Respiration
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
1
New cards
Aerobic Respiration
The **release** of energy, made available by ATP, from the breakdown of molecules (which oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor)
2
New cards
Anaerobic Respiration
The **breakdown** of **molecules** in the **absence** **of** **oxygen**, releasing small amounts of energy
3
New cards
What are the types of phosphorylation?
* **Oxidative** phosphorylation
* Photophosphorylation
* **Substrate-level** phosphorylation
* Photophosphorylation
* **Substrate-level** phosphorylation
4
New cards
What are the stages of **aerobic respiration?**
1\. Gly**c**olysis \n 2. Link reaction \n 3. Krebs cycle \n 4. Electron Transport Chain (**oxidative phosphorylation)**
5
New cards
Where does **glycolysis** occur?
In the cytoplasm of a cell
6
New cards
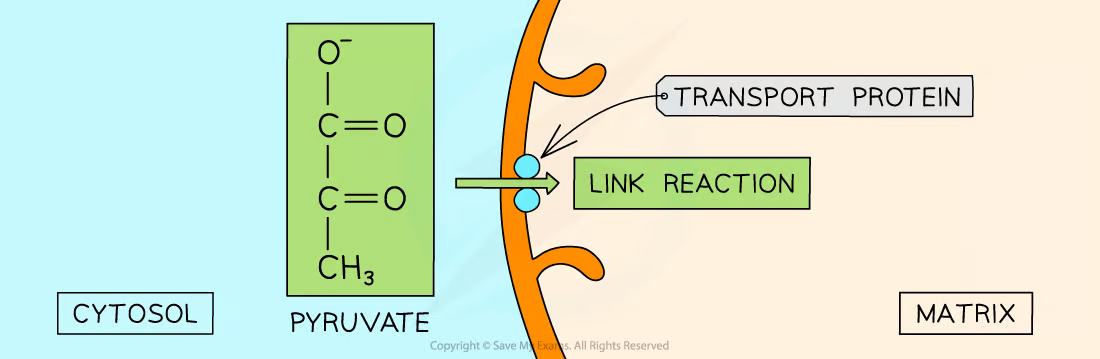
Where in the **cell** does the **link reaction** take place?
Mitochondrial Matrix
7
New cards
Where does the Kreb cycle occur?
Mitochondrial Matrix
8
New cards
Where does **oxidative phosphorylation** occur?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
9
New cards
Why does glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm?
Glucose **cannot pass** through the **membranes of mitochondria**, and the **necessary enzymes** are located in the **cytoplasm**
10
New cards
Dehydrogenation
The **removal** of hydrogen from a molecule
11
New cards
Decarboxylation
The removal of CO2 from a molecule
12
New cards
What are the reactants of glycolysis?
Glucose, 2 ATP, 2 ADP, 2 Pi + 2 NAD
13
New cards
What are the **products** of glycolysis?
2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 Pyruvate molecules
14
New cards
What is the net production of ATP during glycolysis? Why?
**2 ATP**
\
2 ATP are put **into** the system, and **4 ATP** are synthesised
\
2 ATP are put **into** the system, and **4 ATP** are synthesised
15
New cards
How is glucose converted to fructose biphosphate?
The glucose molecule is **phosphorylated** by the addition of two phosphate groups from two molecules of ATP
16
New cards
How many triose phosphate molecules are made for each glucose molecule?
2 triose phosphate molecules
17
New cards
How many pyruvates are produced from one glucose molecule in glycolysis?
2 pyruvates
18
New cards
Draw a labelled flow diagram of glycolysis
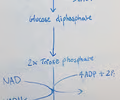
19
New cards
Write a summary word equation for glycolysis
Glucose + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD → Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2ATP
20
New cards
Write a summary word equation for the link reaction
Pyruvate + NAD + CoA → Acetyl CoA + NADH + CO₂
21
New cards
Each turn of the Krebs cycle produces:
* 1 ATP
* 3 NADH
* 1 FADH
* 2 CO2 Molecules
* 3 NADH
* 1 FADH
* 2 CO2 Molecules
22
New cards
How many times does the Krebs cycle occur for each glucose molecule?
Twice
23
New cards
What is a **coenzyme?**
An enzyme required by an enzyme in order to function
24
New cards
How many ATP molecules are synthesised from 1 NADH molecule?
