of external costs?
air and water pollution
texting while driving
chemical runoff that affects fish stock
can the optimal quantity of pollution be zero?
no
definition of Marginal Social Cost (MSC)?
the additional cost imposed on society as a whole by an additional unit of something
example of MSC?
pollution
Acid Rain
Smog
Contaminated water
Noise
is MSC increasing at an increasing rate ?
yes
definition of Marginal Social Benefit (MSB)?
the additional gain to society as a whole from an addition unit of something
is MSB increasing at a decreasing rate?
yes
where is the social optimal quantity at?
where MSB = MSC
definition of the socially optimal quantity?
Is the quantity society would choose if all costs and benefits were fully accounted for.
will a market economy, left to itself, arrive at the socially optimal quantity?
No, it won’t because those who make the decisions would optimise for themselves and not the society
What happens in a externality market without government intervention?
Firms consider the private benefits rather than the social costs
Instead of producing the socially optimal quantity Qopt, they will produce a higher amount Qmkt
what happens at Qmkt?
MSB of an additional unit is zero
MSC of an additional unit is much higher
when does market failure occur?
when free-market equilibrium does not provide the socially optimal amount of a good
define the coase theorem?
The economy can reach an efficient solution by compensating/rewarding externality
when is the coase theorem possible?
if the costs of making a deal are sufficiently low and feasible
what happens when individuals take externalities into account?
they internalize the externality – it becomes part of the decision-making process - In that case, the outcome is efficient without government intervention.
why don’t private parties always internalise externalities?
The problem is transaction costs— costs of making a deal. They often prevent a mutually beneficial trade from occurring.
what are government policies to deal with pollution?
1. environmental standards,
2. emissions taxes,
3. tradable emissions permits.
4. giving subsidies to incentivize
what are environmental standards?
rules that protect the environment by specifying actions by producers and consumers. Recommend rules to be introduced, once legislated, monitor the enforcement
what are two agencies that deal with environmental standards?
Environmental Protection Agency
Environmental Standards Scotland
what can regulation stipulate in a marker?
how much emission is allowed
how much production of a good is allowed
how much of a resource can be extracted
what is the diagram for a market economy that produces too much?
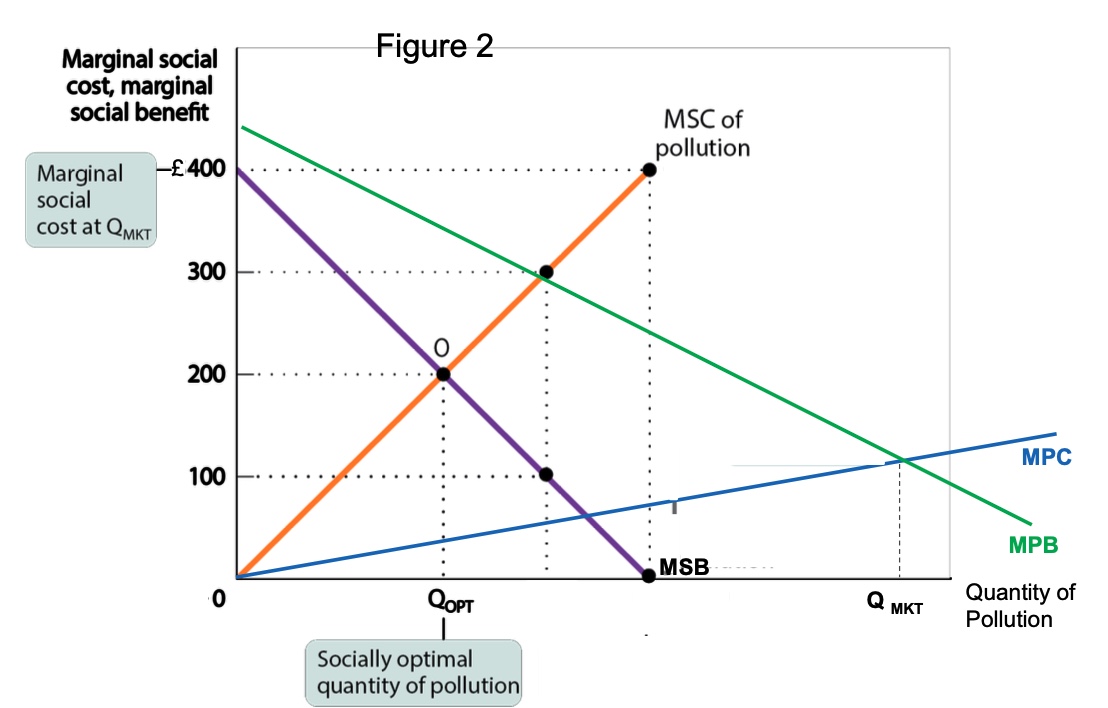
what is the diagram for setting the standard? and explain?