3 ATP
25
New cards
How many ATP molecules are synthesised from 1 FADH molecule?
2 ATP
26
New cards
Where does the electron transport chain occur?
On the inner membrane of the mitochondria
27
New cards
For each glucose molecule entering the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain receives how many NADH?
10 NADH
28
New cards
For each glucose molecule entering the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain receives how many FADH?
2 FADH
29
New cards
Describe the **electron transport chain**
* **Reduced NAD** donates electrons from the hydrogen atoms to the first of the 3 proton pumps
* The electrons move from the first pump to the second, **providing energy to the proton pumps** on the inner mitichondrial matrix
* H+ is pumped into the **inter-membrane space**
* The movement of of protons into the inter-membrane creates a **proton gradient**
* The protons flow down their concentration gradient **through ATP Synthetase**
* The flow of protons causes ATP Synthetase to synthesise ATP from ADP + Pi
* The protons combine with electrons and oxygen to form water
* The electrons move from the first pump to the second, **providing energy to the proton pumps** on the inner mitichondrial matrix
* H+ is pumped into the **inter-membrane space**
* The movement of of protons into the inter-membrane creates a **proton gradient**
* The protons flow down their concentration gradient **through ATP Synthetase**
* The flow of protons causes ATP Synthetase to synthesise ATP from ADP + Pi
* The protons combine with electrons and oxygen to form water
30
New cards
What **maintains** the proton concentration gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane?
The proton pumps pumping protons across the inner membrane
31
New cards
What is the final electron acceptor in respiration?
Oxygen
32
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced from **oxidative phosphorylation** by just glycolysis for each molecule of glucose?
6 ATP (2 NADH molecules are made)
33
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced from oxidative phosphorylation by **just** the **link reaction** for each molecule of glucose?
6 ATP (2 NADH molecules are made)
34
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced from **oxidative phosphorylation** by **just** the **Krebs cycle** for each molecule of glucose?
22 ATP (6 NADH molecules are made, and 2 FADH molecules are made)
35
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced by **substrate-level phosphorylation** by **just glycolysis** for each molecule of glucose?
2 ATP
36
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced by **substrate-level phosphorylation** by **just** the link reaction for each molecule of glucose?
None
37
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced by **substrate-level phosphorylation** by **just** the **Krebs cycle** for each molecule of glucose?
2 ATP
38
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced by **substrate-level phosphorylation** in total for each molecule of glucose?
4 ATP
39
New cards
How many **ATP** are produced in total from **all stages of respiration**?
38 ATP
40
New cards
Why is **38** ATP only a **theoretical** **amount** of ATP generated by respiration?
* ATP is used to transport molecules such as pyruvate, NADH and FADH across the mitochondrial membrane
* Protons may leak out of the inter-membrane space, rather than through ATP synthetase, and compromise the proton gradient
* Molecules many also leak through membranes
* Protons may leak out of the inter-membrane space, rather than through ATP synthetase, and compromise the proton gradient
* Molecules many also leak through membranes
41
New cards
What is the amount of energy required to make ATP?
30\.6 kJ/mole
42
New cards
Can substrate-level phosphorylation occur in the **absence of oxygen**?
Yes
43
New cards
Can **oxidative phosphorylation** occur in the absence of oxygen?
No
44
New cards
What are the **two** different anaerobic pathways?
**Lactate Fermentation:** Glucose is converted into lactate (in animals) \n **Ethanol Fermentation:** Glucose is converted into ethanol (in various micro-organisms such as yeast)
45
New cards
What anaerobic pathway of respiration occurs in yeast?
Glucose is converted into ethanol
46
New cards
What anaerobic pathway of respiration occurs in **animals**?
Glucose is converted into lactate
47
New cards
Draw a flow diagram to show the conversion of glucose into lactate in anaerobic respiration
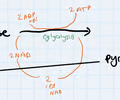
48
New cards
How many ATP are produced by anaerobic respiration of glucose into lactate?
2 ATP
49
New cards
How many ATP are produced by anaerobic respiration of glucose into ethanol?
2 ATP
50
New cards
What are the two alternate respiratory substrates?