inefficient because firm’s MC<MB and firm will feel force to make a non-optimal choice
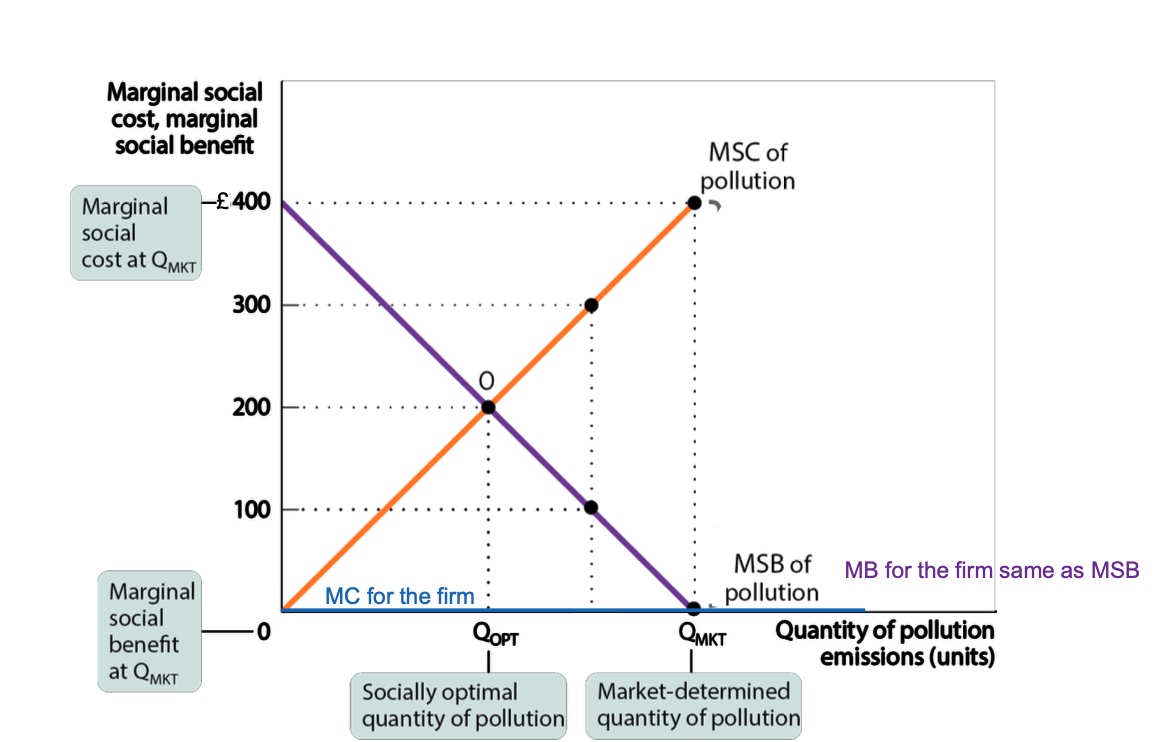
what is the graph for a ban? and explain?
For both firm and society outcome choice is non-optimal because MB>MC
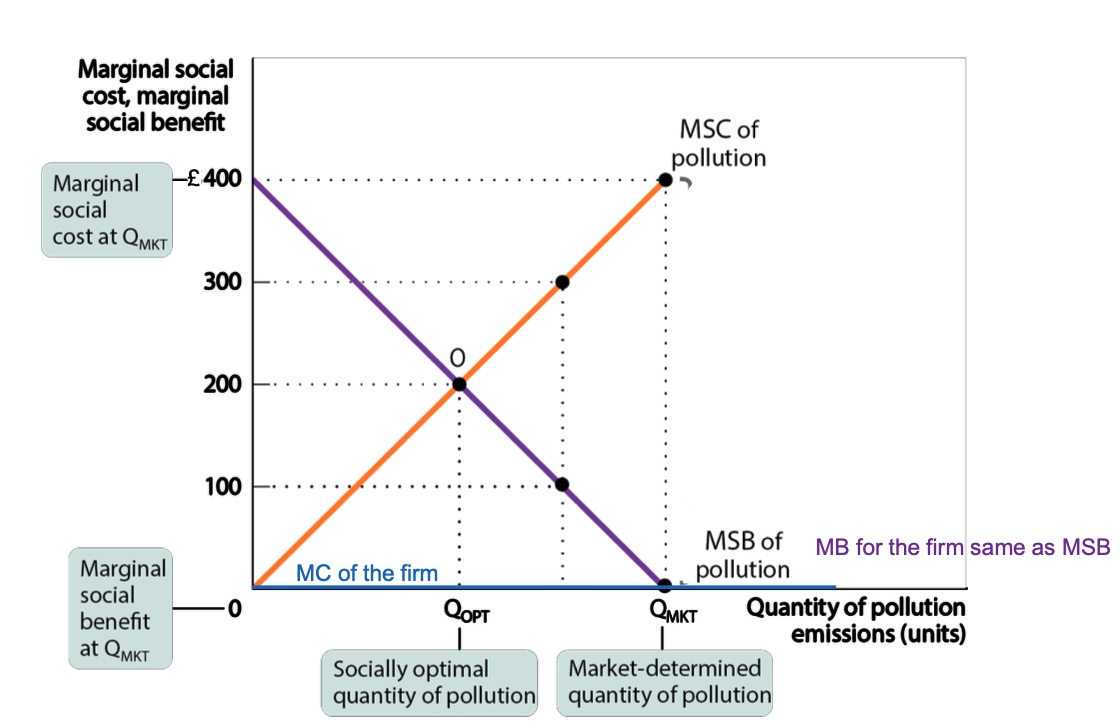
what is emission tax?
A tax that depends on the amount of pollution a firm produces, which increases the cost to the firm.
This tax will increase its cost of production
and hence reduce its optimal production
what is pigouvian tax?
taxes designed to reduce negative externality/ external cost to society
how can socially optimal quantity be achieved?
by an optimal pigouvian tax equal to the marginal external cost
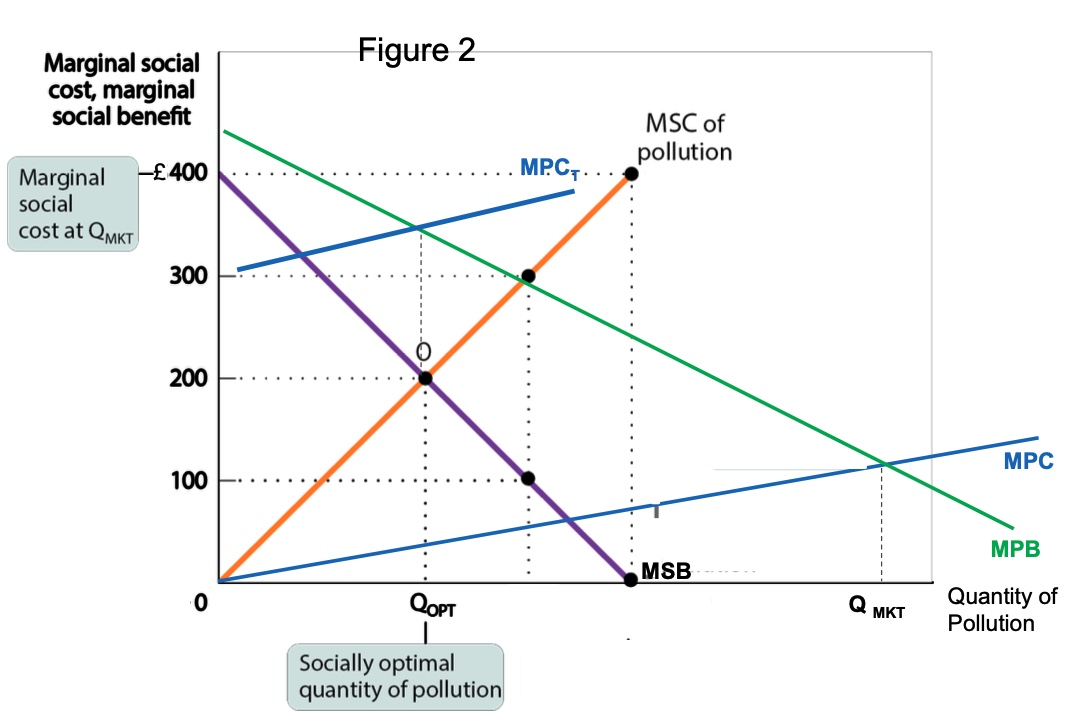
draw the emission tax diagram?