Lipids and proteins
51
New cards
When glycogen stores and blood glucose are low, the alternate respiratory substrate used is…
Lipids
52
New cards
When dietary energy supplies are **low**, the **alternate** respiratory substrate used is…
Protein
53
New cards
Describe how lipids are used as a respiratory substrate
* Lipids are **hydrolysed** into their constituent molecules, **glycerol** and **fatty acids**
* The glycerol is **phosphorylated with ATP**, and **dehydrogenated** with NAD, converting it into triose phosphate
* Triose phosphate enters the glycolysis pathway
* The **fatty acid chains** are **broken** into **2-carbon fragments** and fed into the **Krebs cycle** as **Acetyl CoA**
* Hydrogen released is picked up by NAD and used in the ETC
* The glycerol is **phosphorylated with ATP**, and **dehydrogenated** with NAD, converting it into triose phosphate
* Triose phosphate enters the glycolysis pathway
* The **fatty acid chains** are **broken** into **2-carbon fragments** and fed into the **Krebs cycle** as **Acetyl CoA**
* Hydrogen released is picked up by NAD and used in the ETC
54
New cards
Longer fatty acids chains have more…
carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms
55
New cards
Longer fatty acid chains have more carbons. What effect does this have when long fatty acid chains are used in **respiration**?
More CO₂ is produced as a result. The body would produce more carbon dioxide than can be removed if lipids are respired
56
New cards
Longer fatty acid chains have **more hydrogen atoms**. What effect does this have when long fatty acid chains are used in respiration?
More NAD is reduced, so more ATP is produced. **More water is also produced.**
57
New cards
Describe how ***proteins*** are used as a ***respiratory substrate***
* Amino acids are **deaminated** in the liver
* The amino group is converted into urea
* The amino group is converted into urea
58
New cards
Where in the cell do most of the aerobic respiration reactions take place?
Mitochondria
59
New cards
Outline **Oxidative Phosphorylation**
* Hydrogen atoms are donated by reduced NAD (NADH) and reduced FAD (FADH2) from the Krebs Cycle
* Hydrogen atoms **split into protons (H+ ions) and electrons**
* The high energy electrons enter the electron transport chain and release energy as they move through the **electron transport chain**
* The released energy is used to **transport protons** across the inner mitochondrial membrane **from the matrix into the intermembrane space**
* A **concentration gradient** of protons is established between the intermembrane space and the matrix
* The protons return to the matrix via **facilitated diffusion** through the **channel protein ATP synthase**
* The movement of protons down their concentration gradient provides energy for **ATP synthesis**
* **Oxygen** acts as the 'final electron acceptor' and combines with protons and electrons at the end of the electron transport chain to **form water**
* Hydrogen atoms **split into protons (H+ ions) and electrons**
* The high energy electrons enter the electron transport chain and release energy as they move through the **electron transport chain**
* The released energy is used to **transport protons** across the inner mitochondrial membrane **from the matrix into the intermembrane space**
* A **concentration gradient** of protons is established between the intermembrane space and the matrix
* The protons return to the matrix via **facilitated diffusion** through the **channel protein ATP synthase**
* The movement of protons down their concentration gradient provides energy for **ATP synthesis**
* **Oxygen** acts as the 'final electron acceptor' and combines with protons and electrons at the end of the electron transport chain to **form water**
60
New cards
Where in the cell do the anaerobic respiration reactions take place?
In the cytoplasm
61
New cards
What is the role of the coenzymes NAD and FAD in aerobic respiration?
To **transport hydrogen** from dehydrogenation reactions to the electron transport chain where they are used in chemiosmosis
- They pass electrons to the electron transport chain for ATP synthesis.
- They pass electrons to the electron transport chain for ATP synthesis.
62
New cards
Which stage takes place on the cristae or inner membrane of the mitochondria?
The Electron Transport Chain
63
New cards
Describe the main difference between the way in which ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation and the way in which it is produced in photosynthesis
In photosynthesis the energy used to synthesise ATP is provided by light. In oxidative phosphorylation the energy is provided by chemical reactions
64
New cards
Describe precisely what happens to the pyruvate in the absence of oxygen in animals
Pyruvate is directly reduced to lactate by reduced NAD, during anaerobic respiration
65
New cards
Describe precisely what happens to the pyruvate in the absence of oxygen in yeast
Pyruvate is converted into ethanal by the removal of CO₂. Ethanol is then reduced to ethanol by reduced NADH
66
New cards
Without oxygen, what cannot happen to NADH?