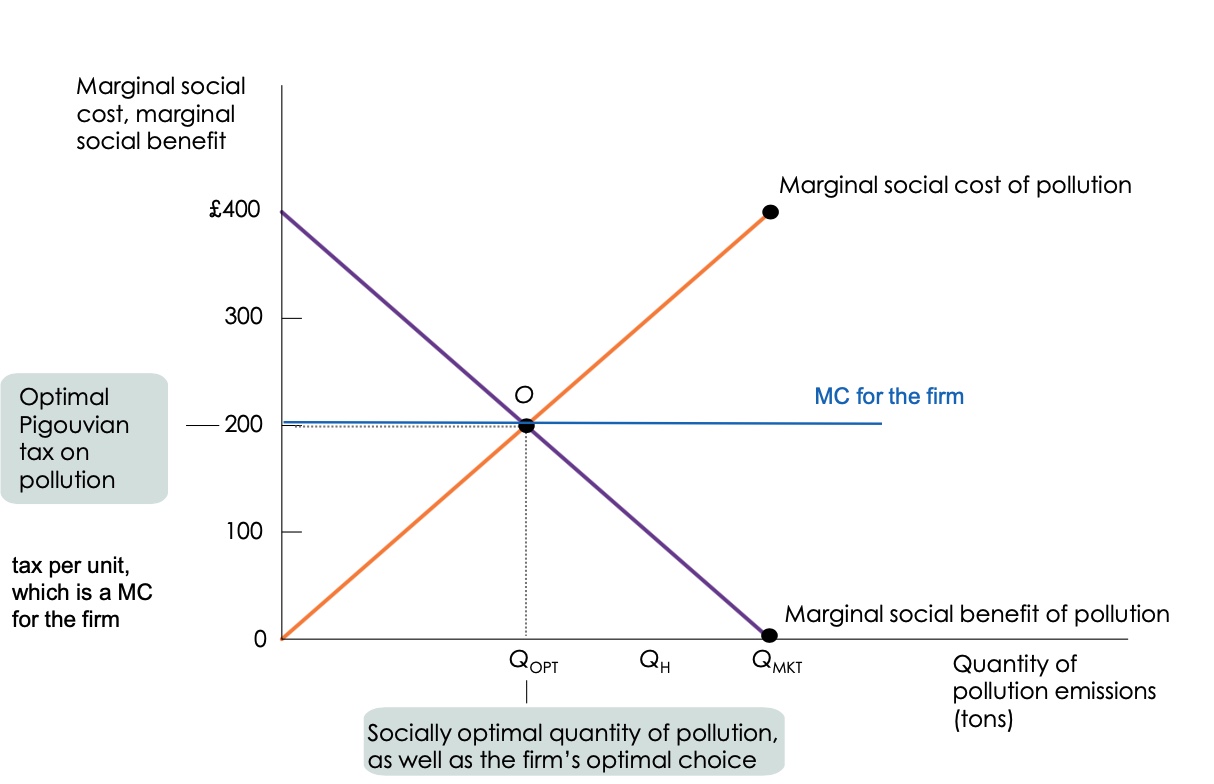
How can a firm choose to be socially optimal?