It cannot be oxidised to regenerate NAD
67
New cards
Explain how ADP is involved in making energy available to the cells
* Energy is used to combine ADP with a phosphate group and make ATP
* Energy is released when ATP is broken down into ADP and a phosphate group \n @@**Only one enzyme is required for this reaction**@@
* Energy is released when ATP is broken down into ADP and a phosphate group \n @@**Only one enzyme is required for this reaction**@@
68
New cards
Explain why anaerobic respiration yields less ATP than aerobic respiration
* Anaerobic respiration only involves glycolysis, not the Krebs cycle or the ETC
* Most ATP produced is as a result of the Krebs cycle (absent in anaerobic)
* Glycolysis normally produces **8 ATP** using NAD but can only produce 2 ATP in the absence of oxygen
* Ethanol and lactic acid still contain energy and are not broken down
* Most ATP produced is as a result of the Krebs cycle (absent in anaerobic)
* Glycolysis normally produces **8 ATP** using NAD but can only produce 2 ATP in the absence of oxygen
* Ethanol and lactic acid still contain energy and are not broken down
69
New cards
Describe the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain
* Oxygen is the final electron acceptor of the ETC
* It accepts electrons and protons, forming water
* This maintains the flow of electrons, ensuring the pumps keep pumping protons
* It accepts electrons and protons, forming water
* This maintains the flow of electrons, ensuring the pumps keep pumping protons
70
New cards
Explain how ATP production continues in humans in anaerobic conditions
Glycolysis continues, with glucose being converted into pyruvate. 2 ATP are produced by substrate-level phosphorylation. Pyruvate is then converted into lactate
71
New cards
A test tube containing a suspension of a unknown organelle is monitored for CO₂ production. Cyanide inhibits the enzyme cytochrome oxidase and prevents the regeneration of NAD. Explain why cyanide could be used to confirm that the sample in the test tube contains mitochondria
* The absence of NAD means that hydrogen atoms are not picked up and dehydrogenation does not take place
* Without dehydrogenation, many reactions do not take place, such as in the Krebs cycle
* Therefore, the mitochondria stops producing CO₂ is produced
* **A sample containing mitochondria will show a sharp drop in CO₂ production**
* Without dehydrogenation, many reactions do not take place, such as in the Krebs cycle
* Therefore, the mitochondria stops producing CO₂ is produced
* **A sample containing mitochondria will show a sharp drop in CO₂ production**
72
New cards
A chemical, Dinitophenol, causes holes to be produced in the inner membrane of mitochondria, through which protons can pass. Explain why this may affect oxidative phosphorylation and suggest why dinitrophenol causes a loss of weight and an increase in body temperature
* The leakage of protons from the inter-membrane space breaks the proton gradient
* Less protons will flow through ATP synthetase and so less ATP is produced as a result
* As less ATP is produced for each glucose molecule respired, more glucose will be used by the body
* As more glucose is used, the breakdown of glycerol and fat stores will occur, causing a loss of weight- As less energy is used to create ATP, more escapes as waste heat energy, which raises the body temperature
* Less protons will flow through ATP synthetase and so less ATP is produced as a result
* As less ATP is produced for each glucose molecule respired, more glucose will be used by the body
* As more glucose is used, the breakdown of glycerol and fat stores will occur, causing a loss of weight- As less energy is used to create ATP, more escapes as waste heat energy, which raises the body temperature
73
New cards
Describe how reduced FAD and reduced NAD are used to create an electrochemical gradient
* Reduced FAD and NAD pass electrons to the ETC
* The high energy electrons provide energy to power proton pumps
* On the inner mitochondrial membrane/cristae
* This pumps H+ into the inter-membrane space
* Reduced NAD powers all 3 pumps whereas Reduce FAD passes to the 2nd pump
* The high energy electrons provide energy to power proton pumps
* On the inner mitochondrial membrane/cristae
* This pumps H+ into the inter-membrane space
* Reduced NAD powers all 3 pumps whereas Reduce FAD passes to the 2nd pump
74
New cards
What are the products of the electron transport chain per molecule of glucose?
34 ATP
75
New cards
Why is ATP known as the *universal energy currency*?
Can be used in all organisms for all reactions
76
New cards
Why is the ATP yield for FAD less than NAD ?
* **Reduced FAD** only uses two proton pumps
* Only *2 ATP* produced per reduced FAD
* Only *2 ATP* produced per reduced FAD
77
New cards
Can you describe glycolysis?
\
* @@**Phosphorylation**@@ of glucose into hexose bisphosphate
* @@**Splitting**@@ of hexose bisphosphate into 2x triose phosphate
* @@**Oxidation**@@ of TP into pyruvate
* @@**Phosphorylation**@@ of glucose into hexose bisphosphate
* @@**Splitting**@@ of hexose bisphosphate into 2x triose phosphate
* @@**Oxidation**@@ of TP into pyruvate
78
New cards
Describe the function of __*enzymes*__ and __*coenzymes*__ (carriers) in the process of respiration
* Coenzyme **decarboxylase** remove carbon dioxide *in the link reaction*
* Coenzyme **dehydrogenase** remove hydrogen atoms in *the link reaction*
* **NAD** is reduced in *glycolysis*
* **FAD** is reduced in *Kreb’s cycle*
* **Reduced NAD** carries protons to the *electron transport chain*
* **ATP synthetase** produces ATP from ADP+Pi
* Coenzyme **dehydrogenase** remove hydrogen atoms in *the link reaction*
* **NAD** is reduced in *glycolysis*
* **FAD** is reduced in *Kreb’s cycle*
* **Reduced NAD** carries protons to the *electron transport chain*
* **ATP synthetase** produces ATP from ADP+Pi
79
New cards
Describe briefly the process of decarboxylation
* CO2 diffuses out of the mitochondria into the blood/plasma
* It is then carried as hydrogen carbonate ions to which it is breathed out
* It is then carried as hydrogen carbonate ions to which it is breathed out
80
New cards
Label the mitochondria with the process in each area
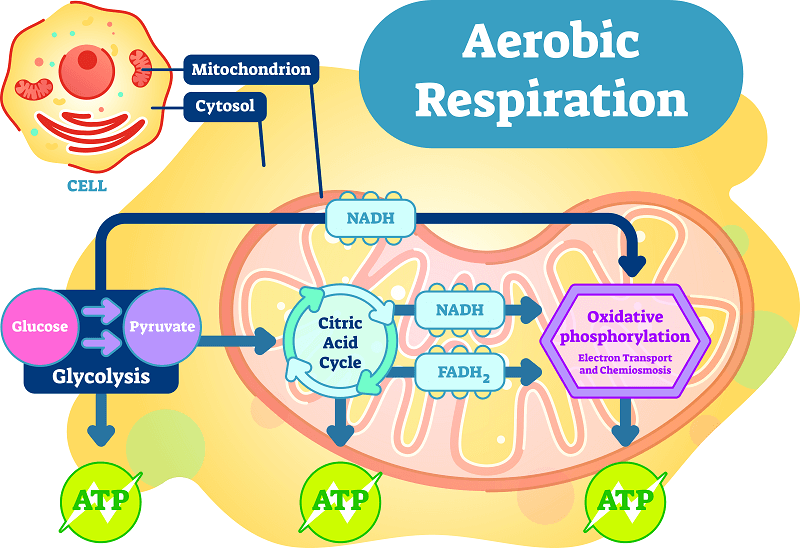
81
New cards
Label the mitochondria
\-
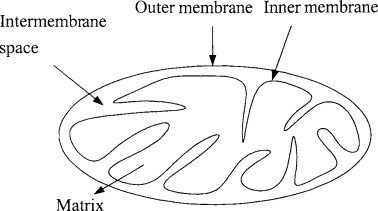
82
New cards
How is **Reduced NAD** produced in the Krebs Cycle?
* Dehydrogenation of intermediate compounds
* Removal of hydrogen ions meand NAD is reduced to NADH2
* Removal of hydrogen ions meand NAD is reduced to NADH2
83
New cards
Describe the position of the 'high energy bond of ATP’ in SLP
Bond between the last two phosphate bonds on ATP