impose a tax on pollution to increase the MC of the firm. So MPC is steeper (MPCt)
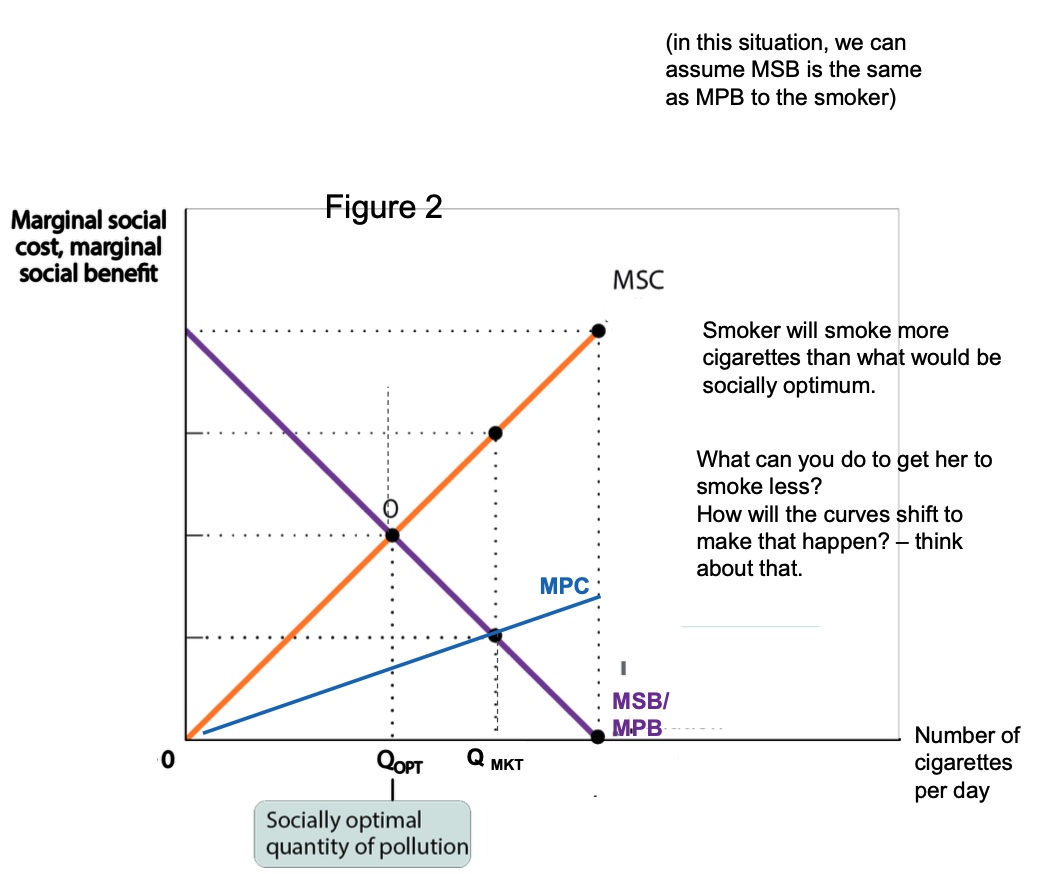
draw a diagram for smoking cigarettes?
definition of permits?
to emit limited quantities of pollutants are issued
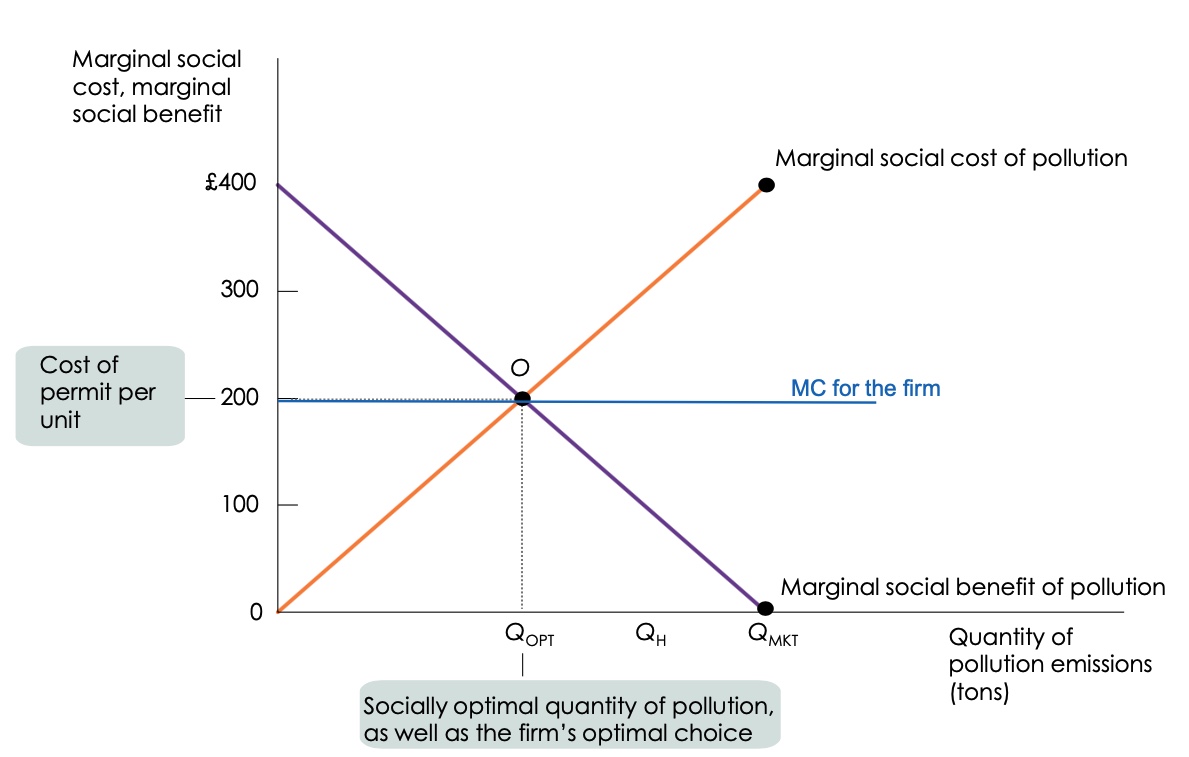
what happens once permits are in the market?
permits can be bought and sold by polluters at a market price according to the demand and supply
what is the diagram for permits for emissions?
what is technology spillover?
a positive externality that results from knowledge spread among individuals and firms
what is the diagram for when a market economy preserves too little farmland?
without gov intervention the quantity preserved farmland will be zero because there is no benefit to farmers to be preserving the land while they have to bear all the costs (shows in MSC)
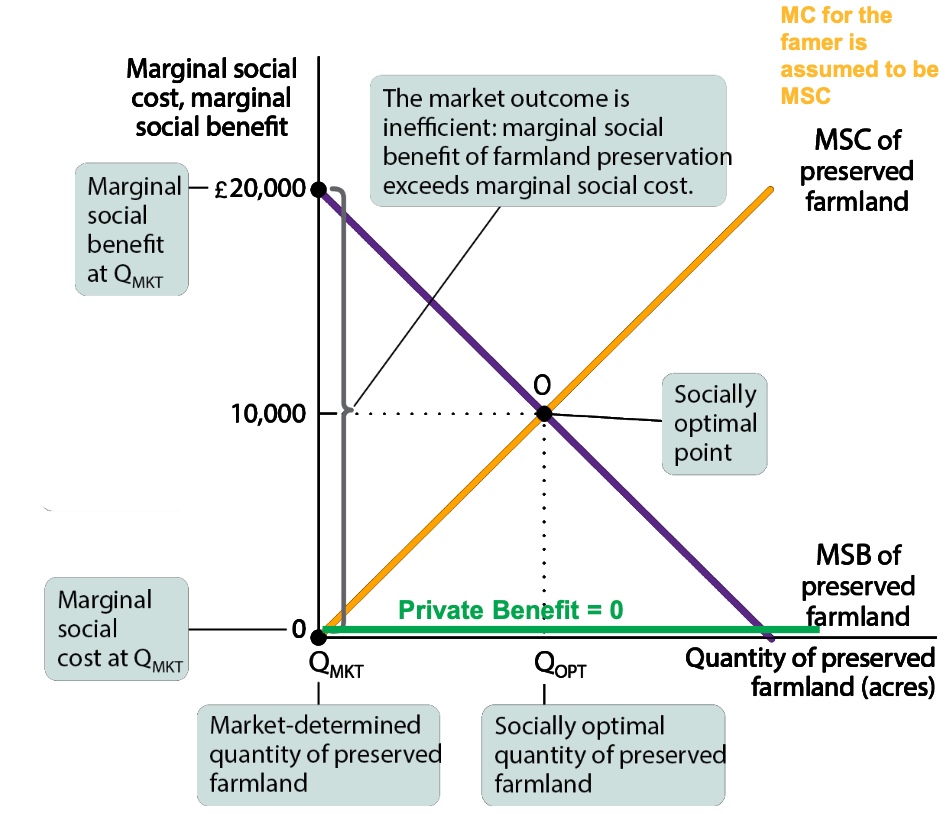
how can the economy produce the socially optimal Qopt?
use a pigouvian subsidy, the payment designed to encourage activities that generate positive externalities
definition of pigouvian subsidy?
a payment designed to encourage activities that yield external benefits
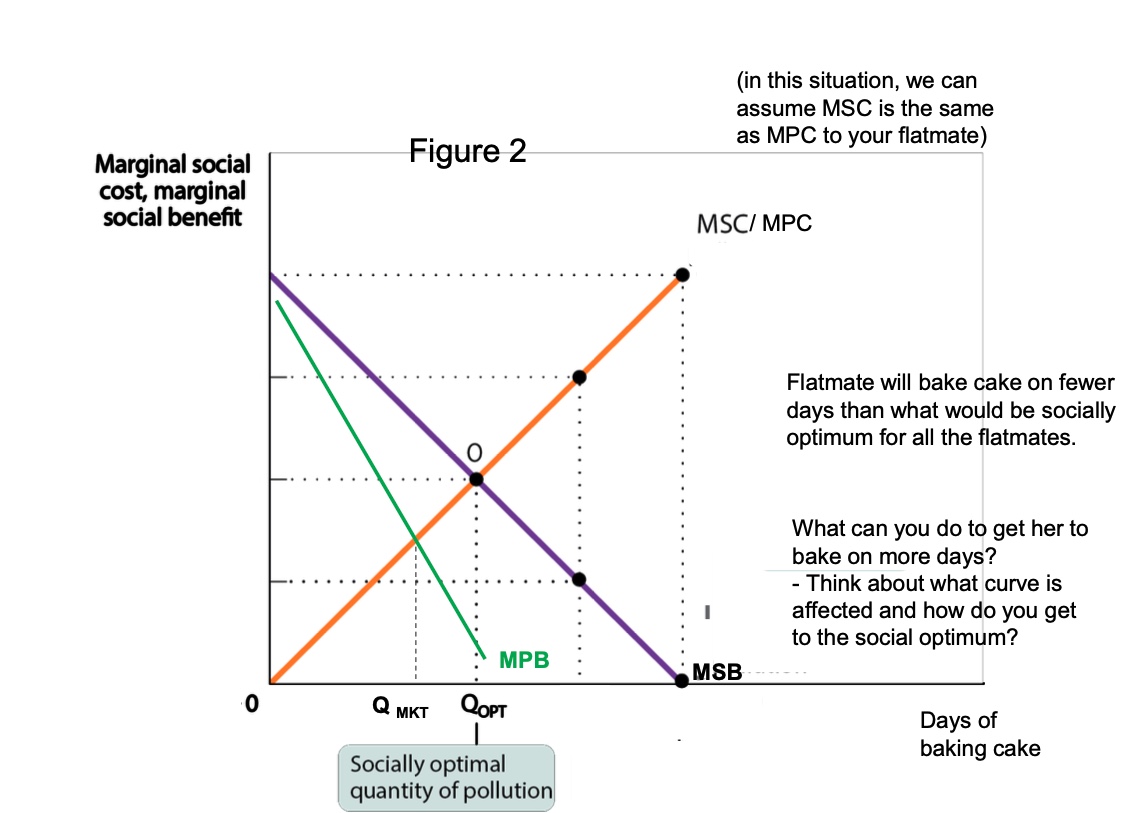
positive externality diagram?
definition of network externality?
when the value of the good to an individual is greater when a large number of other people also use the good
examples of network externality?
▪ Communication systems such as telephones, whatsapp,
(in olden days) - telegraphs, fax machines
▪ Railway systems
▪ Hub-and-spoke air travel
definition bandwagon effect?
when success breeds greater success and failure breeds failure
what are the causes of climate change?
• Fossil fuel is fuel derived from fossil sources such as coal and oil.
• Renewable energy sources are energy sources that are inexhaustible, unlike fossil fuel sources, which are exhaustible.
• Clean energy sources are energy sources that do not emit greenhouse gases. Renewable energy sources are also clean energy sources.